RAK19026 WisMesh Base Board Datasheet
Overview
RAK19026 is a WisBlock Base Board that connects WisBlock IO, and WisBlock Modules. It provides the power supply and interconnection to the modules attached to it.
Different to other WisBlock Base Boards, it has no Core Slot for a WisBlock Core module. Instead it has a WisDuo RAK4630 integrated as its MCU. Beside of the MCU, a GNSS module and acceleration sensor are as well on the Base Board.
Similar to other WisBlock Base Boards it has three slots B-D for WisBlock modules. The WisBlock modules are attached to the top or bottom side of the RAK19026. The Slot D holds modules up to 23 mm in size, while slots B to C support 10 mm WisBlock modules. In addtion it has one IO slot for WisBlock IO modules.
For convenience, there is a USB-C connector that is connected directly to WisDuo MCU’s USB port. It can be used for uploading firmware or serial communication. The USB-C connector is also used as a battery charging port.
WisBlock modules are connected to the RAK19026 WisBlock Base board via high-speed board-to-board connectors. They provide secure and reliable interconnection to ensure the signal integrity of each data bus. A set of screws are used for fixing the modules, which makes it reliable even in an environment with lots of vibrations.
RAK19026 has connectors for the following:
- 1 WisBlock modules compatible with IO slot
- 4 WisBlock modules compatible with slots A-D
- 1 Type-C USB port for programming and debugging
- 3.7 V Rechargeable battery connector
- 5 V Solar panel connector
- Multiple headers with solder contacts
- 4 pin header with I2C, 3.3V and GND
- 4 pin header with IO5, IO6, IO7, and IO8
- 5 pin header with IO1, IO3, IO4, 3.3V, and GND
- 4 pin header for OLED display with I2C, 3.3V and GND
- 5 pin header with SWD, SWCLK, RST, 3.3V, and GND (for programming and debugging with RAKDAP1 or Jlink adapters)
Additionally, it has two user-definable LEDs, one power supply/charging indicator LED, a reset button, a user-definable button and a battery disconnection switch.
The battery can still be recharged through the USB port or the 5 V/Solar panel connector, even if the switch is in OFF position.
If modules require to be placed outside of the WisMesh Base Board, extension cables are available:
RAK19005 WisBlock Sensor Extension Cable to position the WisBlock Sensor modules apart from the WisBlock Base board or in any part of your case.
RAK19008 WisBlock IO Extension Cable to position the WisBlock IO modules apart from the WisBlock Base board or in any part of your case.
If you can't find a WisBlock module that fits your IoT requirements, use the standard connectors of WisBlock to develop your specific function module. WisBlock supports open-source hardware architecture and you can find tutorials showing how to create your own Awesome WisBlock module.
Applications
- Meshtastic device
Main Features
- Flexible building block design, which enables modular function realization and expansion
- High-speed interconnection connectors in the WisMesh Base Board to ensure signal integrity
- Features the RAK4630 WisDuo module with the Nordic nRF52840 MCU and the Semtech SX1262 LoRa transceiver
- Supports multiple types of sensors. A single board can support a combination of two different types of sensors
- Low power battery power supply
- Supports lithium battery charging
- Supports solar panel charging
- Fulfills industrial level design
- User definable button
- Battery disconnection switch
- Integrated GNSS module and acceleration sensor
- Connector for OLED display
- Compact size: 41.6 x 60 mm
Specifications
Overview
There are five (5) slots on RAK19026 WisMesh Base:
- IO SLOT: This slot is used for IO extension modules.
- Three Sensor Slots: The sensor slots B to D are used to connect with the I2C bus, have two GPIO's each and an UART RX/TX.
Also, there are multiple 2.54 mm pitch hole pads for extension interfaces.
 Figure 633: WisMesh Base top view
Figure 633: WisMesh Base top view Figure 634: WisMesh Base bottom view
Figure 634: WisMesh Base bottom viewBlock Diagram
The block diagram in Figure 3 shows the internal architecture and external interfaces of the RAK19026 board.
