RAK7271/RAK7371 Quick Start Guide
Prerequisites
Hardware
Before proceeding with the installation guide for the RAK7271/7371 WisGate Developer Base, ensure you have prepared the necessary items listed below.:
- WisGate Developer Base RAK7271 or RAK7371
- A Host - Linux running PC/laptop or Raspberry Pi
The SIM card slot of the cellular versions is not hot-swappable. Make sure the gateway is switched off before inserting or ejecting the SIM card.
Package Inclusion
- 1pc WisGate Developer Base
- 1pc USB Type C to A Cable
- 1pc LoRa Antenna
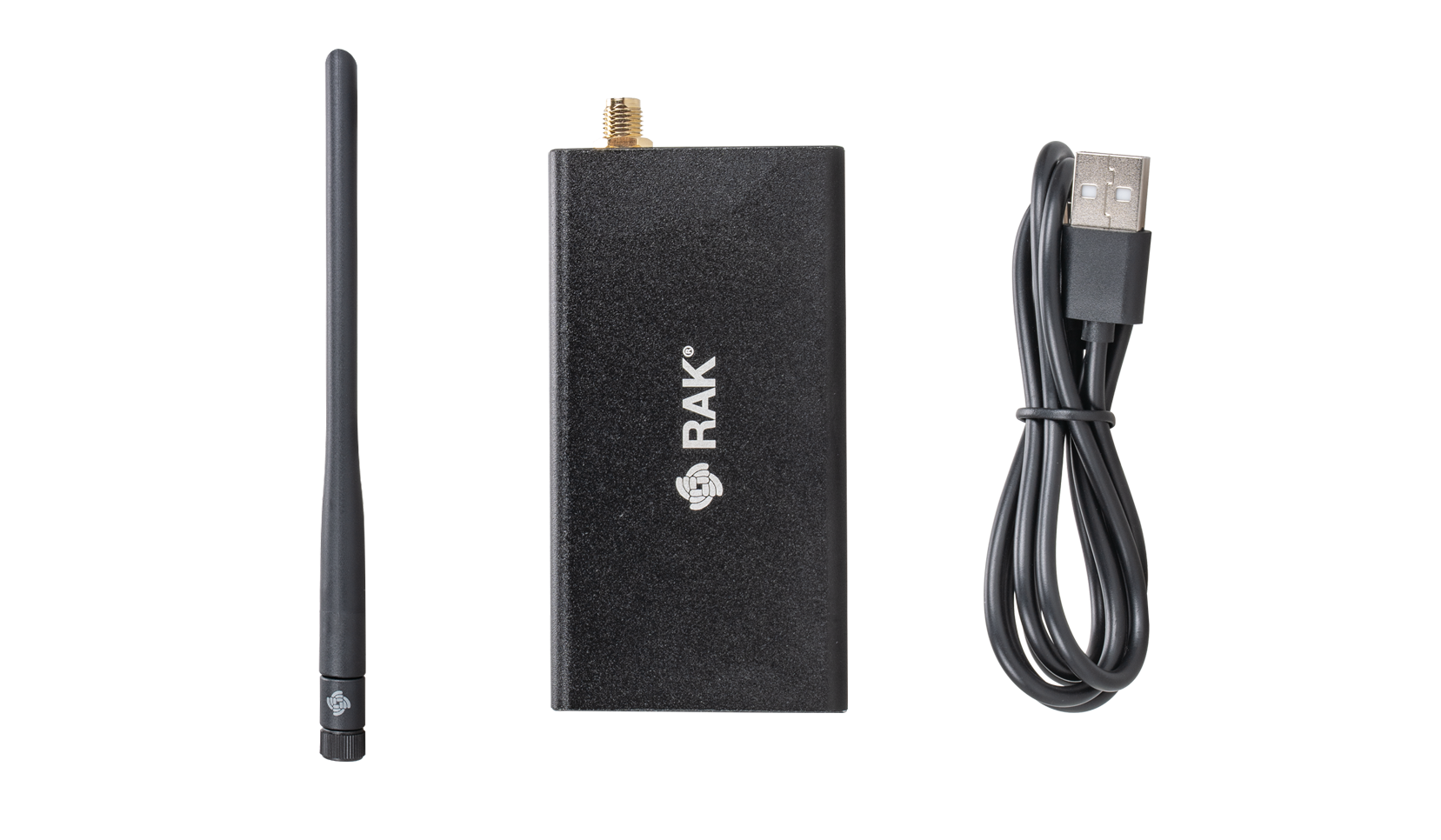 Figure 1: Package Content
Figure 1: Package ContentProduct Configuration
Raspberry Pi as a Host
Interface Between the Raspberry Pi and the WisGate Developer Base
It is assumed that your Raspberry Pi has already been installed with an OS and has internet access. You must also have an access to it over SSH or directly to the command line interface (CLI).
- Connect the WisGate Developer Base using the included cable: insert the Type-C end into the Developer Base and the Type-A end into one of the Raspberry Pi's USB ports.
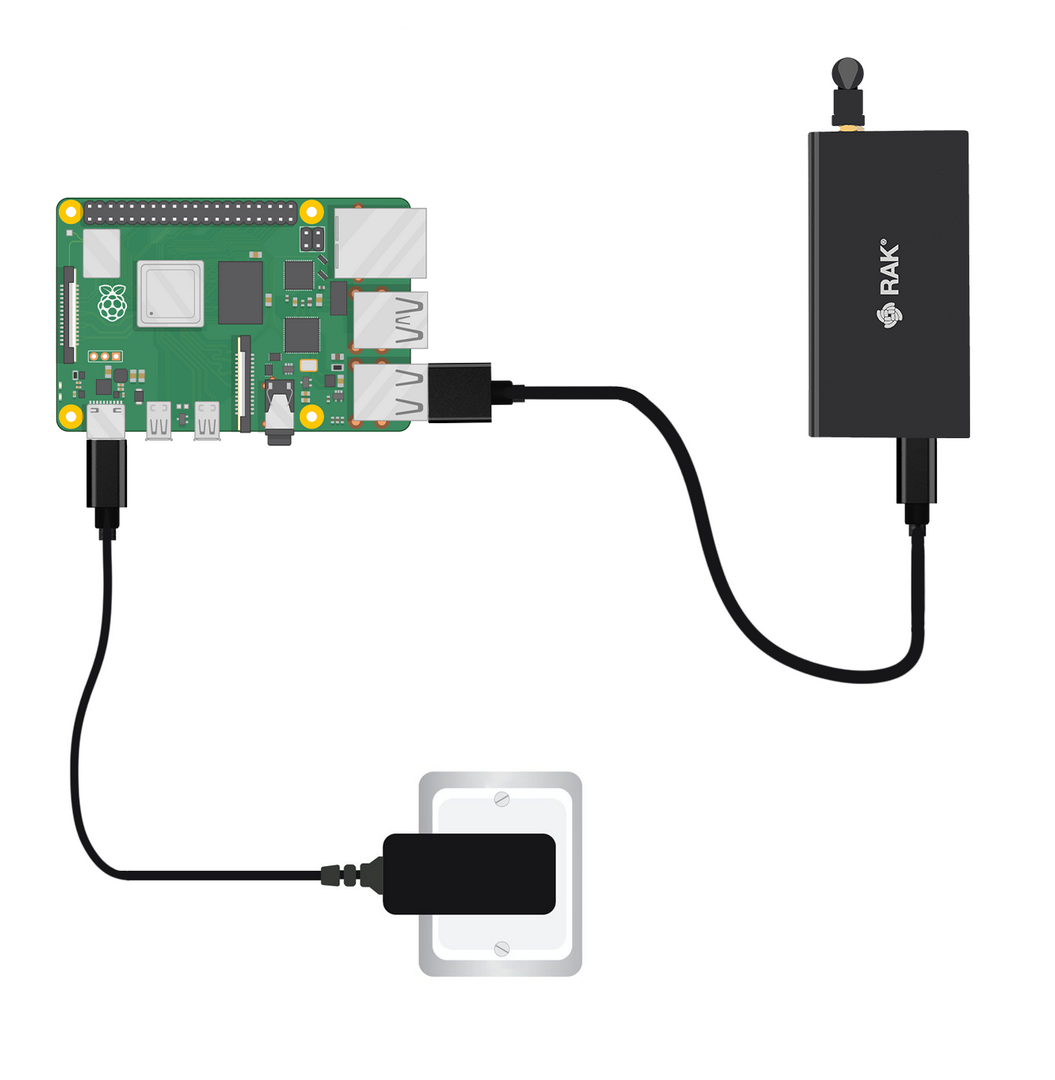 Figure 1: Connect the WisGate Developer Base to the Raspberry Pi
Figure 1: Connect the WisGate Developer Base to the Raspberry Pi- After connecting the Developer Base to the Pi, the Power Led will be steady green. This means that the Base is properly powered.
