RAK13600 WisBlock NFC Reader Module Quick Start Guide
Prerequisite
What Do You Need?
Before going through each and every step on using the RAK13600 WisBlock NFC Reader Module, make sure to prepare the necessary items listed below:
Hardware
- RAK13600 Wisblock Interface Extension Board with Coil Antenna
- Your choice of WisBlock Base
- Your choice of WisBlock Core
- USB Cable
- Li-Ion/LiPo battery (optional)
- Solar charger (optional)
Software
- Download and install the ArduinoIDE.
- To add the RAKwireless Core boards on your Arduino Boards Manager, install the RAKwireless Arduino BSP.
Product Configuration
Hardware Setup
The RAK13600 module is designed as wireless module that allows you to scan NFC and RFID tags and devices. It includes an antenna coil that transmits and receives RF signals from the object being scanned. Without the antenna coil shown in Figure 1, you will not be able to scan NFC/RFID devices. The antenna coil has adhesive transfer tape on it. You can remove the 3M patch film so you stick the antenna coil on the ideal location in your enclosure. The enclosure must be plastic and not metal, since metal enclosures introduce attenuation on RF signals.
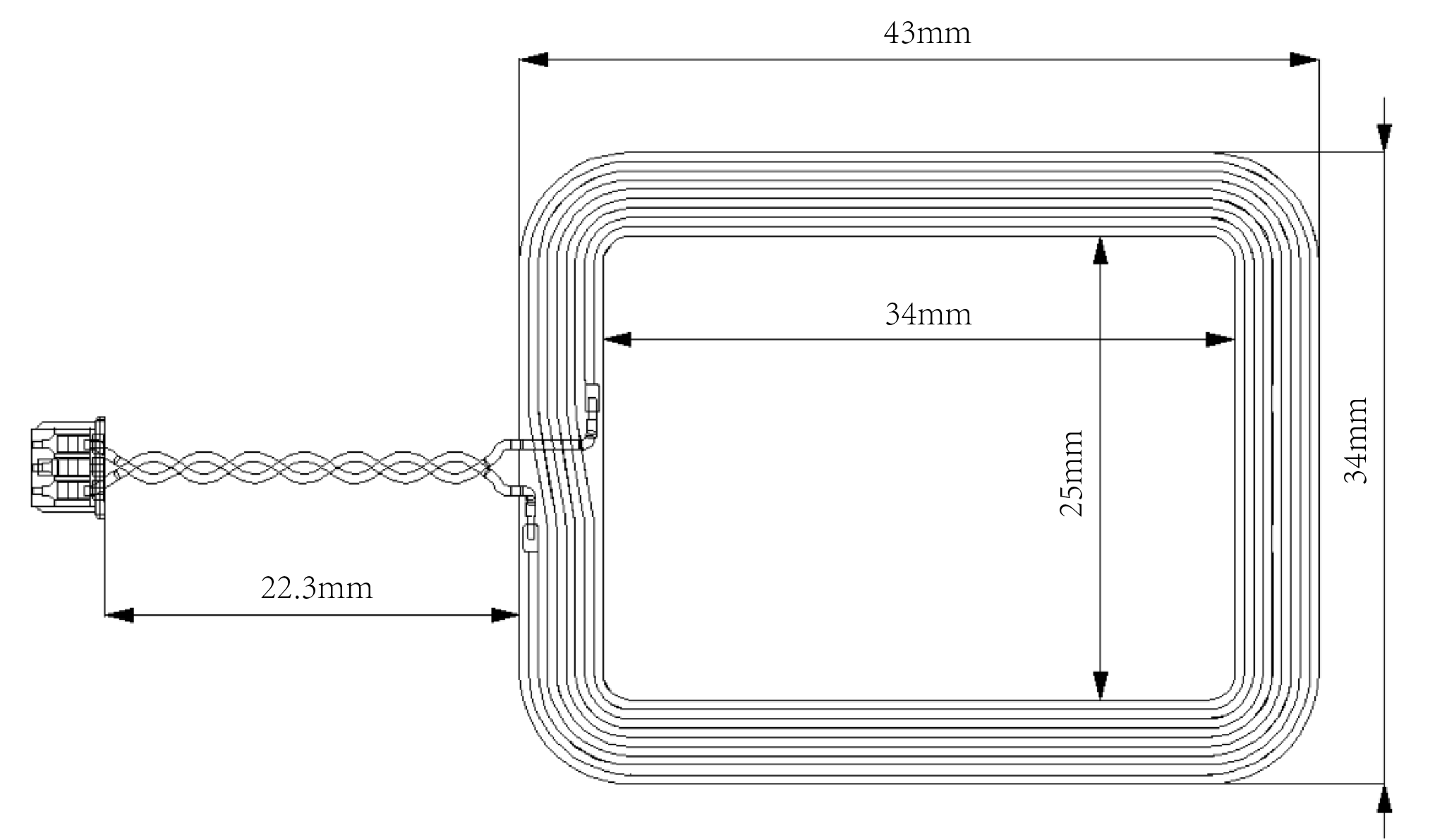 Figure 1: NFC Coil Antenna
Figure 1: NFC Coil AntennaThe RAK13600 module can be mounted on the IO slot of any WisBlock Base board, as shown in Figure 2. Also, always secure the connection of the WisBlock module by using compatible screws. For more information about RAK13600, refer to the Datasheet.
