RAK2245 Pi HAT WisLink LPWAN Concentrator Quick Start Guide
Prerequisites
- RAK2245 Pi HAT WisLink LPWAN Concentrator
- Raspberry Pi 3B+ or Raspberry Pi 4
- 16 GB SD Card + Card Reader
- 5 V at least 2 A Micro USB Power Supply or USB C Power Supply
- A Windows/Mac OS/Linux Computer
- Latest RAK2245 Pi HAT Firmware
Package Inclusions
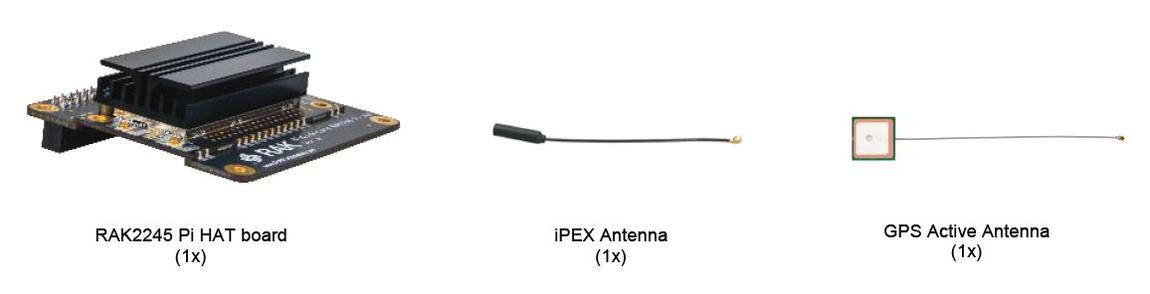 Figure 1: Package Contents
Figure 1: Package ContentsProduct Configuration
Accessing Your Gateway
After burning the firmware image onto the SD Card, make sure you have inserted the SD Card into the Raspberry Pi 3B+ / 4 with the RAK2245 Pi Hat LPWAN Concentrator Module and have the LoRa and GPS Antenna connected. After which, you can now safely power on the gateway. In this document, several ways in accessing the gateway are provided to have different alternatives for you to choose depending on the availability of the requirements needed.
Before powering the Raspberry Pi 3B+ or 4, you should connect the LoRa and GPS antennas. Not doing so might damage the boards.
Wi-Fi AP Mode
By default, the Gateway will work in Wi-Fi AP Mode which means that you can find an SSID named like "Rakwireless_XXXX" on your PC Wi-Fi Network List.
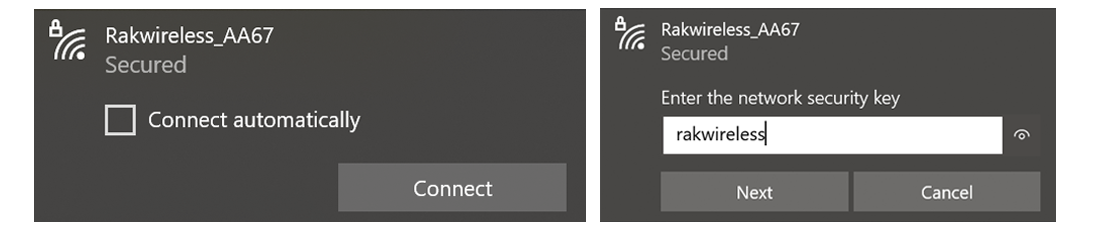 Figure 1: RAKwireless Access Point
Figure 1: RAKwireless Access Point“XXXX” is the last 2 bytes of your Raspberry Pi WiFi MAC address with the RAK2245. Connect to this Wi-Fi SSID using the password provided below. Take note also of the default IP address of the Gateway provided below as this will be needed in connecting via SSH.
- Wi-Fi Password: rakwireless
- Default IP Address:
192.168.230.1
Via the Ethernet Port on the Raspberry Pi
You can also connect your PC with the Gateway through an Ethernet cable. By default, the IP address of the Gateway’s Ethernet interface is 192.168.10.10, so you need to set the IP address of your PC’s Ethernet to the same network segment, for example, 192.168.10.20.
- To do this in Windows, go to Control Panel -> Network and Internet -> Network and Sharing Center and Click Ethernet.
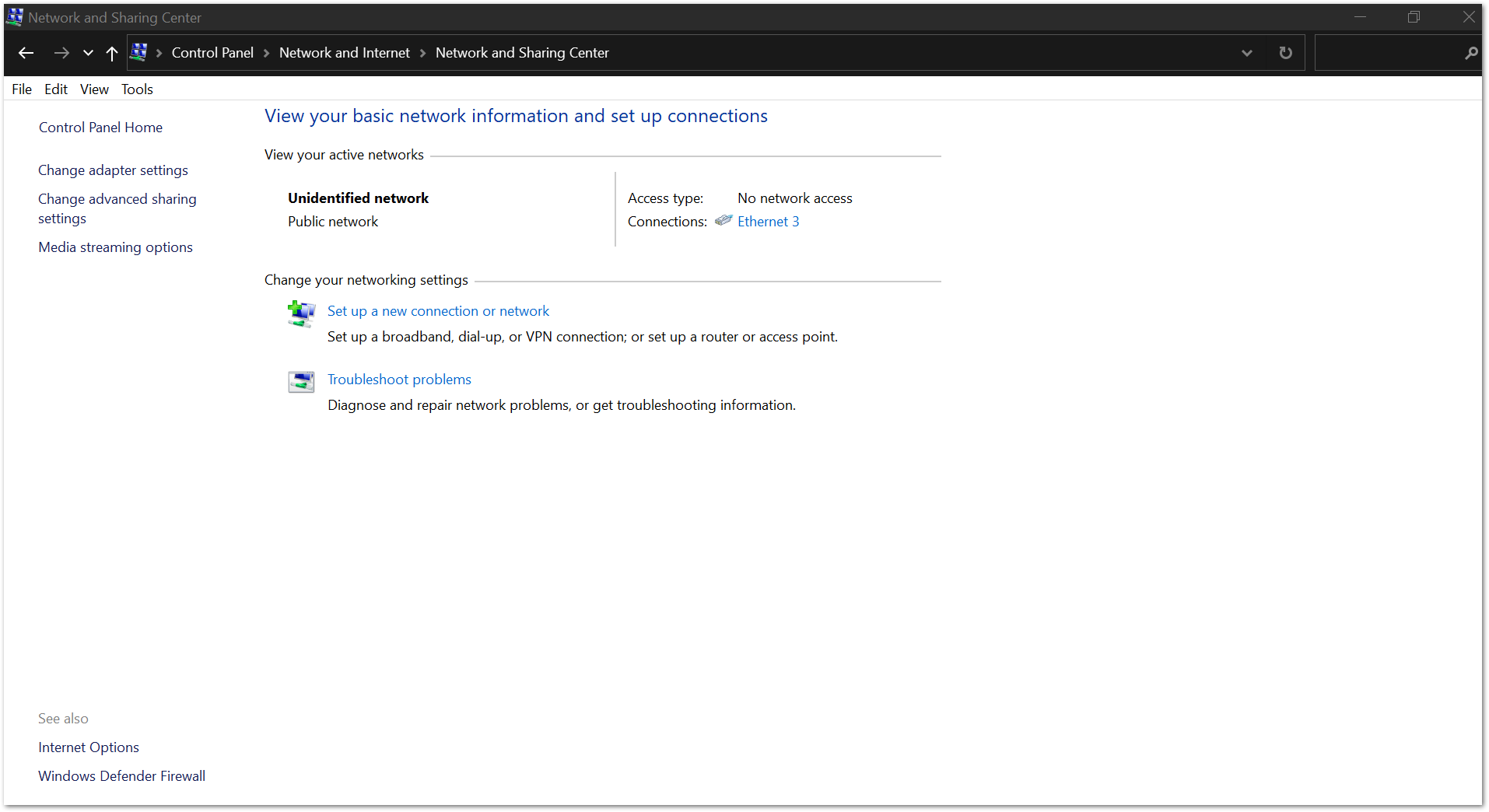 Figure 1: Network and Sharing Center
Figure 1: Network and Sharing Center- Click Properties then Choose Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4).
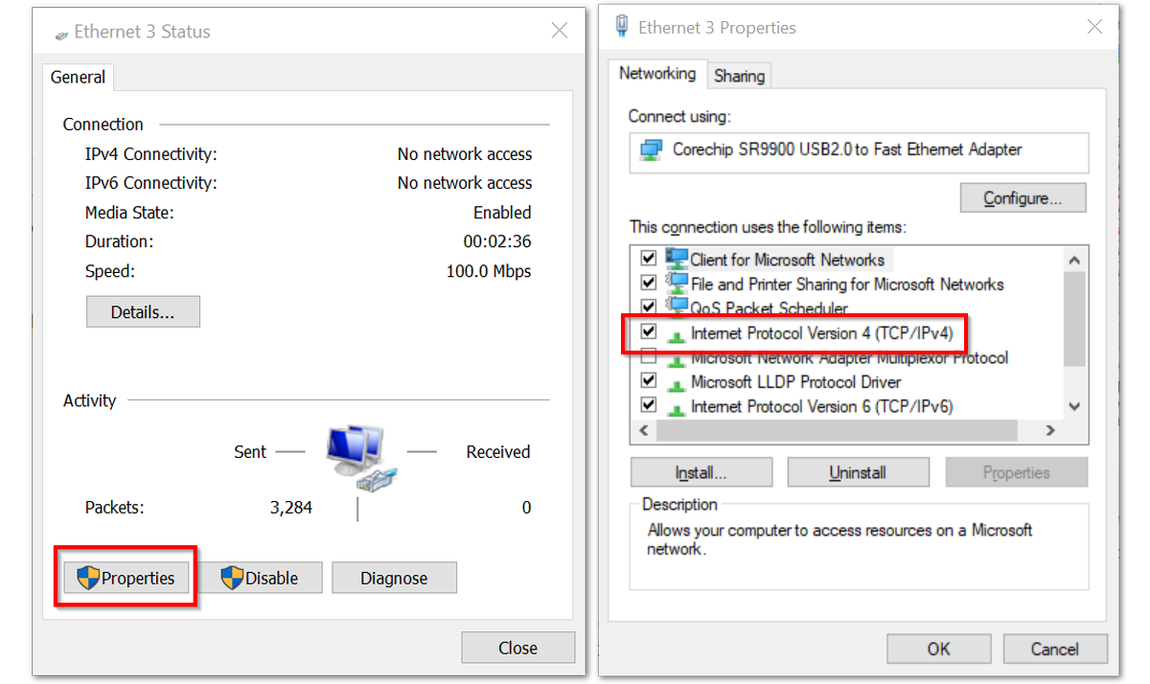 Figure 1: Ethernet Properties
Figure 1: Ethernet Properties- By default, it will obtain an IP Address automatically. Click the Option "Use the following IP Address" and enter the IP Address:
192.168.10.20and press OK.
