RAK5005-O WisBlock Base Board Quick Start Guide
This guide introduces the RAK5005-O WisBlock Base Board and how to use it.
Prerequisite
Package Inclusions
Before proceeding with the steps for using the RAK5005-O WisBlock Base, ensure you have the following items prepared:
Hardware
- USB Cable
- Li-Ion/LiPo battery with JST PHR-2 2 mm female connector (optional)
- Solar charger (optional)
- Your choice of WisBlock Core
- Your choice of WisBlock Modules
NOTE
It is highly recommended to also check the dedicated Quick Start Guide of your chosen WisBlock Modules. Each Quick Start Guide of these modules contains the detailed steps on how to open the example codes and upload them to the WisBlock Core.
Software
Based on the choice of the WisBlock Core, select a Development Environment:
Programming via Arduino IDEIn Arduino IDE, once you installed the BSP, the examples for WisBlock Core will be automatically included on the list of examples.
Programming via PlatformIO IDEProduct Configuration
Overview
To give you a better understanding of how the WisBlock Base works, a block diagram, data bus, and power supply diagram of RAK5005-O are provided in this section.
Block Diagram
The block diagram in Figure 1 shows the internal architecture and external interfaces of the RAK5005-O board.
 Figure 1: RAK5005-O WisBlock Base block diagram
Figure 1: RAK5005-O WisBlock Base block diagramData Bus of RAK5005-O
 Figure 1: RAK5005-O WisBlock Base Data Bus
Figure 1: RAK5005-O WisBlock Base Data BusThe MCU in the WisBlock Core module offers the I2C, UART, and SPI data buses to the sensor modules. Through these buses, the MCU can control and retrieve data from the sensors. In addition, the IO module connects to the USB, GPIO, and ADC buses allowing you to access all of the MCU interfaces.
Some types of MCU have fewer IO pins. In such cases, not all the pins of the data bus are connected. For example, only I2C and UART are connected. Some MCU IO pins have an alternate function. Then you can modify its function by software or rework the hardware to redefine the function of IO. Refer to the datasheet of WisBlock Core to get all the details.
Power Supply Diagram of RAK5005-O
 Figure 1: Power Supply Block Diagram
Figure 1: Power Supply Block DiagramThe RAK5005-O is designed to be powered by a battery and provides the charger circuitry for Lithium batteries. The charger circuitry can be connected to a wall outlet charger through the micro USB connector, or the specific connector for a solar panel.
A low quiescent current LDO is used for generating 3.3 V. This 3.3 V power supply drives the consumption of the WisBlock Core module the sensor modules, and the IO module directly. The max current supported by the 3.3 V LDO is 750 mA.
VDD is generated by the MCU module to drive sensor and IO modules. The MCUs are usually powered by the 3.3 V, and can provide different levels of voltage: 3.3 V, 2.5 V, and 1.8 V to their IO pins through regulators in the WisBlock Core board.
3V3_S is another 3.3 V power supply, it can be controlled by the MCU in order to disconnect the power sensors during idle periods to save power. 3V3_S is controlled by an IO2 pin on the WisBlock Core board.
- Set IO2=1, 3V3_S is ON.
- Set IO2=0, 3V3_S is OFF.
Hardware Setup
RAK5005-O WisBlock Base Board Installation Guide
RAK5005-O WisBlock Base Board is the main board that allows you to attach MCU, sensors, and IO modules through the standardized expansion connectors. These connectors provide a data bus interconnection between the modules attached to the RAK5005-O Base Board.
This guide shows the details related to the installation of modules into the RAK5005-O board. The following section discusses the general concepts to manipulate the WisConnector in any WisBlock. The installation and removal details of each type of WisBlock module: Core, Sensor, and IO are explained.
Attaching a WisConnector
The WisConnector is the interface between the RAK5005-O module and the WisBlock Core, Sensor, and IO modules. Before connecting these modules, read the following instructions.
This guide uses two arrows. Refer to Figure 4 for its representation.
 Figure 1: Notation within the guide
Figure 1: Notation within the guide- Align the connectors (header and socket) in parallel. Position the header corresponding to the lap joint of the socket.
 Figure 1: Alignment of WisConnector
Figure 1: Alignment of WisConnector- Fit the connectors by tilting the header for less than 20 degrees. Gently place the header on top of the socket and do not apply force during this process.
 Figure 1: Fit the WisConnector’s header inside of the socket
Figure 1: Fit the WisConnector’s header inside of the socket- After following the alignment steps, the connectors should look like Figure 7. At this point, they are not buckled yet.
 Figure 1: WisConnector’s header matched inside of the socket
Figure 1: WisConnector’s header matched inside of the socket- Apply even forces by pressing the header to the socket, as shown in Figure 8. Do this until you hear a sound confirming that it is buckled.
 Figure 1: Apply forces to buckle the header to the socket
Figure 1: Apply forces to buckle the header to the socket - In the process of buckling, avoid applying uneven forces on both sides.
 Figure 1: Avoid applying uneven forces
Figure 1: Avoid applying uneven forces- When the buckling process is complete, check if the header and socket are kept in parallel.