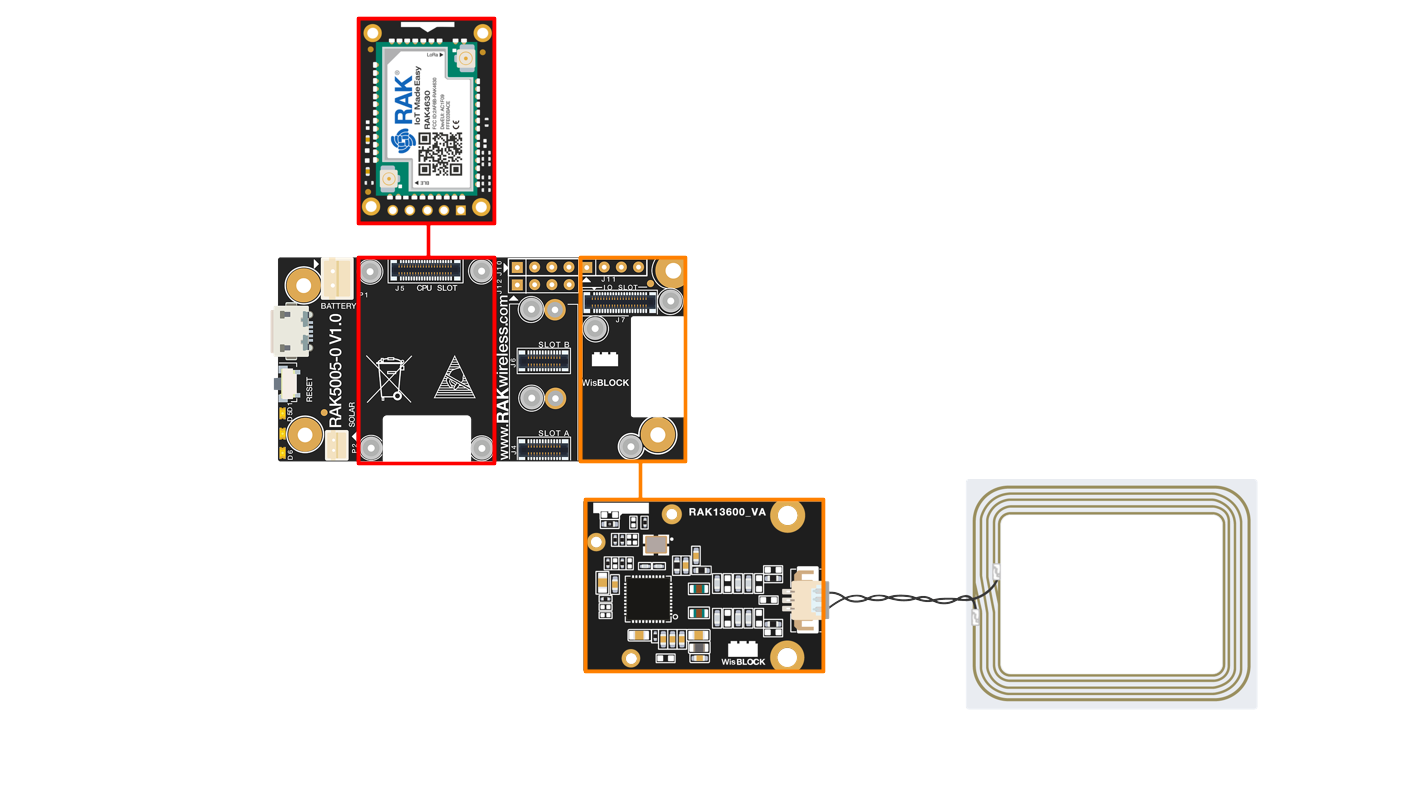 Figure 1: RAK13600 on WisBlock Base with WisBlock Core
Figure 1: RAK13600 on WisBlock Base with WisBlock CoreAssembling and Disassembling of WisBlock Modules
Assembling
As shown in Figure 3, the location for the IO slot is properly marked by silkscreen. Follow carefully the procedure defined in WisBlock Base module assembly/disassembly instructions to attach a WisBlock module. Once attached, carefully fix the module with three M1.2 x 3 mm screws compatible with the module.
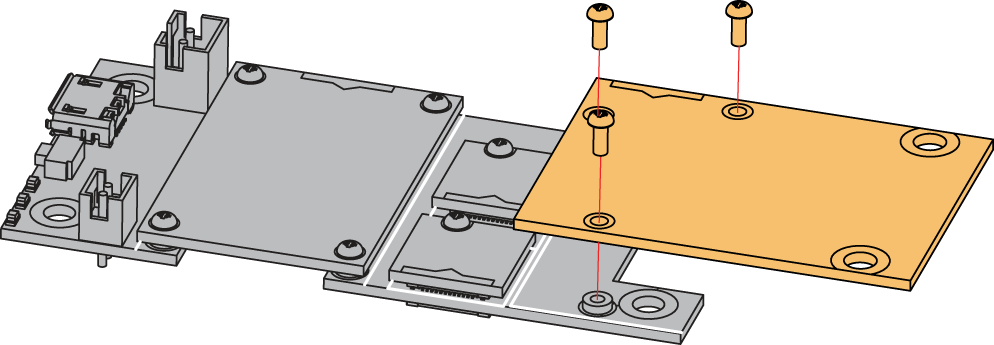 Figure 1: RAK13600 connection to WisBlock Base Board
Figure 1: RAK13600 connection to WisBlock Base BoardDisassembling
The procedure in disassembling any type of WisBlock modules is the same.
- First, remove the screws.
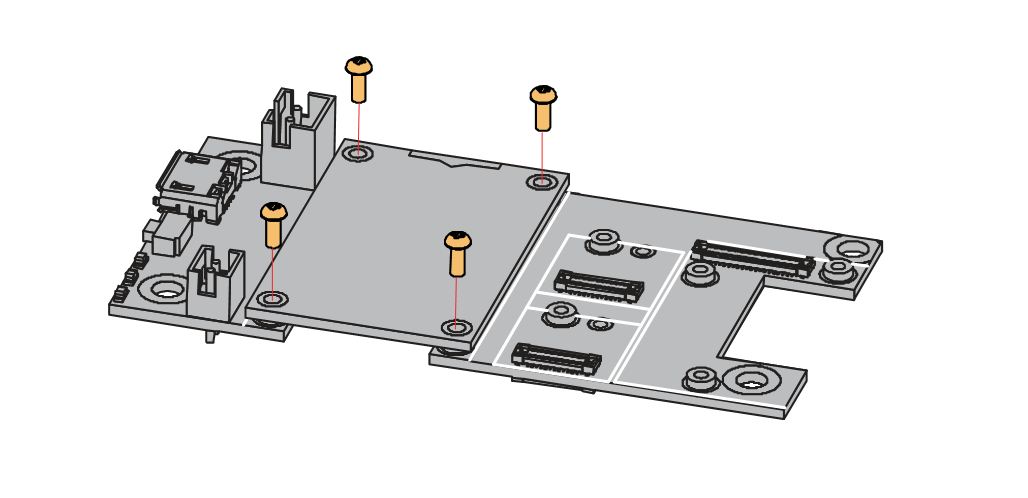 Figure 1: Removing screws from the WisBlock module
Figure 1: Removing screws from the WisBlock module- Once the screws are removed, check the silkscreen of the module to find the correct location where force can be applied.