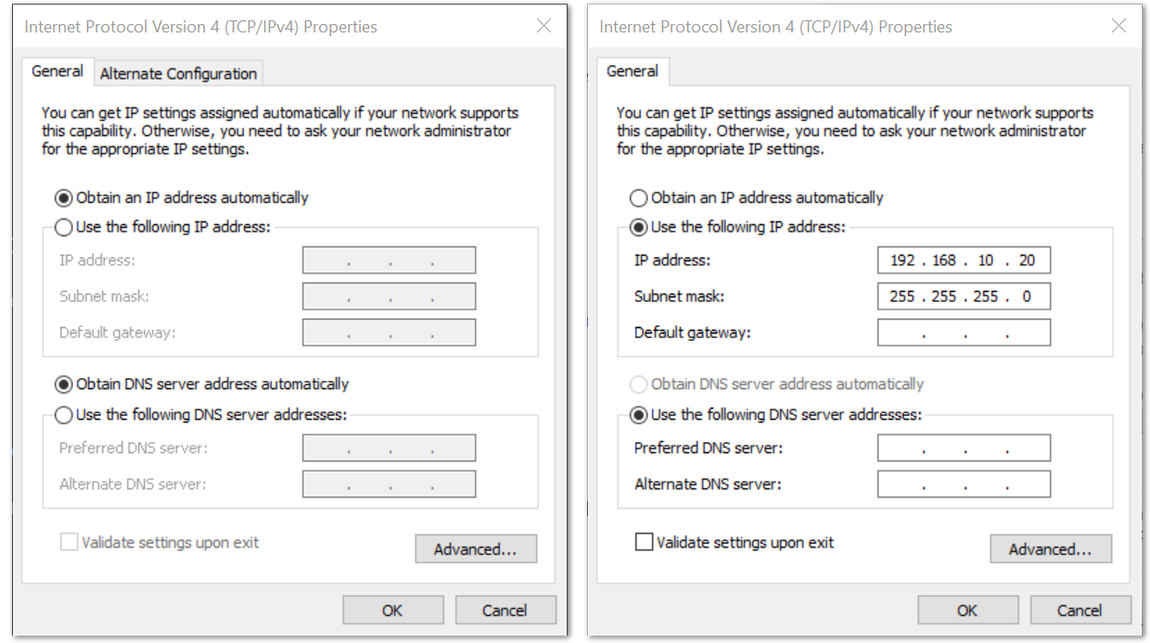 Figure 1: TCP/IPv4 Properties
Figure 1: TCP/IPv4 PropertiesNow , you should be able to access your Gateway from your PC successfully using the IP Address 192.168.10.10 through SSH.
Log into the Gateway
1. Windows OS
SSH (Secure Shell) is typically used to log in to a remote machine and execute commands. There are a lot of free and good SSH Clients out there namely Putty, BitVise SSH Client, MobaXterm and many more. Feel free to choose one that fits your needs. You will be using Putty for this guide.
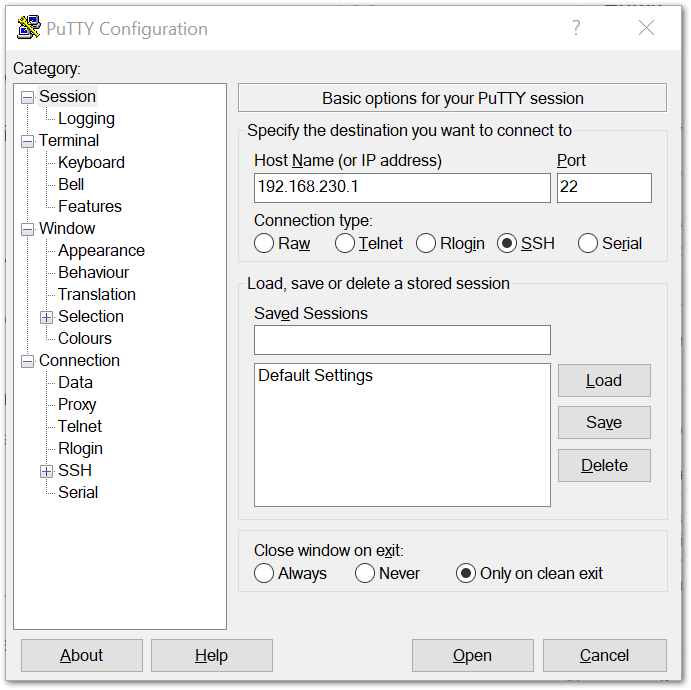 Figure 1: Putty Software for SSH in Windows
Figure 1: Putty Software for SSH in Windows- If you have connected to the Gateway through Wi-Fi AP Mode, the IP Address is
192.168.230.1 - If you have connected to the Gateway through Ethernet, the IP Address is
192.168.10.10 - It will then prompt you to enter the username and password. The default username and password is provided below:
- Username: pi
- Password: raspberry
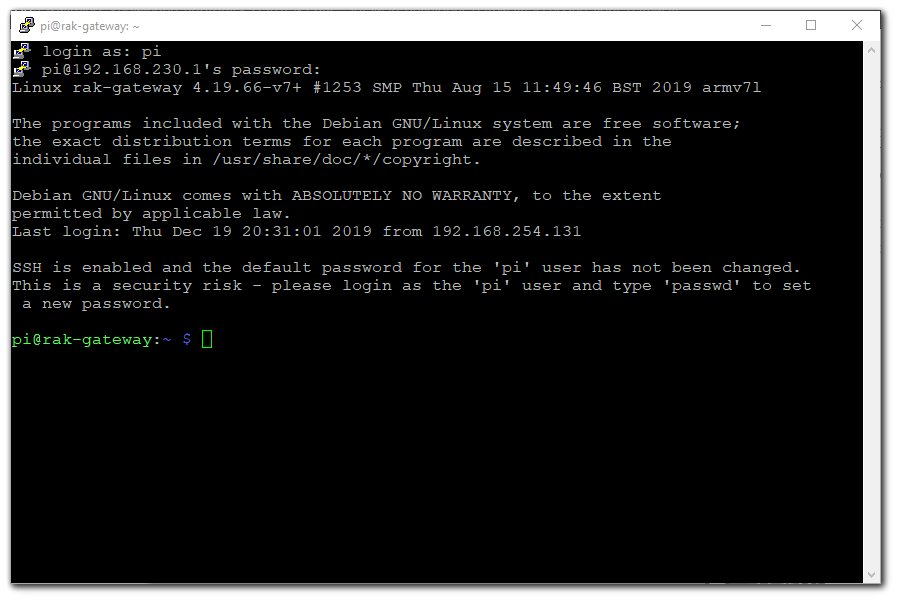 Figure 1: Command line after log in
Figure 1: Command line after log in2. Mac OS
Open the Terminal of Mac OS. Launch the Terminal application, which is found in "/Applications/Utilities/" directory but you can also launch it from Spotlight by hitting Command + Spacebar and typing “Terminal” and then return:
 Figure 1: Opening Terminal in Mac OS
Figure 1: Opening Terminal in Mac OSOpen the terminal of Mac OS. Enter root mode by typing the following command: "sudo -i"
 Figure 1: SSH in Mac OS
Figure 1: SSH in Mac OS- If you are not in root mode, enter "
ssh pi@192.168.230.1" in the terminal to login to your Gateway, the default password is "raspberry". - If you connect your PC with the Gateway through Ethernet Cable, you should enter "
ssh pi@192.168.10.10", the default password is "raspberry".
 Figure 1: Log-in Successful Notification
Figure 1: Log-in Successful Notification3. Linux OS
If the OS of your PC is Linux, you should do the same as the Mac OS, except the root mode.
Accessing the Internet
Assuming you have successfully logged into your Gateway using SSH. Enter the following command in the command line:
sudo gateway-config
You will now then see a page like the following picture below:
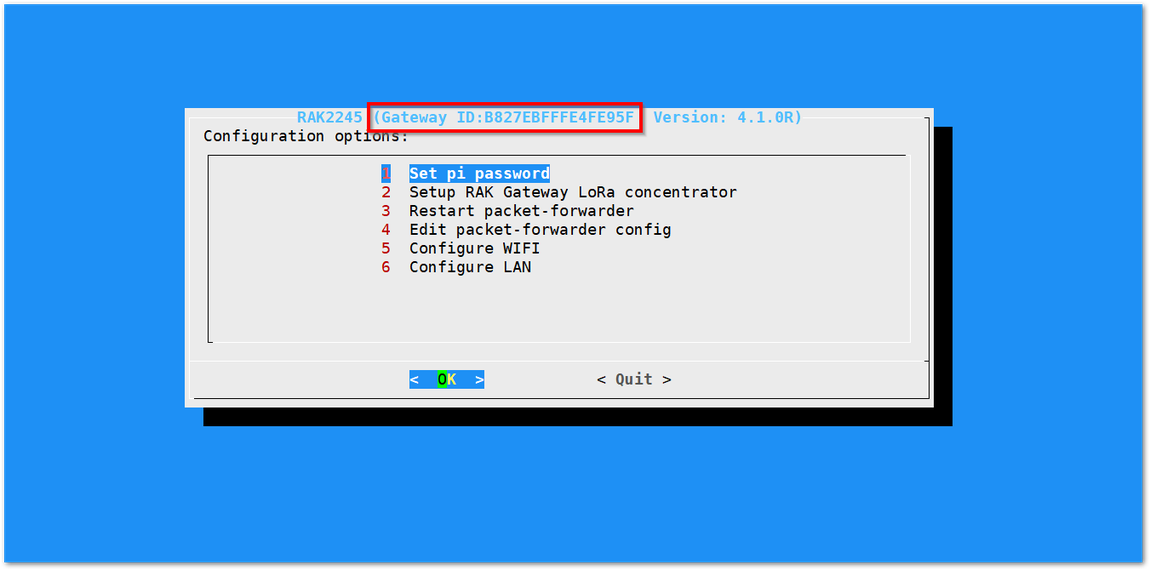 Figure 1: Configuration Options for the Gateway
Figure 1: Configuration Options for the Gateway- Set pi password - used to set/change the password of the Gateway.
- Set up RAK Gateway LoRa Concentrator - used to configure the frequency, which the Gateway will operate on, and the LoRaWAN Server which the Gateway will work with.
- Restart packet -forwarder - used to restart the LoRa packet forwarded process.
- Edit packet-forwarder config- used to open the global_conf.json file, in order to edit parameters manually.
- Configure Wifi - used to configure the Wi-Fi settings in order to connect to a network.
- Configure LAN - used to configure the Ethernet adapter settings.
Connect through Wi-Fi
If you want to connect through Wi-Fi, it can easily be done with the Wireless capabilities of the Raspberry Pi 3B+/4 by choosing "5 Configure WIFI". By default, the RAK2245 Pi HAT Edition LPWAN Gateway Concentrator Module works in Wi-Fi AP Mode. In order for the Gateway to connect to the router, it must work in Wi-Fi Client Mode.
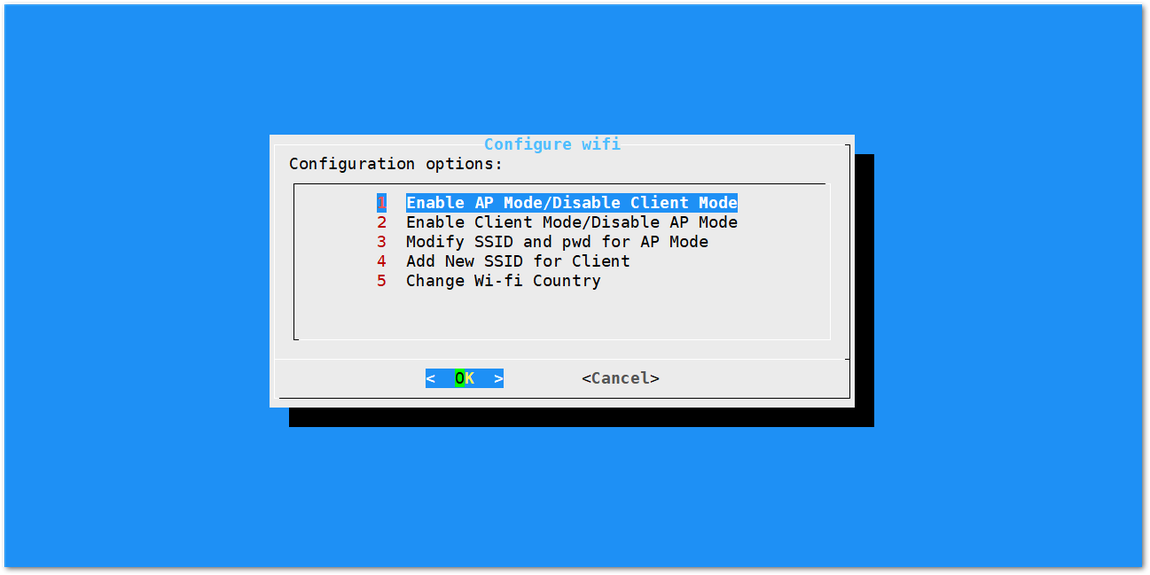 Figure 1: Configuration options for WIFI
Figure 1: Configuration options for WIFIThere are 5 options to choose from in the Wi-Fi configuration menu:
- Enable AP Mode/Disable Client Mode - the Gateway will work in Wi-Fi Access Point Mode after rebooting while the Wi-Fi Client Mode will be disabled (this is the default mode).
