RAK3172-SiP WisDuo LPWAN SiP Quick Start Guide
The RAK3172-SiP does not have pre-flashed LoRaWAN credentials and you have to define and setup your own unique credentials for the SiP's.
Prerequisites
Before going through the steps in the installation guide of the RAK3172-SiP WisDuo LPWAN SiP, make sure to prepare the necessary items listed below:
Hardware
- RAK3172-SiP WisDuo LPWAN SiP
- Adapter PCB board for the RAK3172-SiP to access UART2 pins
- USB-Serial Converter
- Computer
Software
- Download and install the Arduino IDE.
If you are using Windows 10. Do NOT install the Arduino IDE from the Microsoft App Store. Instead, install the original Arduino IDE from the Arduino official website. The Arduino app from the Microsoft App Store has problems using third-party Board Support Packages.
- Add RAK3172 as a supported board in Arduino IDE by updating Board Manager URLs in Preferences settings of Arduino IDE with this JSON URL
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/RAKWireless/RAKwireless-Arduino-BSP-Index/main/package_rakwireless_com_rui_index.json. After that, add RAKwireless RUI STM32 Boards via Arduino board manager. - RAK Serial Port Tool
List of Acronyms
| Acronym | Definition |
|---|---|
| DFU | Device Firmware Upgrade |
| JTAG | Joint Test Action Group |
| LoRa | Long Range |
| OTAA | Over-The-Air-Activation (OTAA) |
| ABP | Activation-By-Personalization (ABP) |
| TTN | The Things Network |
| DEVEUI | Device EUI (Extended Unique Identification) |
| APPEUI | Application EUI (Extended Unique Identification) |
| APPKEY | Application Key |
| DEVADDR | Device Address |
| NWKSKEY | Network Session Key |
| APPSKEY | Application Session Key |
| P2P | Point-to-Point |
Product Configuration
RAK3172-SiP as a Stand-Alone Device Using RUI3
Hardware Setup
The RAK3172-SiP requires a few hardware connections before you can make it work. The bare minimum requirement is to have the power section properly configured, reset button, antenna, and USB connection.
Firmware update is done via UART2 pins. If you connect the module to an external device that will be interfacing with UART2, take extra precautions in your board design to ensure you can still perform FW update to it. There should be a way in your board design that can disconnect the external device to RAK3172-SiP UART2 before connecting the module to the PC (via USB-UART converter) for the FW update process.
An alternative option to update firmware aside from UART2 is to use SWD pins (SWCLK & SWDIO). This method will require you to use external tools like ST-LINK or RAKDAP1.
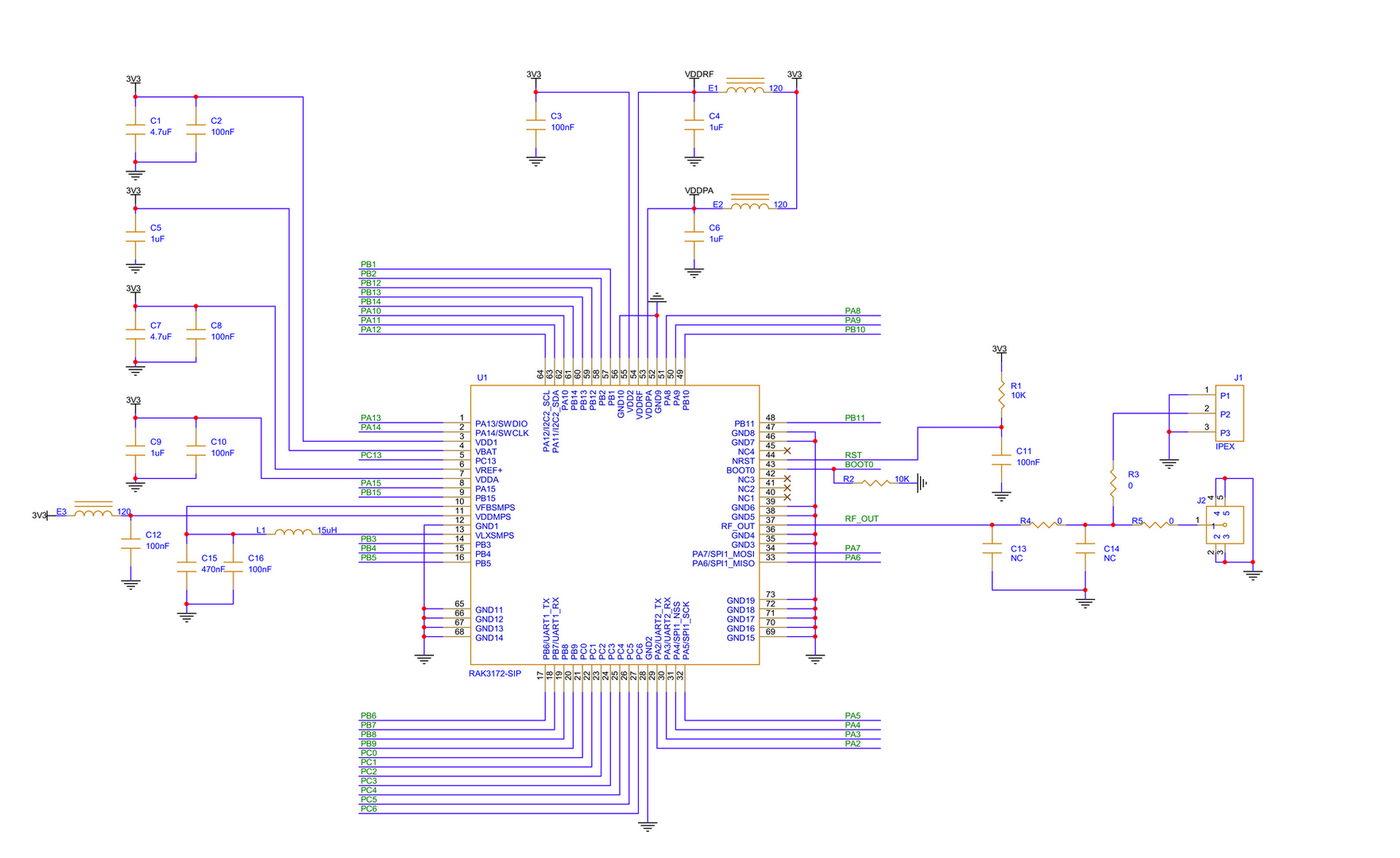 Figure 1: RAK3172-SiP minimum schematic
Figure 1: RAK3172-SiP minimum schematicEnsure that the antenna is properly connected to Pin 37 to have a good LoRa signal. Also, note that you can damage the RF section of the chip if you power the module without an antenna connected to the J1 using an IPEX connector.
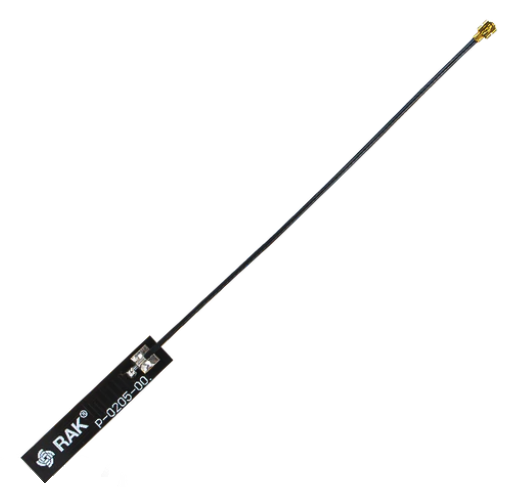 Figure 1: IPEX PCB LoRa Antenna
Figure 1: IPEX PCB LoRa AntennaYou can also use an RP-SMA connector in J2 where you can connect the LoRa antenna, as shown in Figure 3.
 Figure 1: RP-SMA LoRa Antenna
Figure 1: RP-SMA LoRa AntennaWhen using the LoRa transceiver, make sure that an antenna is always connected. Using this transceiver without an antenna can damage the module.
Software Setup
The default firmware of the RAK3172-SiP module is based on RUI3, which allows you to develop your custom firmware to connect sensors and other peripherals to it. To develop your custom firmware using Arduino IDE, first, you need to add RAKwireless RUI STM32 Boards in the Arduino board manager, which will be discussed in this guide. You can then use RUI3 APIs for your intended application and upload also the custom firmware via UART. The AT commands of the RAK3172-SiP module are still available even if you compile custom firmware via RUI3. You can send AT commands via UART2 connection.
RAK3172-SiP RUI3 Board Support Package in Arduino IDE
If you don't have an Arduino IDE yet, you can download it on the Arduino official website and follow the installation procedure in the miscellaneous section of this document.
For Windows 10 and up users: If your Arduino IDE is installed from the Microsoft App Store, you need to reinstall your Arduino IDE by getting it from the Arduino official website. The Arduino app from the Microsoft App Store has problems using third-party Board Support Packages.
Once the Arduino IDE has been installed successfully, configure the IDE to add the RAK3172-SiP to its board selection by following these steps:
- Open Arduino IDE and go to File > Preferences.
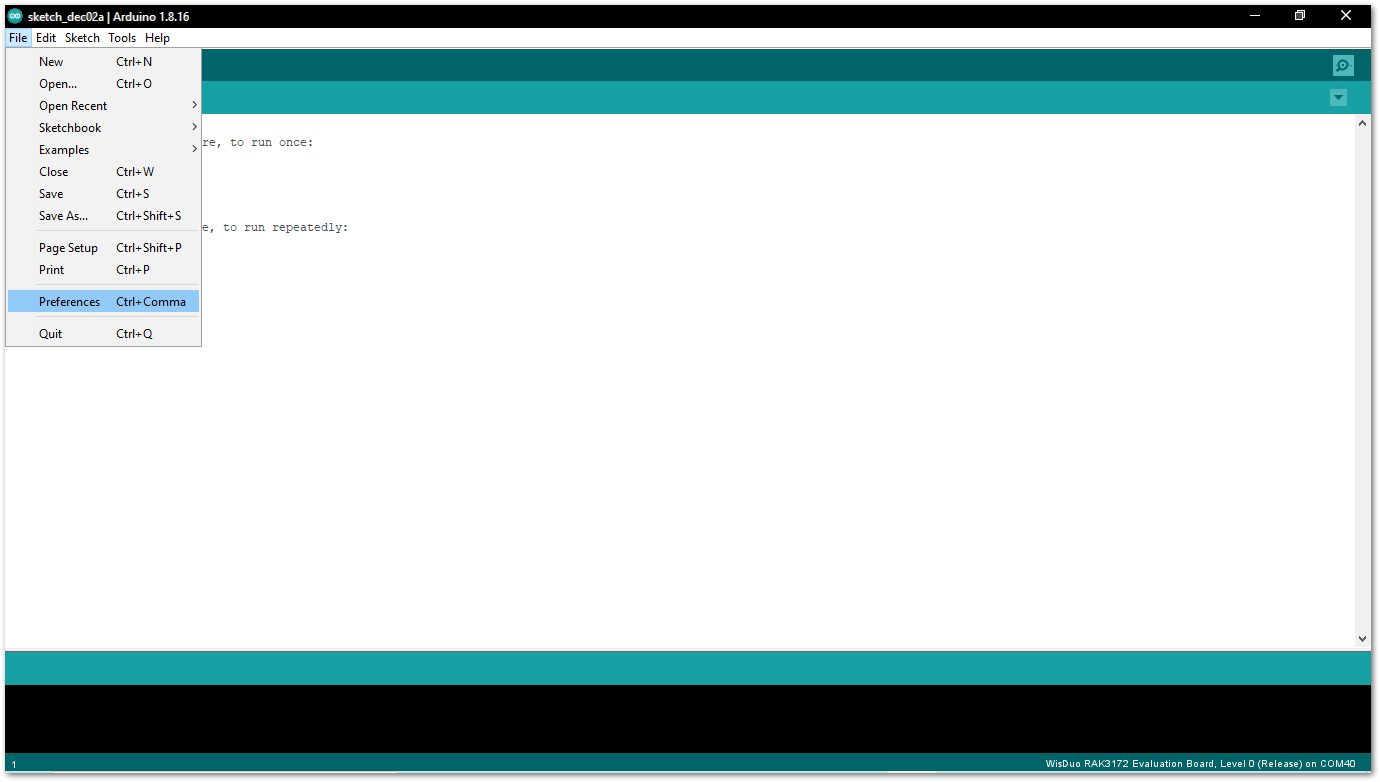 Figure 1: Arduino preferences
Figure 1: Arduino preferences- To add the RAK3172-SiP to your Arduino Boards list, edit the Additional Board Manager URLs. Click the icon, as shown in Figure 5.
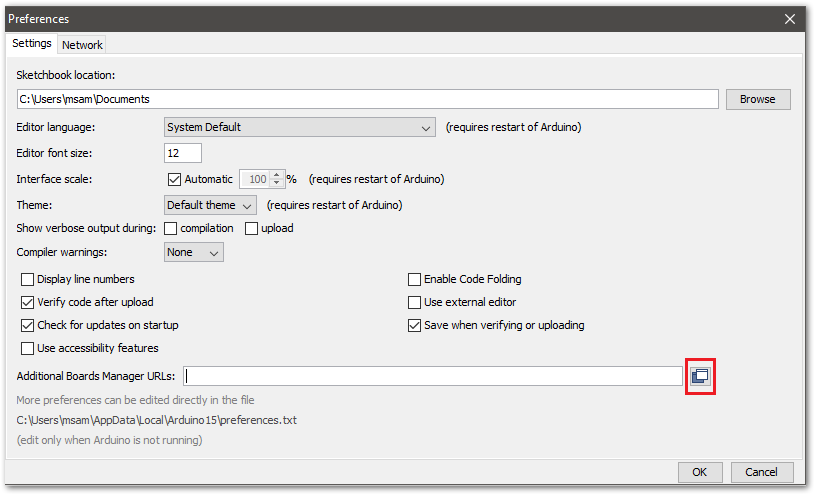 Figure 1: Modifying Additional Board Manager URLs
Figure 1: Modifying Additional Board Manager URLs- Copy the URL
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/RAKWireless/RAKwireless-Arduino-BSP-Index/main/package_rakwireless_com_rui_index.jsonand paste it on the field, as shown in Figure 6. If there are other URLs already there, just add them on the next line. After adding the URL, click OK.