 Figure 1: Power On the Developer Base
Figure 1: Power On the Developer Base- Check if the base is properly connected by running this command on the CLI:
lsusb
- In the output, you should see a STMicroelectronics Virtual COM Port line. This means your RAK WisGate Developer Base is properly connoted to the Raspberry Pi.
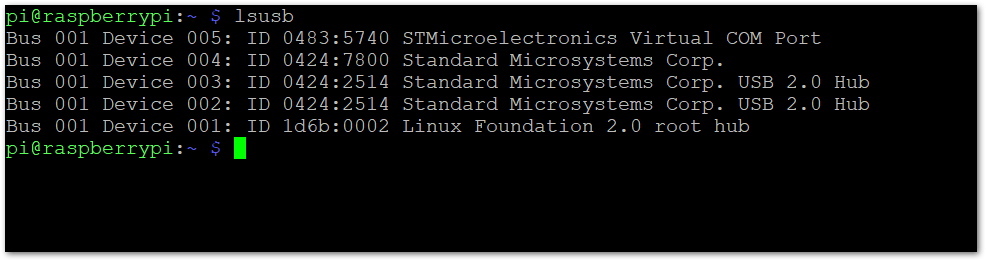 Figure 1: Check the Connection
Figure 1: Check the Connectionpi@raspberrypi:~ $ lsusb
Bus 001 Device 005: ID 0483:5740 STMicroelectronics Virtual COM Port
Bus 001 Device 004: ID 0424:7800 Standard Microsystems Corp.
Bus 001 Device 003: ID 0424:2514 Standard Microsystems Corp. USB 2.0 Hub
Bus 001 Device 002: ID 0424:2514 Standard Microsystems Corp. USB 2.0 Hub
Bus 001 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0002 Linux Foundation 2.0 root hub
pi@raspberrypi:~ $
Install the Software
To use the Base, you must install and configure the necessary software.
- To download the software, execute the following commands in the CLI:
- This command will check for the latest updates of the OS and download the Git tool that will allow downloading the software:
sudo apt update; sudo apt install git -y
- Download the required software.
git clone https://github.com/RAKWireless/rak_common_for_gateway.git
- Enter the created directory.
cd ~/rak_common_for_gateway
- Start the installation.
sudo ./install.sh
- You will be prompted to select the model of the concentrator you are installing.
- Select 9. RAK2287 USB if you are using the WisGate Developer Base RAK7271.
- Choose 10. RAK5146 USB if you are using the WisGate Developer Base RAK7371.
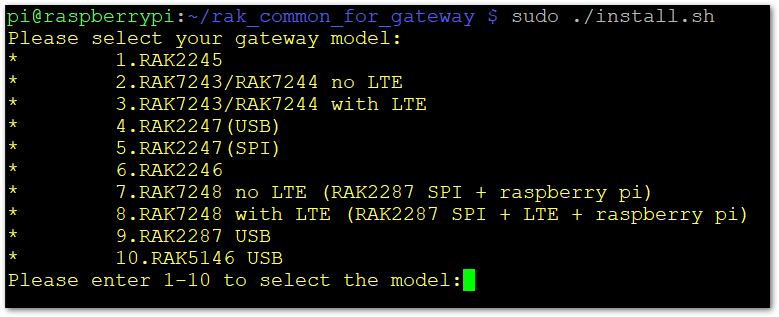 Figure 1: Select the Concentrator Model
Figure 1: Select the Concentrator ModelThe script will also install ChirpStack, an open-source LoRaWAN Network Server stack. It enables you to set up a fully functional LoRaWAN Server locally on the Raspberry Pi.
If you prefer not to install ChirpStack, run the installation script with the following parameter.:
sudo ./install.sh --chirpstack=not_install
- After a few minutes, the installation will be completed.
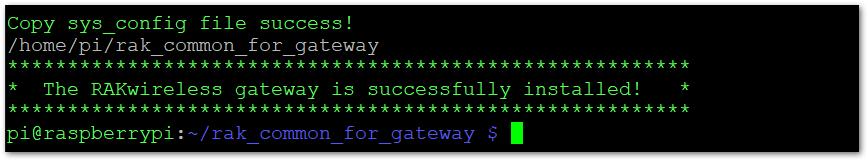 Figure 1: Successful Installation
Figure 1: Successful InstallationCopy sys_config file success!
/home/pi/rak_common_for_gateway
***********************************************************
* The RAKwireless gateway is successfully installed! *
***********************************************************
pi@raspberrypi:~/rak_common_for_gateway $
Linux Machine as a Host
Interface Between the Linux Machine and the WisGate Developer Base
Connect the two devices using the included USB cable to the host PC. It is recommended to use Ubuntu 18.04 LTS as the operating system.
 Figure 1: Connect the WisGate Developer Base to the Host
Figure 1: Connect the WisGate Developer Base to the HostSoftware Installation
To use the Base, you need to install and configure the required software. The procedure varies slightly between the two variants of the WisGate Developer Base.
For RAK7271 WisGate Developer Base with RAK2287 Inside
- Install the required make and gcc tools.
sudo apt install make
sudo apt install gcc
- Download the archive from the Semtech repository:
wget https://github.com/Lora-net/sx1302_hal/archive/V2.0.1.tar.gz
- After the download is complete, extract the files with the command:
tar -zxvf V2.0.1.tar.gz
- Enter the created folder.
cd sx1302_hal-2.0.1
- Run the make command to compile the software.