- Enable Client Mode/Disable AP Mode - the Gateway will work in Wi-Fi Client mode after rebooting, while Wi-FI AP Mode will be disabled.
- Modify SSID and pwd for AP Mode - used to modify the SSID and password of the Wi-Fi AP. Only works if the Wi-Fi AP Mode is enabled.
- Add New SSID for Client - this is used if you want to connect to a new Wi-Fi Network. Only works in Wi-Fi Client mode.
- Change Wi-Fi Country - this is used to modify the Resident Country to match with Wi-Fi standards.
In order to enable Wi-Fi Client Mode, you have to disable first the AP Mode.
Once Wi-Fi AP Mode has been disabled by choosing "2 Enable Client Mode/Disable AP Mode", you can now then connect to a new Wi-Fi Network by choosing "4 Add New SSID for Client":
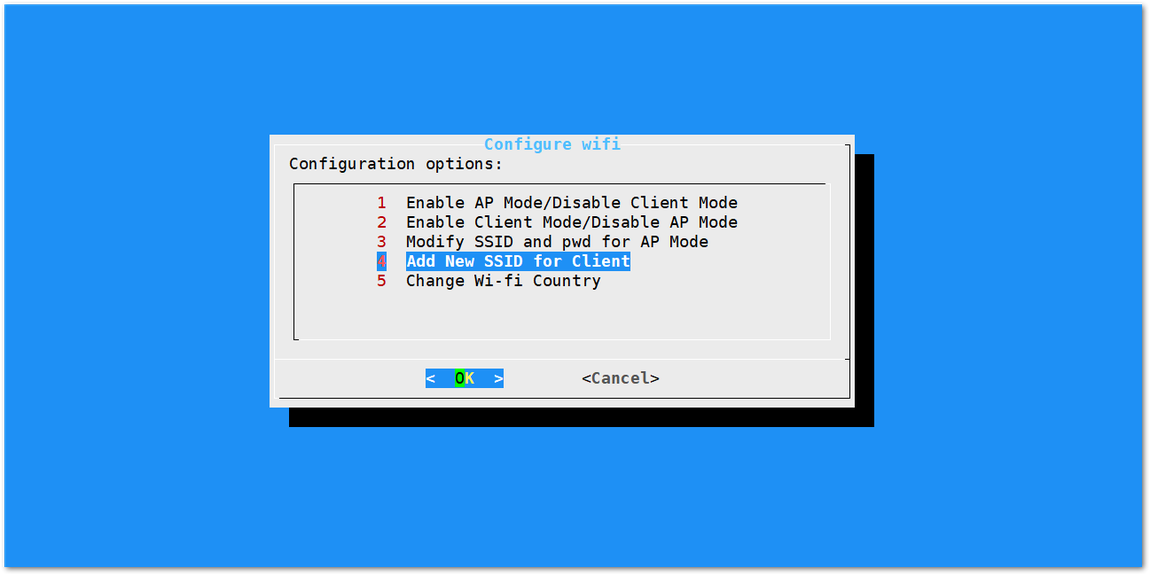 Figure 1: Add a new SSID
Figure 1: Add a new SSID- Start by selecting your country of residence:
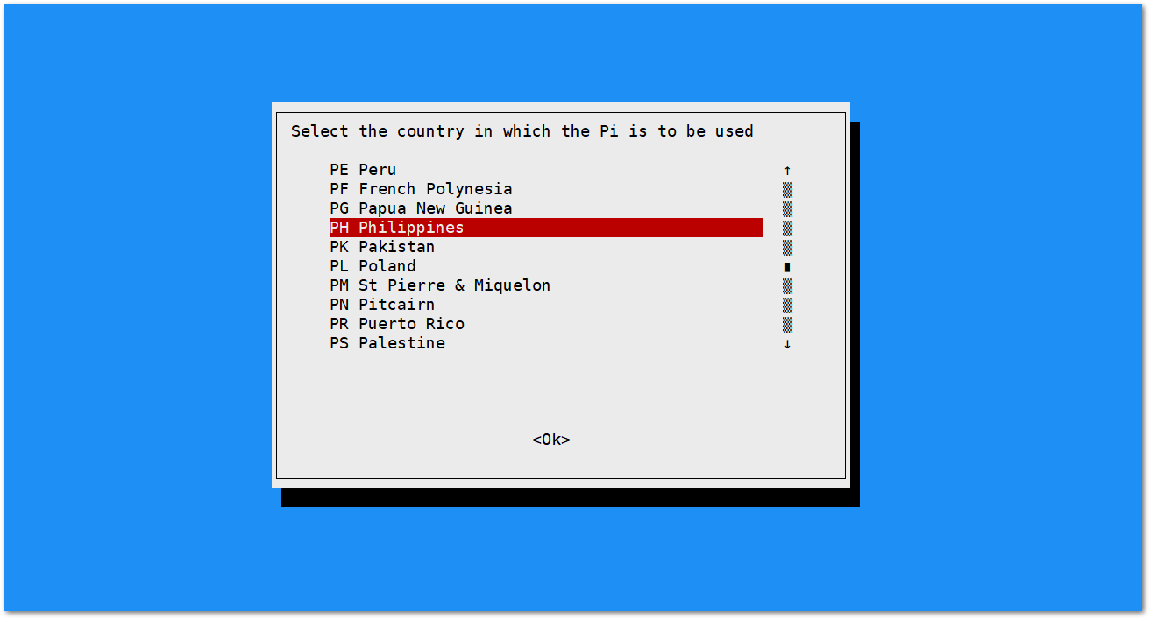 Figure 1: Selecting Country of Residence
Figure 1: Selecting Country of Residence- Enter the SSID of the network you want to connect:
Please ensure to input the correct Wi-Fi SSID and Password or you will not be able to connect to the RAK2245 Pi hat again via SSH in Wi-Fi AP Mode. If stuck in this situation, please follow this procedure listed in the Reverting to Wi-Fi AP Mode section which is applicable for all Raspberry Pi based gateways to work again in Wi-Fi AP mode.
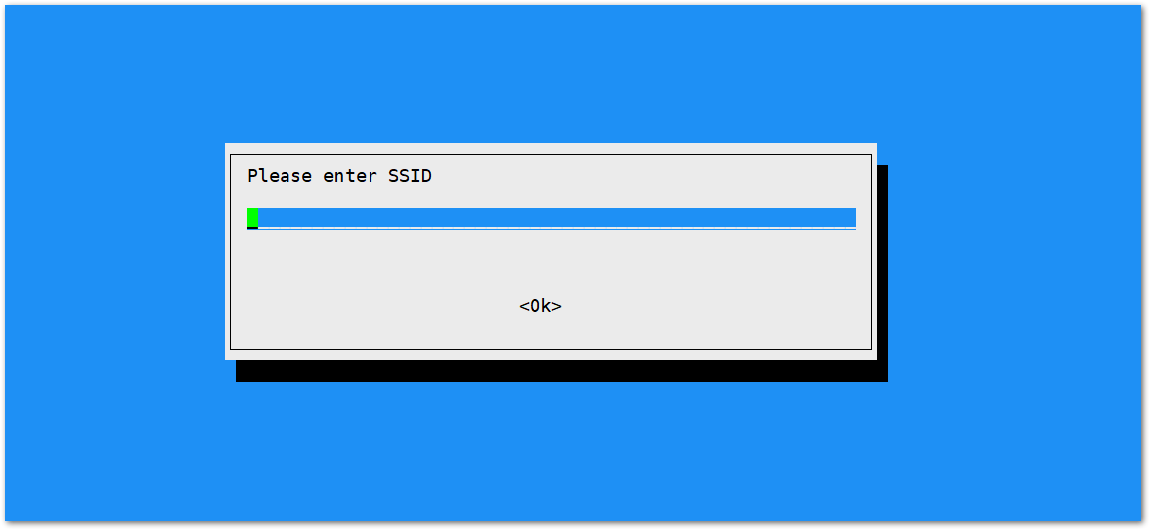 Figure 1: SSID of the Network you want to connect to
Figure 1: SSID of the Network you want to connect to- Enter also the password. Just leave it empty if None.
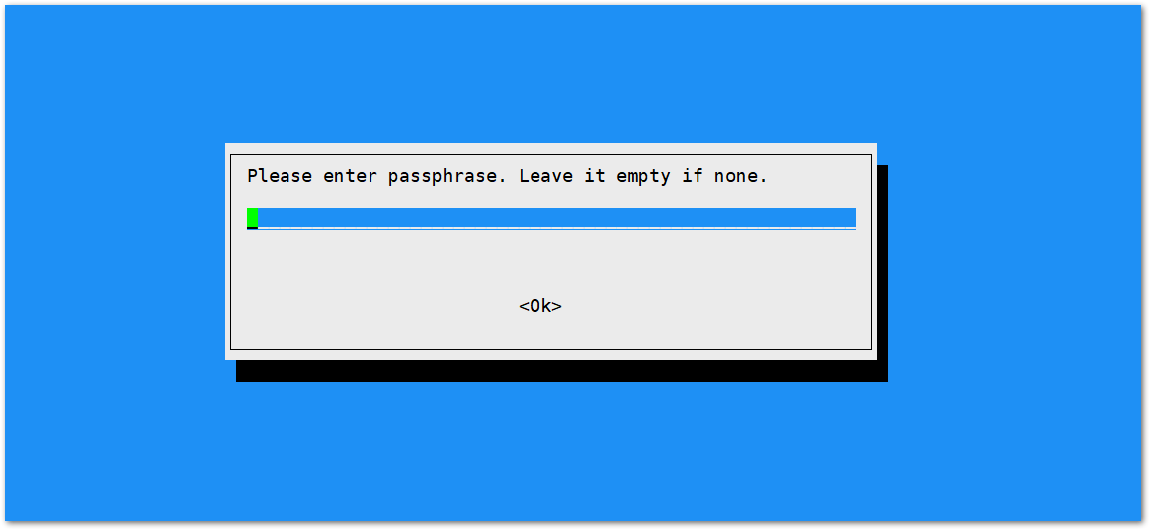 Figure 1: Password of the Wi-Fi
Figure 1: Password of the Wi-FiConnect through Ethernet
If you want to connect to router through Ethernet Cable, do the following steps:
- In the main configuration menu, choose “6 Configure LAN”. This will let you set up a static IP address for the Gateway’s Ethernet adapter.
- Just fill a static IP Address according to the IP address of the router you want to connect. Please note that the gateway and the router must be in the same network segment, otherwise the connection will fail.
- By default, the IP Address of the Gateway's Ethernet is
192.168.10.10
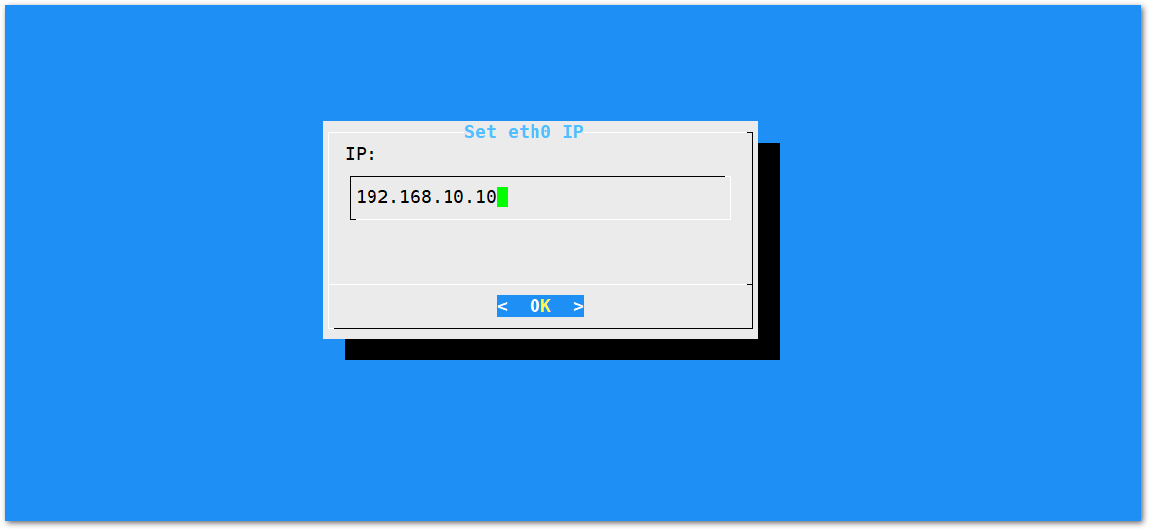 Figure 1: Default Gateway Ethernet IP Address
Figure 1: Default Gateway Ethernet IP Address- Then configure the IP address of the Router. This is the LAN Interface IP address of the router.