 Figure 635: RAK19026 WisMesh Base block diagram
Figure 635: RAK19026 WisMesh Base block diagramHardware
The hardware specification is categorized into six parts. It shows the interfacing, pinouts and the corresponding functions and diagrams. It also presents the electrical, environmental, and mechanical parameters that include the tabular data of the functionalities and standard values of the RAK19026 WisMesh Base.
Interfaces
RAK19026 WisMesh Base provides the following interfaces, headers, a button, and WisBlock Connectors.
- One Type-C USB connector
- One connector for the IO slot
- Three connectors for WisBlock sensor modules (slots B to D)
- Multiple pin header 2.54 mm hole pads
- 4 pin header with I2C, 3.3V and GND
- 4 pin header with IO5, IO6, IO7, and IO8
- 5 pin header with IO1, IO3, IO4, 3.3V, and GND
- 4 pin header for OLED display with I2C, 3.3V and GND
- 5 pin header with SWD, SWCLK, RST, 3.3V, and GND (for programming and debugging)
- 2-pin battery interface
- 2-pin solar panel interface
Additionally, the RAK19026 has two user-definable LEDs, one power supply/charging indicator LED, a reset button, a user-definable button and a battery ON/OFF switch.
Figure 4 and Figure 5 show the location of RAK19026 main components.
 Figure 636: RAK19026 top view components
Figure 636: RAK19026 top view components Figure 637: RAK19026 bottom view components
Figure 637: RAK19026 bottom view componentsType-C USB port
The Type-C USB connector is compliant with the USB 2.0 specification. This USB interface directly communicates with the connected WisBlock Core module. It is also used as a charging input port for the battery. Here are some of the advantages of the Type-C USB connector:
- Smaller and reversible connector shape
- Port can be input or output
- Fast battery charging
 Figure 638: USB Type-C receptacle pinout
Figure 638: USB Type-C receptacle pinoutJ10, J11, J12 Headers
On the RAK19026 Base Board, there are five 2.54 mm pitch headers for IO extension. I2C, SWD pins from the WisDuo module are exposed on these headers.
J2 Header Pinout (I2C OLED display)
| Pin | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3V3 | 3.3 V |
| 2 | GND | Ground pin |
| 3 | SCL | I2C1 clock |
| 4 | SDA | I2C2 data |
J3 Header Pinout
| Pin | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3V3 | 3.3 V |
| 2 | IO1 | General purpose IO |
| 3 | IO3 | General purpose IO |
| 4 | IO4 | General purpose IO |
| 5 | GND | Ground pin |
J4 Header Pinout
| Pin | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | IO5 | General purpose IO |
| 2 | IO6 | General purpose IO |
| 3 | IO7 | General purpose IO |
| 4 | IO8 | General purpose IO |
J10 Header Pinout
| Pin | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3V3 | 3.3 V |
| 2 | GND | Ground pin |
| 3 | SCL | I2C1 clock |
| 4 | SDA | I2C2 data |
J7 Header Pinout
| Pin | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3V3 | 3.3 V |
| 2 | SWDIO | Debug IO |
| 3 | SWDCLK | Debug CLK |
| 4 | GND | Ground pin |
| 5 | RESET | MCU Reset pin |
This header includes all required signals to connect a JLink or DAPLink debug/flash adapter.
Battery and Solar Panel / 5V Connection
RAK19026 can be powered via the USB cable or Li-Ion/LiPo battery via the dedicated connectors, as shown in below. The matching connector for the battery wires is a JST PHR-2 2 mm pitch female.
The battery can be recharged as well via a small solar panel or a regulated 5V supply, as shown below. The matching connector for the battery wires is a JST ZHR-2 1.5 mm pitch female.
 Figure 639: Battery connector pin order
Figure 639: Battery connector pin order- Battery can cause harm if not handled properly.
- Only 3.7-4.2 V Rechargeable LiPo batteries are supported. It is highly recommended not to use other types of batteries with the system unless you know what you are doing.
- If a non-rechargeable battery is used, it has to be unplugged first before connecting the USB cable to the USB port of the board to configure the device. Not doing so might damage the battery or cause a fire.