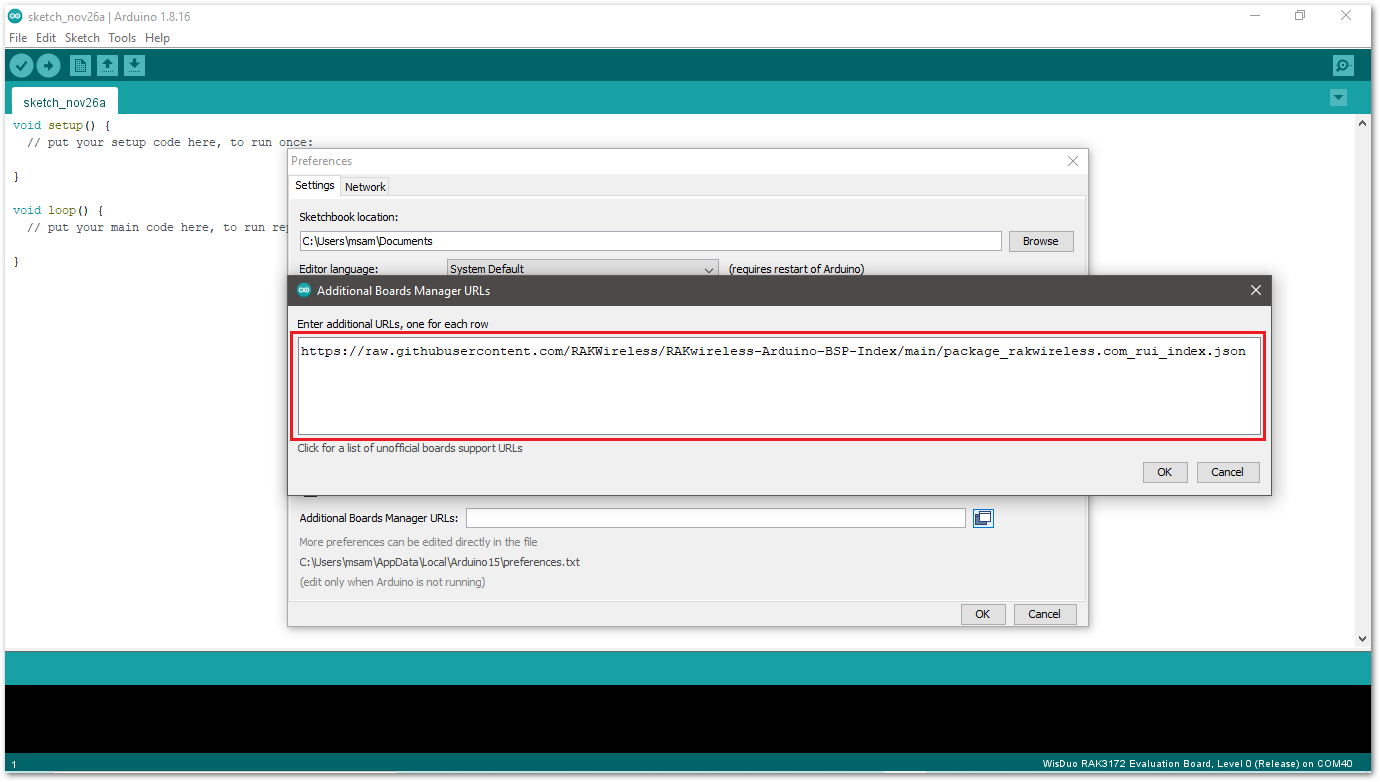 Figure 1: Add additional board manager URLs
Figure 1: Add additional board manager URLs- Restart the Arduino IDE.
- Open the Boards Manager from the Tools Menu.
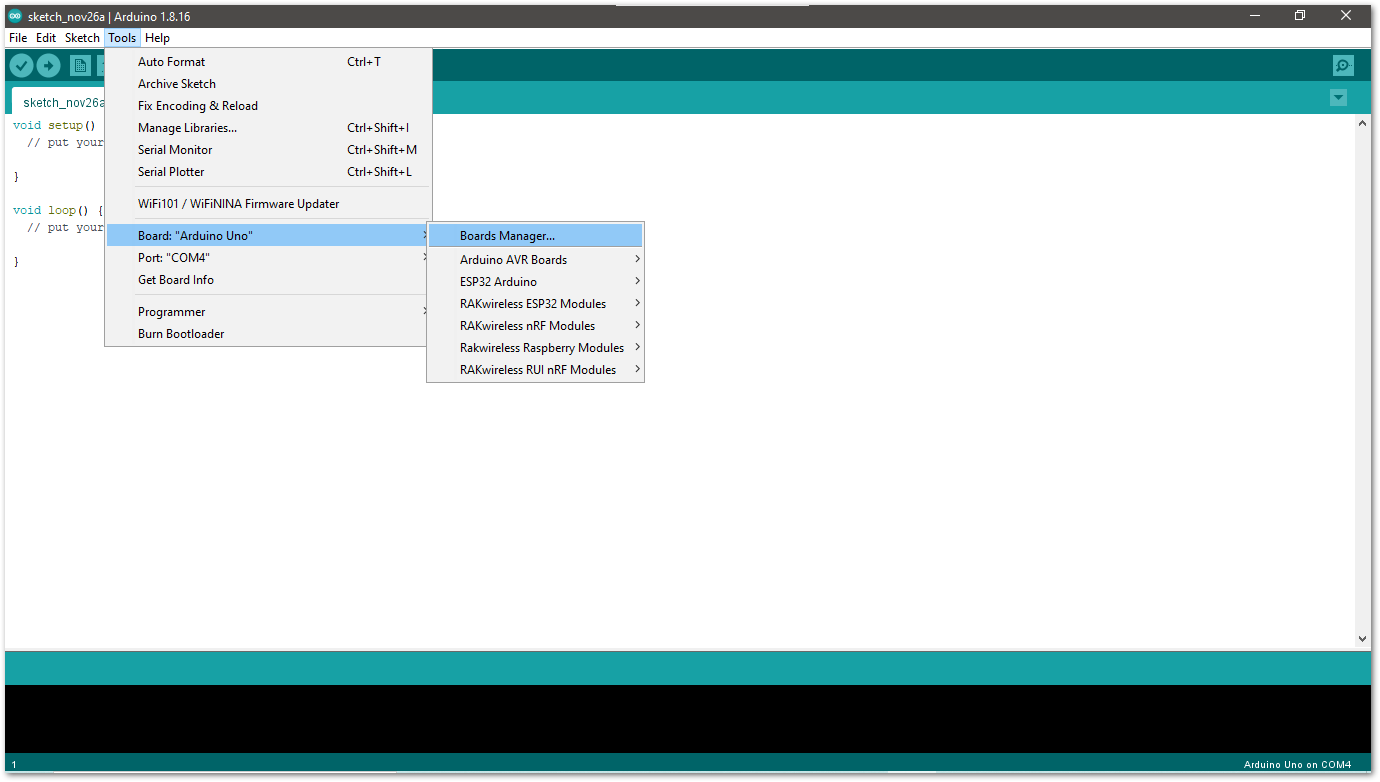 Figure 1: Opening Arduino boards manager
Figure 1: Opening Arduino boards manager- Write
RAKin the search bar, as shown in Figure 8. This will show the available RAKwireless module boards that you can add to your Arduino Board list. Select and install the latest version of the RAKwireless RUI STM32 Boards.
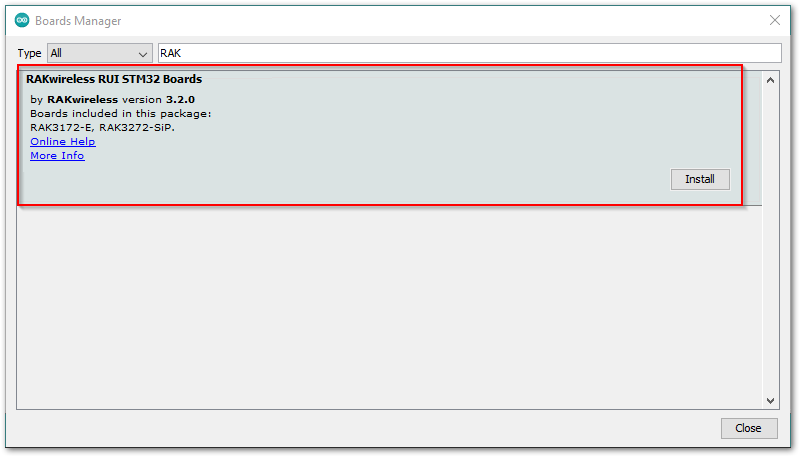 Figure 1: Installing RAKwireless RUI STM32 boards
Figure 1: Installing RAKwireless RUI STM32 boards- Once the BSP is installed, select Tools > Boards Manager > RAKWireless RUI STM32 Modules > WisDuo RAK3272-SiP Board.
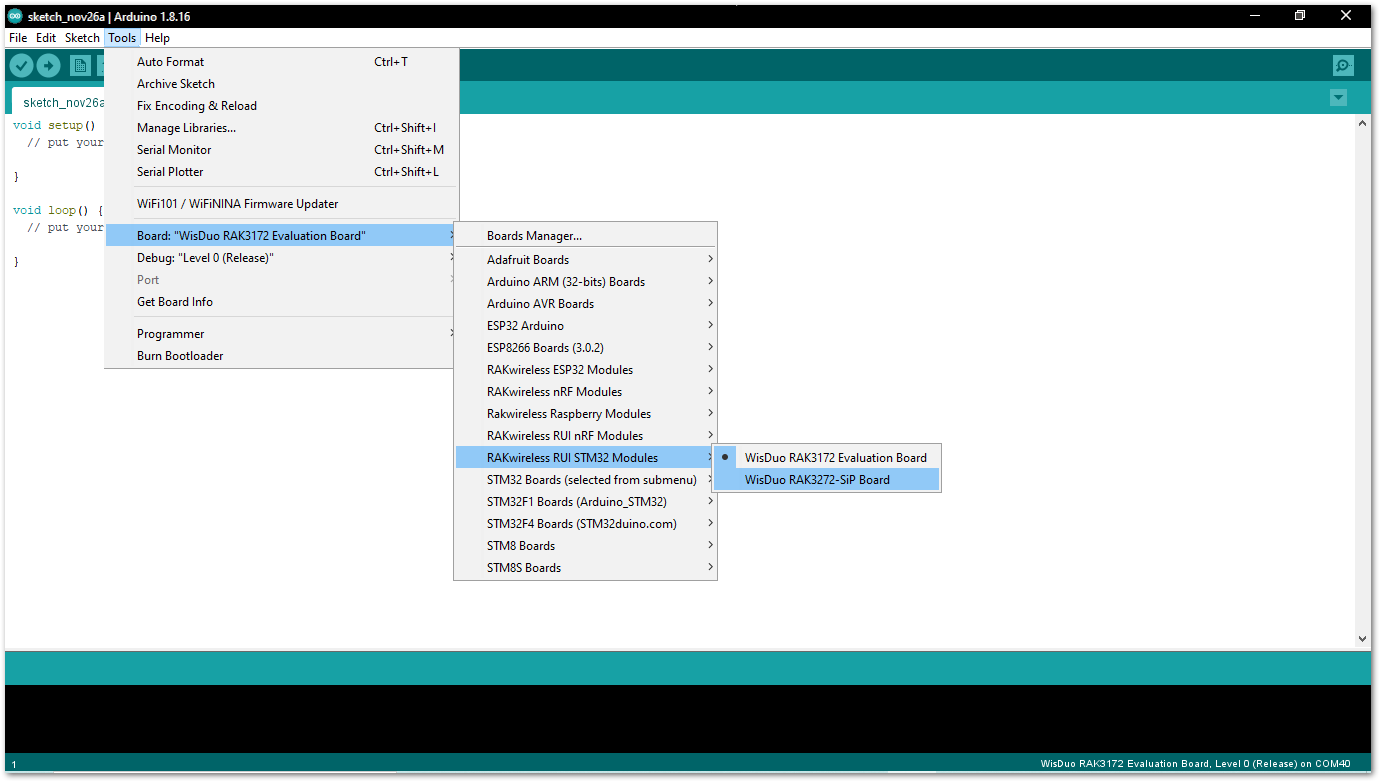 Figure 1: Selecting RAK3272-SiP Board for RAK3172-SiP Module
Figure 1: Selecting RAK3272-SiP Board for RAK3172-SiP ModuleCompile an Example with Arduino Serial
- After completing the steps on adding your RAK3172-SiP to the Arduino IDE, try to run a simple program to test your setup. You need to add a USB connection to the bare minimum schematic of the RAK3172-SiP module, as shown in Figure 10.