 Figure 1: Correct way to buckle the WisConnector’s header to the socket
Figure 1: Correct way to buckle the WisConnector’s header to the socket- After buckling, if the header and socket are still not in parallel state (not fully assembled in one place), press on both sides of the long side using even forces to complete the correct buckling.
 Figure 1: WisConnector’s header is not parallel to the socket
Figure 1: WisConnector’s header is not parallel to the socket- Repeat alignment steps if the connector cannot be buckled smoothly. Do not apply force to the buckle until all the above steps have been completed. Otherwise, there is a risk of damaging the connector.
Detaching a WisConnector
- To disconnect the header from the socket, pull out in parallel with even forces.
 Figure 1: Correct way: Applying even forces to detach the header from the socket
Figure 1: Correct way: Applying even forces to detach the header from the socket- Avoid pulling out the header asymmetrically in the long-side direction, as shown on Figure 13.
 Figure 1: Wrong way: Applying uneven forces to detach the header from the socket
Figure 1: Wrong way: Applying uneven forces to detach the header from the socket- The short-side of the connector can be pulled out asymmetrically, but apply the force vertically and avoid rotating the header.
 Figure 1: Wrong way: Do not rotate the header
Figure 1: Wrong way: Do not rotate the header- Avoid applying forces in a single corner.
 Figure 1: Wrong way: Do not apply force in a single corner of the header
Figure 1: Wrong way: Do not apply force in a single corner of the headerAssembling a WisBlock Module
WisBlock Core
A WisBlock Core module is designed to be installed on the CPU slot of the RAK5005-O Base Board. As shown in Figure 16, the location is properly marked by silkscreen. Follow carefully the procedure defined in attaching a WisConnector section in order to attach a Core module. Once attached, fix the module with one or more pieces of M1.2 x 3 mm screws depending on the WisBlock Core.
 Figure 1: WisBlock Core silkscreen on the RAK5005-O Base Board
Figure 1: WisBlock Core silkscreen on the RAK5005-O Base BoardWisBlock Sensor
The RAK1910 GPS module must be installed only on the front side of the RAK5005-O Base Board. The RAK1910 is a full-length module that uses the space of two WisBlock IO modules.
A WisBlock Sensor module is designed to be installed on the Sensor slot of the RAK5005-O Base Board. There are four (4) available sensor slots in the RAK5005-O Base Board, two (2) on each side of the Base Board. As shown in Figure 17, the location of the slots is properly marked by silkscreen.
To attach a WisBlock Sensor module, follow the procedure of the attaching a WisConnector section, carefully. Once attached, fasten the module with an M1.2 x 3 mm screw.
 Figure 1: WisBlock Sensor silkscreens on the RAK5005-O Base Board
Figure 1: WisBlock Sensor silkscreens on the RAK5005-O Base BoardA WisBlock IO module is designed to be installed on the IO slot of the RAK5005-O Base Board. There is a single IO slot in the RAK5005-O Base Board. As shown in Figure 18, the location is properly marked by silkscreen. Follow carefully the procedure of the section, attaching a WisConnector, to attach a WisBlock Sensor module. Once attached, fix the module with three pieces of M1.2 x 3 mm screws.
 Figure 1: WisBlock IO silkscreen on the RAK5005-O Base Board
Figure 1: WisBlock IO silkscreen on the RAK5005-O Base BoardDisassembling a WisBlock Module
- The procedure to disassemble any type of WisBlock modules is the same. You start by removing the screws as shown in Figure 19.
 Figure 1: Removing screws from the WisBlock module
Figure 1: Removing screws from the WisBlock module- Once the screws are removed, on the PCB of a WisBlock module, there is a silkscreen that shows the correct location where force can be applied. By applying even forces under the marked area, the module can be detached from the Base Board. See Figure 20 and Figure 21.
 Figure 1: Detaching silkscreen on the WisBlock module
Figure 1: Detaching silkscreen on the WisBlock module Figure 1: Applying even forces on the proper location of a WisBlock module to detach the module from the Base Board
Figure 1: Applying even forces on the proper location of a WisBlock module to detach the module from the Base BoardBattery Connection
RAK5005-O can be powered via the USB cable or Li-Ion/LiPo battery via the dedicated connectors, as shown in Figure 22. The matching connector for the battery wires is a JST PHR-2 2 mm pitch female.