sudo make
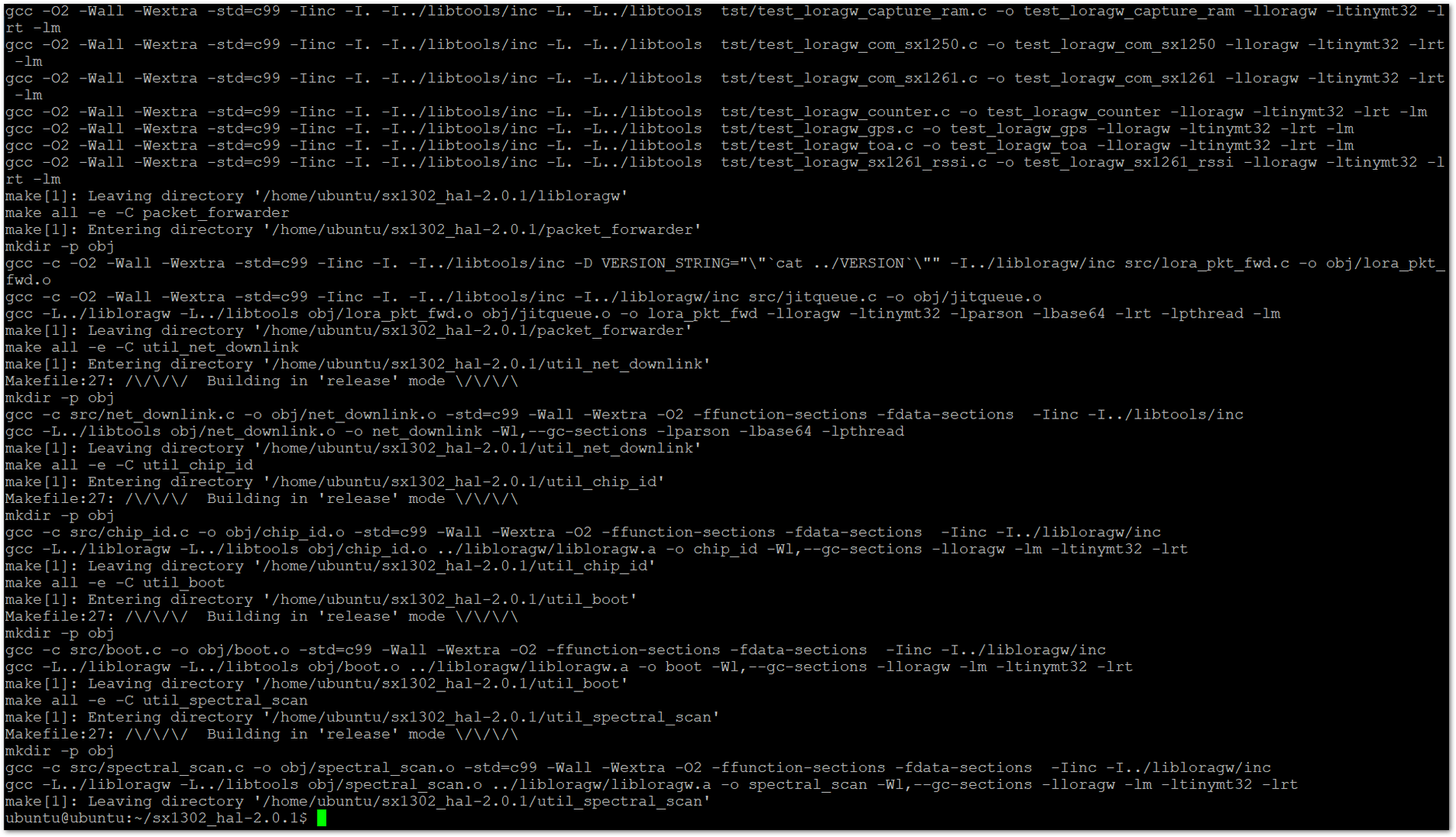 Figure 1: Install the Software
Figure 1: Install the SoftwareAfter the compilation is complete, configure the correct channel plan by setting the appropriate global_conf.json file for the packet forwarder.
-
Navigate to the Packet forwarder folder.
cd packet_forwarder -
Then list the files and folders:
ls -l
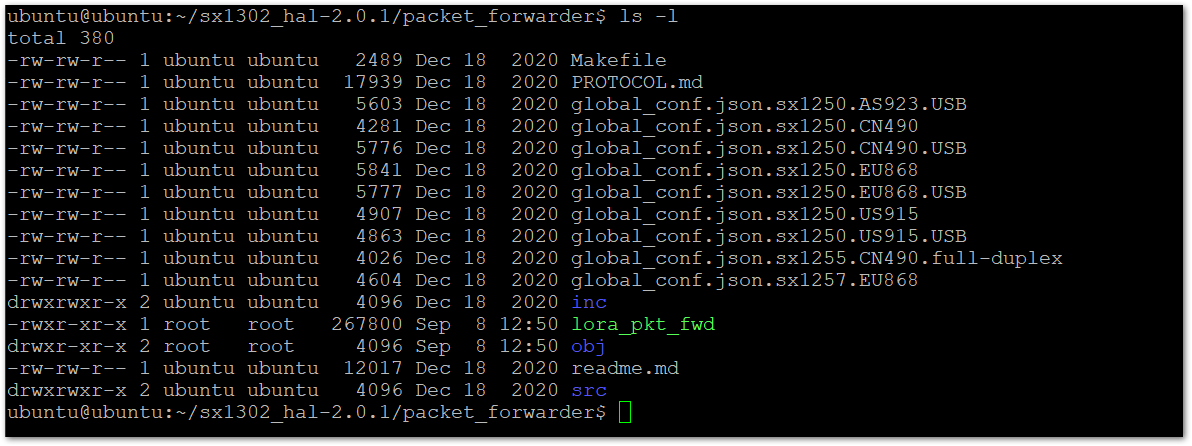 Figure 1: List the Content of the Folder
Figure 1: List the Content of the Folder- You can see that there is a different example configuration files for different LoRaWAN bands and different types of concentrators. In this setup, you are using RAK Developer Base, which is the USB, and the EU868 band. Run this command to rename the correct file to
global_conf.json:
cp global_conf.json.sx1250.EU868.USB global_conf.json
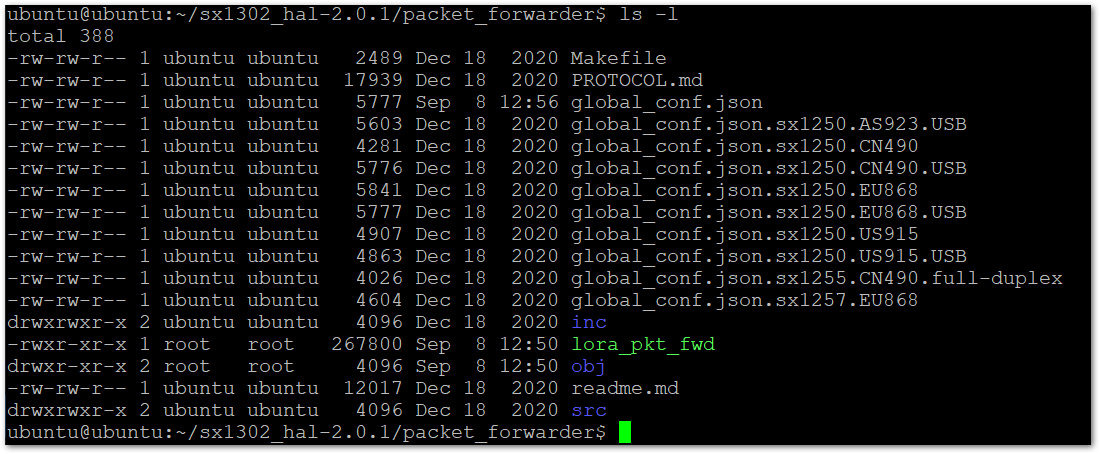 Figure 1: List the Content of the Folder After Renaming
Figure 1: List the Content of the Folder After Renaming- Start the packet forwarder process to bridge the LoRaWAN radio component with the Network Server.