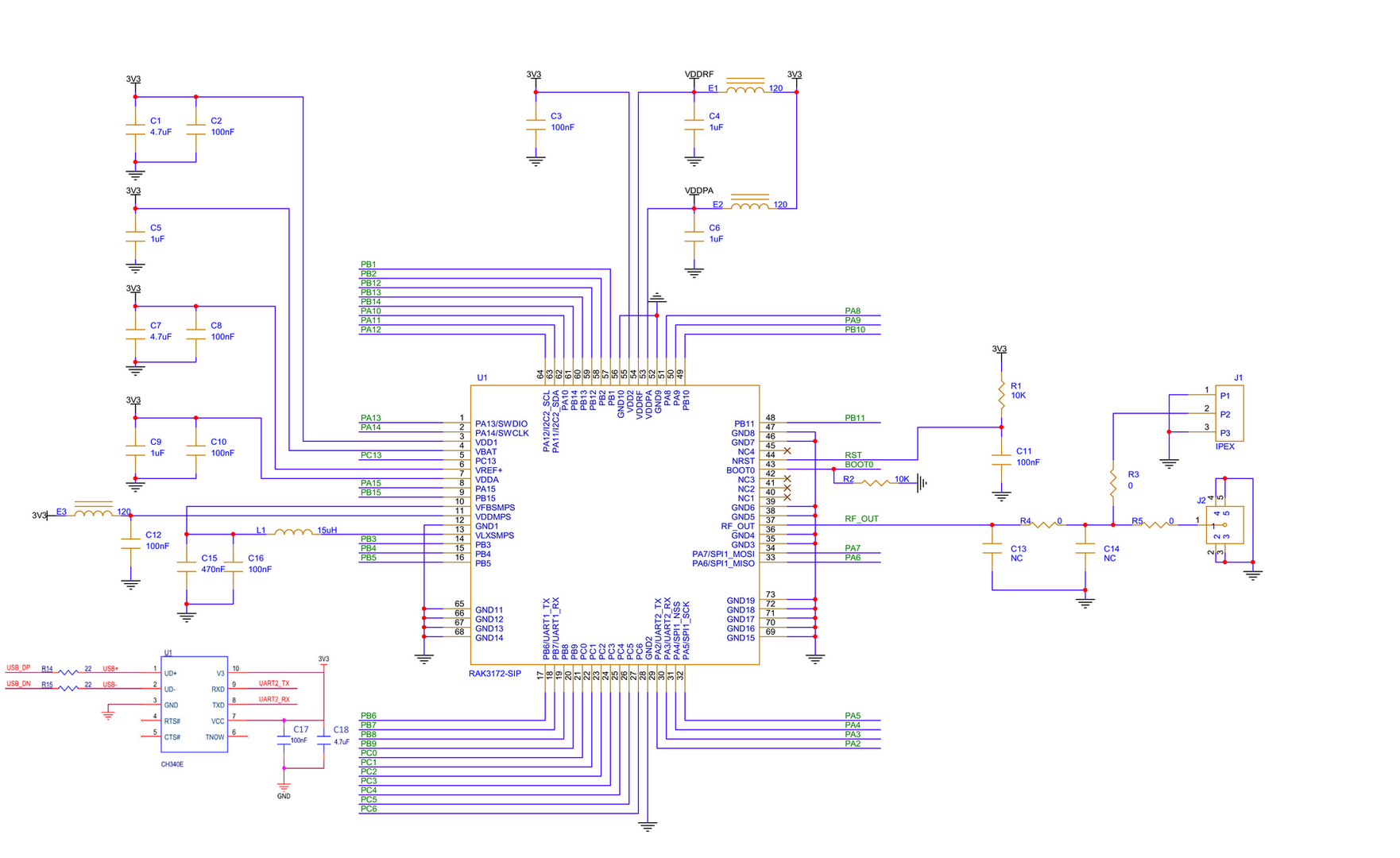 Figure 1: RAK3172-SiP with USB to Serial Schematic
Figure 1: RAK3172-SiP with USB to Serial Schematic- Connect the RAK3172-SiP via UART and check RAK3172-SiP COM Port using Windows Device Manager. Double-click the reset button if the module is not detected.
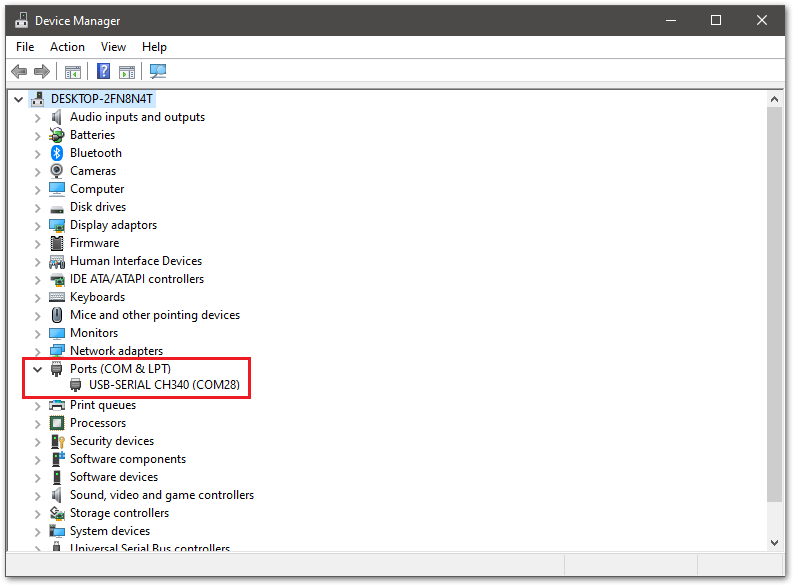 Figure 1: Device manager ports (COM & LPT)
Figure 1: Device manager ports (COM & LPT)- Choose RAK3172-SiP on board selection select via Tools > Boards Manager > RAKWireless RUI STM32 Modules > WisDuo RAK3272-SiP Board.
 Figure 1: Selecting RAK3272-SiP Board for RAK3172-SiP Module
Figure 1: Selecting RAK3272-SiP Board for RAK3172-SiP Module- Open the Tools menu and select a COM port. COM28 is currently used.
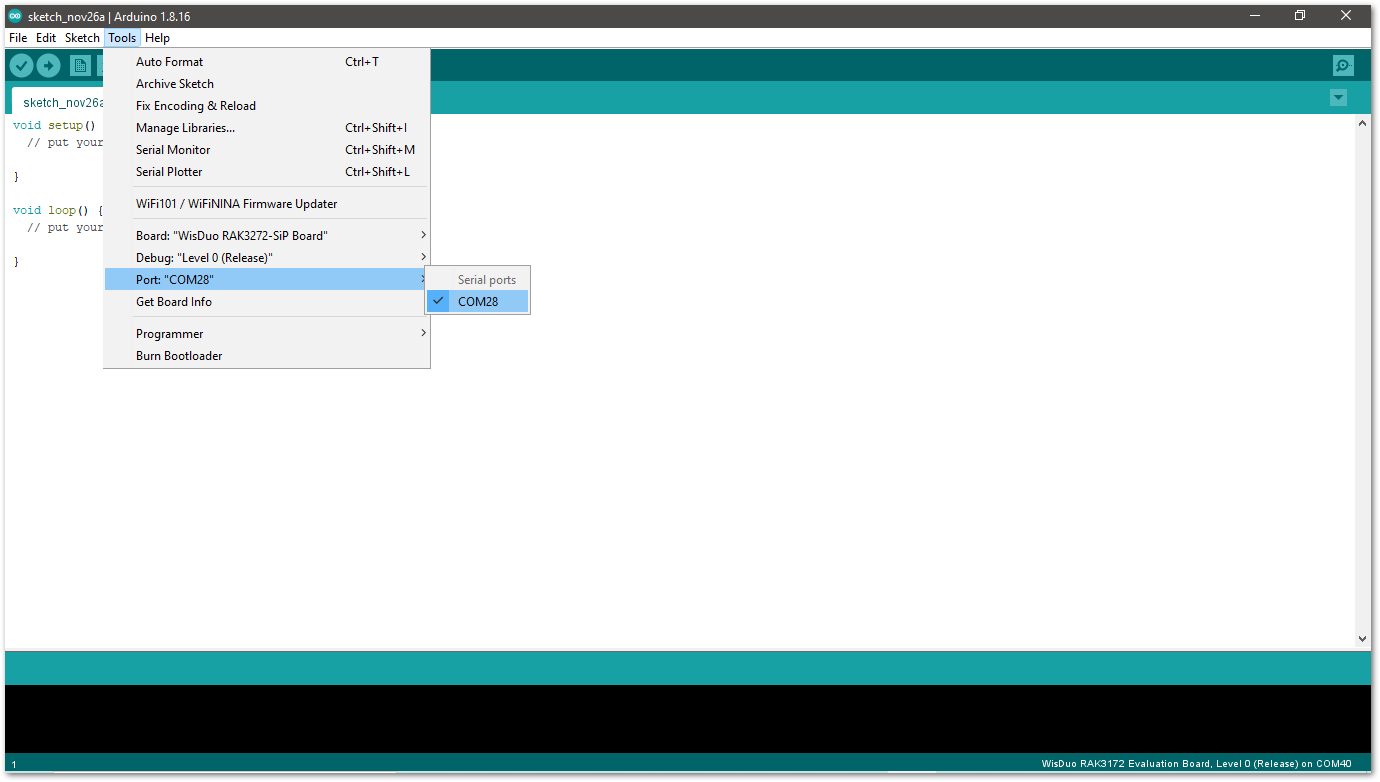 Figure 1: Select COM port
Figure 1: Select COM port- You can see the serial monitor icon and click it to connect the COM port.
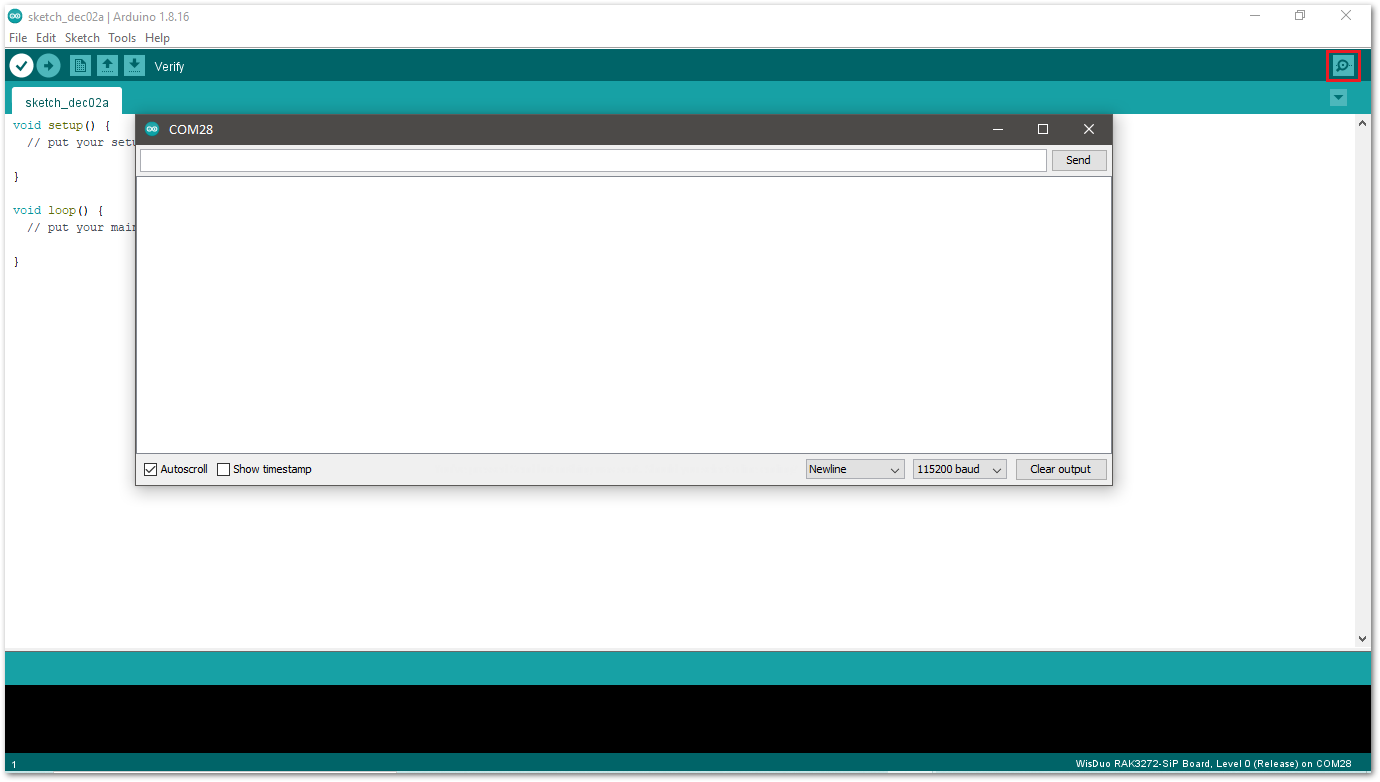 Figure 1: Open Arduino serial monitor
Figure 1: Open Arduino serial monitor- If the connection is successful, you can send AT Commands to RAK3172-SiP. For example: To check the RUI version, type
AT+VER=?on the text area, then click on the Send button, as shown in Figure 15.