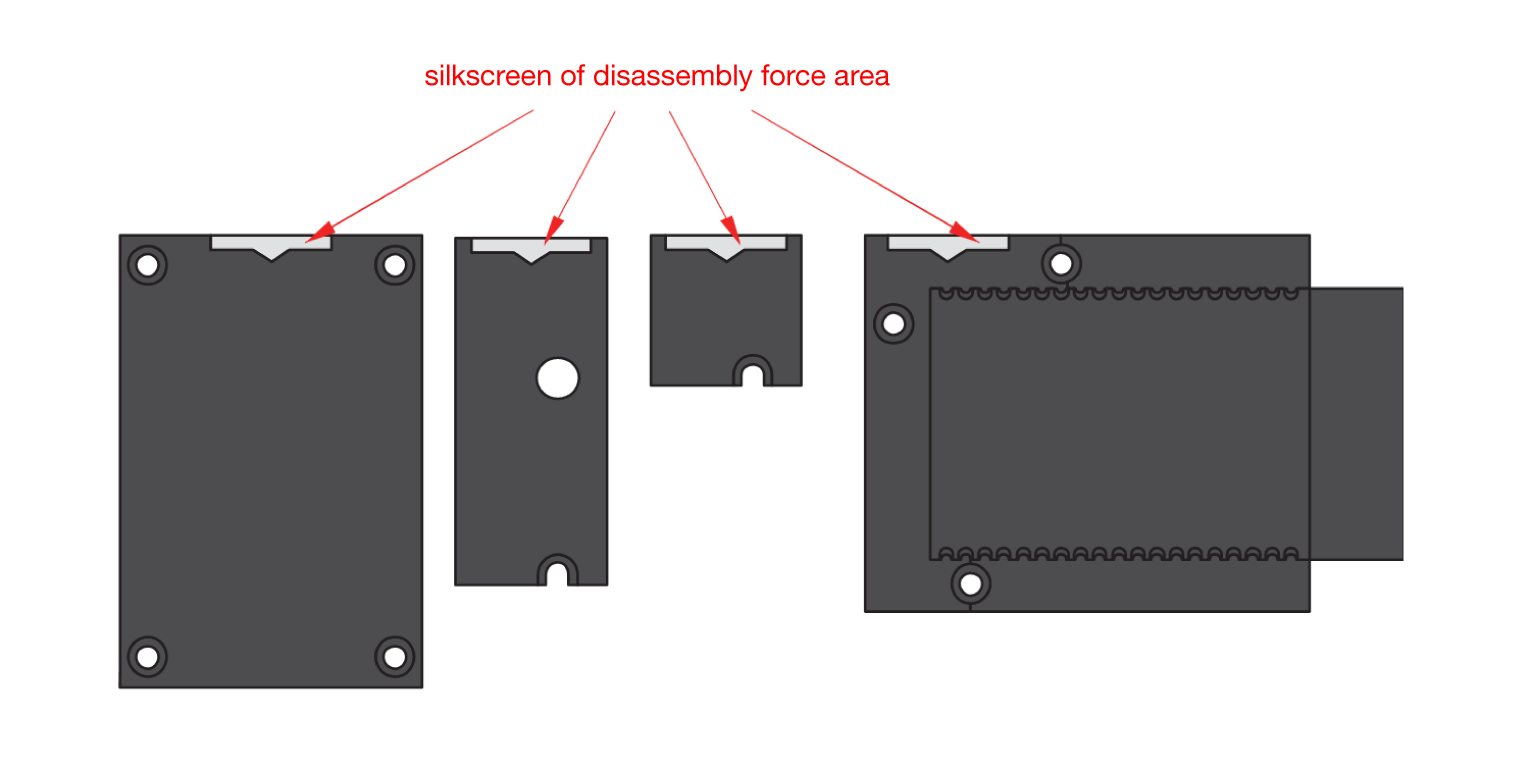 Figure 1: Detaching silkscreen on the WisBlock module
Figure 1: Detaching silkscreen on the WisBlock module- Apply force to the module at the position of the connector, as shown in Figure 6, to detach the module from the baseboard.
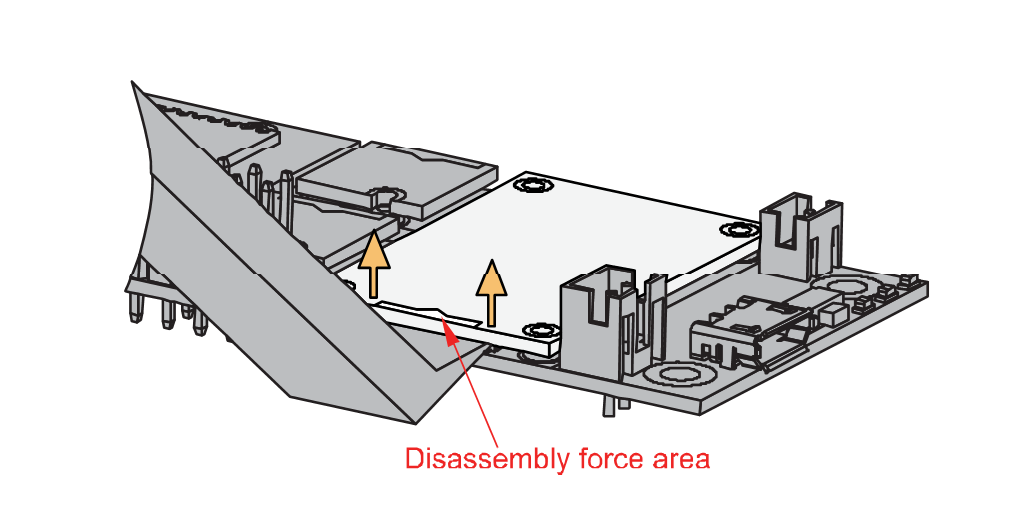 Figure 1: Applying even forces on the proper location of a WisBlock module
Figure 1: Applying even forces on the proper location of a WisBlock moduleIf you will connect other modules to the remaining WisBlock Base slots, check on the WisBlock Pin Mapper tool for possible conflicts. RAK13600 uses I2C and IO pins. It can cause possible conflict, especially on some IO modules.
After all this setup, you can now connect the battery (optional) and USB cable to start programming your WisBlock Core.
- Battery can cause harm if not handled properly.
- Only 3.7-4.2 V Rechargeable LiPo batteries are supported. It is highly recommended not to use other types of batteries with the system unless you know what you are doing.
- If a non-rechargeable battery is used, it has to be unplugged first before connecting the USB cable to the USB port of the board to configure the device. Not doing so might damage the battery or cause a fire.
- Make sure the battery wires match the polarity on the RAK WisBlock Base Board. Not all batteries have the same wiring.
- Only 5 V solar panels are supported. Do not use 12 V solar panels. It will destroy the charging unit and eventually other electronic parts.
Software Configuration and Example
The RAK13600 is based on the popular NFC/RFID chip PN532. You need to install the RAK13600-PN532 library to use the module. By default, the module communicates via I2C to the WisBlock Core module. The following guide shows how to test your RAK13600 module using a standard RFID card, as shown in Figure 7.