sudo ./lora_pkt_fwd
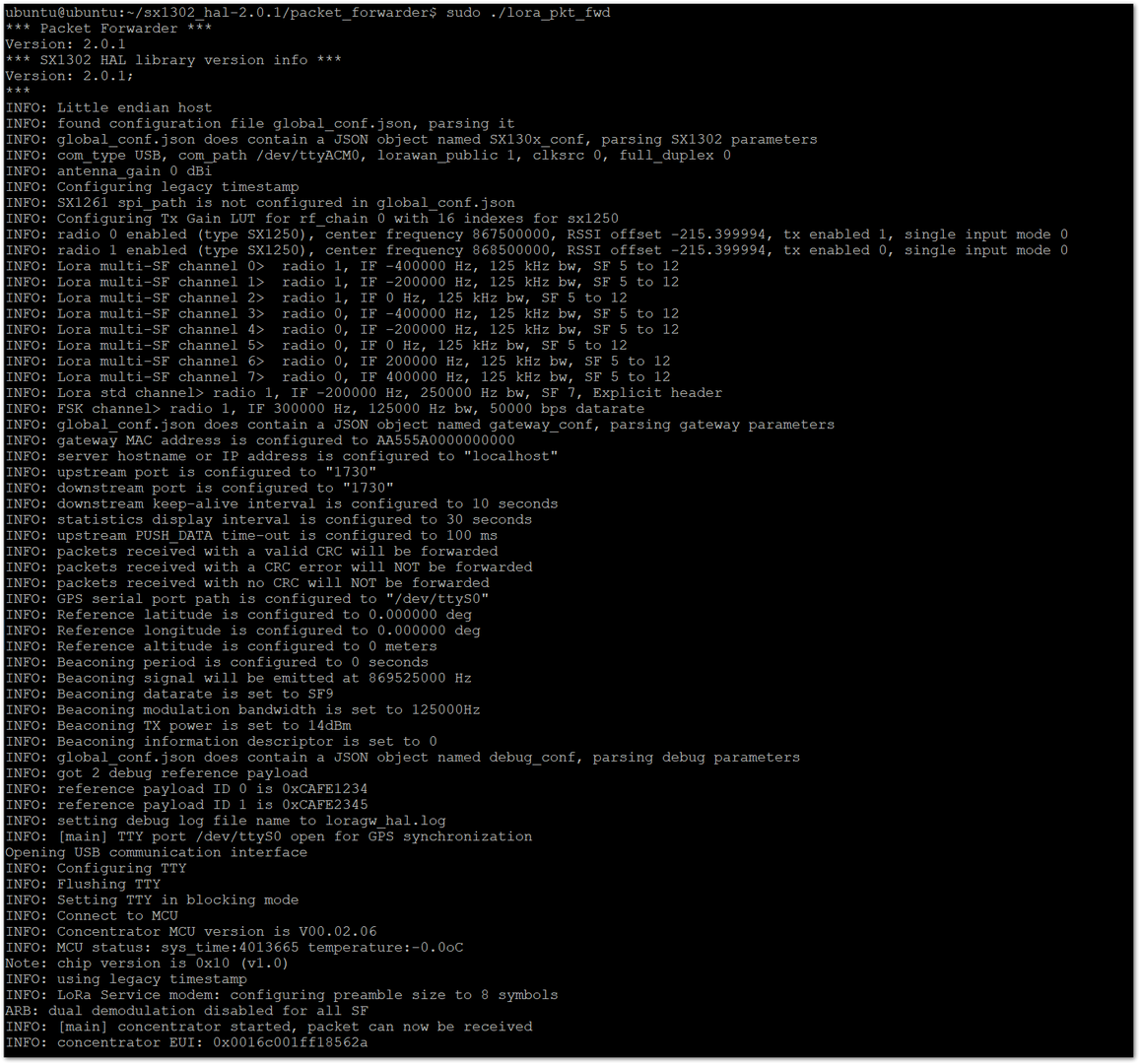 Figure 1: Start the Packet Forwarder
Figure 1: Start the Packet Forwarder- At the end of this example, you can see the concentrator's EUI. Save it somewhere as it will be needed to register your gateway in the Network Server later.
You can also retrieve the EUI using the chip_id tool located in the util_chip_id folder. Navigate to the folder and execute the following command:
sudo ./chip_id -u -d /dev/ttyACM0
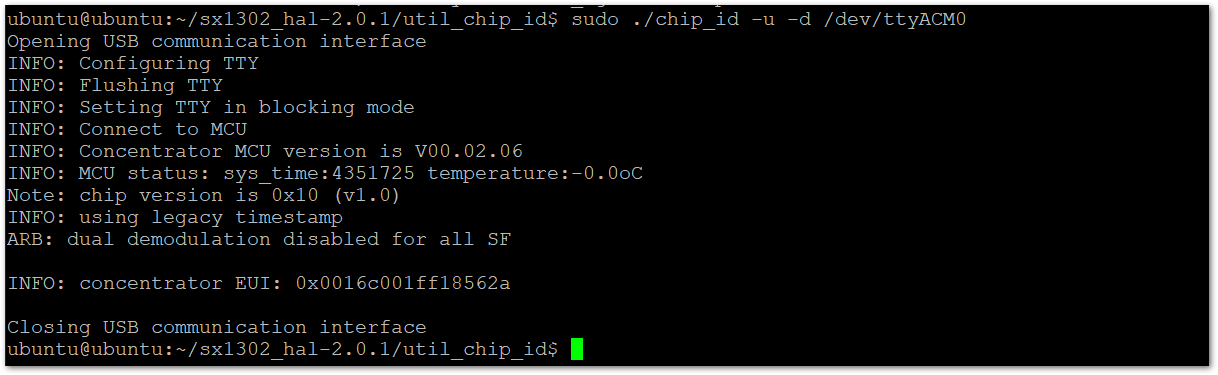 Figure 1: Concentrator EUI
Figure 1: Concentrator EUIFor RAK7371 WisGate Developer Base with RAK5146 Inside
- Install the required make and gcc tools.
sudo apt install make
sudo apt install gcc
- Clone the software from the Git reposiory:
sudo git clone https://github.com/Lora-net/sx1302_hal.git
- After the download is complete, navigate to the newly created folder.
cd sx1302_hal
- Run the make command to compile the software.
sudo make
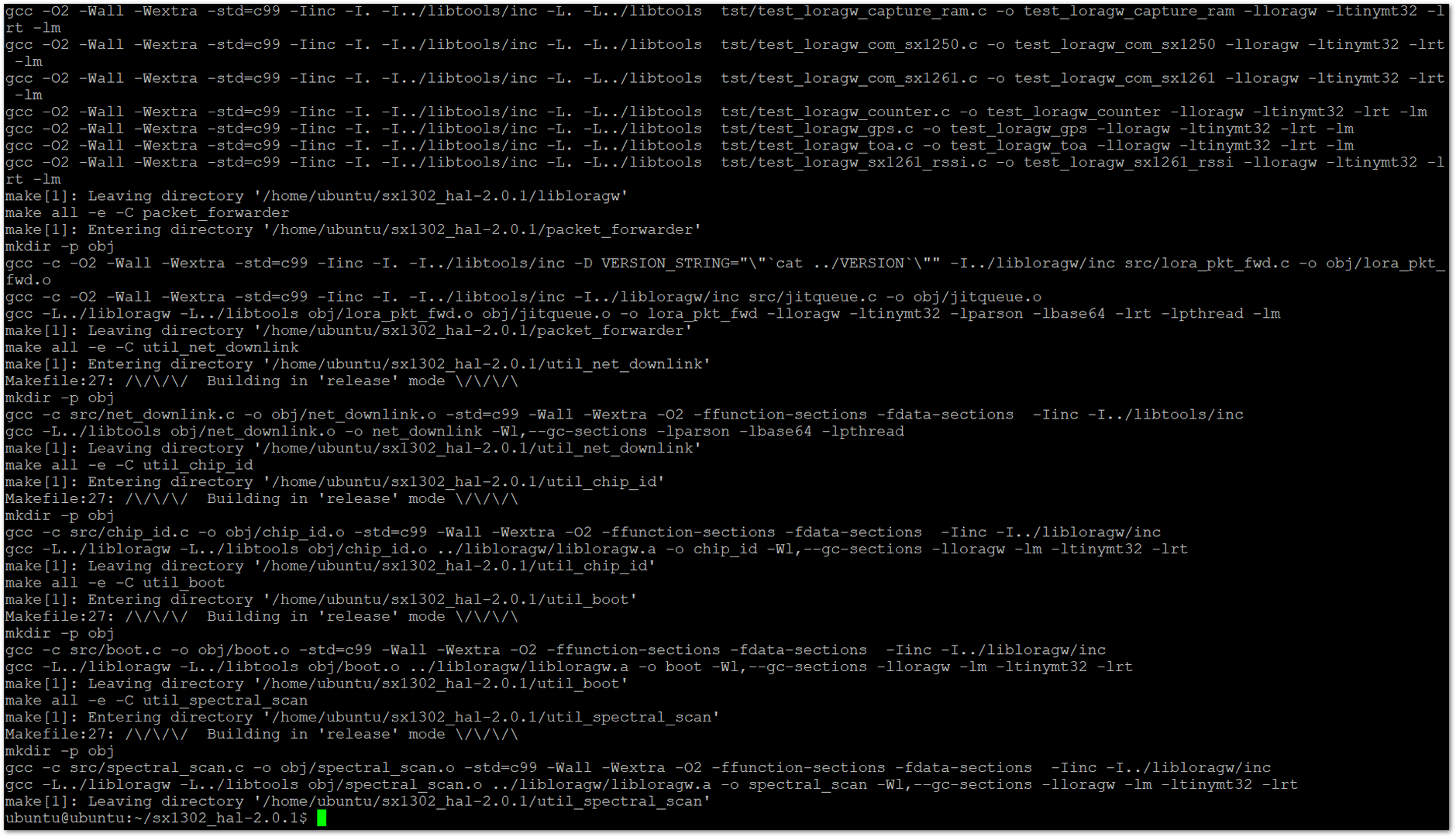 Figure 1: Install the Software
Figure 1: Install the Software- Open the Packet forwarder folder with the following command:
cd packet_forwarder
- And then list the files and folders.