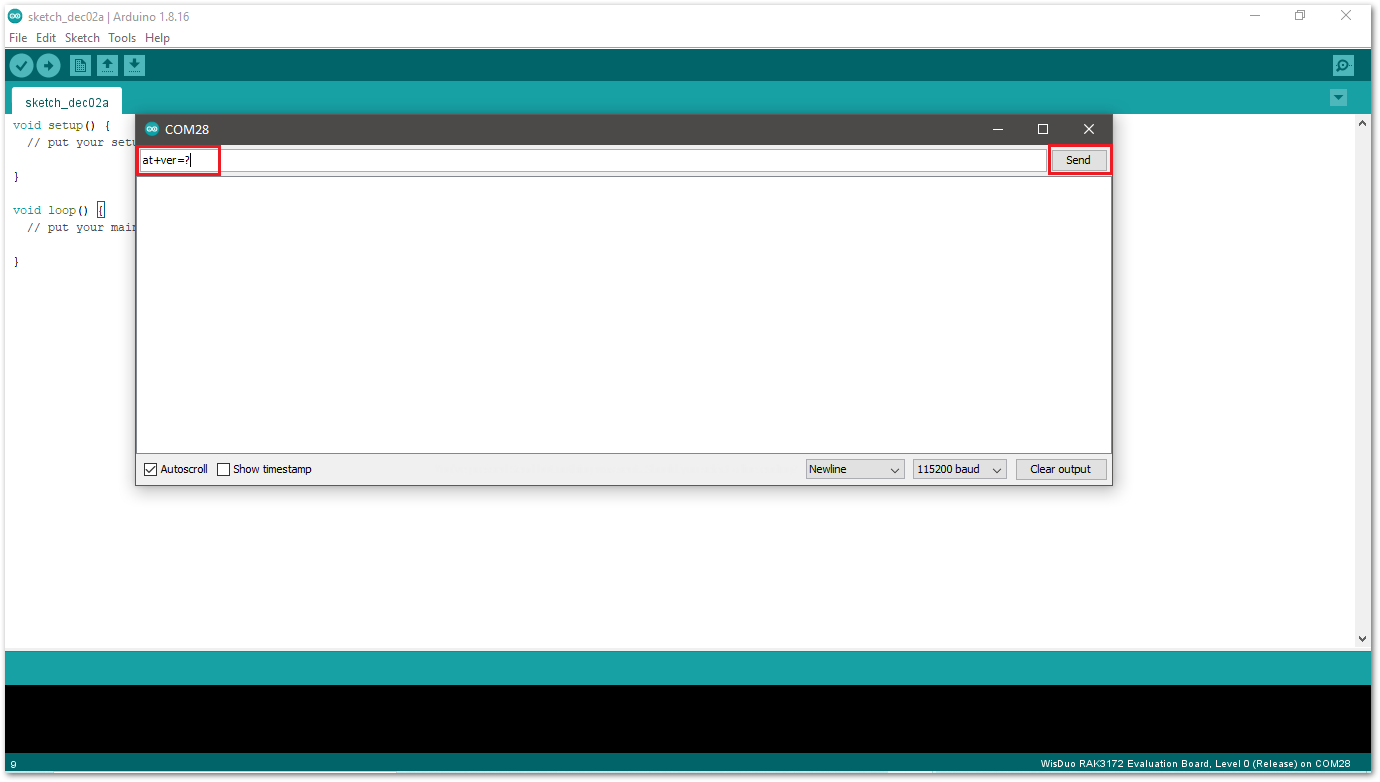 Figure 1: Send AT command
Figure 1: Send AT command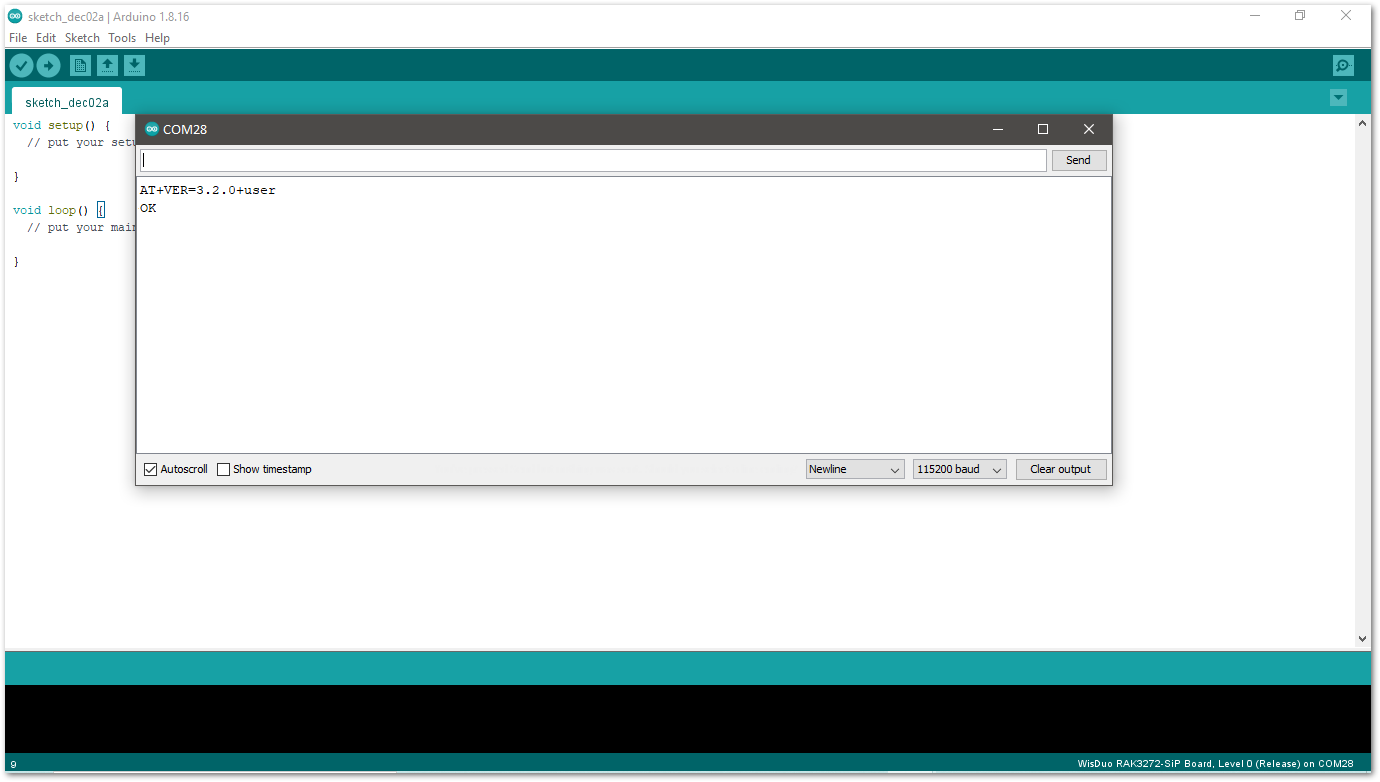 Figure 1: Arduino serial monitor COM28
Figure 1: Arduino serial monitor COM28- Open Arduino_Serial example code.
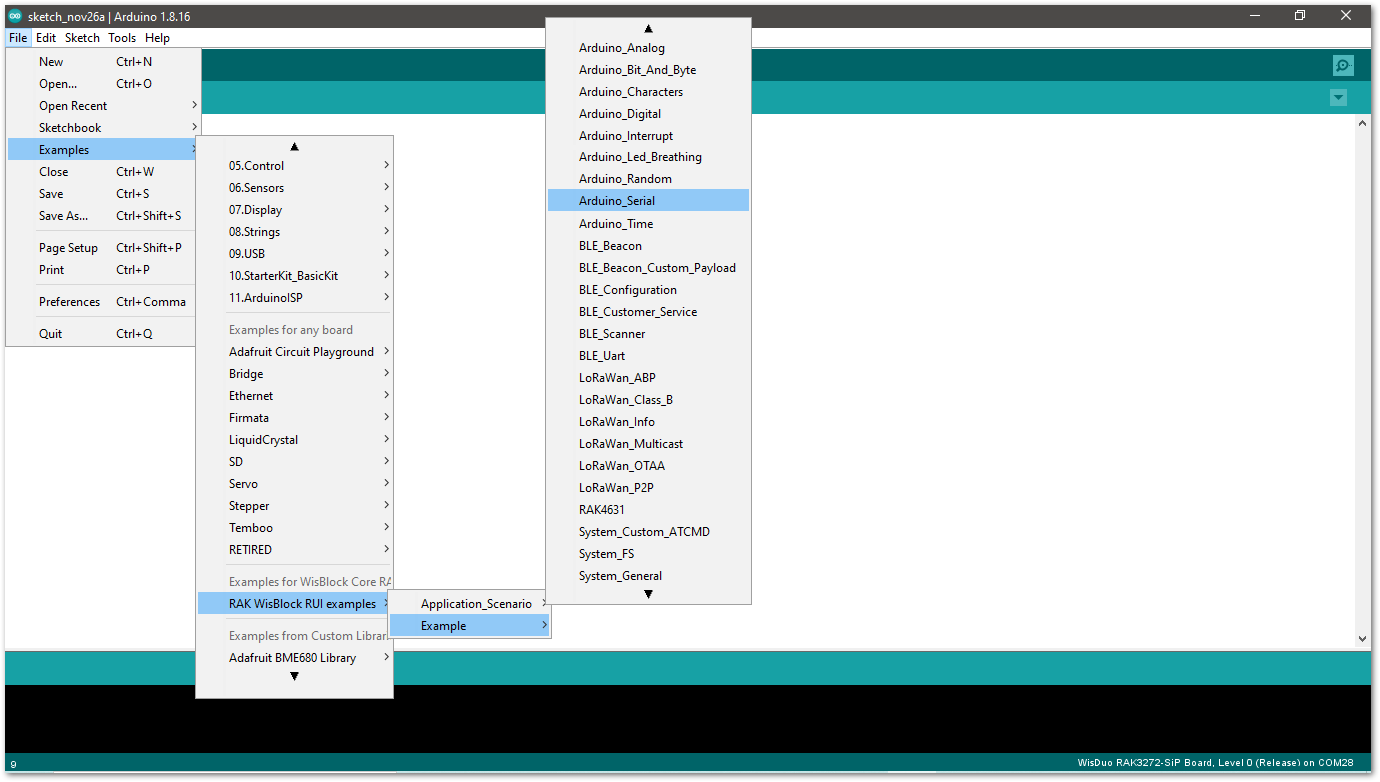 Figure 1: Arduino Serial example
Figure 1: Arduino Serial example- Click on the Verify icon to check if you have successfully compiled the example code.
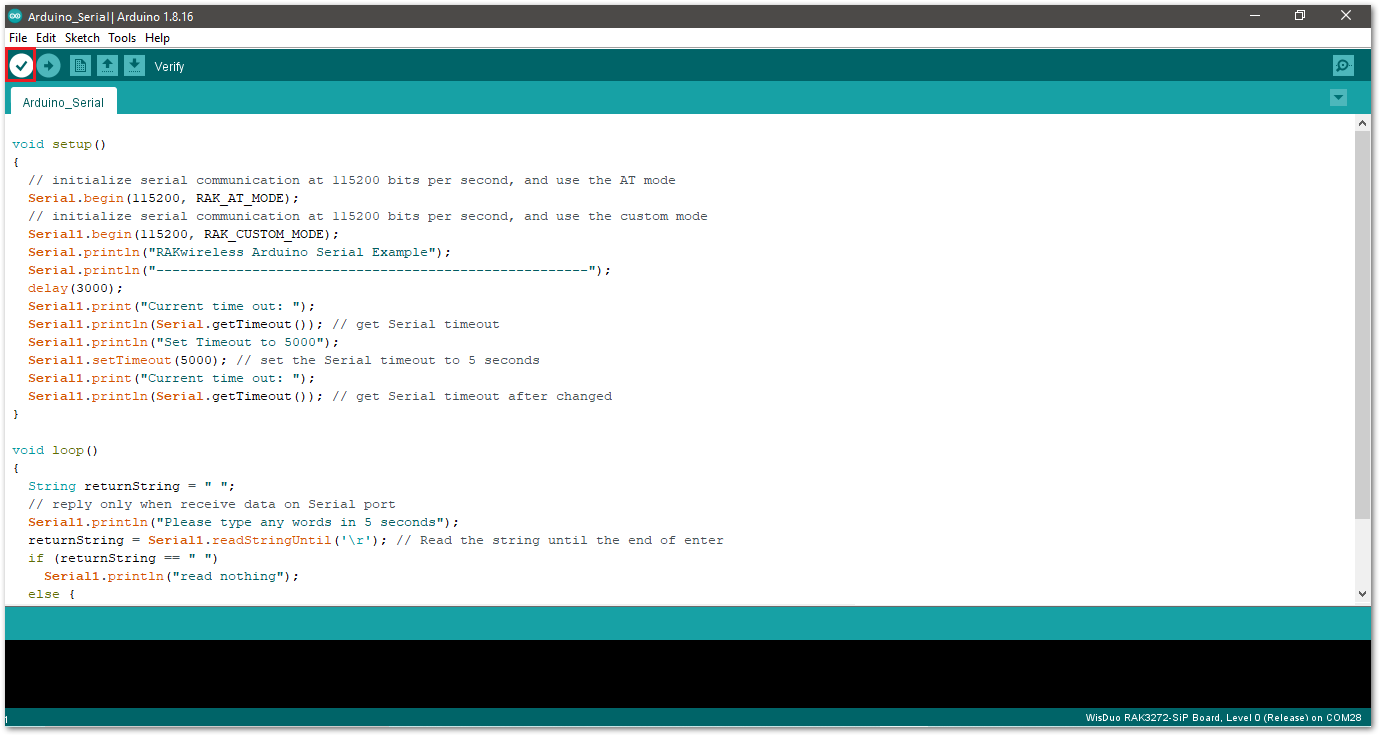 Figure 1: Verify the example code
Figure 1: Verify the example code- Click the Upload icon to send the compiled firmware to your RAK3172.