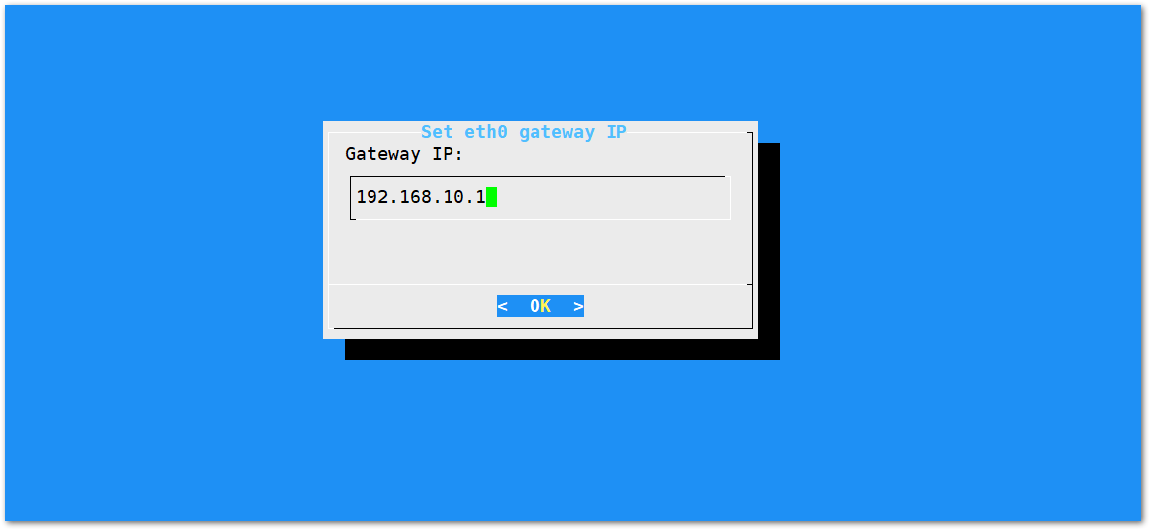 Figure 1: LAN Interface IP Address of the Router
Figure 1: LAN Interface IP Address of the Router- Press OK then the success message will appear.
- Lastly, reboot the Gateway using the command "
sudo reboot" in the command line and it will connect to the router successfully through Ethernet.
sudo reboot
Optional Configurations
These configurations under this section are only optional and situational.
Reverting to Wi-Fi AP Mode
In the event that you have entered either or both incorrect Wi-Fi SSID and Password in the Wi-Fi Client Mode setup for the RAK2245 Pi HAT Edition LPWAN Gateway Concentrator Module to connect to the router, follow these set of steps for you to work again in Wi-Fi AP Mode and redo the setup.
- Remove the SD Card from your Raspberry Pi with the RAK2245 Pi HAT and insert it into your PC. Your PC should be able to detect it same with the image below:
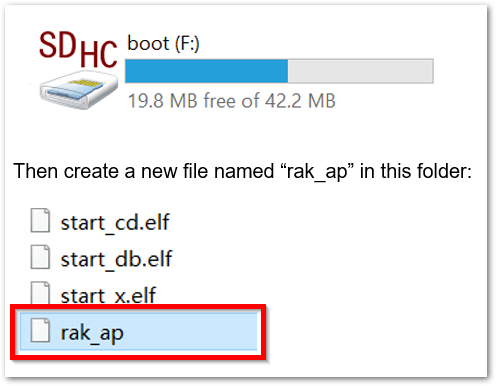 Figure 1: Creating rak_ap file to your SD Card
Figure 1: Creating rak_ap file to your SD Card- Using your "Command Prompt" or "Terminal", navigate to your SD Card and type this command to generate the "rak_ap" file.
cd > rak_ap
- Check if the rak_ap file is created successfully. If so, re-insert the SD Card into your Raspberry Pi with the RAK2245 Pi HAT Edition LPWAN Gateway Concentrator Module and it should work again in Wi-Fi AP Mode.
Configuring the Gateway
Assuming you have successfully logged into your Gateway using SSH, enter the following command in the command line:
sudo gateway-config
You will now then see a page like the following picture below
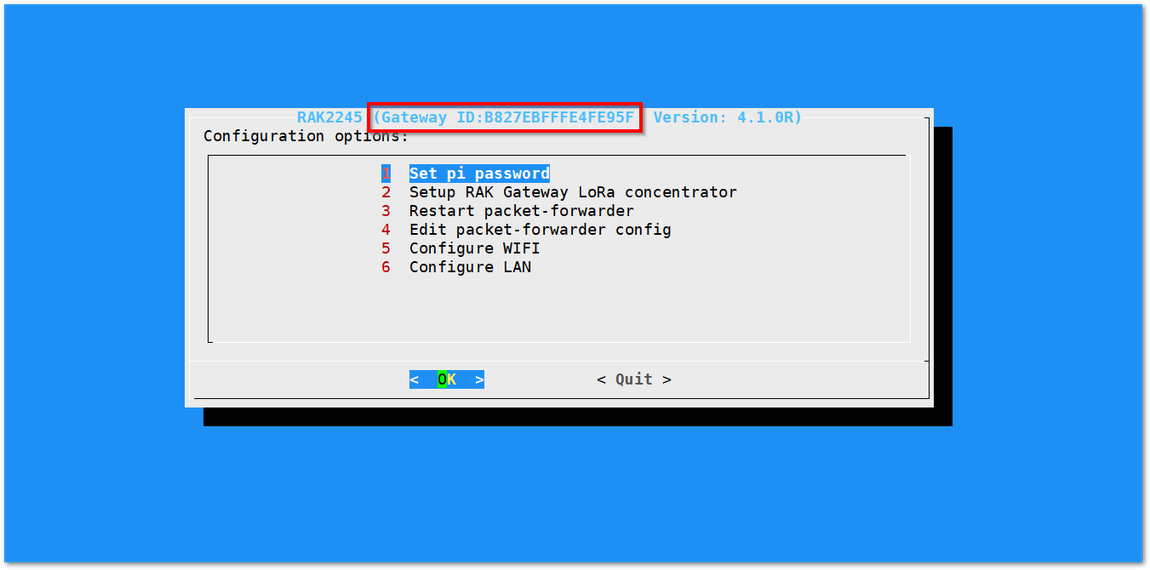 Figure 1: Config Options for the Gateway
Figure 1: Config Options for the Gateway- Set pi password - used to set/change the password of the Gateway.
- Set up RAK Gateway LoRa Concentrator - used to configure the frequency, which the Gateway will operate on, and the LoRaWAN Server which the Gateway will work with.
- Restart packet -forwarder - used to restart the LoRa packet forwarded process.
- Edit packet-forwarder config- used to open the global_conf.json file, in order to edit LoRaWAN parameters manually.
- Configure Wifi - used to configure the Wi-Fi settings in order to connect to a network.
- Configure LAN - used to configure the Ethernet adapter settings.
A unique ID will be generated for Gateway. This is also called Gateway EUI squared in red in the figure above and is essential for registering the gateway with any LoRa Network Server (TTN, ChirpStack)
There is also another way to get your "Gateway ID", just enter the command below in the command line:
sudo gateway-version
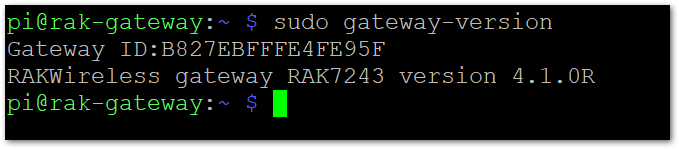 Figure 1: Gateway ID using the command line
Figure 1: Gateway ID using the command lineSetting a new password for the Gateway
It is a good security practice to change the default password "raspberry" which is the same on all Raspberry Pi devices.
- First, choose "1 Set pi password" option referred on the image below.
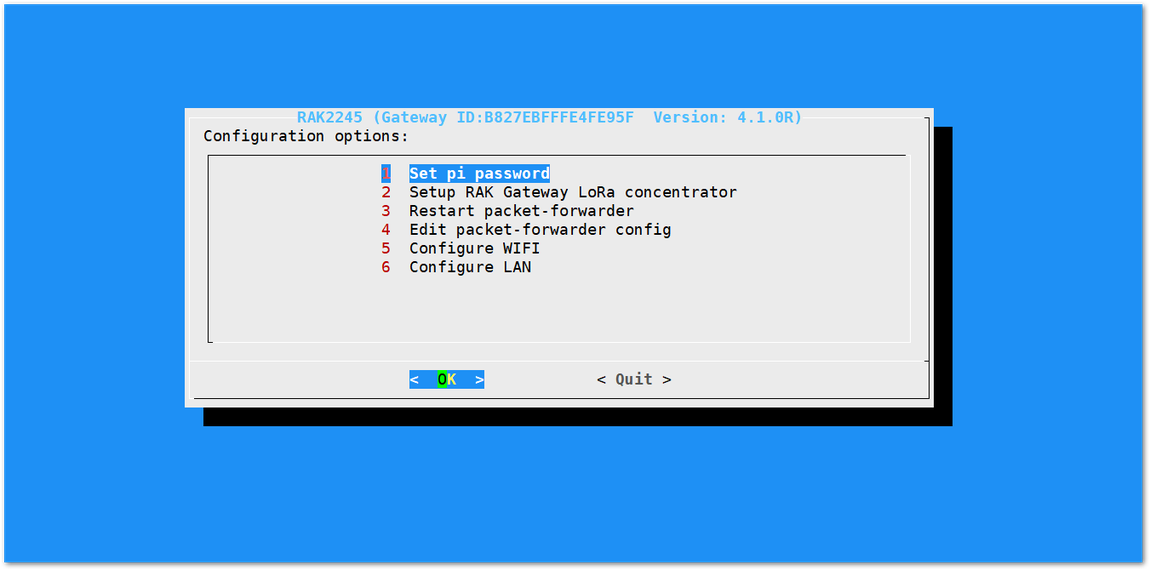 Figure 1: Set Pi Password
Figure 1: Set Pi Password- Next, press "Yes" and you will be asked to enter your new password twice then press "Enter".