ls -l
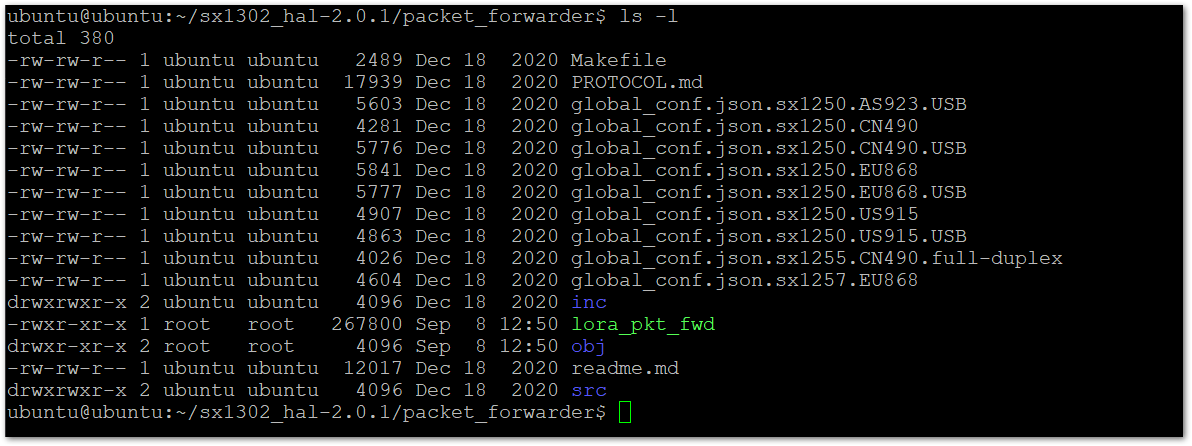 Figure 1: List the Content of the Folder
Figure 1: List the Content of the Folder- You will find different example configuration files for various LoRaWAN bands and concentrator types. For this setup, you are using the RAK Developer Base (USB) with the EU868 band. Run the following command to rename the appropriate file to
global_conf.json.
cp global_conf.json.sx1250.EU868.USB global_conf.json
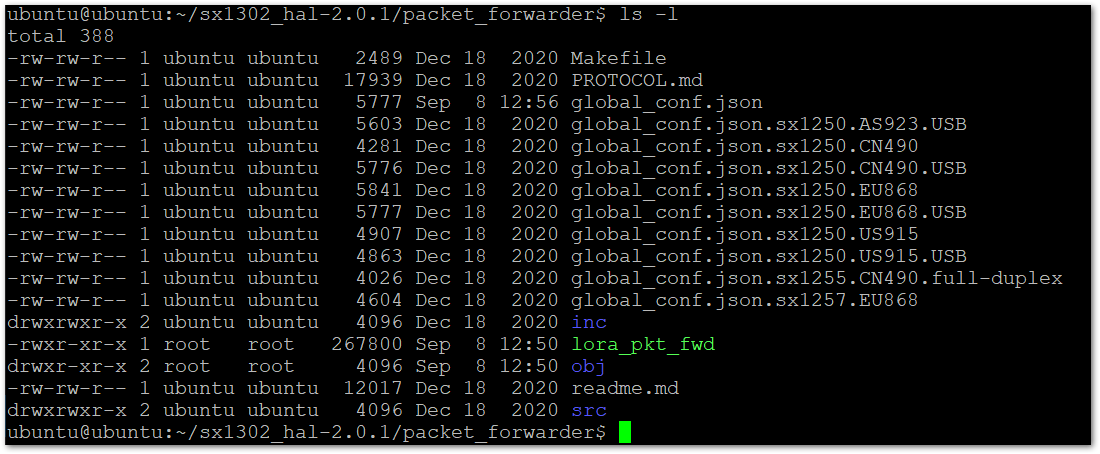 Figure 1: List the Content of the Folder After Renaming
Figure 1: List the Content of the Folder After Renaming- Start the packet forwarder process to bridge the LoRaWAN radio component with the Network Server.
sudo ./lora_pkt_fwd
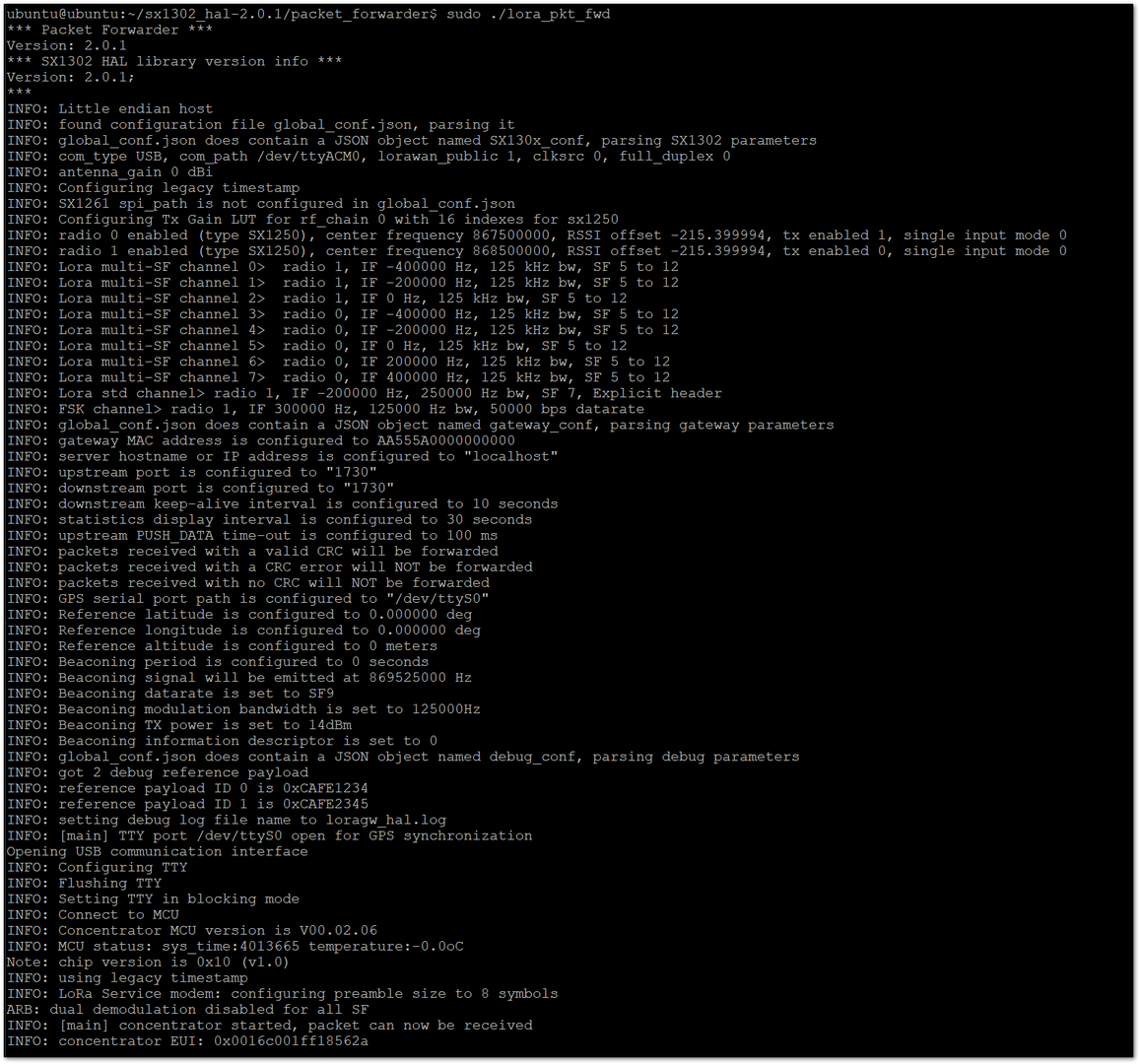 Figure 1: Start the Packet Forwarder
Figure 1: Start the Packet Forwarder- At this stage, you can view the concentrator's EUI. Be sure to save it, as it will be required to register your gateway in the Network Server later.
