RAK13101 WisBlock GSM/GPRS Module Quick Start Guide
Prerequisite
What Do You Need?
Before going through each and every step on using the RAK13101 WisBlock module, make sure to prepare the necessary items listed below:
Hardware
- RAK13101
- Your choice of WisBlock Base
- Your choice of WisBlock Core
- USB Cable
- GNSS and GSM Antennas
- Li-Ion/LiPo battery (optional)
- Solar charger (optional)
Software
- Download and install Arduino IDE.
- To add the RAKwireless Core boards on your Arduino board, install the RAKwireless Arduino BSP. Follow the steps in the GitHub repo.
Product Configuration
Hardware Setup
You can integrate the RAK13101 module on your WisBlock project to extend its functionality and have GSM/GPRS/GNSS capability. This is ideal for tracking applications with GSM/GPSR cellular connectivity in the area. For more information about RAK13101, refer to its Datasheet.
RAK13101 module can be mounted to the IO slot of the WisBlock Base and communicates to the WisBlock Core via UART. The module is activated via WB_IO5 pin of the WisBlock Core. Two antennas must be connected to the module as well, one for the GNSS antenna port and one for the GSM antenna port. An external battery (Li-Ion/LiPo 3.7-4.2V) is also required to power up the module properly.
- Batteries can cause harm if not handled properly.
- Only 3.7-4.2 V Rechargeable LiPo batteries are supported. It is highly recommended not to use other types of batteries with the system unless you know what you are doing.
- If a non-rechargeable battery is used, it has to be unplugged before connecting the USB cable to the USB port of the board to configure the device. Not doing so might damage the battery or cause a fire.
- Only 5 V solar panels are supported. Do not use 12 V solar panels. It will destroy the charging unit and eventually other electronic parts.
- Make sure the battery wires match the polarity on the WisBlock Base board. Not all batteries have the same wiring.
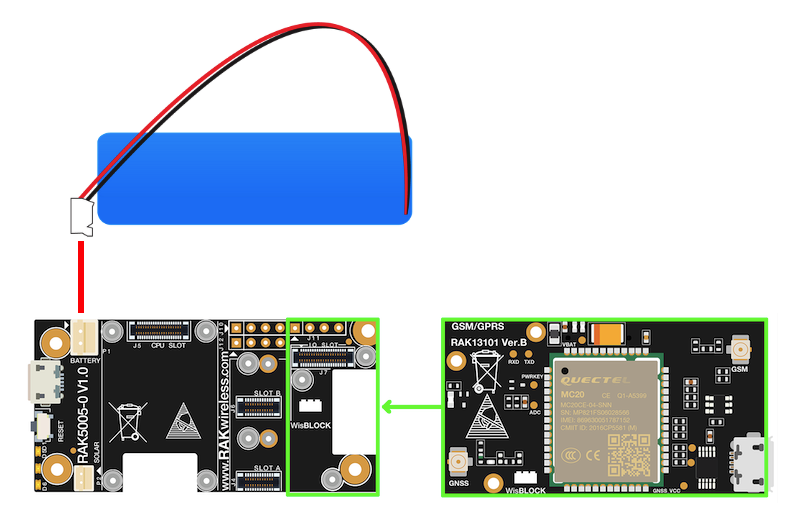 Figure 1: RAK13101 connection to WisBlock Base
Figure 1: RAK13101 connection to WisBlock Base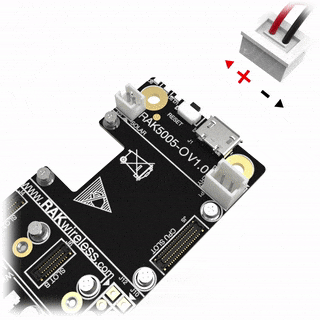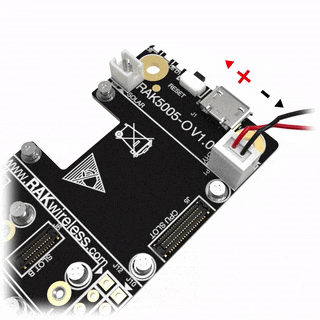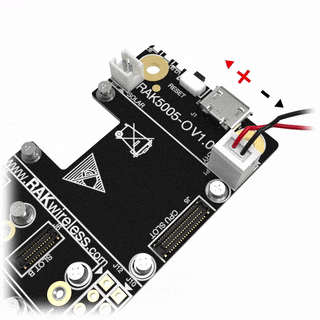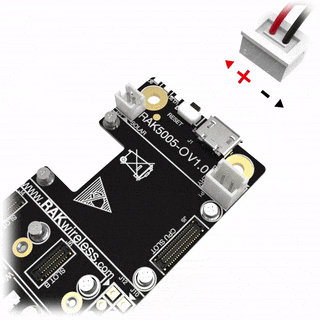 Figure 1: WisBlock Base RAK5005-O battery polarity and connection
Figure 1: WisBlock Base RAK5005-O battery polarity and connectionAssembling and Disassembling of WisBlock Modules
Assembling
As shown in Figure 3, the location for Slot A, B, C, and D are properly marked by silkscreen. Follow carefully the procedure defined in RAK5005-O module assembly/disassembly instructions to attach a WisBlock module. Once attached, carefully fix the module with one or more pieces of M1.2 x 3 mm screws depending on the module.