- Make sure the battery wires match the polarity on the RAK19007 board. Not all batteries have the same wiring.
- Only 5 V solar panels are supported. Do not use 12 V solar panels. It will destroy the charging unit and eventually other electronic parts.
- The GND pin of the Solar Panel Connector is located on edge of the board. Make sure the Solar Panel wires are matching the polarity on the RAK19007 board.
LEDs
Three LEDs are used to indicate the operating status. Below are the functions of the LEDs:
- 🔴 Red LED - Connected to the charger chip to indicate the charger status. When the battery is charging, this red LED is on. When the battery is full, this LED is weak light or off.
- 🟢 Green LED - Connected to the WisBlock Core module, controlled by MCU defined by the user.
- 🔵 Blue LED - Connected to the Wisblock Core module, controlled by MCU defined by the user.
RESET Push Button
The Reset Push Button is connected to the WisBlock Core module. When pushed, it resets the MCU.
GNSS Module
The GNSS module on the RAk19026 uses the u-blox ZOE-M8Q module. It supports a wide variety of satellite data protocols such as GPS, GLONASS, QZSS, and BeiDou. This ensures the retrieval of precise location data. The module features exceptional performance, high sensitivity, and minimal acquisition time. A very suitable module for your low-power IoT solution needs.
Features
- Module Specification
- Uses the very accurate GNSS Module: u-blox ZOE-M8Q chip
- Location Accuracy of ±2.5 meter
- Velocity Accuracy of ±0.05 m/s
- GPS, GLONASS, QZSS, and BeiDou Satellite support
- Serial and I2C communication to WisBlock Core support
- 10 Hz Update Rate
- 29 seconds Location Fix from Cold Start, 1 second from Hot Start
- Operating Voltage: 3.3 V
- Operating Current: < 15 µA
- Chipset: u-blox ZOE-M8Q
Chipset
The RAk19026 utilizes a very accurate u-blox ZOE-M8Q chip. See the manufacturer's u-blox ZOE-M8Q Page for more details.
| Vendor | Part number |
|---|---|
| u-blox | ZOE-M8Q |
Acceleration Sensor
The acceration sensor on the RAk19026 is a ST LIS3DH 3-axis acceleration sensor. A ready-to-use SW library and tutorial make it easy to build up a motion detection and acceleration data acquisition system. It has an ultra-low-power high-performance three-axis linear accelerometer with a digital I2C interface. The device features ultra-low-power operational modes that allow advanced power saving and smart embedded functions.
The accelerometer of the RAK1904 module can be dynamically configured to work in the scales of ±2 g/±4 g/±8 g/�±16g and is capable of measuring accelerations with output data rates from 1 Hz to 5.3 kHz.
Features
- User selectable scales: ±2g/±4g/±8g/±16g
- Data acquisition rates: from 1 Hz to 5.3 kHz
- Voltage Supply: 3.3 V
- Current Consumption: 0.5 uA to 11 uA
- Chipset: ST LIS3DH
- Module size: 10 x 10 mm#### Pin Definition
Chipset
| Vendor | Part number |
|---|---|
| ST | LIS3DH |
Connectors for WisBlock Sensor
The WisBlock sensor module connector is a 24-pin board-to-board connector.
 Figure 640: WisBlock Sensor module connector
Figure 640: WisBlock Sensor module connectorThere are three connectors reserved for the sensor modules on the RAK19026.