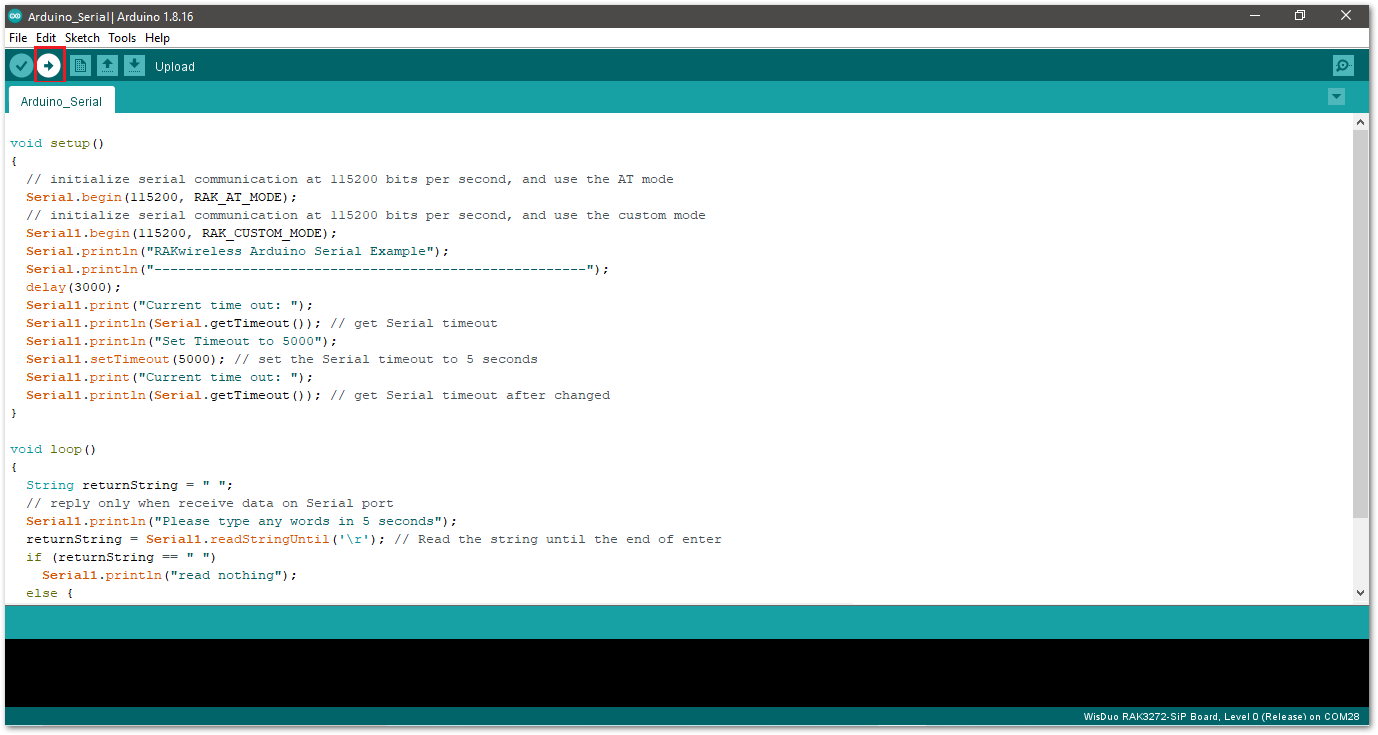 Figure 1: Upload the example code
Figure 1: Upload the example code- If the upload is successful, you will see the Device programmed message.
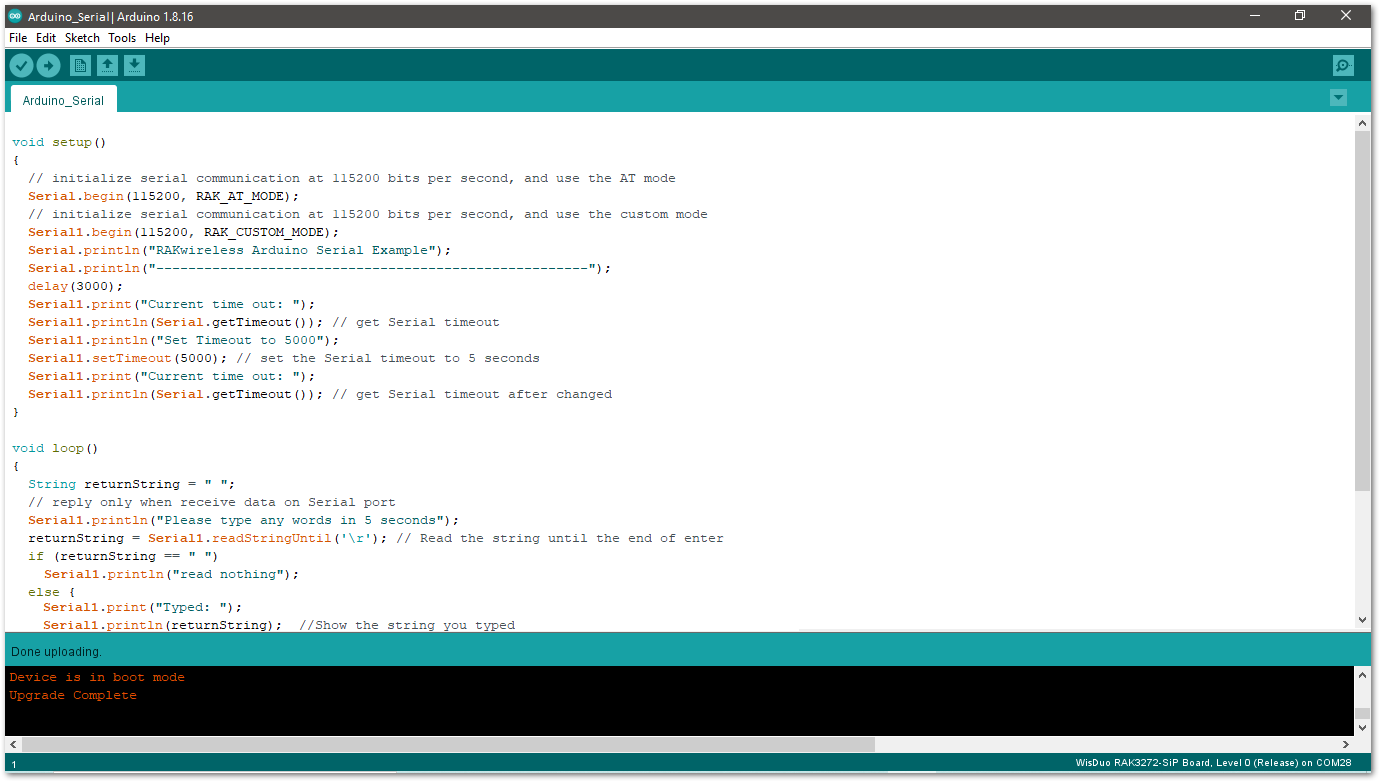 Figure 1: Device programmed successfully
Figure 1: Device programmed successfully- After the Device Programmed is completed, you will see the working Arduino_Serial example.
RAK3172-SiP I/O Pins and Peripherals
This section discusses how to use and access RAK3172-SiP pins using RUI3 API. It shows basic code using digital I/O, analog input, UART, and I2C.
How to Use Digital I/O
You can use any of the pins below as Digital Pin.
| Port Name | Alternative Pin Usage |
|---|---|
| PA4 | SPI1_NSS |
| PA5 | SPI1_CLK |
| PA6 | SPI1_MISO |
| PA7 | SPI1_MOSI |
| PA8 | - |
| PA9 | I2C_SCL |
| PA10 | I2C_SDA / PIN_A4 |
| PA15 | PIN_A3 |
| PB1 | - |
| PB2 | PIN_A2 |
| PB3 | PIN_A0 |
| PB4 | PIN_A1 |
| PB5 | - |
| PB6 | UART1_TX |
| PB7 | UART1_RX |
| PB8 | - |
| PB9 | - |
| PB10 | - |
| PB11 | - |
| PB12 | - |
| PB13 | - |
| PB14 | - |
| PB15 | - |
| PC0 | - |
| PC1 | - |
| PC2 | - |
| PC3 | - |
| PC4 | - |
| PC5 | - |
| PC6 | - |
| PC13 | - |
In Figure 21, the available I/O pins are shown in purple.
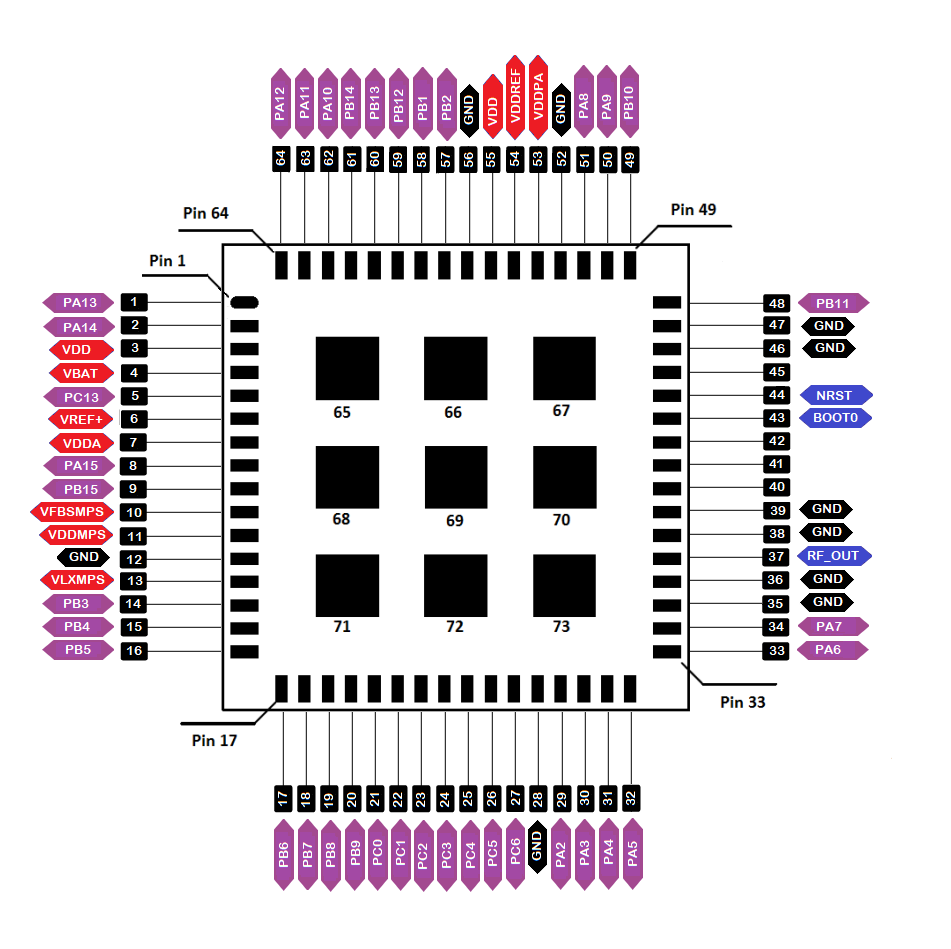 Figure 1: Available Digital I/O pins in RAK3172-SiP module
Figure 1: Available Digital I/O pins in RAK3172-SiP moduleThe pins listed below must not be used.
| Port Name | Pin Usage | Pin Number |
|---|---|---|
| PA2 | UART2_TX | 29 |
| PA3 | UART2_RX | 30 |
| PA13 | SWDIO | 1 |
| PA14 | SWCLK | 2 |
The GPIO pin name is the one to be used on the digitalRead and digitalWrite and NOT the pin numbers.
- Use Arduino digitalRead to read the value from a specified Digital I/O pin, either HIGH or LOW.
- Use Arduino digitalWrite to write a HIGH or a LOW value to a Digital I/O pin.
Example code
void setup()
{
pinMode(PA15, OUTPUT); //Change the P0_04 to any digital pin you want. Also, you can set this to INPUT or OUTPUT
}
void loop()
{
digitalWrite(PA15,HIGH); //Change the PA15 to any digital pin you want. Also, you can set this to HIGH or LOW state.
delay(1000); // delay for 1 second
digitalWrite(PA15,LOW); //Change the PA15 to any digital pin you want. Also, you can set this to HIGH or LOW state.
delay(1000); // delay for 1 second
}
How to Use Analog Input
You can use any of the pins below as Analog Input.
| Port Name | ADC | Pin Number |
|---|---|---|
| PB3 | PIN_A0 | 14 |
| PB4 | PIN_A1 | 15 |
| PB2 | PIN_A2 | 57 |
| PA10 | PIN_A3 | 62 |
| PA15 | PIN_A4 | 8 |
- Use Arduino analogRead to read the value from the specified Analog Input pin.