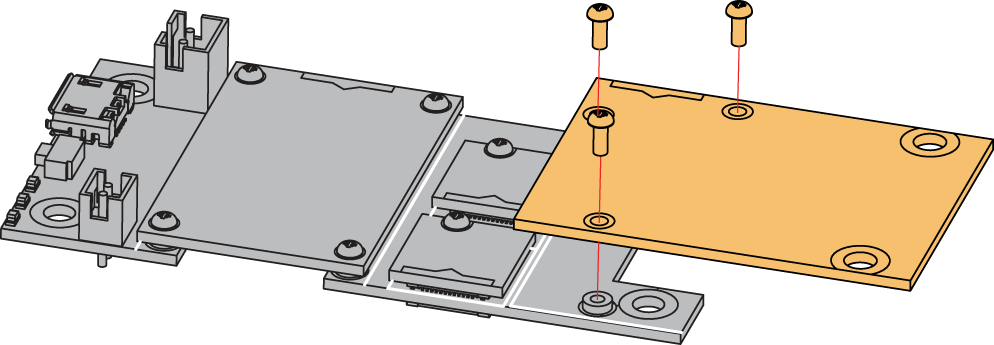 Figure 1: RAK13101 connection to WisBlock Base
Figure 1: RAK13101 connection to WisBlock BaseDisassembling
The procedure in disassembling any type of WisBlock modules is the same.
- Remove the screws.
 Figure 1: Removing screws from the WisBlock module
Figure 1: Removing screws from the WisBlock module- Once the screws are removed, check the silkscreen of the module to find the correct location where force can be applied.
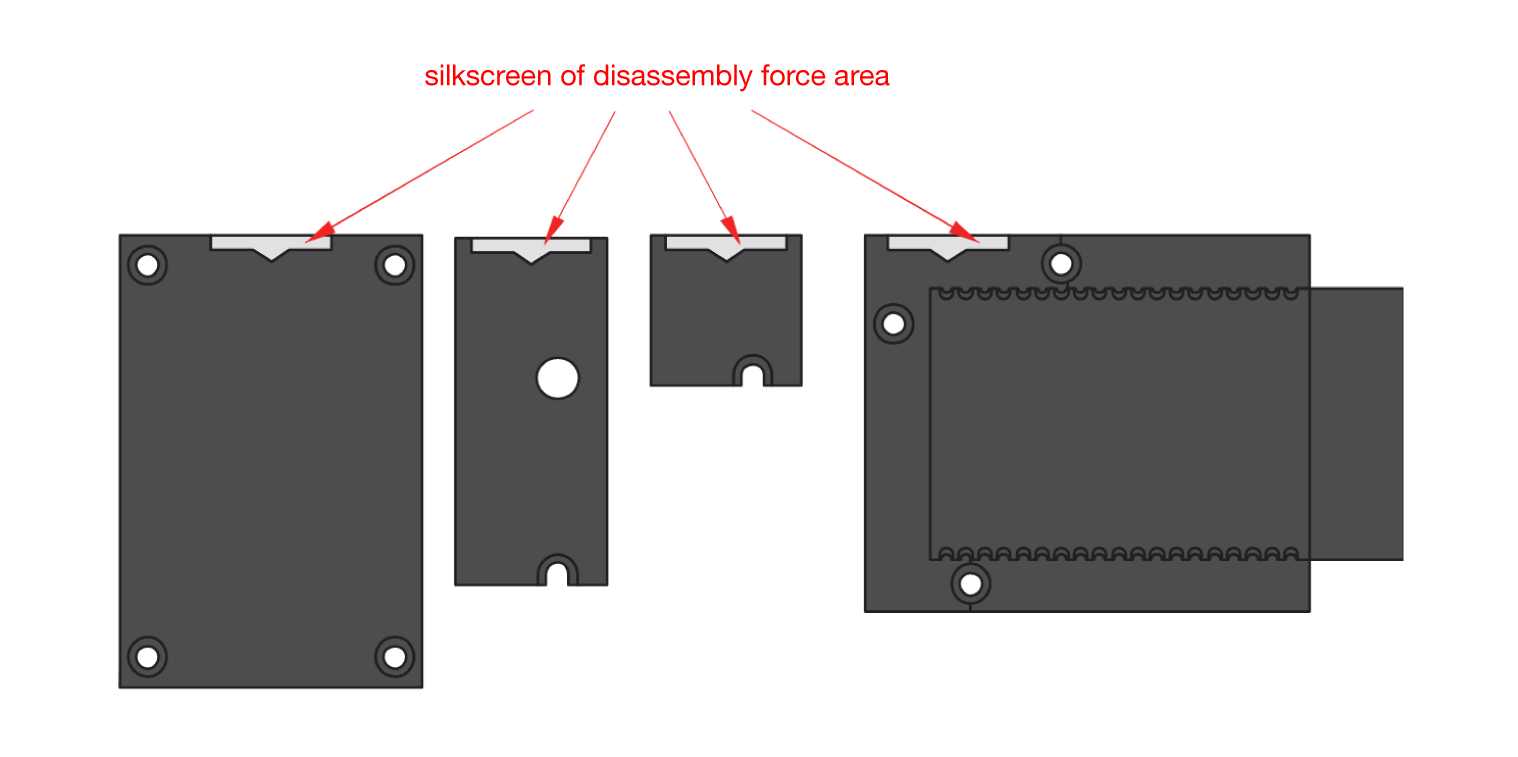 Figure 1: Detaching silkscreen on the WisBlock module