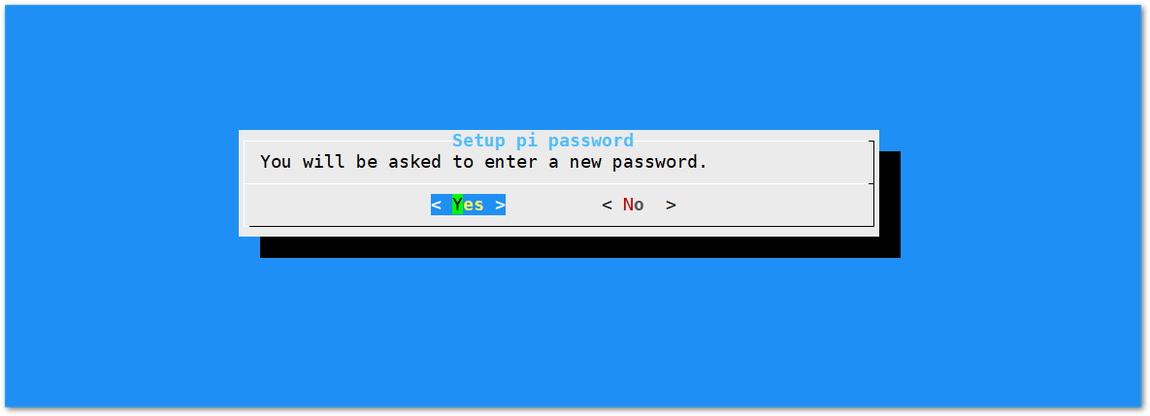 Figure 1: Confirm Password Change
Figure 1: Confirm Password Change- Alright, the success message for changing password will then pops up.
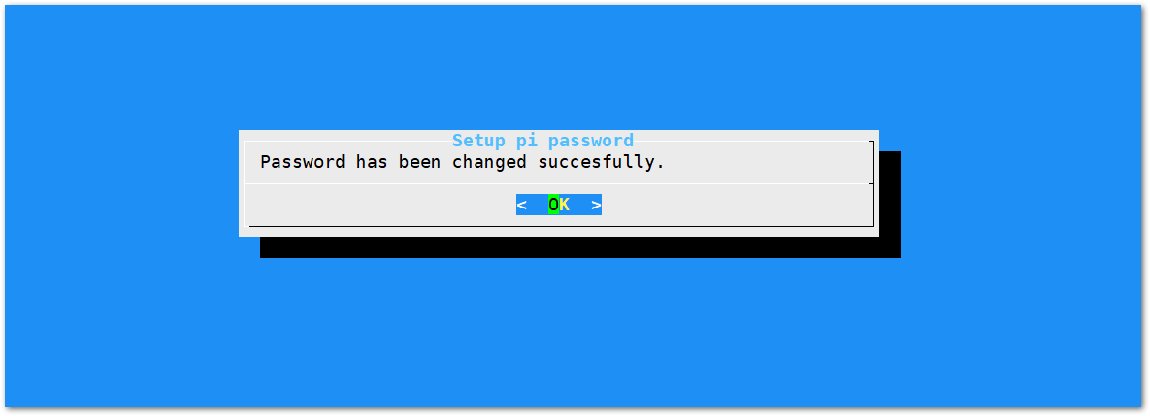 Figure 1: Successful Password Change
Figure 1: Successful Password ChangeSetup RAK Gateway LoRa Concentrator
This menu allows you to select your LoRa frequency band and one of the two available Networks Server options by choosing "2 Setup RAK Gateway LoRa concentrator"
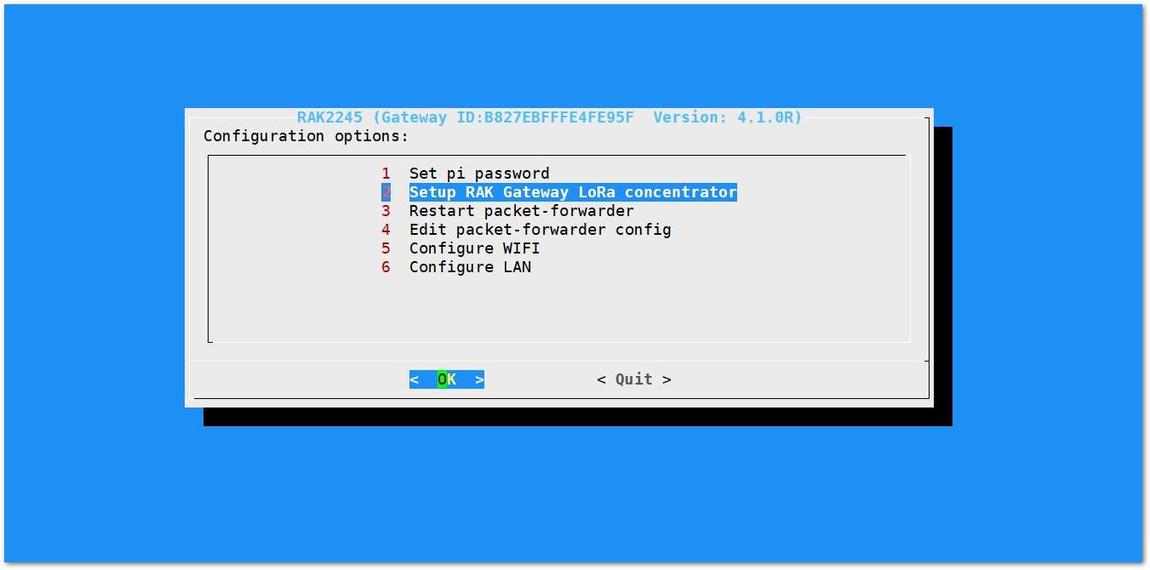 Figure 1: Choosing Setup RAK Gateway LoRa concentrator
Figure 1: Choosing Setup RAK Gateway LoRa concentratorYou can choose one of two supported LoRa Servers here: TTN or ChirpStack.
Server is TTN
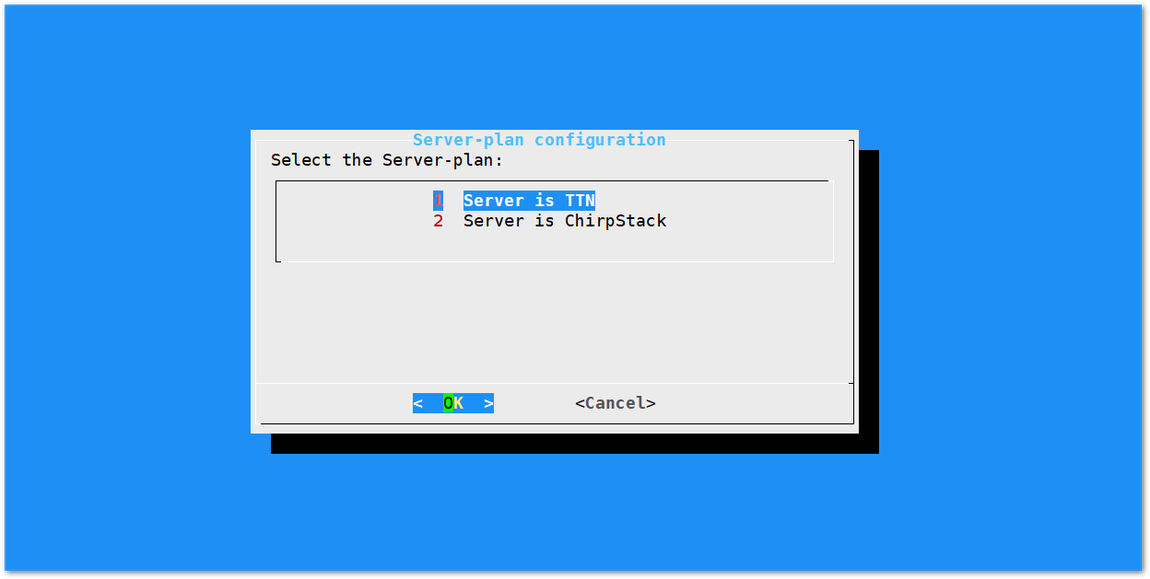 Figure 1: Server is TTN
Figure 1: Server is TTN- TTN (The Things Network) - If you choose TTN as the LoRa Server, you will see the following page. Visit this article for more information on your local TTN frequency plan. This will allow you to choose the correct plan.
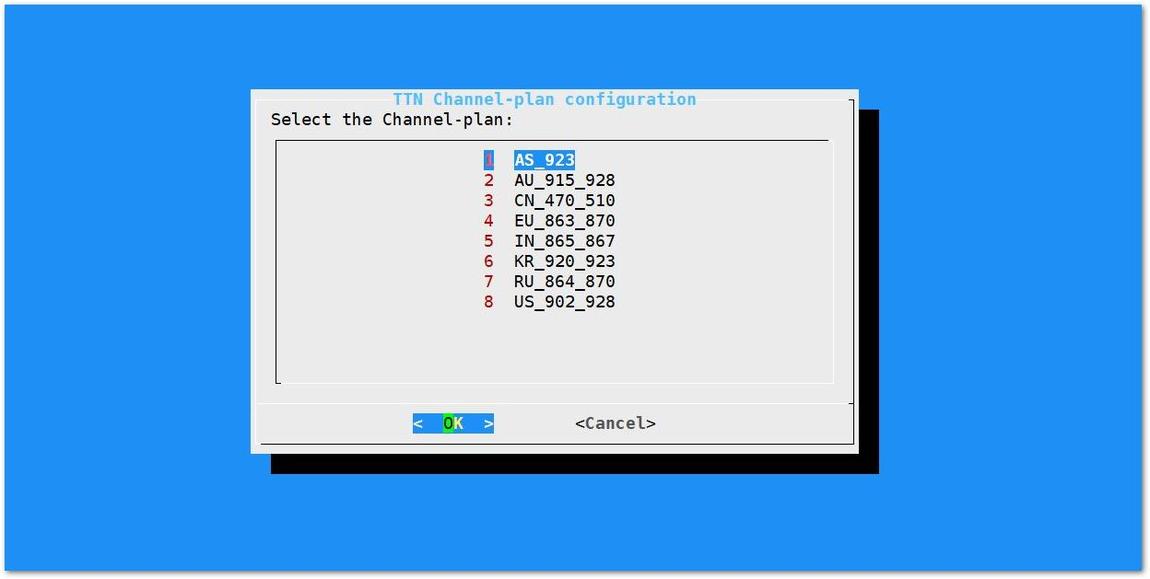 Figure 1: Selecting the TTN Channel Plan
Figure 1: Selecting the TTN Channel PlanAfter choosing the correct frequency, the success message will appear as shown below.
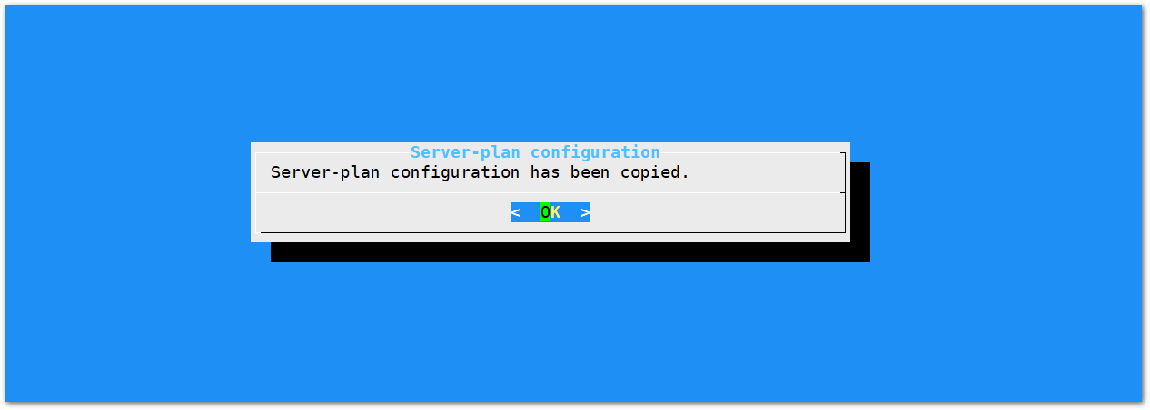 Figure 1: Successfully Changed the Frequency
Figure 1: Successfully Changed the FrequencyServer is Chirpstack
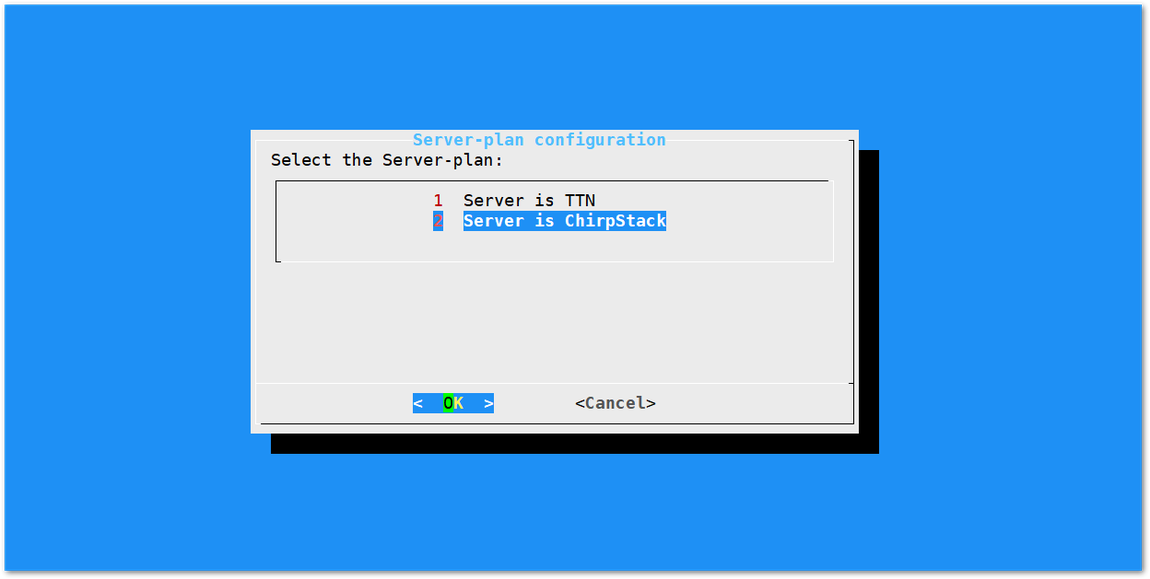 Figure 1: Server Is Chirpstack
Figure 1: Server Is ChirpstackChirpStack - If you choose Chirpstack as your LoRa Server, you will see the following page with two options available:
- ChirpStack Channel Plan Configuration - used to configure your Regional Frequency Band.