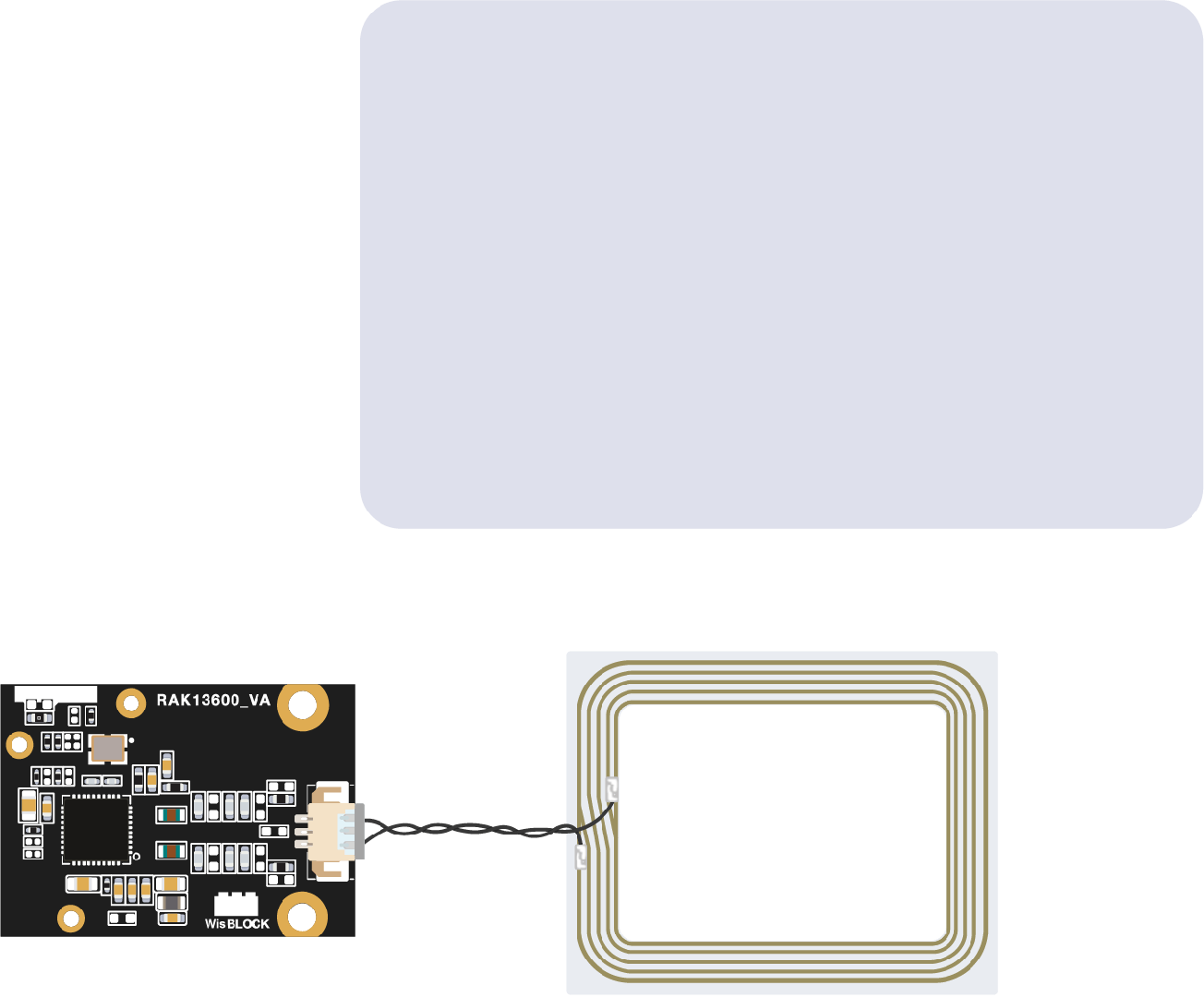 Figure 1: RAK13600 with Coil and RFID Card
Figure 1: RAK13600 with Coil and RFID Card- Open the Arduino IDE and select the WisBlock Core you use, as shown in Figure 8 to Figure 10.
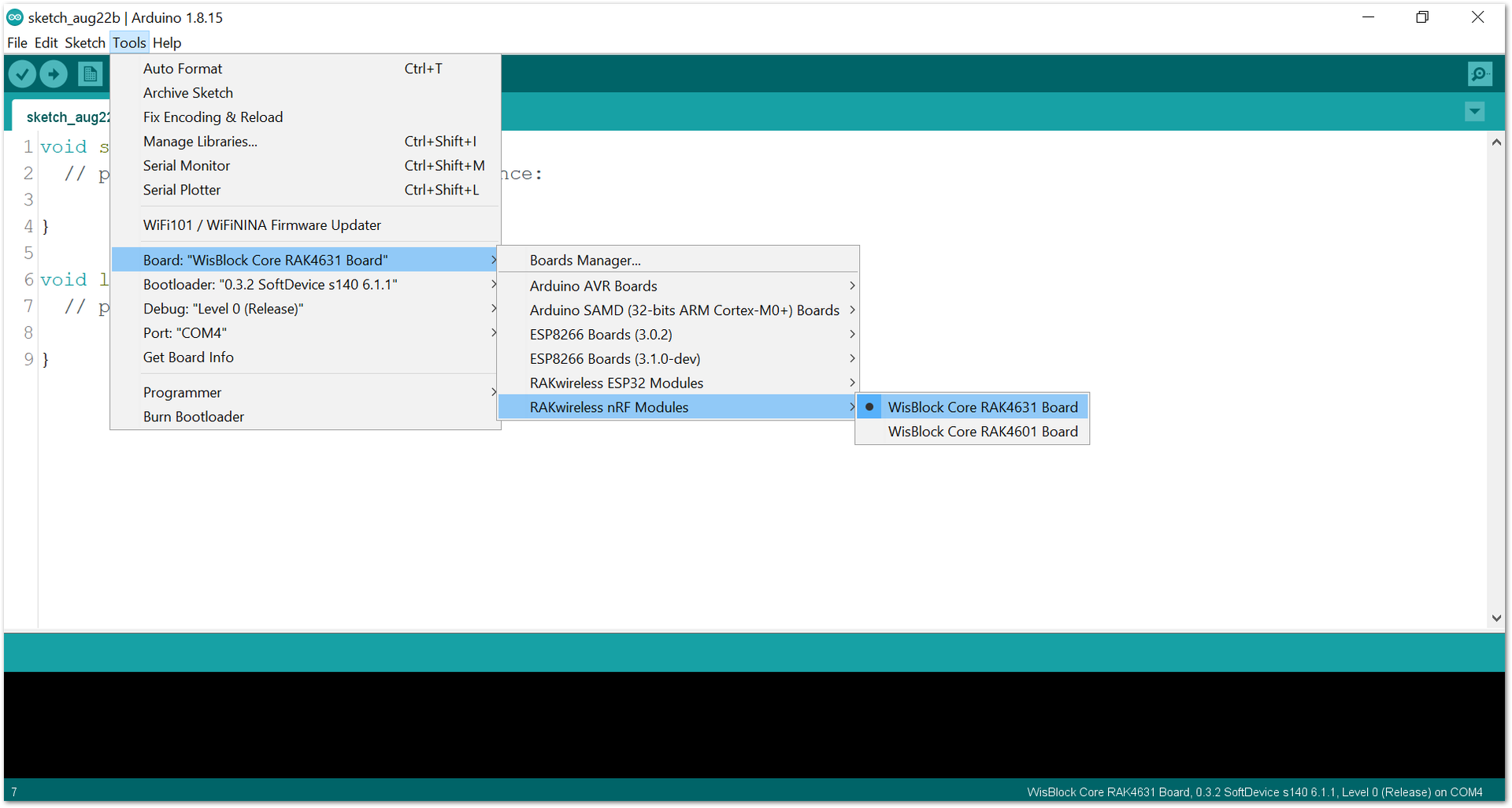 Figure 1: Selecting RAK4631 as WisBlock Core
Figure 1: Selecting RAK4631 as WisBlock Core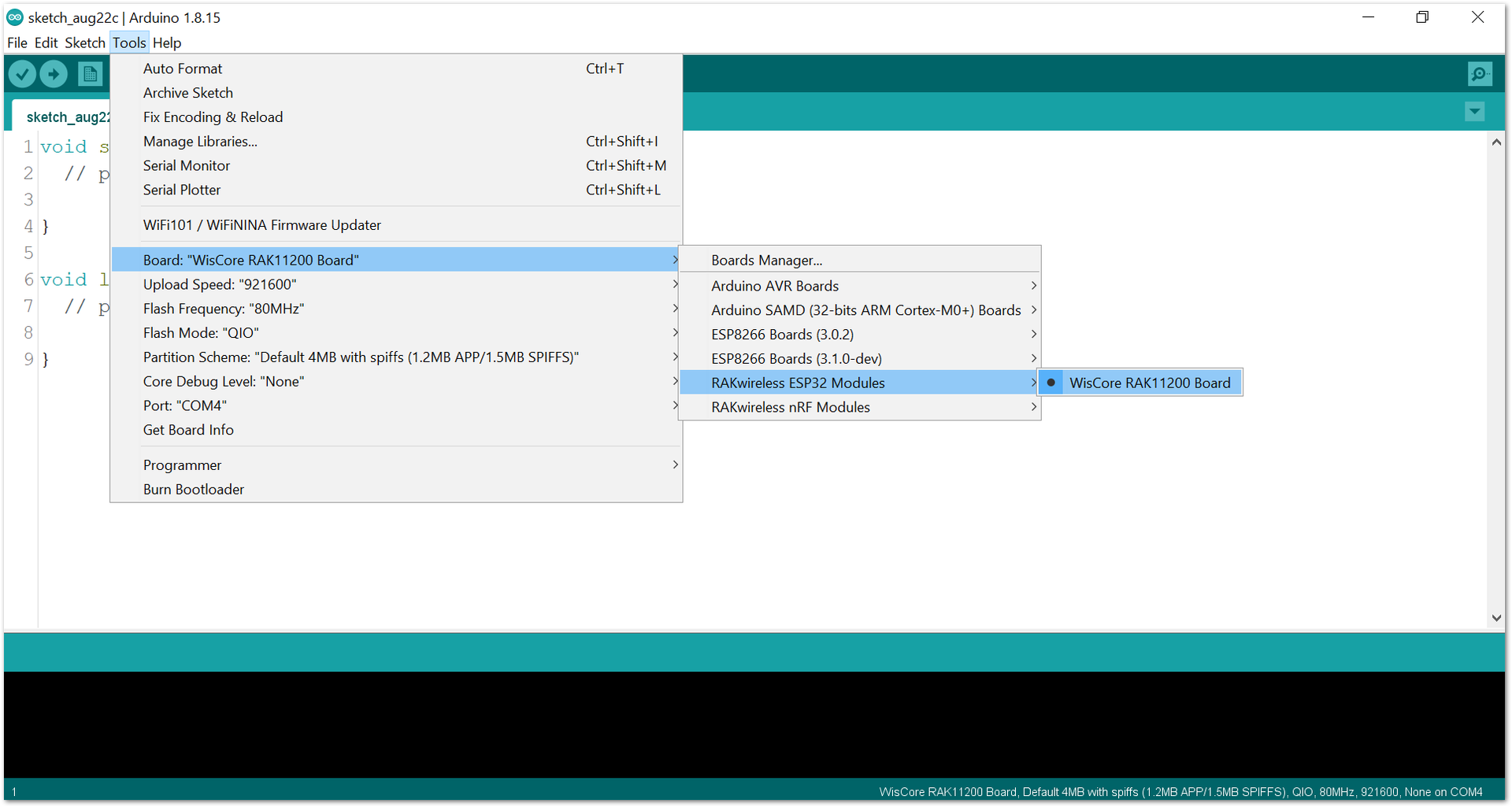 Figure 1: Selecting RAK11200 as WisBlock Core
Figure 1: Selecting RAK11200 as WisBlock Core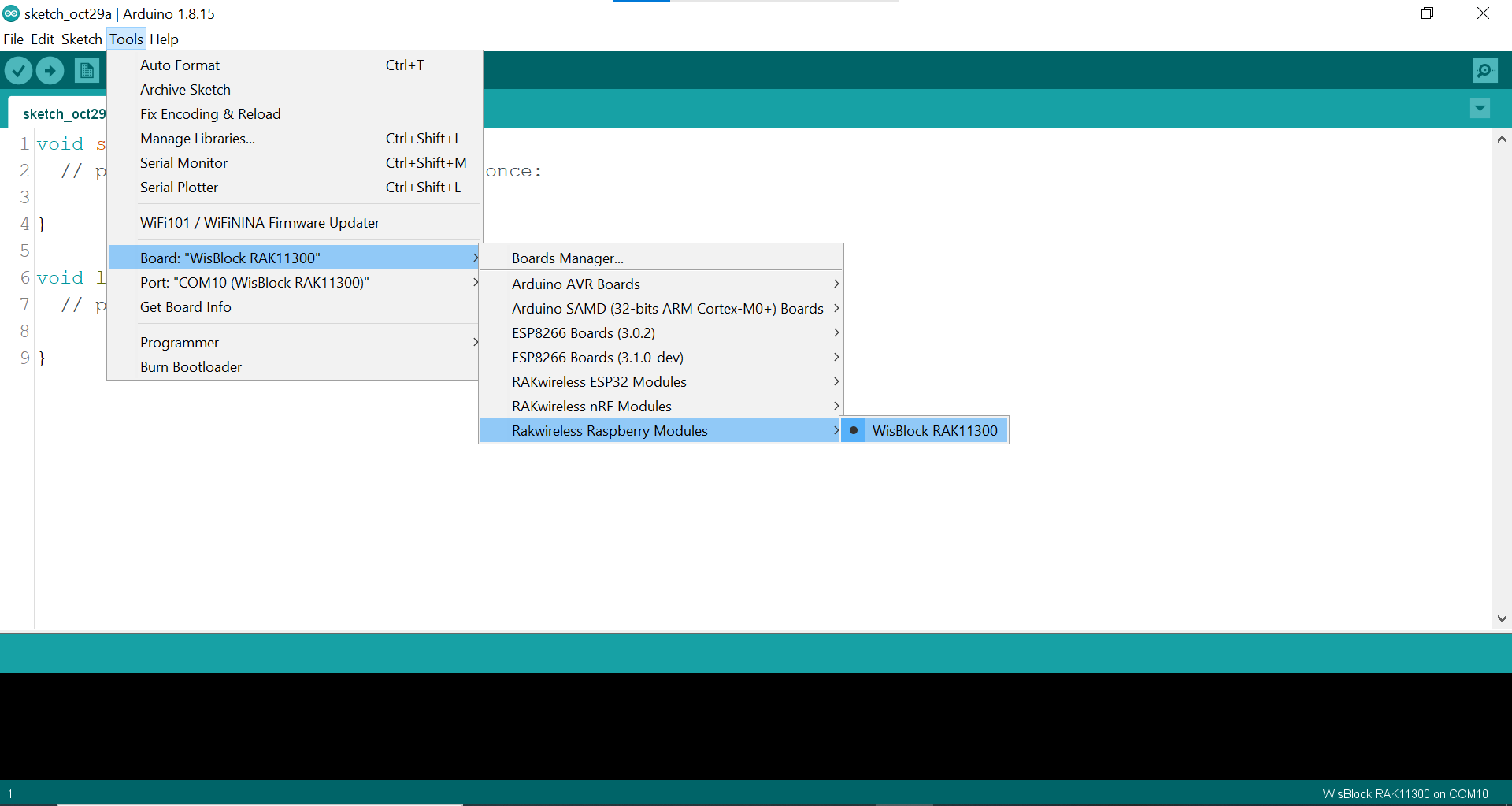 Figure 1: Selecting RAK11300 as WisBlock Core
Figure 1: Selecting RAK11300 as WisBlock Core- Copy the example code below and paste it on the Arduino IDE:
Click to view the example
/**
@file readMifareClassic.ino
@author rakwireless.com
@brief This example will wait for any ISO14443A card or tag, and depending on the size of the UID will attempt to read from it.
@version 0.1
@date 2021-10-14
@copyright Copyright (c) 2021
**/
#include <Wire.h>
#include <SPI.h>
#include <RAK13600-PN532.h> // Click here to get the library: http://librarymanager/All#RAK13600-PN532
// If using the breakout or shield with I2C, define just the pins connected