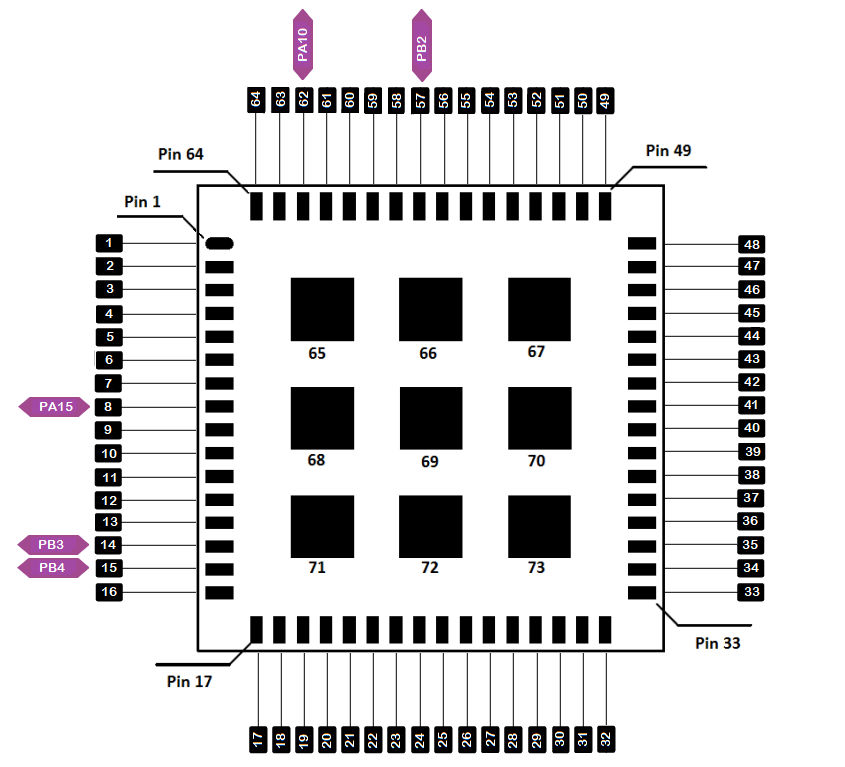 Figure 1: Available Analog pins in RAK3172-SiP Module
Figure 1: Available Analog pins in RAK3172-SiP ModuleExample code
#define analogPin PB3
int val = 0; // variable to store the value read
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(115200);
}
void loop()
{
val = analogRead(analogPin); // read the input pin
Serial.println(val); // debug value
delay(100);
}
How to Use Serial Interfaces
UART
There are two UART peripherals available on the RAK3172-SiP module. There are also different Serial Operating Modes possible in RUI3, namely Binary Mode, AT Mode, and Custom Mode.
UART Pin map table
| Port Name | Serial Port | Serial Instance Assignment | Default Mode | Pin Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PB6 | UART1_RX | Serial1 | Custom Mode | 17 |
| PB7 | UART1_TX | Serial1 | Custom Mode | 18 |
| PA3 | UART2_RX | Serial | AT Command | 30 |
| PA2 | UART2_TX | Serial | AT Command | 29 |
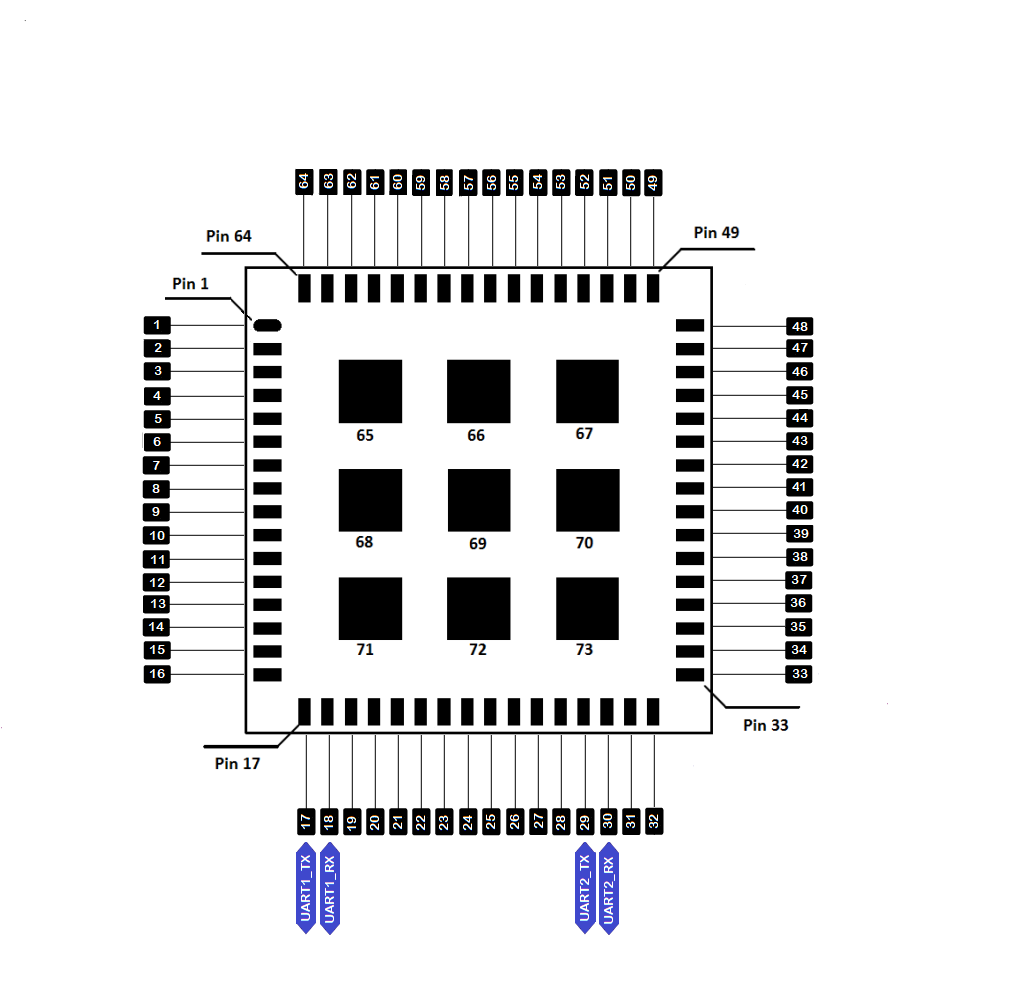 Figure 1: Available UART pins in RAK3172-SiP Module
Figure 1: Available UART pins in RAK3172-SiP ModuleExample Code
void setup()
{
Serial1.begin(115200); // use Serial1 for UART1 and Serial for UART2
// you can designate separate baudrate for each.
Serial.begin(115200);
}
void loop()
{
Serial1.println("RAK3172-SiP UART1 TEST!");
Serial.println("RAK3172-SiP UART2 TEST!");
delay(1000); // delay for 1 second
}
I2C
There is one I2C peripheral available on RAK3172-SiP Module.
| Port Name | I2C Pin Name | Pin Number |
|---|---|---|
| PA9 | I2C_SCL | 50 |
| PA10 | I2C_SDA | 62 |
Use Arduino Wire library to communicate with I2C devices.
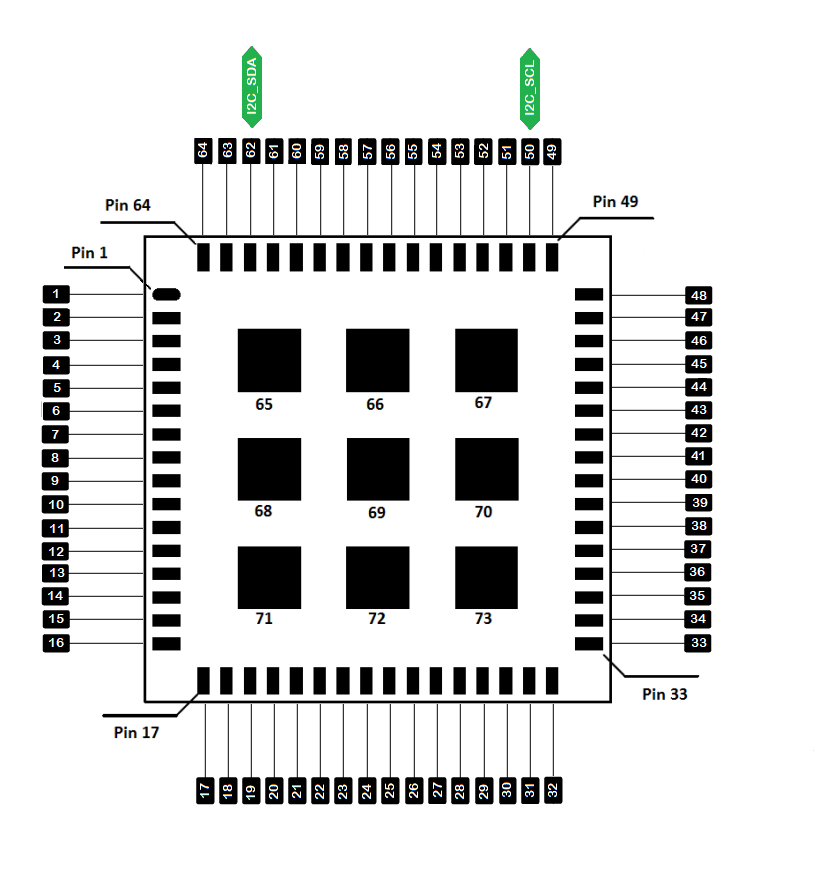 Figure 1: Available I2C pins in RAK3172-SiP Module
Figure 1: Available I2C pins in RAK3172-SiP ModuleExample Code
Make sure you have an I2C device connected to specified I2C pins to run the I2C scanner code below:
#include <Wire.h>
void setup()
{
Wire.begin();
Serial.begin(115200);
while (!Serial);
Serial.println("\nI2C Scanner");
}
void loop()
{
byte error, address;
int nDevices;
Serial.println("Scanning...");
nDevices = 0;
for(address = 1; address < 127; address++ )
{
// The i2c_scanner uses the return value of
// the Write.endTransmission to see if
// a device did acknowledge to the address.
Wire.beginTransmission(address);
error = Wire.endTransmission();
if (error == 0)
{
Serial.print("I2C device found at address 0x");
if (address<16)
Serial.print("0");
Serial.print(address,HEX);
Serial.println(" !");
nDevices++;
}
else if (error==4)
{
Serial.print("Unknown error at address 0x");
if (address<16)
Serial.print("0");
Serial.println(address,HEX);
}
}
if (nDevices == 0)
Serial.println("No I2C devices found\n");
else
Serial.println("done\n");
delay(5000); // wait 5 seconds for next scan
}
The Arduino Serial Monitor shows the I2C device found.
17:29:15.690 -> Scanning...
17:29:15.738 -> I2C device found at address 0x28 !
17:29:15.831 -> done
17:29:15.831 ->
17:29:20.686 -> Scanning...
17:29:20.733 -> I2C device found at address 0x28 !
17:29:20.814 -> done
17:29:20.814 ->
SPI
If your RUI3 project uses SPI, then PA4 to PA7 pins are reserved for RUI3 SPI interface.
| Port Name | SPI Pin Name | Pin Number |
|---|---|---|
| PA4 | SPI1_CS | 31 |
| PA5 | SPI1_CLK | 32 |
| PA6 | SPI1_MISO | 33 |
| PA7 | SPI1_MOSI | 34 |
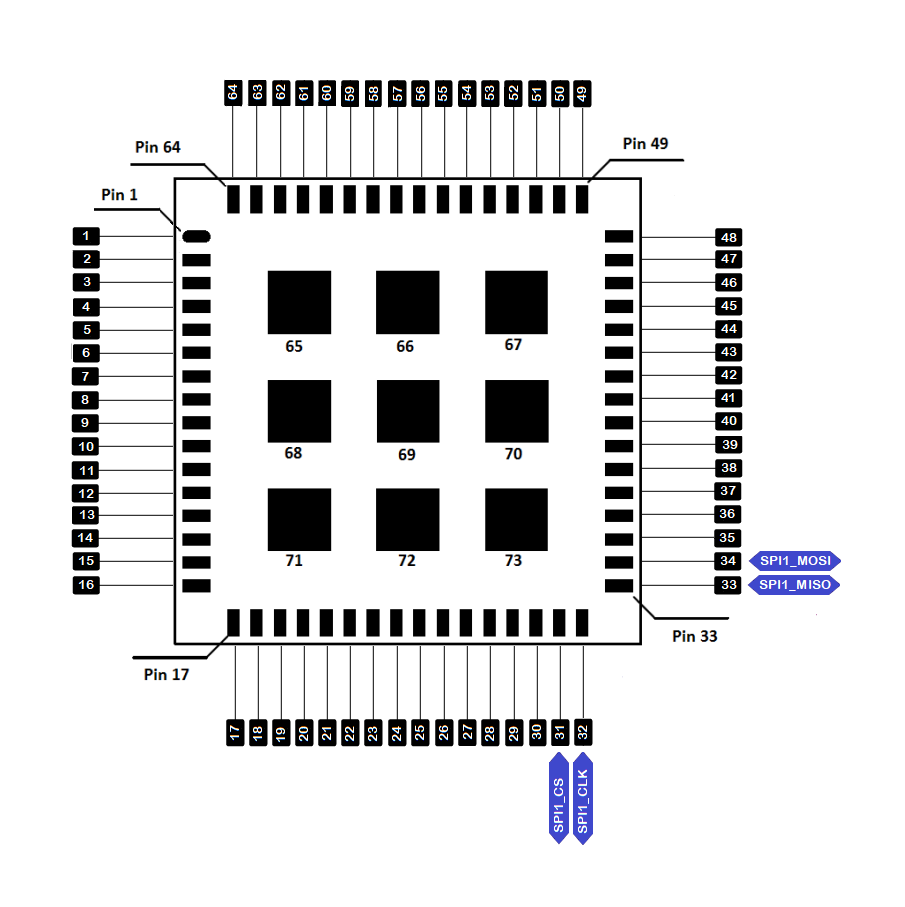 Figure 1: Available SPI pins in RAK3172-SiP Module
Figure 1: Available SPI pins in RAK3172-SiP ModuleMore examples for the RAK3172-SiP can be found in the RUI3-Best-Practices on Github.
RAK3172-SiP as a LoRa/LoRaWAN Modem via AT Command
AT Command via UART2
RAK3172-SiP module can be configured using AT commands via the UART2 interface. You need a USB to UART TTL adapter to connect the RAK3172-SiP to your computer's USB port and a serial terminal tool. You can use the RAK Serial Port Tool so you can easily send AT commands and view the replies from the console output. The RAK Serial Port Tool commands still use the RUI V2 AT commands by default. You can modify it to have RUI3 AT commands and then save it.