Figure 1: Detaching silkscreen on the WisBlock module- Apply force to the module at the position of the connector, as shown in Figure 6, to detach the module from the baseboard.
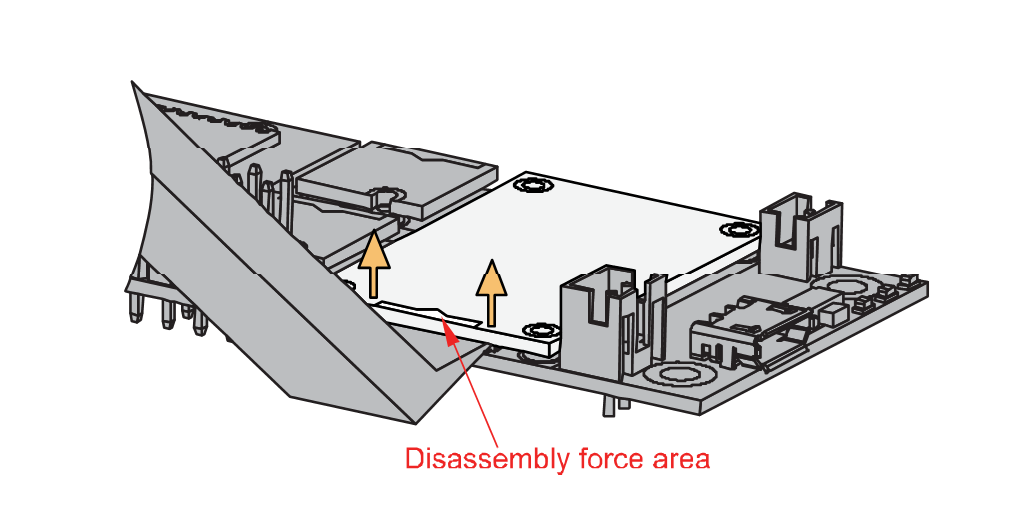 Figure 1: Applying even forces on the proper location of a WisBlock module
Figure 1: Applying even forces on the proper location of a WisBlock moduleIf you will connect other modules to the remaining WisBlock Base slots, check on the WisBlock Pin Mapper tool for possible conflicts. RAK13101 uses UART communication lines, and it can cause possible conflict especially on some modules that also use UART.