You can also retrieve the EUI using the chip_id tool located in the util_chip_id folder. Navigate to the folder and execute the following command:
sudo ./chip_id -u -d /dev/ttyACM0
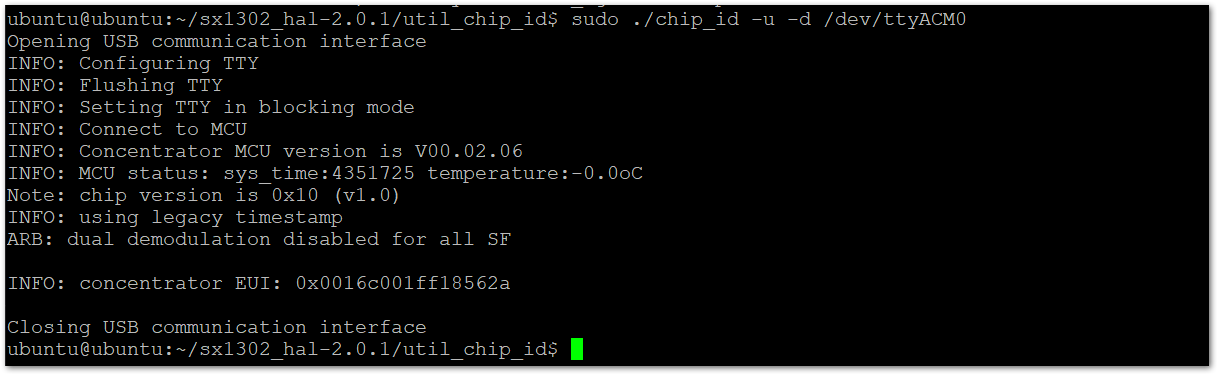 Figure 1: Concentrator EUI
Figure 1: Concentrator EUIConnect to The Things Network V3 (TTNv3)
Using Raspberry Pi as a Host
Connecting to TTN is straightforward using the RAKwireless scripts.
- Open the configuration tool by running the command in the Raspberry Pi CLI.
sudo gateway-config
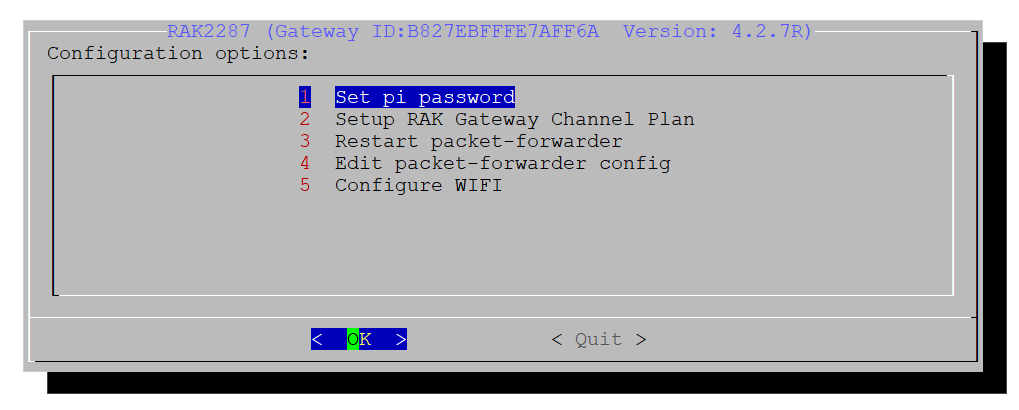 Figure 1: Open the Configuration Tool
Figure 1: Open the Configuration Tool- Select the option 2 Setup RAK Gateway Channel Plan.
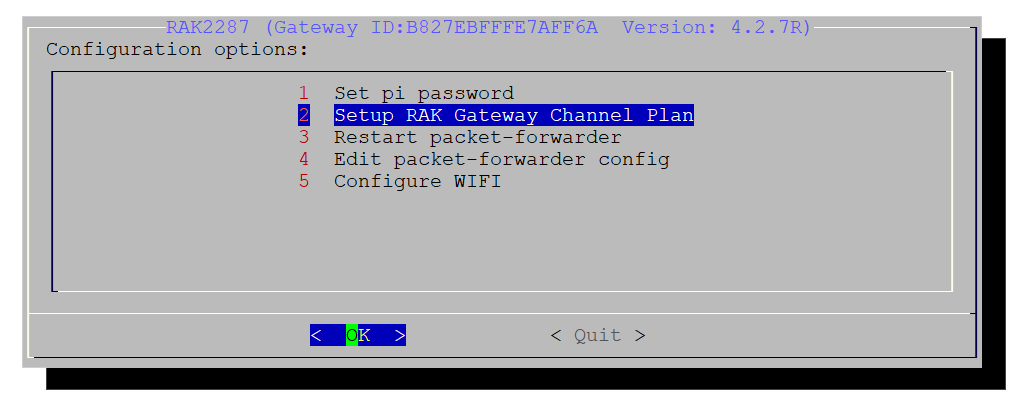 Figure 1: Make a Selection
Figure 1: Make a Selection- On the next window, choose the option 1 Server is TTN.
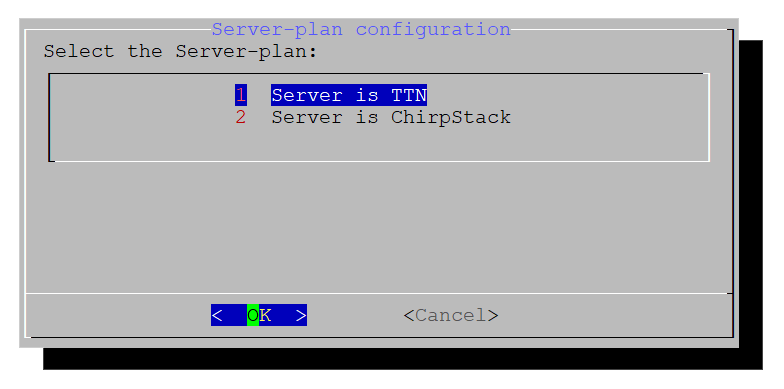 Figure 1: Select the Server
Figure 1: Select the Server- Select the correct band.
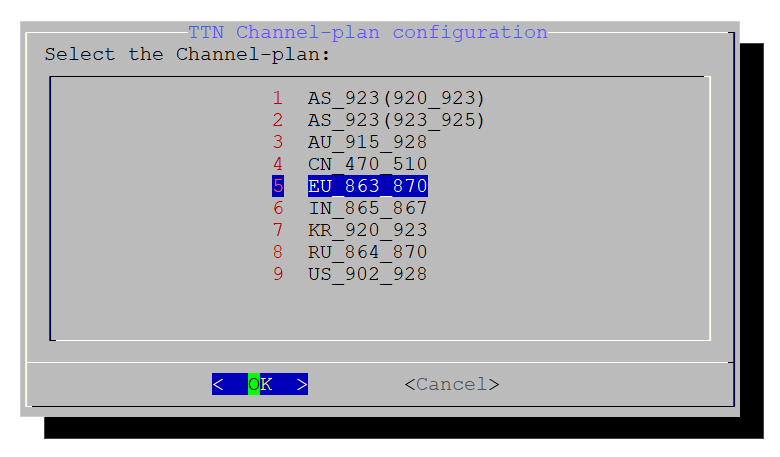 Figure 1: Select the Channel Plan
Figure 1: Select the Channel Plan- Select option 4 Edit packet-forwarder config.