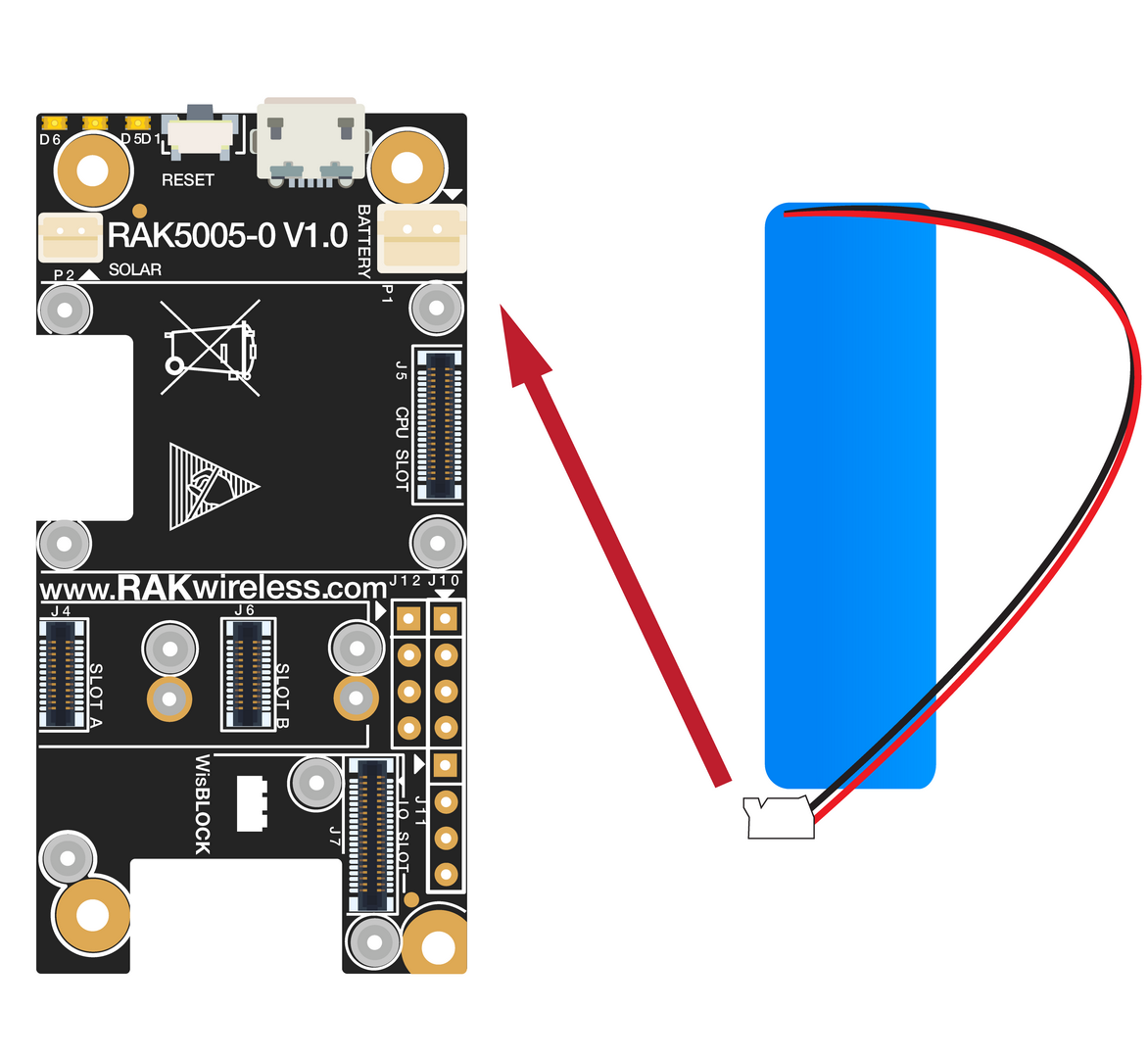 Figure 1: Battery connection
Figure 1: Battery connection Figure 1: Battery connector polarity
Figure 1: Battery connector polarityThe battery can be recharged as well via a small Solar Panel, as shown in Figure 22. The matching connector for the solar panel wires is a JST ZHR-2 1.5 mm pitch female. The GND pin of the battery connector is located on the edge of the board.
- Improper handling of battery is harmful.
- Only 3.7~4.2 V Rechargeable LiPo batteries are supported. It is highly recommended not to use other types of batteries with the system unless you know what you are doing.
- If a non-rechargeable battery is used, it has to be unplugged first before connecting the USB cable to the USB port of the board to configure the device. Not doing so might damage the battery or cause fire.
- Make sure the battery wires match the polarity on the RAK5005-O board. Not all batteries have the same wiring.
Solar Panel Connection
 Figure 1: Solar panel connection
Figure 1: Solar panel connection Figure 1: Solar panel connector polarity
Figure 1: Solar panel connector polarity- Only 5 V solar panels are supported. Do not use 12 V solar panels. It will destroy the charging unit and eventually other electronic parts.
- The GND pin of the Solar Panel Connector is located on edge of the board. Make sure the Solar Panel wires are matching the polarity on the RAK5005-O board.
The full specification of the Solar Panel Connection can be found on the datasheet of the WisBlock Base.
Software Setup
The WisBlock Core is designed to be interfaced with other WisBlock Modules like sensors, displays, and other interfaces. To make useful devices, you need to upload a source code to the WisBlock Core. Before you continue, you should have either an Arduino BSP or PlatformIO already set up.
WisBlock Examples Repository
To quickly build your IoT device with less hassle, example codes for WisBlock Core are provided.
You can access the codes on the WisBlock Example code repository. The example codes on folder common are compatible with RAK4631 and RAK11200 WisBlock cores.