Software Configuration and Example
The RAK13101 WisBlock GSM/GPRS Module uses UART serial communication lines. In this example code, you will be able to send AT commands to the RAK13101 module. This will ensure that your RAK13101 is functional and ready for your IoT project.
Initial Test of the RAK13101 WisBlock Module
If you already installed the RAKwireless Arduino BSP, the WisBlock Core and example code should now be available on the Arduino IDE.
- You need to select first the WisBlock Core you have, as shown in Figure 7 to Figure 9.
 Figure 1: Selecting RAK4631 as WisBlock Core
Figure 1: Selecting RAK4631 as WisBlock Core Figure 1: Selecting RAK11200 as WisBlock Core
Figure 1: Selecting RAK11200 as WisBlock Core Figure 1: Selecting RAK11300 as WisBlock Core
Figure 1: Selecting RAK11300 as WisBlock Core- Next, copy the following sample code into your Arduino IDE:
Click to view the example
/**
@file Unvarnished_Transmission.ino
@author rakwireless.com
@brief unvarnished transmission via USB
@version 0.1
@date 2021-6-28
@copyright Copyright (c) 2020
**/
#include <Wire.h>
#define POWER_KEY WB_IO5
void setup()
{
time_t serial_timeout = millis();
Serial.begin(115200);
while (!Serial)
{
if ((millis() - serial_timeout) < 5000)
{
delay(100);
}
else
{
break;
}
}
Serial.println("AT CMD TEST!");
// Check if the modem is already awake
time_t timeout = millis();
bool moduleSleeps = true;
Serial1.begin(9600);
delay(1000);
Serial1.println("ATI");
//MC20 init
while ((millis() - timeout) < 6000)
{
if (Serial1.available())
{
String result = Serial1.readString();
Serial.println("Modem response after start:");
Serial.println(result);
moduleSleeps = false;
}
}
if (moduleSleeps)
{
// Module slept, wake it up
pinMode(POWER_KEY, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(POWER_KEY, 0);
delay(200);
digitalWrite(POWER_KEY, 1);
delay(2000);
digitalWrite(POWER_KEY, 0);
delay(1000);
}
Serial.println("MC20 power up!");
}
void loop()
{
int timeout = 100;
String resp = "";
String snd = "";
char cArr[128] = {0};
while (timeout--)
{
if (Serial1.available() > 0)
{
resp += char(Serial1.read());
}
if (Serial.available() > 0)
{
snd += char(Serial.read());
}
delay(1);
}
if (resp.length() > 0)
{
Serial.print(resp);
}
if (snd.length() > 0)
{
memset(cArr, 0, 128);
snd.toCharArray(cArr, snd.length() + 1);
Serial1.write(cArr);
delay(10);
}
resp = "";
snd = "";
}
- You can now select the right serial port and upload the code, as shown in Figure 10 and Figure 11.
If you are using RAK11200 as WisBlock Core, you need to configure the BOOT0 pin before uploading. You need to short it to the ground then press the reset button of the WisBlock Base before releasing the BOOT0 pin. If not done properly, uploading the source code to RAK11200 will fail. Check the full details on the RAK11200 Quick Start Guide.