Firmware update and AT command functionality are done via UART2 pins. If you will connect the module to an external host MCU that will send AT commands via UART2, take extra precautions in your board design to ensure you can still perform FW update to it. There should be a way in your board design that can disconnect the host MCU UART to connect to RAK3172 UART2 before connecting the module to the PC (via USB-UART converter) for the FW update process.
An alternative option to update firmware aside from UART2 is to use SWD pins (SWCLK & SWDIO). This method will require you to use external tools like ST-LINK or RAKDAP1.
Connect to the RAK3172-SiP
- Connect the RAK3172-SiP to the serial port of a general-purpose computer (USB port) using a USB to UART TTL adapter like RAKDAP1, as shown in Figure 26.
There are other connections needed on the RAK3172-SiP aside from the VDD, GND, and UART2 pins. Check the minimal needed external connections in RAK3272-SiP Breakout Board Schematic.
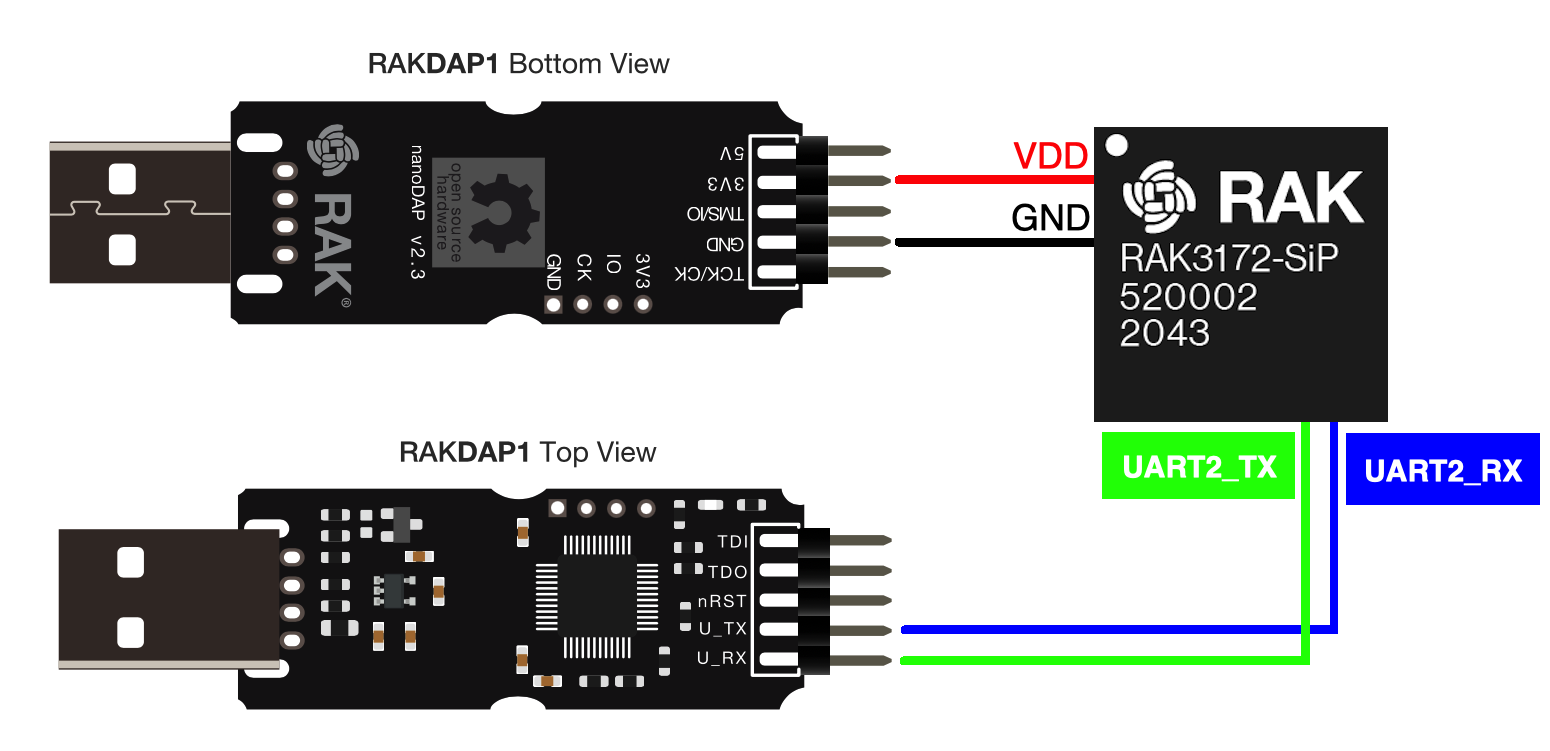 Figure 1: RAK3172-SiP UART2 connection
Figure 1: RAK3172-SiP UART2 connection- Any serial communication tool can be used. But it is recommended to use the RAK Serial Port Tool.
- Configure the serial communication tool by selecting the proper port detected by the computer and configure the link as follows:
- Baud Rate: 115200 baud
- Data Bits: 8 bits
- Stop Bits: 1 stop bit
- Parity: NONE
RAK3172-SiP Configuration for LoRaWAN or LoRa P2P
To enable the RAK3172-SiP module as a LoRa P2P module or a LoRaWAN end-device, the module must be configured and parameters must be set by sending AT commands. You can configure the RAK3172-SiP in two ways:
- LoRaWAN End-Device - RAK3172 as LoRaWAN IoT device.
- LoRa P2P - Point to point communication between two RAK3172-SiP.
Configuring RAK3172-SiP as LoRaWAN End-Device
To enable the RAK3172-SiP as a LoRaWAN end-device, a device must be registered first in the LoRaWAN network server. This guide will cover both TTN and Chirpstack LoRaWAN network servers and the associated AT commands for the RAK3172-SiP.
Connecting to The Things Network (TTN)
In this section, a quick tutorial guide will show how to connect the RAK3172-SiP to the TTN platform.
In this guide, you need to have a working gateway that is connected to TTN or you have to be within the coverage of a TTN community network.