#define PN532_IRQ (WB_IO6)
#define PN532_RESET (WB_IO5) // Not connected by default on the NFC Shield
// Or use this line for a breakout or shield with an I2C connection:
NFC_PN532 nfc(PN532_IRQ, PN532_RESET);
void setup(void) {
Serial.begin(115200);
pinMode(WB_IO2, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(WB_IO2, HIGH);
delay(300);
while (!Serial) delay(10); // for Leonardo/Micro/Zero
Serial.println("Hello!");
nfc.begin();
uint32_t versiondata = nfc.getFirmwareVersion();
if (! versiondata) {
Serial.print("Didn't find PN53x board");
while (1); // halt
}
// Got ok data, print it out!
Serial.print("Found chip PN5"); Serial.println((versiondata>>24) & 0xFF, HEX);
Serial.print("Firmware ver. "); Serial.print((versiondata>>16) & 0xFF, DEC);
Serial.print('.'); Serial.println((versiondata>>8) & 0xFF, DEC);
// configure board to read RFID tags
nfc.SAMConfig();
Serial.println("Waiting for an ISO14443A Card ...");
}
void loop(void) {
uint8_t success;
uint8_t uid[] = { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }; // Buffer to store the returned UID
uint8_t uidLength; // Length of the UID (4 or 7 bytes depending on ISO14443A card type)