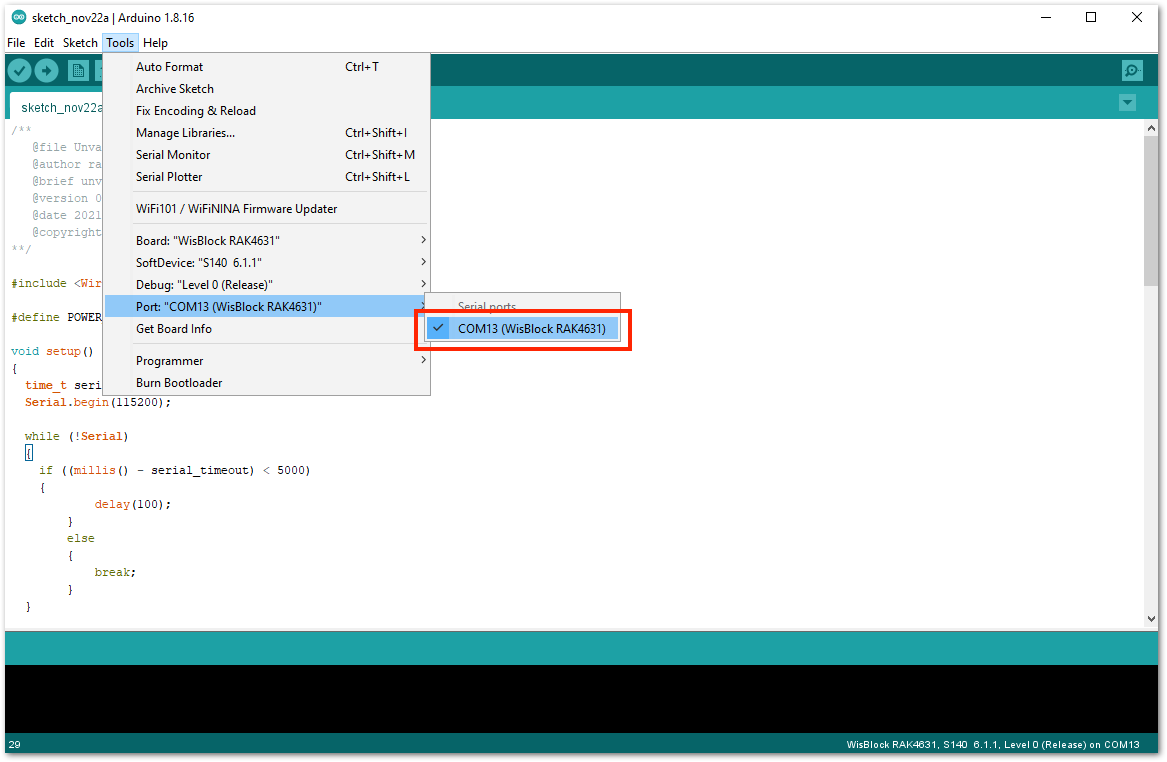 Figure 1: Selecting the correct Serial Port
Figure 1: Selecting the correct Serial Port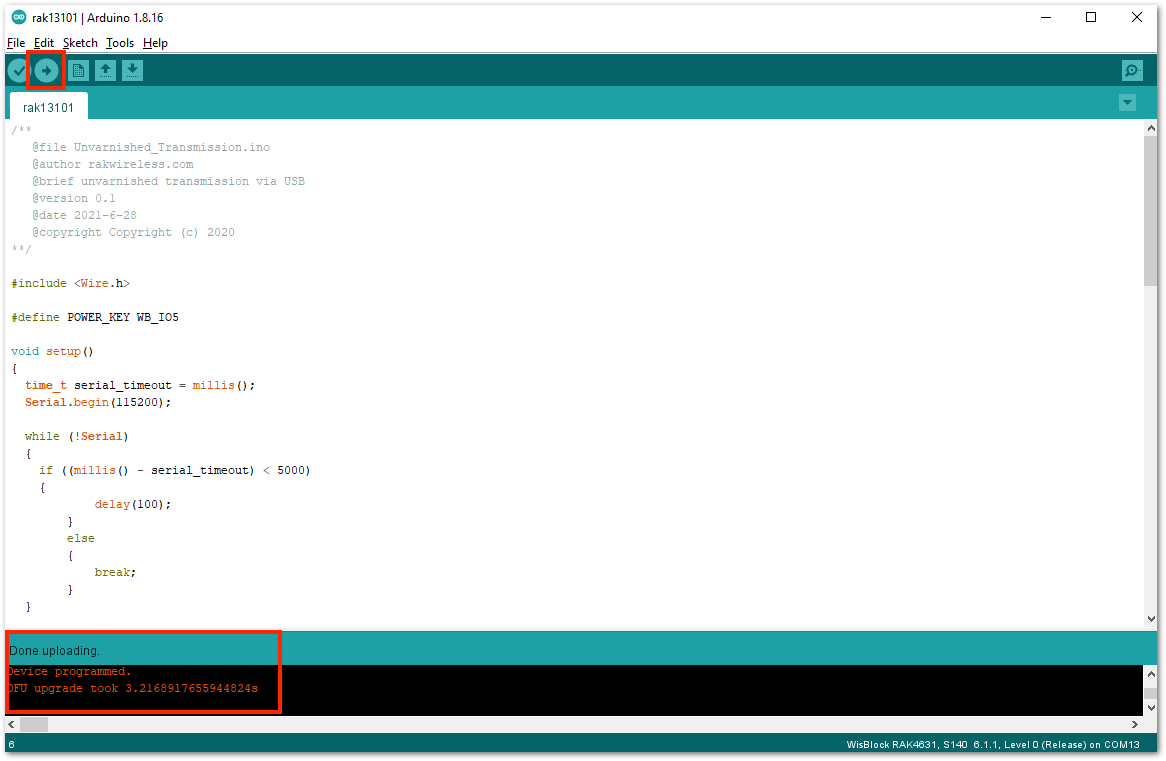 Figure 1: Uploading the RAK13101 example code
Figure 1: Uploading the RAK13101 example codeIf you experience any error in compiling the example sketch, check the updated code for the RAK13101 Module that can be found on the WisBlock Example Code Repository.
- When you successfully uploaded the example sketch, open the Serial Monitor of the Arduino IDE to see the initial logs, as shown in Figure 12. If you