| Connector D | Connector C | Connector B | Pin Number | Pin Number | Connector B | Connector C | Connector D |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TXD1 | NC | NC | 1 | 2 | GND | GND | GND |
| SPI_CS | SPI_CS | SPI_CS | 3 | 4 | SPI_CLK | SPI_CLK | SPI_CLK |
| SPI_MISO | SPI_MISO | SPI_MISO | 5 | 6 | SPI_MOSI | SPI_MOSI | SPI_MOSI |
| I2C1_SCL | I2C1_SCL | I2C1_SCL | 7 | 8 | I2C1_SDA | I2C1_SDA | I2C1_SDA |
| VDD | VDD | VDD | 9 | 10 | IO1 | IO4 | IO6 |
| 3V3_S | 3V3_S | 3V3_S | 11 | 12 | IO2 | IO3 | IO5 |
| NC | NC | NC | 13 | 14 | 3V3_S | 3V3_S | 3V3_S |
| NC | NC | NC | 15 | 16 | VDD | VDD | VDD |
| NC | NC | NC | 17 | 18 | NC | NC | NC |
| NC | NC | NC | 19 | 20 | NC | NC | NC |
| NC | NC | NC | 21 | 22 | NC | NC | NC |
| GND | GND | GND | 23 | 24 | NC | NC | RXD1 |
As for the following table, it shows the pin name and description of each pin in the WisBlock Sensor module connector.
| Pin Number | Connector B | Connector C | Connector D | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | NC | NC | TXD1 | I/O | UART TX signal |
| 2 | GND | GND | GND | S | Ground |
| 3 | SPI_CS | SPI_CS | SPI_CS | I/O | SPI chip select signal |
| 4 | SPI_CLK | SPI_CLK | SPI_CLK | I/O | SPI clock |
| 5 | SPI_MISO | SPI_MISO | SPI_MISO | I/O | SPI MISO signal |
| 6 | SPI_MOSI | SPI_MOSI | SPI_MOSI | I/O | SPI MOSI signal |
| 7 | I2C1_SCL | I2C1_SCL | I2C1_SCL | I/O | I2C clock signal |
| 8 | I2C1_SDA | I2C1_SDA | I2C1_SDA | I/O | I2C data signal |
| 9 | VDD | VDD | VDD | S | Generated by CPU module. Used to power sensor board if MCU IO level is not 3.3 V |
| 10 | IO1 | IO4 | IO6 | I/O | General purpose IO. IO2 controls the power switch of 3V3_S. When the 3V3_S function is used, IO2 can not be used as an interrupt of the sensor. |
| 11 | 3V3_S | 3V3_S | 3V3_S | S | 3.3 V power supply. Can be shut down by the CPU module. |
| 12 | IO2 | IO3 | IO5 | I/O | General purpose IO - IO controls the power switch of 3V3_S. When the 3V3_S function is used, IO2 cannot be used as an interrupt of the sensor. |
| 13 | NC | NC | NC | NC | Not connected |
| 14 | 3V3_S | 3V3_S | 3V3_S | S | 3.3 V power supply. Can be shut down by the CPU module. |
| 15 | NC | NC | NC | NC | Not connected |
| 16 | VDD | VDD | VDD | S | Generated by CPU module. Used to power sensor board if the MCU IO level is not 3.3 V. |
| 17 | NC | NC | NC | NC | Not connected |
| 18 | NC | NC | NC | NC | Not connected |
| 19 | NC | NC | NC | NC | Not connected |
| 20 | NC | NC | NC | NC | Not connected |
| 21 | NC | NC | NC | NC | Not connected |
| 22 | NC | NC | NC | NC | Not connected |
| 23 | GND | GND | GND | S | Ground |
| 24 | NC | NC | RXD1 | I/O | UART RX signal |
Connector for WisBlock IO Slot
The WisBlock Module IO Slot connector, as shown in Figure 13, is a 40-pin board-to-board connector.
The two WisBlock 40-pin connectors have the same connections for all IO, signal, and serial pins (UART, SPI, I2C).