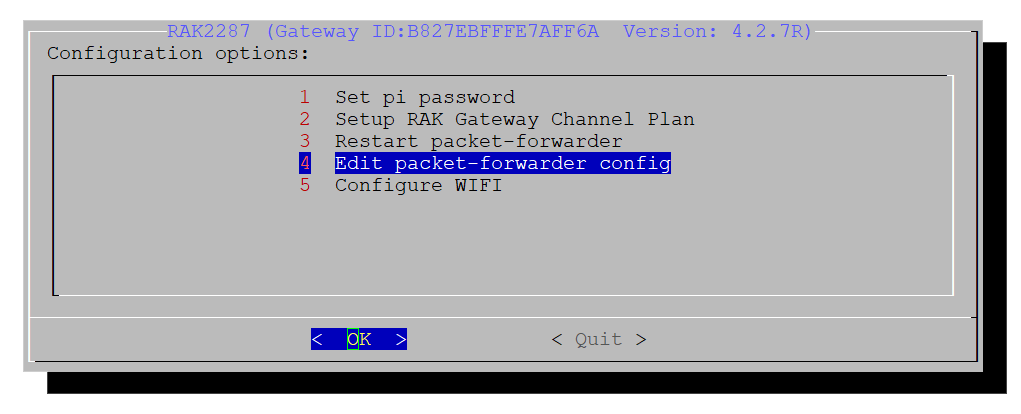 Figure 1: Configuration Options
Figure 1: Configuration Options- Based on your location, set the appropriate TTN address for the packet forwarder. The configuration file will open for editing.
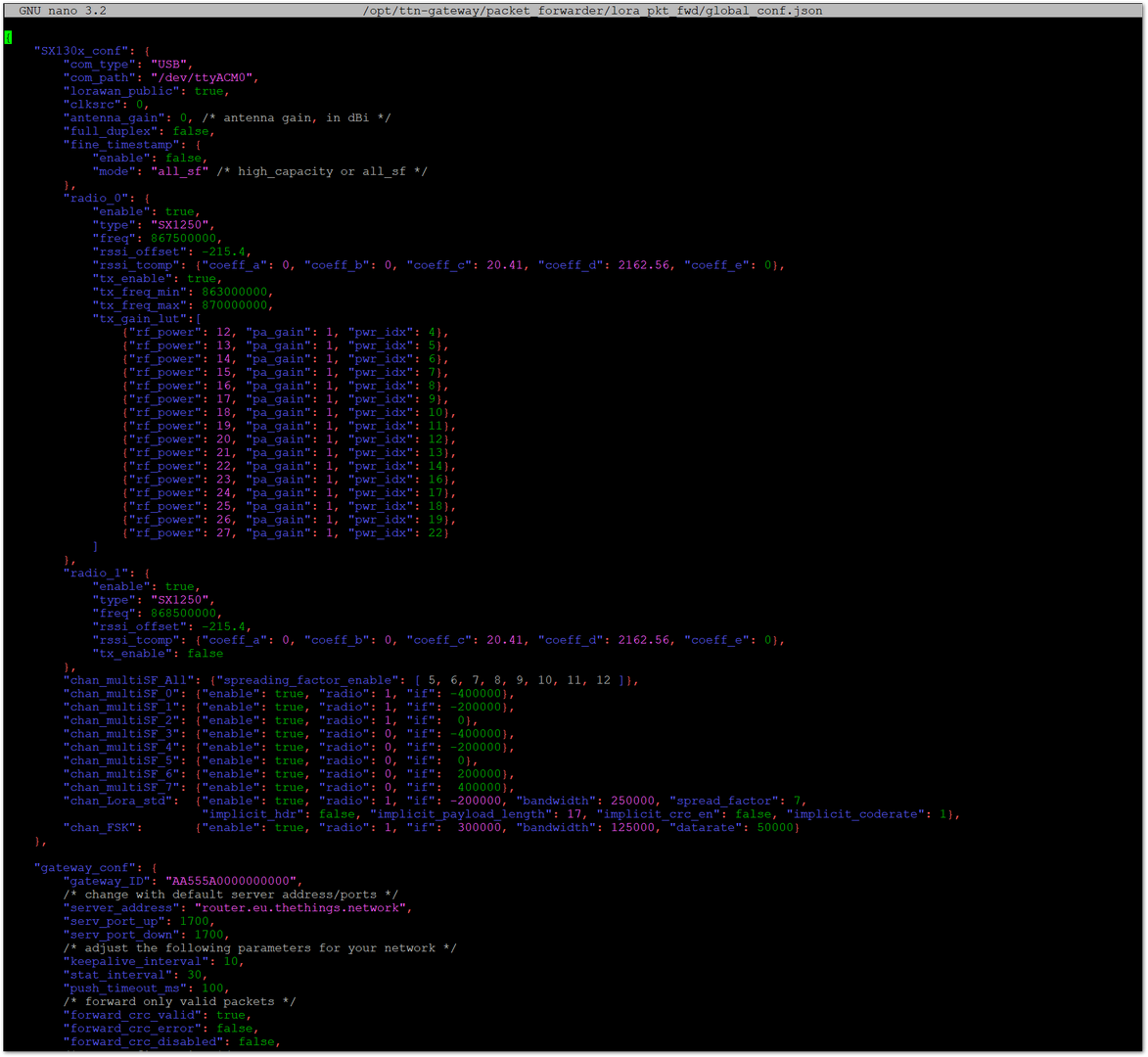 Figure 1: File Content Configuration
Figure 1: File Content Configuration - Find the "gateway_conf" section:
"gateway_conf": {
"gateway_ID": "AA555A0000000000",
/* change with default server address/ports */
"server_address": "router.eu.thethings.network",
"serv_port_up": 1700,
"serv_port_down": 1700,
- In the configuration file, update the "server_address" line to the appropriate TTN URL. For example, the URL for Europe is:
eu1.cloud.thethings.network
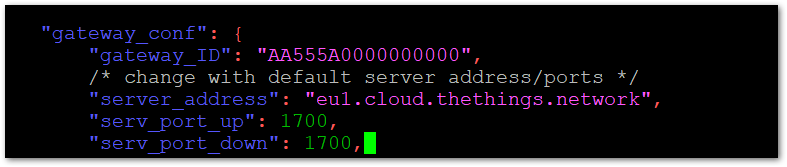 Figure 1: Change the server address
Figure 1: Change the server address-
To save the changes, press Ctrl+X and then confirm by pressing Y.
-
Restart the packet forwarder by choosing the Option 3.
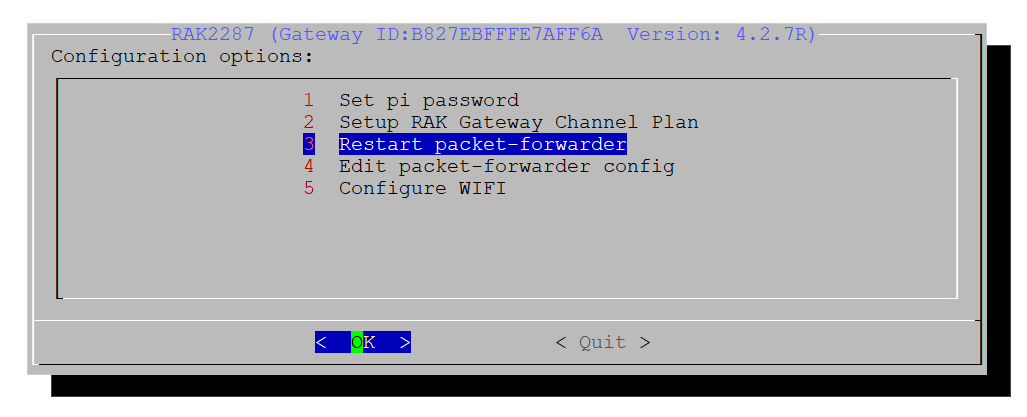 Figure 1: Restart the Packet Forwarder
Figure 1: Restart the Packet Forwarder- Quit to exit from the configuration menu.