do not see any logs, you can try to disconnect the USB cable and battery, then reconnect again with the battery first. If you see that the LED of the RAK13101 is blinking after a few seconds, the module is now initialized properly.
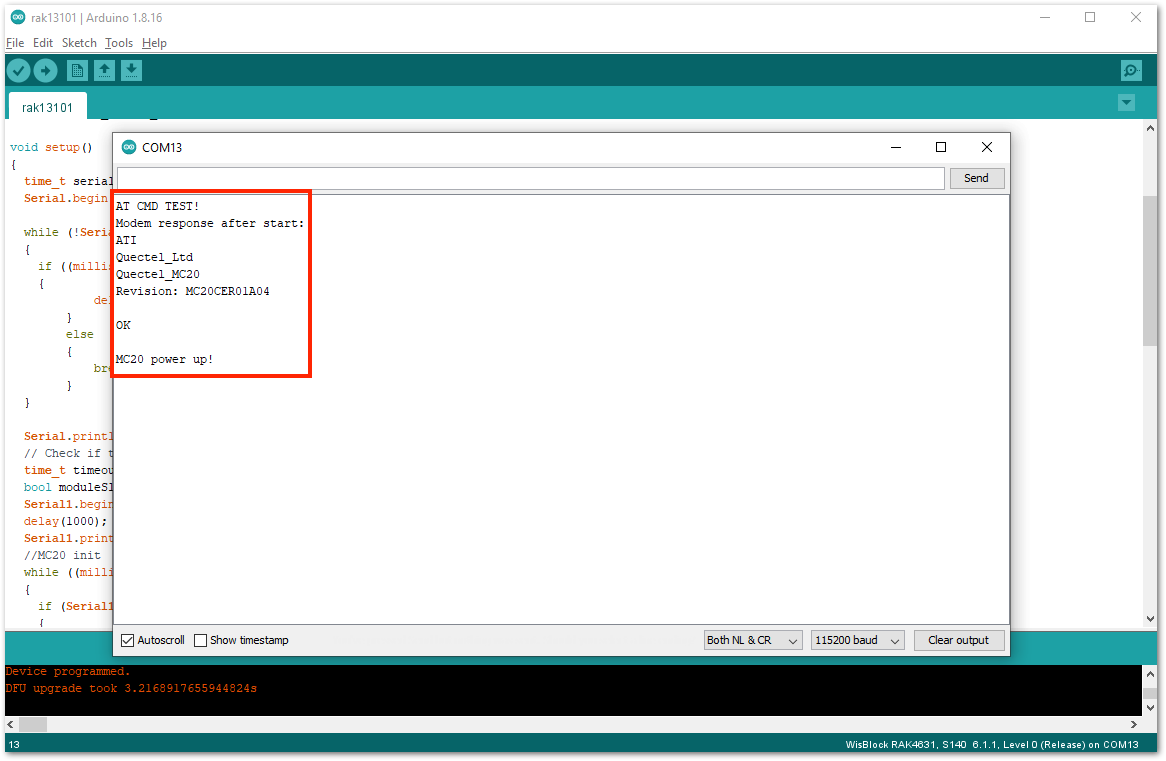 Figure 1: RAK13101 initial logs
Figure 1: RAK13101 initial logs- There are times that you might not see the initial logs if you open the Serial Monitor. The best way to test if the module is working is by sending actual AT commands, as shown in Figure 13. You can try to send the basic commands,
ATandATI.