// Wait for an ISO14443A type cards (Mifare, etc.). When one is found
// 'uid' will be populated with the UID, and uidLength will indicate
// if the uid is 4 bytes (Mifare Classic) or 7 bytes (Mifare Ultralight)
success = nfc.readPassiveTargetID(PN532_MIFARE_ISO14443A, uid, &uidLength);
if (success) {
// Display some basic information about the card
Serial.println("Found an ISO14443A card");
Serial.print(" UID Length: ");Serial.print(uidLength, DEC);Serial.println(" bytes");
Serial.print(" UID Value: ");
nfc.PrintHex(uid, uidLength);
if (uidLength == 4)
{
// We probably have a Mifare Classic card ...
uint32_t cardid = uid[0];
cardid <<= 8;
cardid |= uid[1];
cardid <<= 8;
cardid |= uid[2];
cardid <<= 8;
cardid |= uid[3];
Serial.print("Seems to be a Mifare Classic card #");
Serial.println(cardid);
}
Serial.println("");
}
delay(2000);
}
- Install the RAK13600-PN532 library by clicking the link highlighted by red box, as shown in Figure 11.
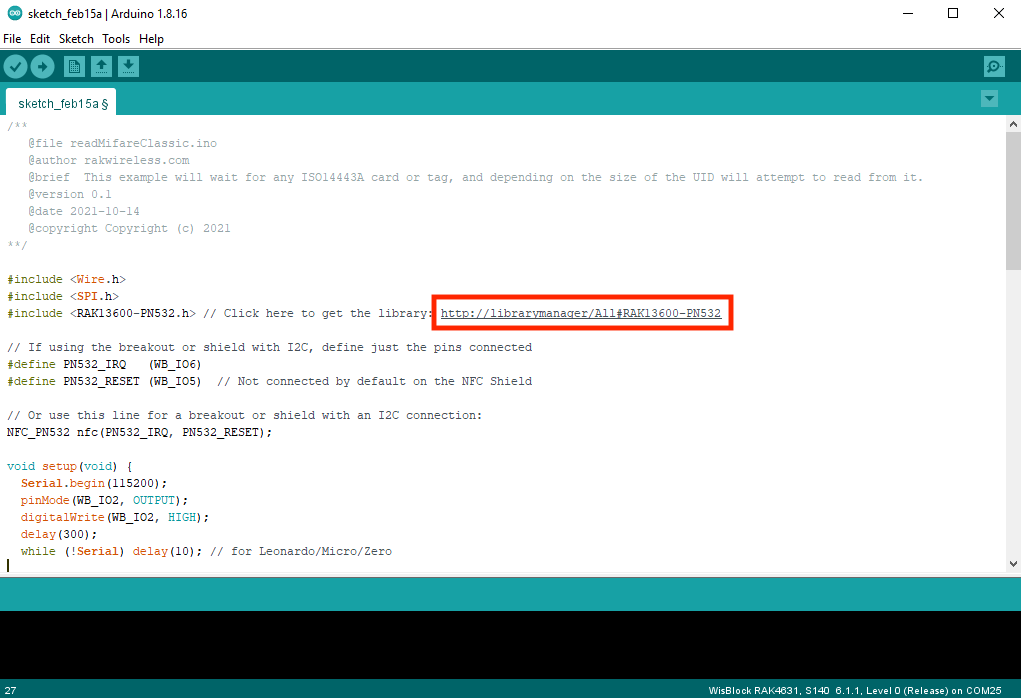 Figure 1: Getting the RAK13600-PN532 Library
Figure 1: Getting the RAK13600-PN532 Library- You will be directed to the Library Manager then you have to click install.