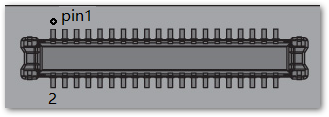 Figure 641: WisBlock IO slot connector
Figure 641: WisBlock IO slot connectorPinout definition for IO slot:
| Connector B | Connector A | Pin Number | Pin Number | Connector A | Connector B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VBAT | VBAT | 1 | 2 | VBAT | VBAT |
| GND | GND | 3 | 4 | GND | GND |
| 3V3 | 3V3 | 5 | 6 | 3V3_S | 3V3_S |
| USB+ | USB+ | 7 | 8 | USB– | USB– |
| VBUS | VBUS | 9 | 10 | SW1 | SW1 |
| TXD0 | TXD0 | 11 | 12 | RXD0 | RXD0 |
| RESET | RESET | 13 | 14 | LED1 | LED1 |
| LED2 | LED2 | 15 | 16 | LED3 | LED3 |
| VDD | VDD | 17 | 18 | VDD | VDD |
| I2C1_SDA | I2C1_SDA | 19 | 20 | I2C1_SCL | I2C1_SCL |
| AIN0 | AIN0 | 21 | 22 | AIN1 | AIN1 |
| NC | NC | 23 | 24 | NC | NC |
| SPI_CS | SPI_CS | 25 | 26 | SPI_CLK | SPI_CLK |
| SPI_MISO | SPI_MISO | 27 | 28 | SPI_MOSI | SPI_MOSI |
| IO1 | IO1 | 29 | 30 | IO2 | IO2 |
| IO3 | IO3 | 31 | 32 | IO4 | IO4 |
| TXD1 | TXD1 | 33 | 34 | RXD1 | RXD1 |
| I2C2_SDA | I2C2_SDA | 35 | 36 | I2C2_SCL | I2C2_SCL |
| IO5 | IO5 | 37 | 38 | IO6 | IO6 |
| GND | GND | 39 | 40 | GND | GND |
As for the following table, it shows the pin name and description of the WisBlock IO module connector.
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | VBAT | S | Power supply from battery |
| 2 | VBAT | S | Power supply from battery |
| 3 | GND | S | Ground |
| 4 | GND | S | Ground |
| 5 | 3V3 | S | 3.3 V power supply |
| 6 | 3V3_S | S | 3.3 V power supply. Can be shut down by a CPU module. |
| 7 | USB+ | I/O | USB D+ |
| 8 | USB– | I/O | USB D– |
| 9 | VBUS | S | 5 V input for USB |
| 10 | SW1 | I/O | User Defined Button (available on RAK4631/RAK4631-R and 11200 WisBlock Cores) |
| 11 | TXD0 | I/O | MCU UART0 TX signal |
| 12 | RXD0 | I/O | MCU UART0 RX signal |
| 13 | RESET | I | Connected to the reset switch, for MCU reset |
| 14 | LED1 | I/O | LED for battery charge indicator |
| 15 | LED2 | I/O | LED for custom used |
| 16 | LED3 | I/O | LED for custom used |
| 17 | VDD | S | Generated by CPU module - Used for power sensor board if the MCU IO level is not 3.3 V |
| 18 | VDD | S | Generated by CPU module - Used for power sensor board if the MCU IO level is not 3.3 V. |
| 19 | I2C1_SDA | I/O | The first set of I2C data signal |
| 20 | I2C1_SCL | I/O | The first set of I2C clock signal |
| 21 | AIN0 | A | Analog input for ADC |
| 22 | AIN1 | A | Analog input for ADC |
| 23 | NC | NC | Not connect |
| 24 | NC | NC | Not connect |
| 25 | SPI_CS | I/O | SPI chip select signal |
| 26 | SP_CLK | I/O | SPI clock |
| 27 | SPI_MISO | I/O | SPI MISO signal |
| 28 | SPI_MOSI | I/O | SPI MOSI signal |
| 29 | IO1 | I/O | General purpose IO |
| 30 | IO2 | I/O | Used for 3V3_S enable |
| 31 | IO3 | I/O | General purpose IO |
| 32 | IO4 | I/O | General purpose IO |
| 33 | TXD1 | I/O | MCU UART1 TX signal |
| 34 | RXD1 | I/O | MCU UART1 RX signal |
| 35 | I2C2_SDA | I/O | The second set of I2C data signal |
| 36 | I2C2_SCL | I/O | The second set of I2C clock signal |
| 37 | IO5 | I/O | General purpose IO |
| 38 | IO6 | I/O | General purpose IO |
| 39 | GND | S | Ground |
| 40 | GND | S | Ground |
Electrical Characteristics
Absolute Maximum Ratings
The Absolute Maximum Ratings of the device are shown in the table below. The stress ratings are the functional operation of the device.