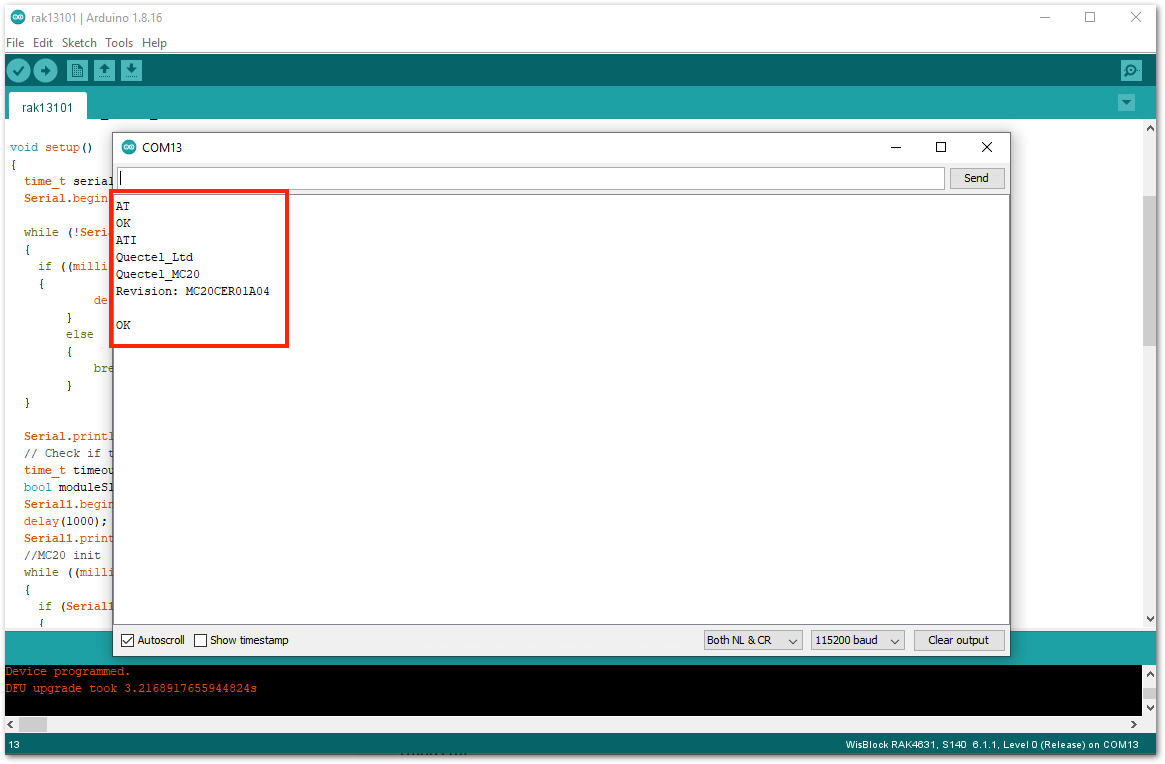 Figure 1: RAK13101 AT and ATI command
Figure 1: RAK13101 AT and ATI command