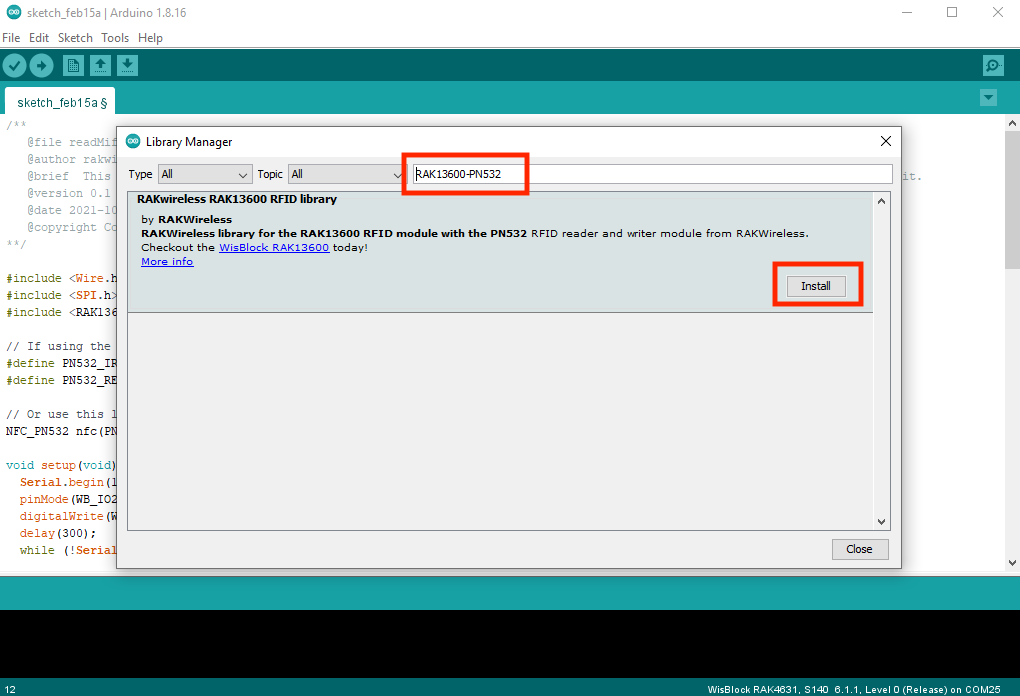 Figure 1: Installing RAK13600-PN532 Library
Figure 1: Installing RAK13600-PN532 Library- Next, you need to install an additional library from Adafruit. You need to type on the library search box
adafruit busiothen install it by clicking install. After the successful installation of the two libraries, you can now close the Library Manager window.
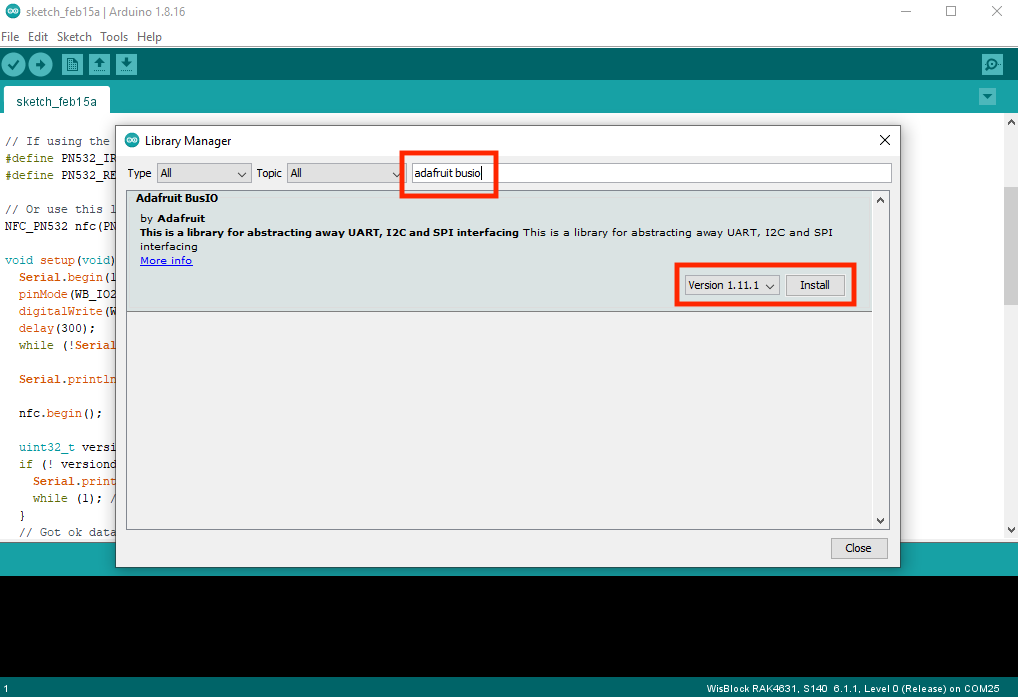 Figure 1: Installing Adafruit BusIO Library
Figure 1: Installing Adafruit BusIO Library- Select the right Serial Port and upload the code, as shown in Figure 14 and Figure 15.