Now, you have a fully working gateway that is configured to use TTN as Network Server.
- To register the gateway with TTN, you will need its EUI. Use the following command in the CLI to retrieve the EUI:
sudo gateway-version
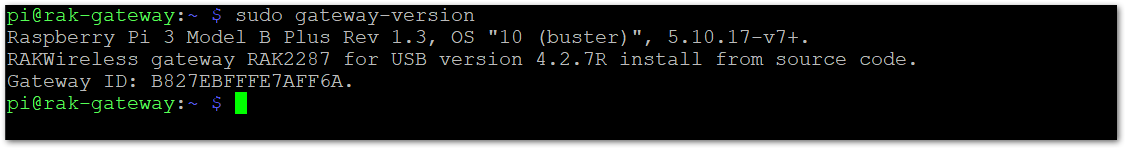 Figure 1: Get the Gateway's EUI
Figure 1: Get the Gateway's EUIpi@rak-gateway:~ $ sudo gateway-version
Raspberry Pi 3 Model B Plus Rev 1.3, OS "10 (buster)", 5.10.17-v7+.
RAKwireless gateway RAK2287 for USB version 4.2..7R install from source code.
Gateway ID: B827EBFFFE7AFF6A.
pi@rak-gateway:~ $
- Open the TTN website in your browser, login, and navigate to the console page. Click on +Add Gateway button.
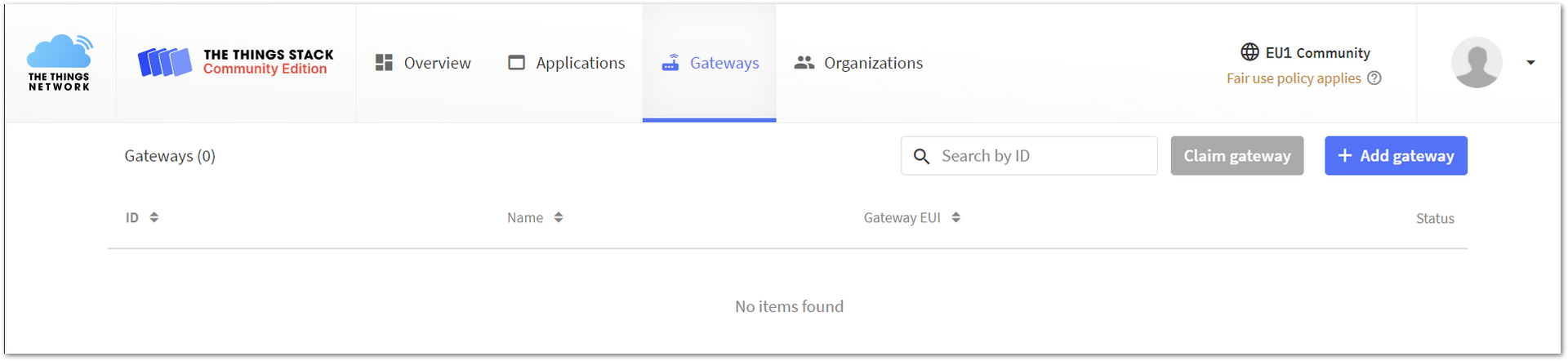 Figure 1: Add the Gateway
Figure 1: Add the Gateway- Enter the EUI along with the required details such as description and channel plan. If you have followed the steps correctly, your gateway will appear as connected and show activity.
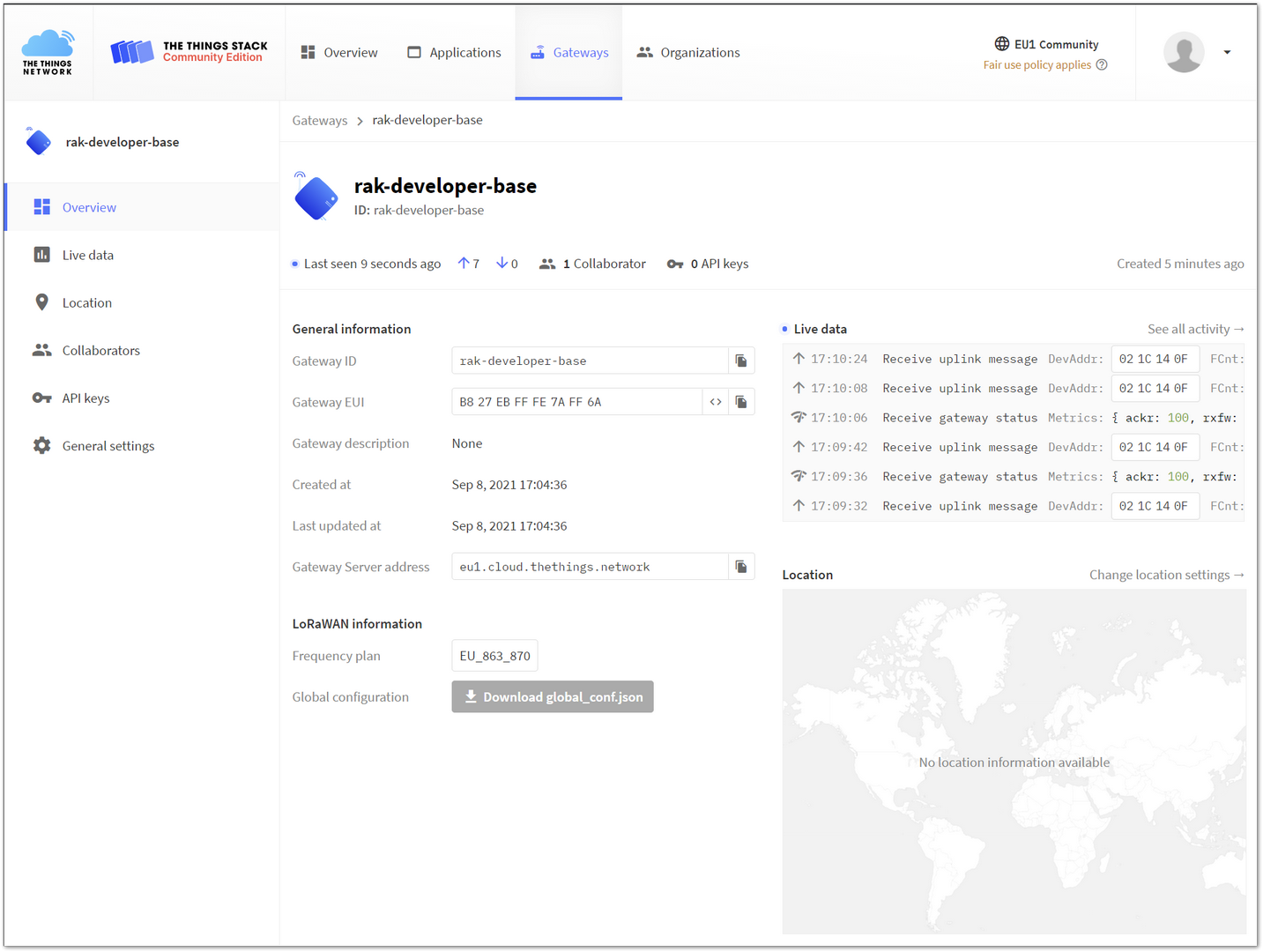 Figure 1: Registered Gateway
Figure 1: Registered Gateway