- ChirpStack ADR Configure - used to enable/disable the Adaptive Data Rate (ADR) functionality.
First, select "1 ChirpStack Channel-plan configuration" for configuring your frequency channel. Then, set the IP address of the ChirpStack.
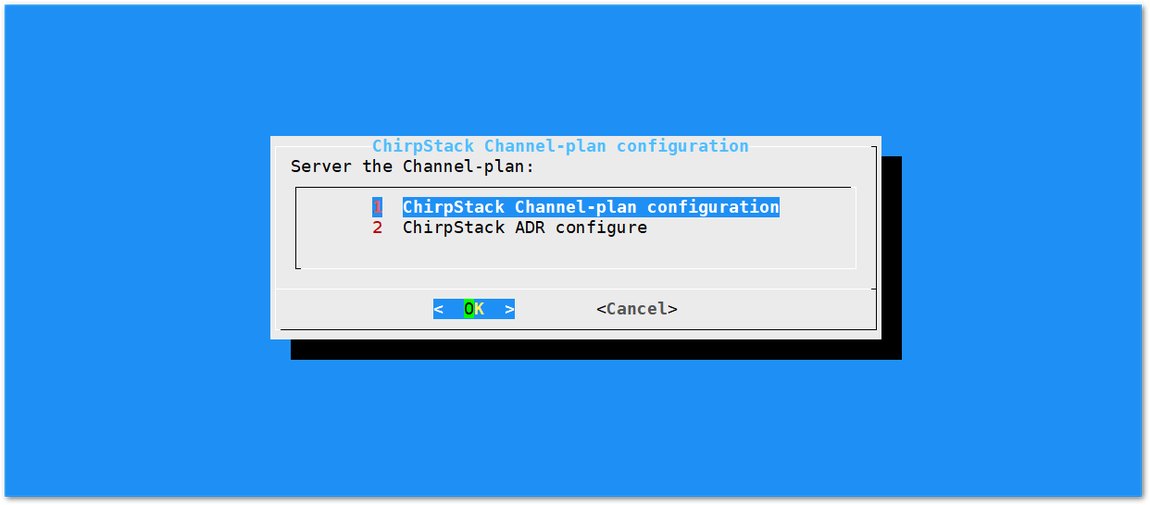 Figure 1: Regional Frequency Band Option
Figure 1: Regional Frequency Band Option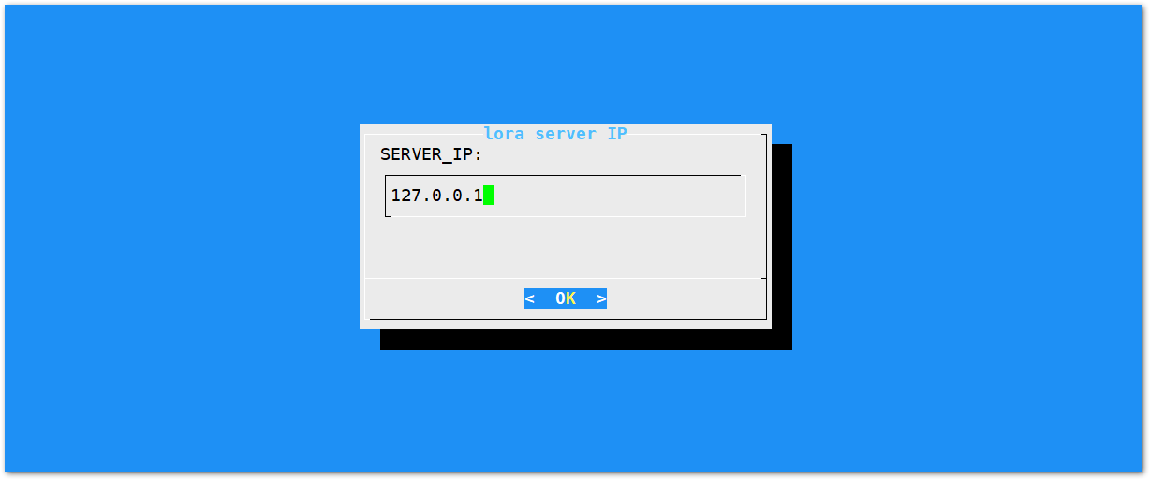 Figure 1: Default LoRaServer IP Address
Figure 1: Default LoRaServer IP AddressThe default IP Address is "127.0.0.1". If you want to use an external LoRaServer, you need to set it to its IP Address.
- If you have instead selected "Chirpstack ADR Configure" you can enable/disable the Adaptive Data Rate (ADR) functionality:
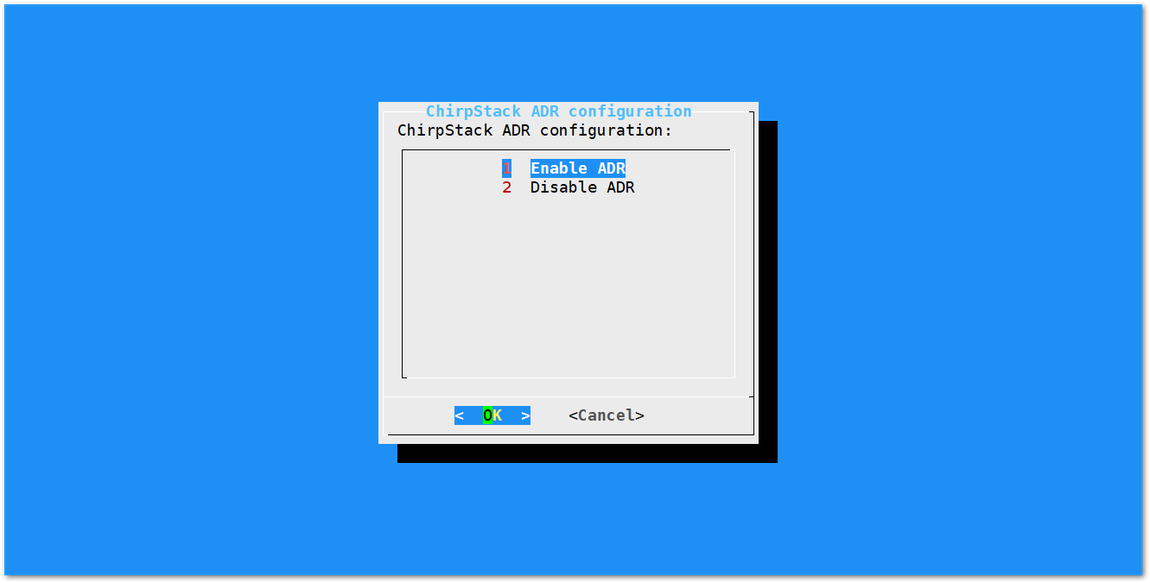 Figure 1: Chirpstack ADR Enable/Disable
Figure 1: Chirpstack ADR Enable/DisableConnecting to the Things Network (TTN)
The Things Network is about enabling low power devices to use long range gateways to connect to an open-source, decentralized network to exchange data with Application. Learn more about the Things Network here.
- First, you should have connected your Gateway to the router in order to access the internet according to the method which has been introduced in the Accessing the Internet document.
- Second, config your Gateway and choose TTN as the LoRa Server and choose a correct frequency according to the method which has been introduced in the Configuring the Gateway document.
- Now go to the TTN Website and Login. You will then see the following page:
 Figure 1: The Things Network Home Page
Figure 1: The Things Network Home Page- Choose Console then Click Gateways.
 Figure 1: The Things Network Console Page
Figure 1: The Things Network Console Page- All of your Registered Gateways will be displayed here in this page. Click "register gateway"
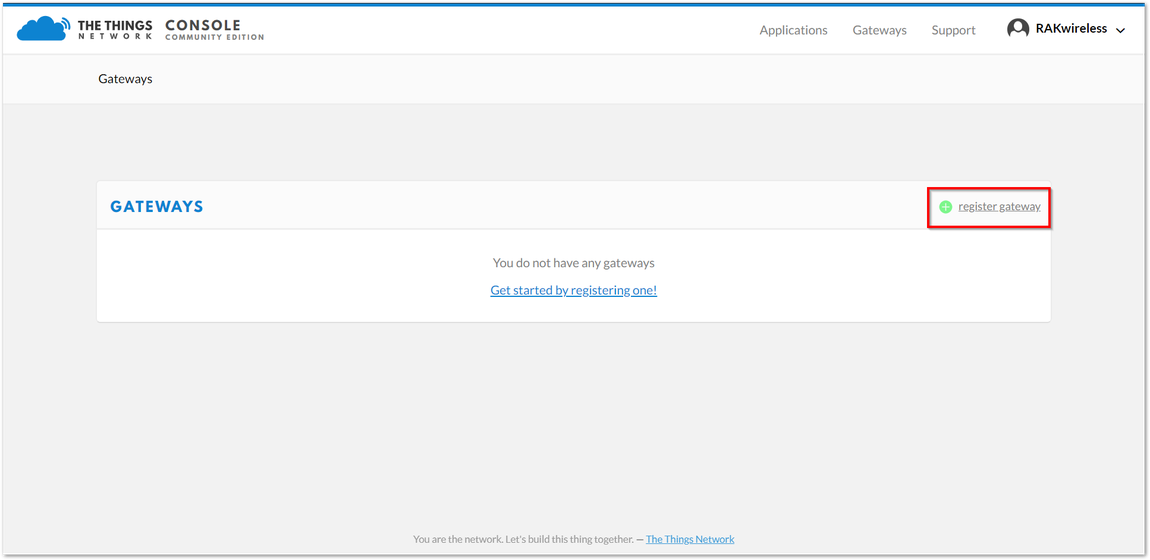 Figure 1: Adding a Gateway to TTN
Figure 1: Adding a Gateway to TTN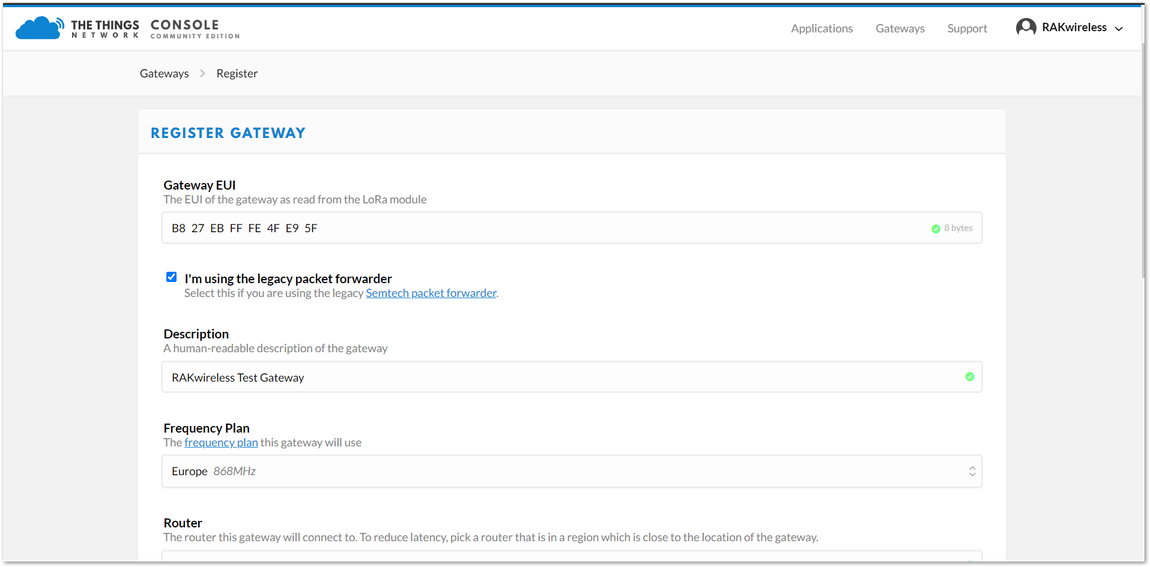 Figure 1: Registering your Gateway
Figure 1: Registering your Gateway- Gateway EUI - refers to the Gateway ID you obtained from the previous steps. In case you forgot, just type
gateway-versionin the command line. This must be the same with the Gateway's True Gateway ID otherwise you will fail to register your Gateway on TTN.