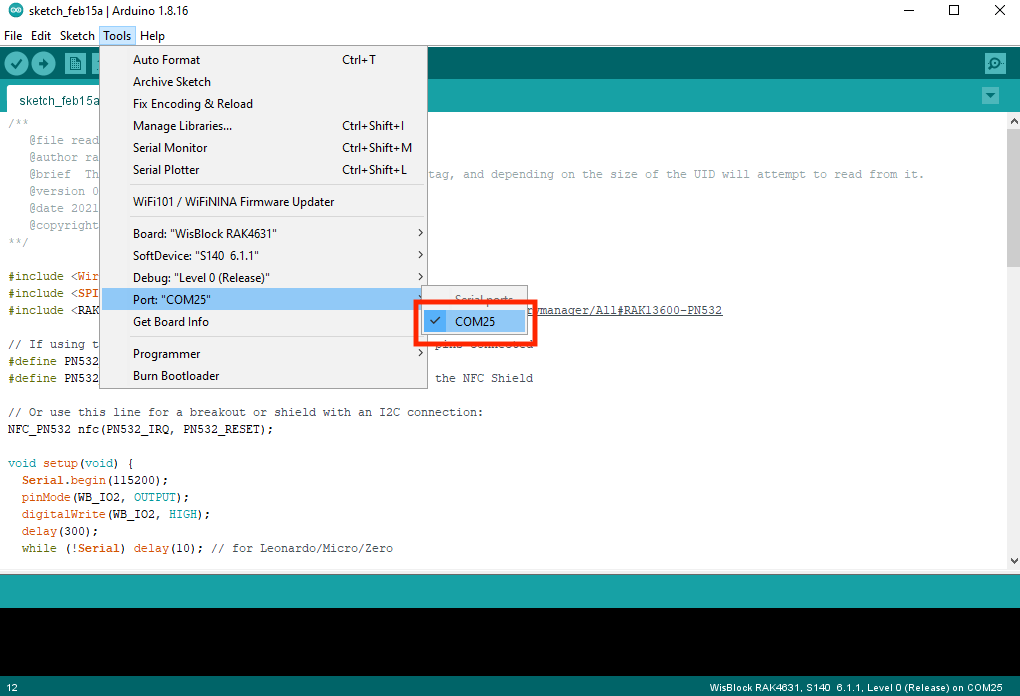 Figure 1: Selecting the correct Serial Port
Figure 1: Selecting the correct Serial Port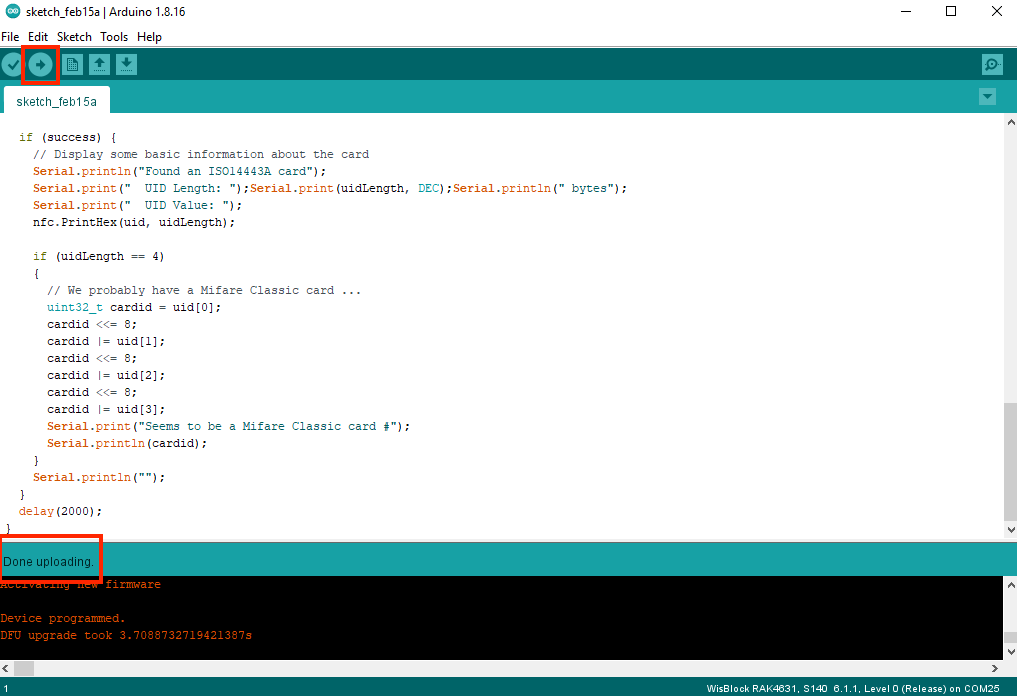 Figure 1: Uploading the sample code
Figure 1: Uploading the sample codeIf you experience any error in compiling the demo sketch, check the updated code for the RAK13600 readMifareClassic example. Other example codes for RAK13600 are also available on the RAK13600 WisBlock Example Code Repository.
If you are using RAK11200 as the WisBlock Core, it requires the BOOT0 pin to be configured properly before uploading. If not done properly, uploading the source code to RAK11200 will fail. Check the full details on the RAK11200 Quick Start Guide.
- When you have successfully uploaded the example code, open the serial monitor by clicking the magnifying glass icon on the upper right of the Arduino IDE then place the RFID card on top of the antenna coil. You should see the details of the card, as shown in Figure 16.
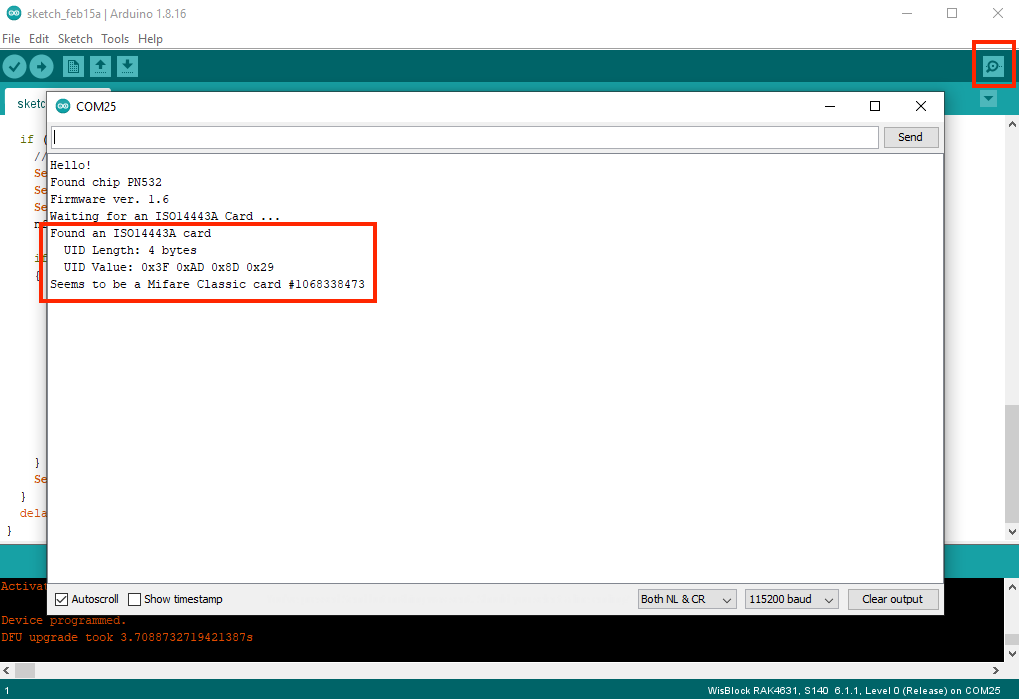 Figure 1: RFID Card Information Read by the RAK13600
Figure 1: RFID Card Information Read by the RAK13600