- If the stress rating goes above what is listed, it may cause permanent damage to the device.
- Under the listed conditions is not advised.
- Exposure to maximum rating conditions may affect the device reliability.
| Ratings | Maximum Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Power supply on the USB port (VBUS) | –0.3 to 5.5 | V |
| Battery voltage (VBAT) | –0.3 to 4.3 | V |
| Solar panel voltage (CONN_S) | –0.3 to 5.5 | V |
| IOs of WisBlock connector | –0.3 to VDD+0.3 | V |
| ESD | 2000 | V |
The RAK19026, as any electronic equipment, is sensitive to electrostatic discharge (ESD). Improper handling can cause permanent damage to the module.
Current Consumption
The RAK19026 is designed for low-power IoT products, and the power supply uses a high-efficiency low grounding current regulator. When there is no module on RAK19026, the leakage current is lower than 2 µA. With WisBlock Core and WisBlock Sensor on it, the sleep current is lower than 10 µA. When a LoRa module is transmitting, the current may reach 130 mA.
| Conditions | Current | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Leakage current, without any module on RAK19026 | 2 | µA |
| Idle current, with MCU and sensors in sleep mode | 10 | µA |
| Working current, with LoRa module transmitting | 130 | mA |
Battery Connector
The RAK19026 WisMesh Base can be powered by a rechargeable battery, connected to the P2 connector. The nominal operating voltage of the battery should be within the range shown in the following table. The matching connector for the battery wires is an JST PHR-2 2 mm pitch female.
| Minimum | Typical | Maximum | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3.3 | 3.7 | 4.3 | V |
The Type-C USB connector is used as a charging port. The voltage and current fed to the battery through the port should not exceed its charging limits, as shown in the table below.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Charging voltage | 4.5 – 5.5 V |
| Charging current | 350 mA |
A suitable Li-Ion battery should have the following parameters as shown in the table below:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Standard voltage | 3.7 V |
| Charging voltage | 4.2 V |
| Capacity | As required |
| Discharge current | At least 500 mA |
Do not use a non-rechargeable battery.
Solar Panel Connector
A 5 V solar panel can be connected to the board via the P1 connector. The solar panel can also be used to charge the Li-Ion battery. The matching connector for the solar panel wires is an JST ZHR-2 1.5 mm pitch female.
Mechanical Characteristics
Board Dimensions
- You may also refer and download the M1.2 Stand-off fastener/inserts datasheet.
Top components
 Figure 642: RAK19026 mechanical dimensions
Figure 642: RAK19026 mechanical dimensionsBottom components
 Figure 643: RAK19026 mounting holes location and diameter top view
Figure 643: RAK19026 mounting holes location and diameter top viewWisConnector PCB Layout
 Figure 644: WisConnector PCB footprint and recommendations
Figure 644: WisConnector PCB footprint and recommendationsEnvironmental Characteristics
The table below lists the operation and storage temperature requirements of RAK19026:
| Parameter | Minimum | Typical | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operational Temperature Range | –35º C | +25º C | +75º C |
| Extended Temperature Range | –40º C | +25º C | +80º C |
| Storage Temperature Range | –40º C | +25º C | +80º C |
Schematic Diagram
The component schematics diagram of the RAK19026 is shown in Figure 15 and Figure 16.
 Figure 645: RAK19026 schematic diagram (Power)
Figure 645: RAK19026 schematic diagram (Power) Figure 646: RAK19026 schematic diagram (RAK4630)
Figure 646: RAK19026 schematic diagram (RAK4630) Figure 647: RAK19026 schematic diagram (GNSS)
Figure 647: RAK19026 schematic diagram (GNSS) Figure 648: RAK19026 schematic diagram (Pin Headers - Acceleration Sensor)
Figure 648: RAK19026 schematic diagram (Pin Headers - Acceleration Sensor) Figure 649: RAK19026 schematic diagram (Module Slots)
Figure 649: RAK19026 schematic diagram (Module Slots)