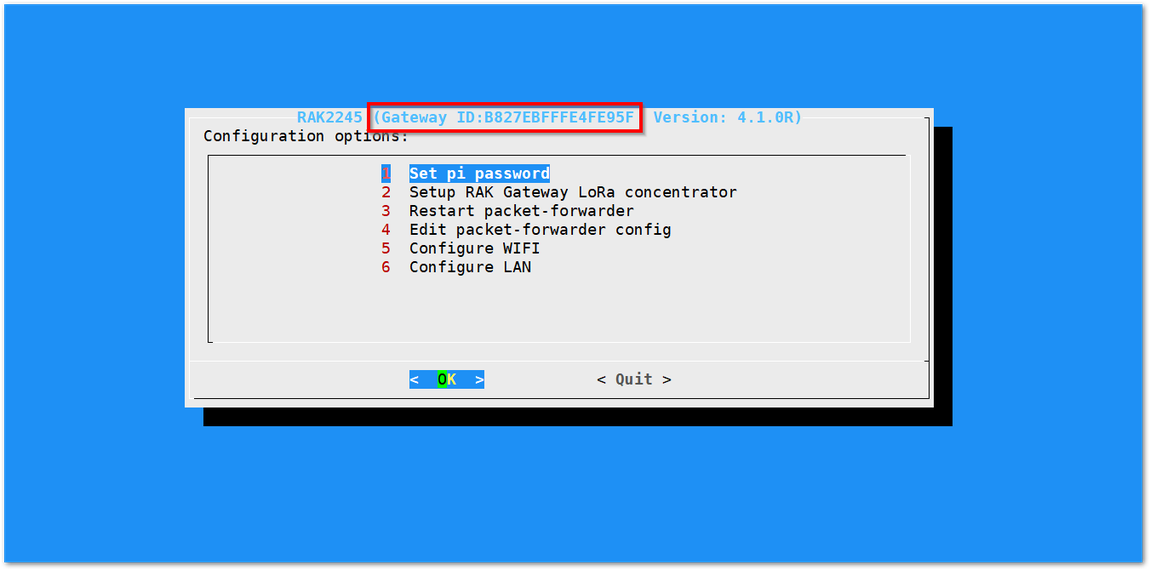 Figure 1: RAK2245 Pi Hat Gateway ID in SSH
Figure 1: RAK2245 Pi Hat Gateway ID in SSHMake sure to select the "I'm using the legacy packet forwarder" check box.
- Description - A human readable description of your Gateway.
- Frequency Plan - This is the frequency you want to use and it must be the same with Gateway and the Node.
- Router - The router this gateway will connect to. To reduce latency, pick a router that is in a region which is close to the location of the gateway.
- Location - Choose the location of the Gateway by entering its coordinates. This is reflected on the Gateway World Map.
- Antenna Placement - Where is your antenna placed? Is it placed indoors or outdoors?
Click Register Gateway and wait for a couple of minutes . If the status of your gateway is Connected, Congratulations! 🎉 Your Gateway is now connected to the The Things Network (TTN).
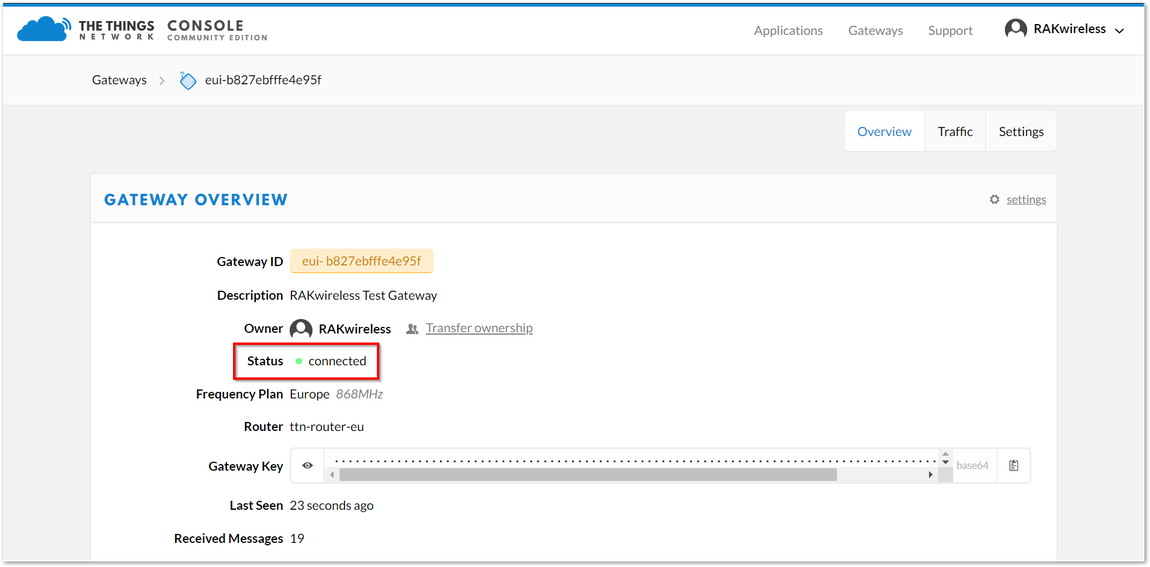 Figure 1: RAK2245 Pi Hat TTN Connection Success
Figure 1: RAK2245 Pi Hat TTN Connection SuccessConnect the Gateway with Chirpstack
The ChirpStack or previously known as LoRaServer project provides open-source components for building LoRaWAN networks. You can learn more about ChirpStack here.
For the RAK2245 Pi HAT Edition LPWAN Gateway Concentrator Module, there are 2 ways to use the ChirpStack:
1. Using the built-in ChirpStack
There is a built-in ChirpStack in every RAK Developer gateway if you use the latest firmware.
- When you use it for the first time after burning the latest firmware, the Gateway will work in the EU868 Band and use the built-in ChirpStack as its default LoRa Server. If you don't want to change the frequency or LoRa Server, you don't have to do anything as this will be configured automatically when the Gateway boots.
- However if it is not the first time and you want to use the built-in ChirpStack as the LoRa Server, follow the steps discussed in Configuring the Gateway the Gateway section.
- Optional: If ever you disabled the AP Mode and you have connected it to your own Wifi network (Client Mode). You can search for your gateway’s IP Address via Advanced IP Scanner. Copy the IP Address of your Gateway, it should have a Manufacturer name of Raspberry Pi Foundation:
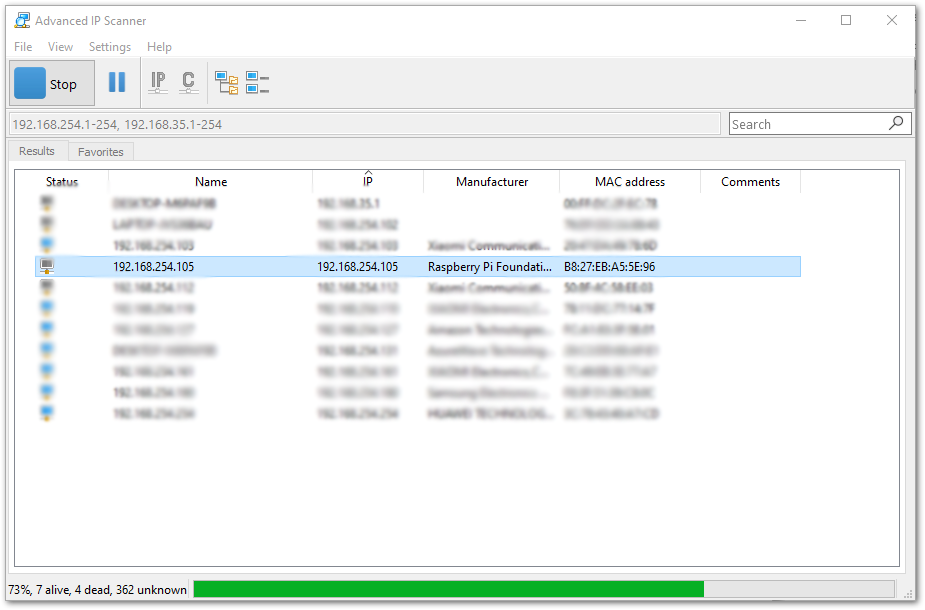 Figure 1: IP address of your Raspberry Pi with the RAK2245 Pi Hat using IP Scanner
Figure 1: IP address of your Raspberry Pi with the RAK2245 Pi Hat using IP Scanner- There is a Web-based UI that comes with the ChirpStack instance. Simply open a browser and enter the following credentials:
- Browser Address:
<Gateway IP address>:8080(Example: http://192.168.254.176:8080) - Username: admin
- Password: admin
- Browser Address:
It is advisable to change your password to tighten the security of your account. You can change this by clicking the "change password" button at the user icon.
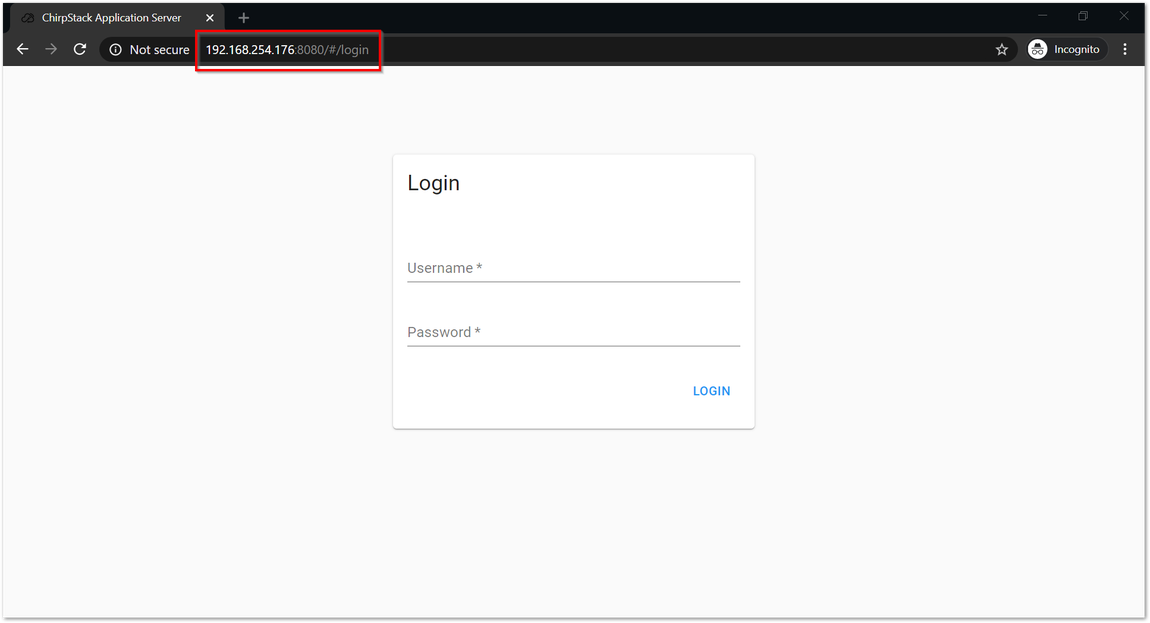 Figure 1: ChirpStack Web-based UI
Figure 1: ChirpStack Web-based UI- Everything should be pre-configured: Device profiles have been created, the Gateway has been registered with the server, etc. If you go to the Gateways tab and click on rak_gateway, you should see the Gateway details page.
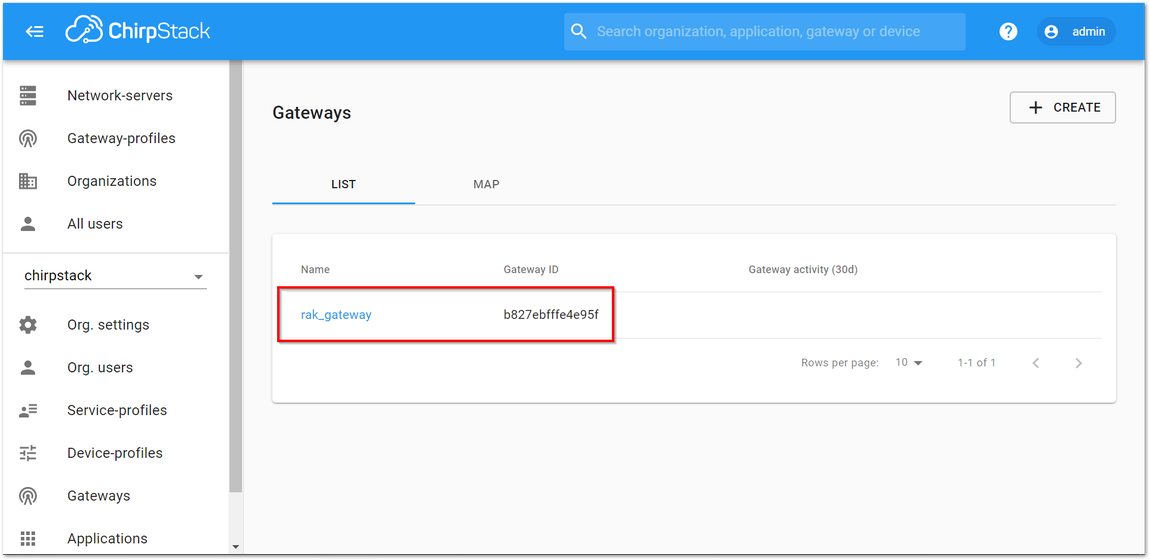 Figure 1: Available Gateways in Chirpstack
Figure 1: Available Gateways in Chirpstack- Go to the rak_gateway and see the "Last seen" status. It must be a few seconds ago which signifies that the Gateway is visible in the ChirpStack server.
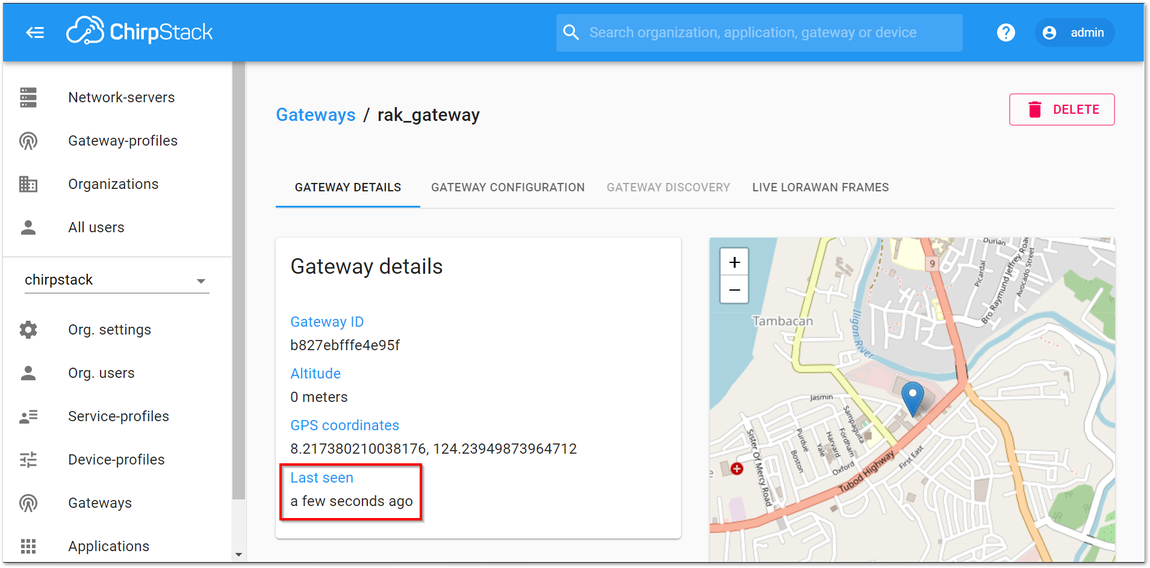 Figure 1: Last Seen Status
Figure 1: Last Seen Status2. Using an Independent ChirpStack
You can setup an Independent ChirpStack by yourself. This is a lot more complicated having to deploy a remote ChirpStack by yourself but Chirpstack provided a detailed guide on how to do it here.
 Figure 1: Chirpstack Getting Started Guide on Ubuntu
Figure 1: Chirpstack Getting Started Guide on UbuntuRemember to run the "sudo gateway-config" command in the CLI and point the Gateway to the IP address of the machine you just installed Chirpstack on. This can be done in item 2 in the menu Setup RAK Gateway LoRa concentrator.
- Assuming you have set it up correctly, Login to your ChirpStack to register your Gateway by opening the ChirpStack's web page in a browser by entering:
- Browser Address:
<IP Address of ChirpStack>:8080 - Username: admin
- Password: admin
- Browser Address:
 Figure 1: ChirpStack Login Page
Figure 1: ChirpStack Login Page- Click "Gateways" and Press "+ CREATE" to register your Gateway
 Figure 1: ChirpStack Registered Gateways
Figure 1: ChirpStack Registered Gateways- Click "Create" to register your Gateway and fill up the necessary information.
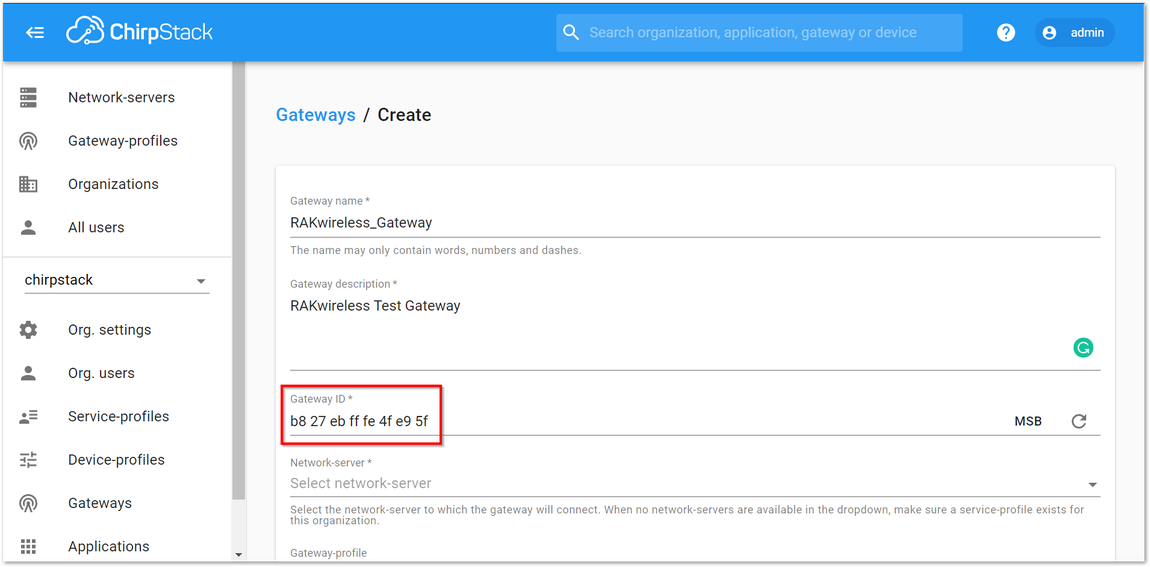 Figure 1: Registering your own Gateway
Figure 1: Registering your own Gateway-
Fill in the Gateway ID that we got from the Configuring the Gateway document, also called Gateway EUI.
-
If you have properly configured your Gateway and there is a network connection between the external ChirpStack and your Gateway, you should see the following page and status:
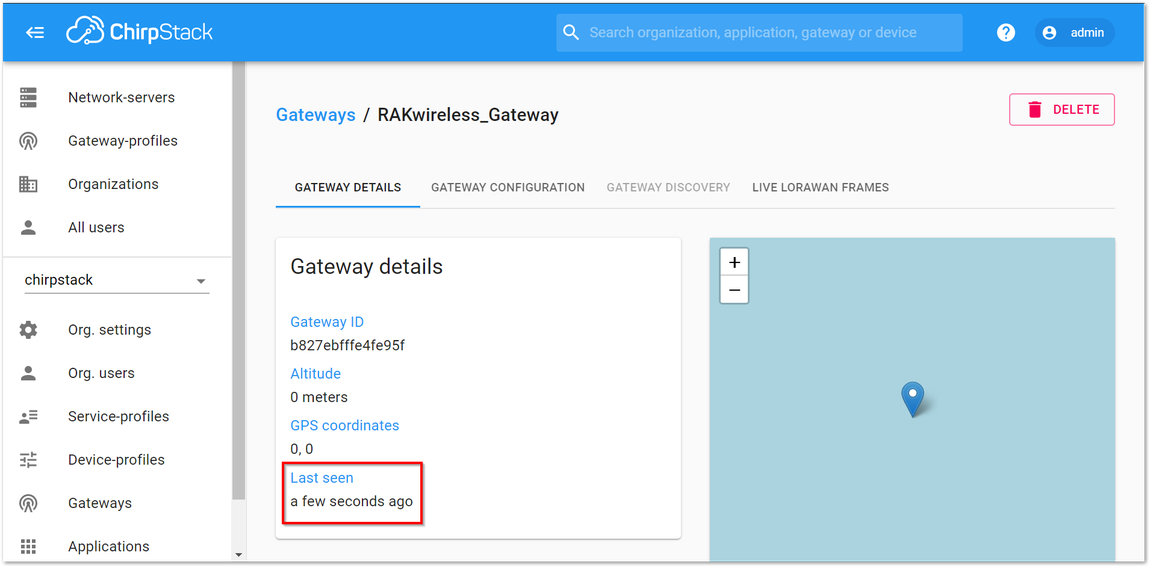 Figure 1: Successfully Registered the Gateway
Figure 1: Successfully Registered the Gateway