 Figure 1: RAK3172-SiP EVB in the context of the TTN
Figure 1: RAK3172-SiP EVB in the context of the TTNAs shown in Figure 27, The Things Stack (TTN V3) is an open-source LoRaWAN Network Server suitable for global, geo-distributed public and private deployments, as well as for small local networks. The architecture follows the LoRaWAN Network Reference Model for standards compliance and interoperability. This project is actively maintained by The Things Industries.
LoRaWAN is a protocol for low-power wide-area networks. It allows large-scale Internet of Things deployments where low-powered devices efficiently communicate with Internet-connected applications over long-range wireless connections.
The RAK3172-SiP WisDuo can be part of this ecosystem as a device, and the objective of this section is to demonstrate how simple it is to send data to The Things Stack using the LoRaWAN protocol. To achieve this, the RAK3172-SiP WisDuo must be located inside the coverage of a LoRaWAN gateway connected to The Things Stack server.
Registration to TTN and Creating LoRaWAN Applications
- The first step is to go to The Things Network and sign up for an account shown in Figure 28. Then select a cluster as shown in Figure 30.
 Figure 1: Signing up an account in TTN
Figure 1: Signing up an account in TTN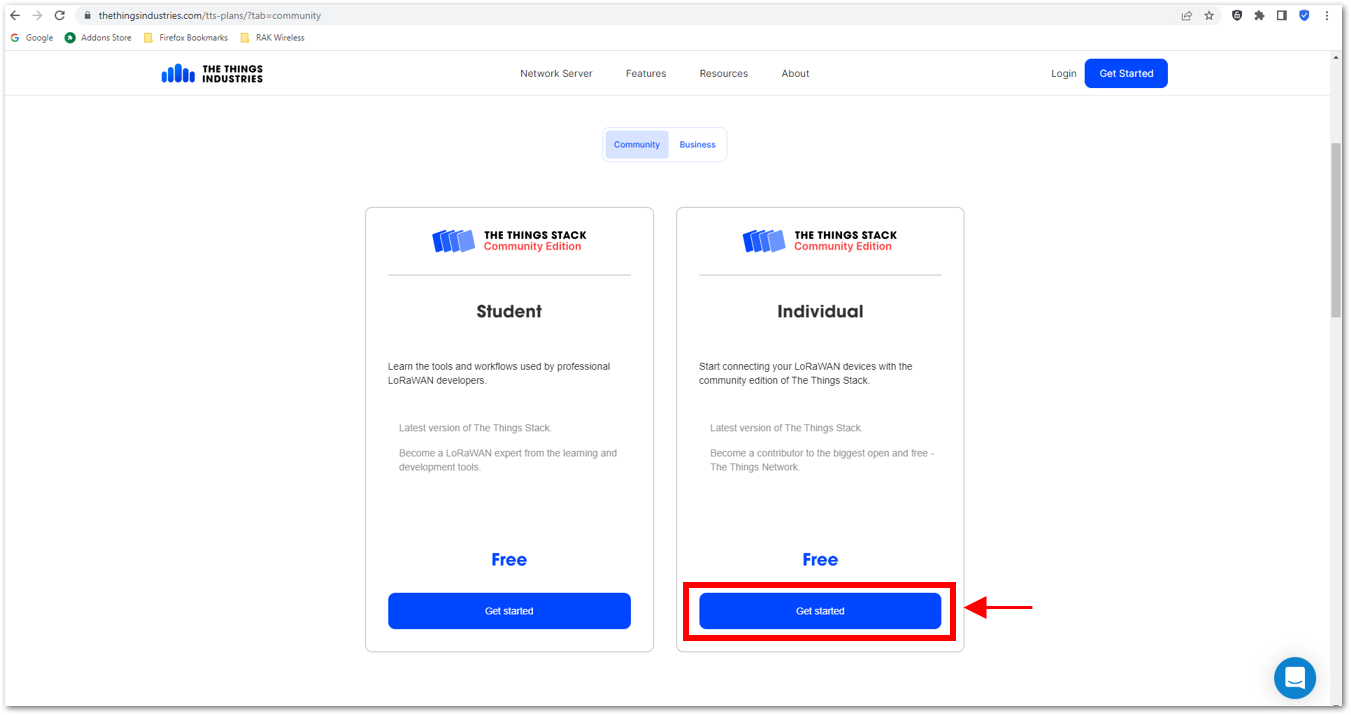 Figure 1: Signing up an account in TTN
Figure 1: Signing up an account in TTN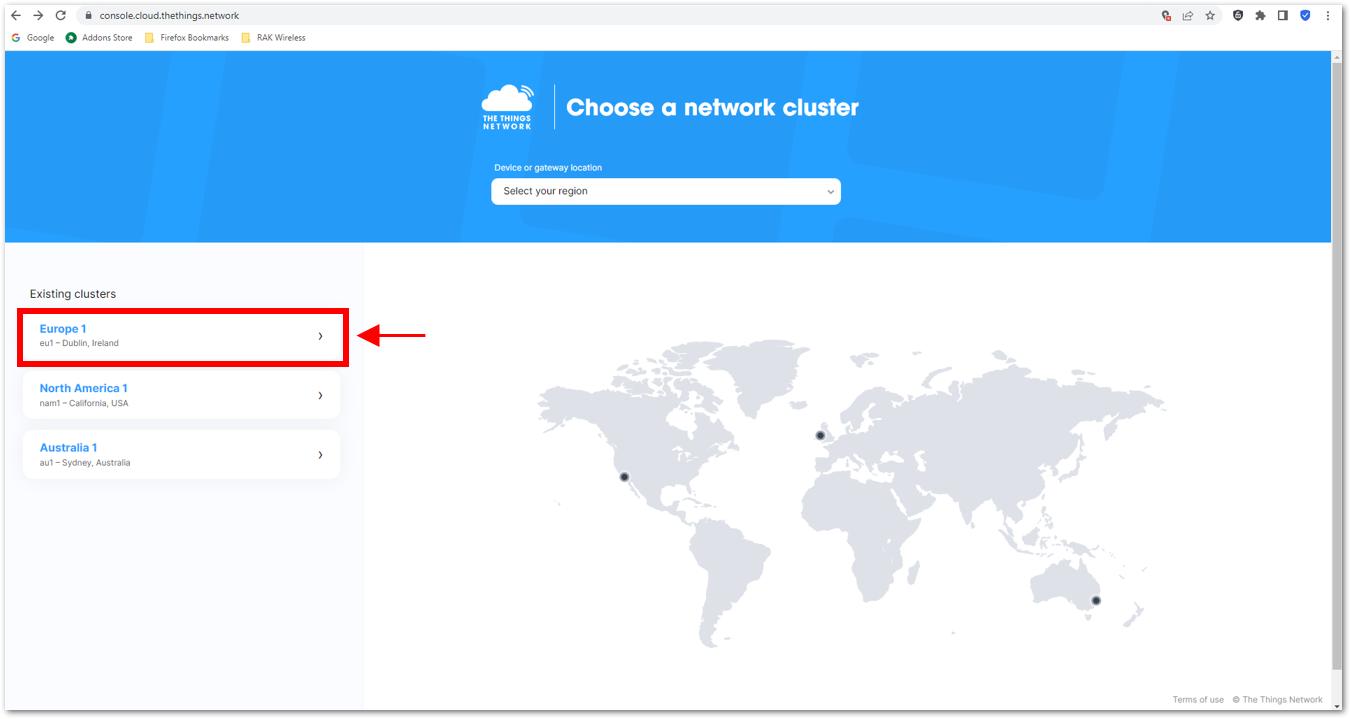 Figure 1: Selecting Cluster in TTN
Figure 1: Selecting Cluster in TTN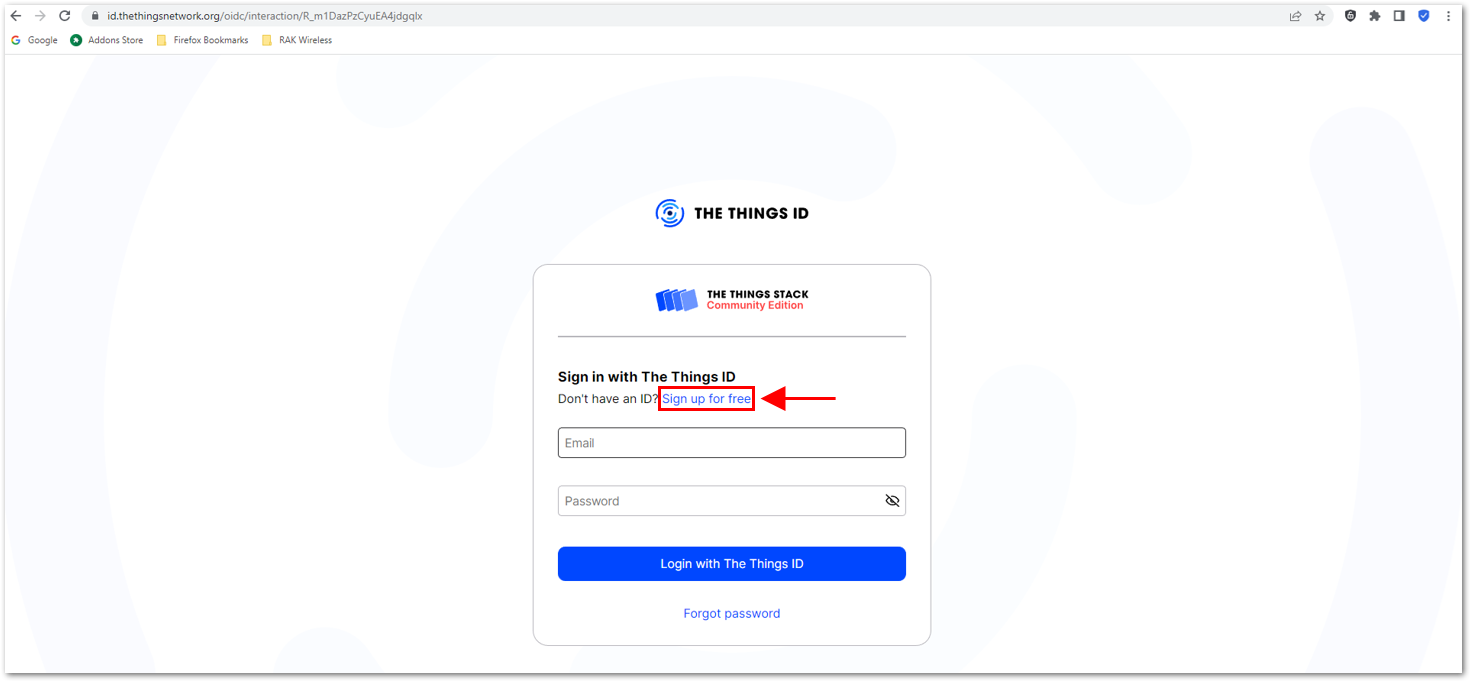 Figure 1: Signing up through the Things ID
Figure 1: Signing up through the Things ID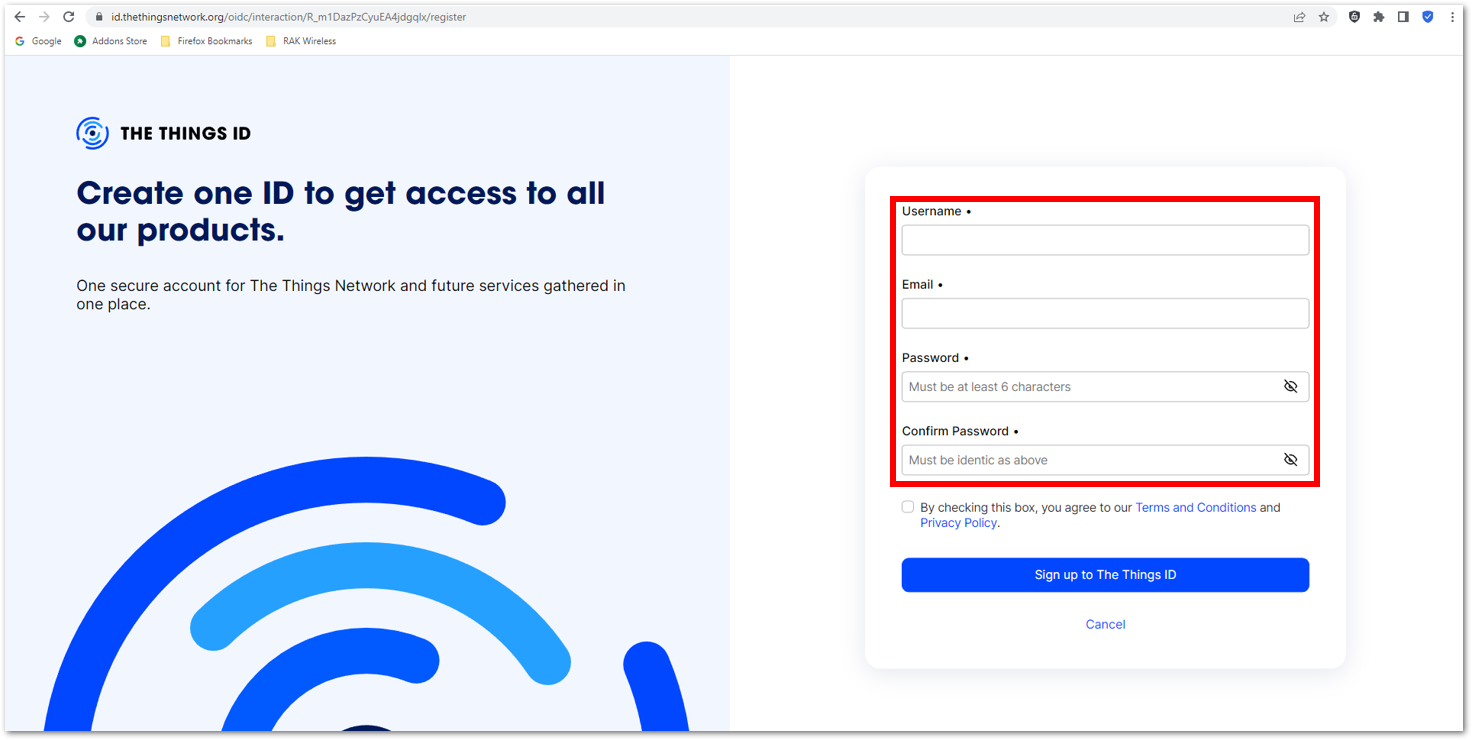 Figure 1: Creation of an account through the Things ID
Figure 1: Creation of an account through the Things ID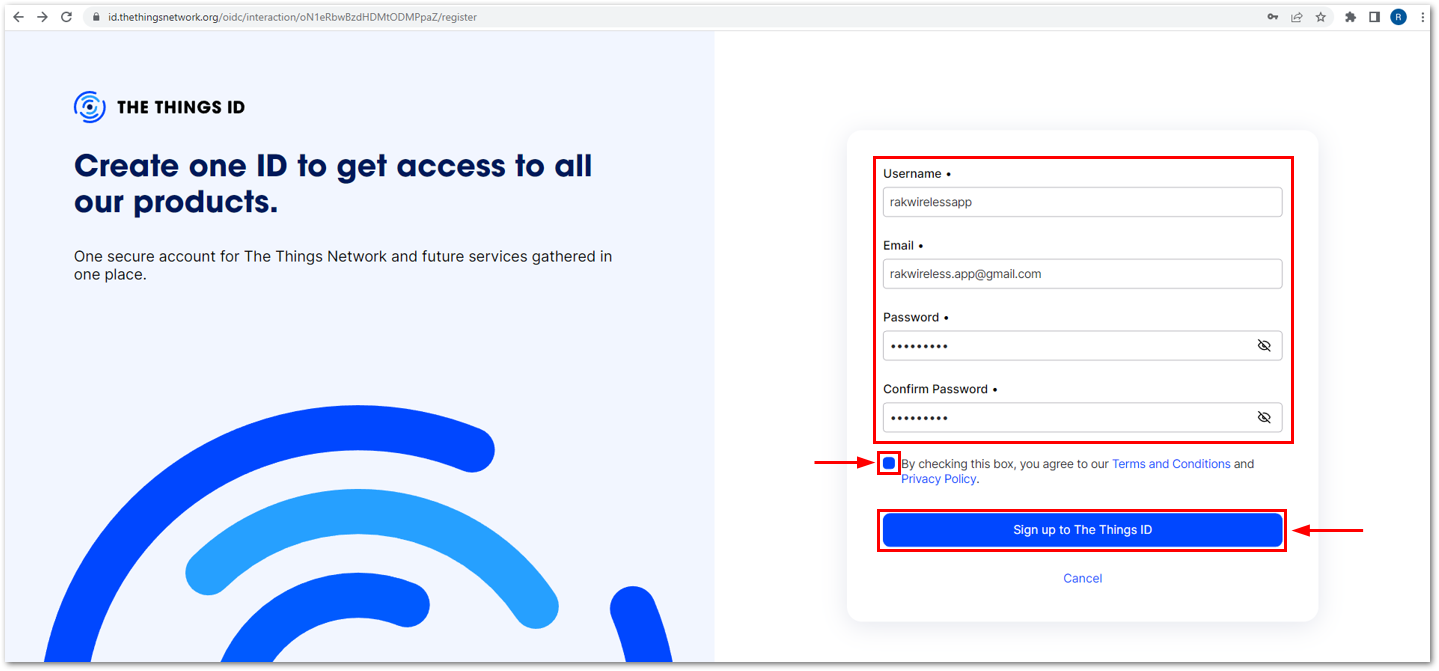 Figure 1: Creation of an account through the Things ID
Figure 1: Creation of an account through the Things IDYou can use the same login credentials on the TTN V2 if you have one. If you have no account yet, you need to create one.
- Now that you are logged in to the platform, the next step is to create an application. Click Create an application.
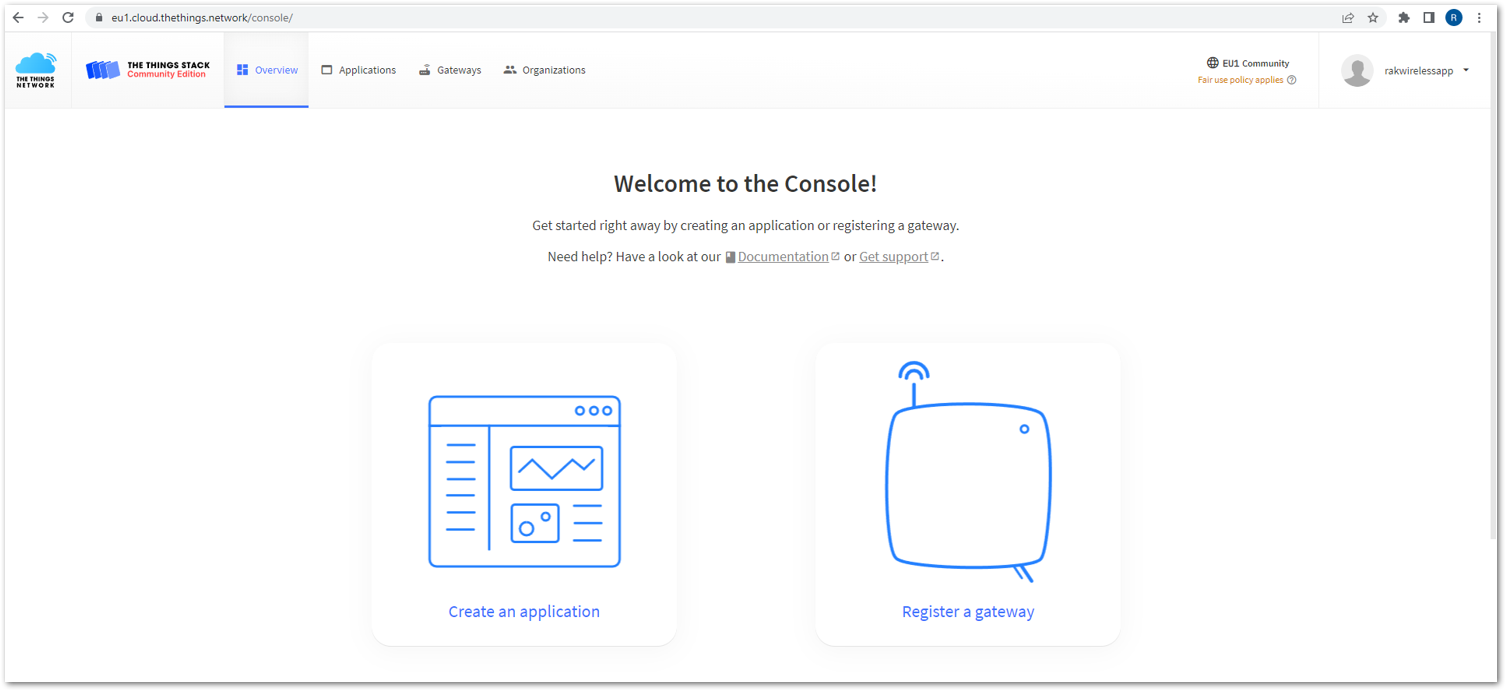 Figure 1: The Things Stack Platform
Figure 1: The Things Stack Platform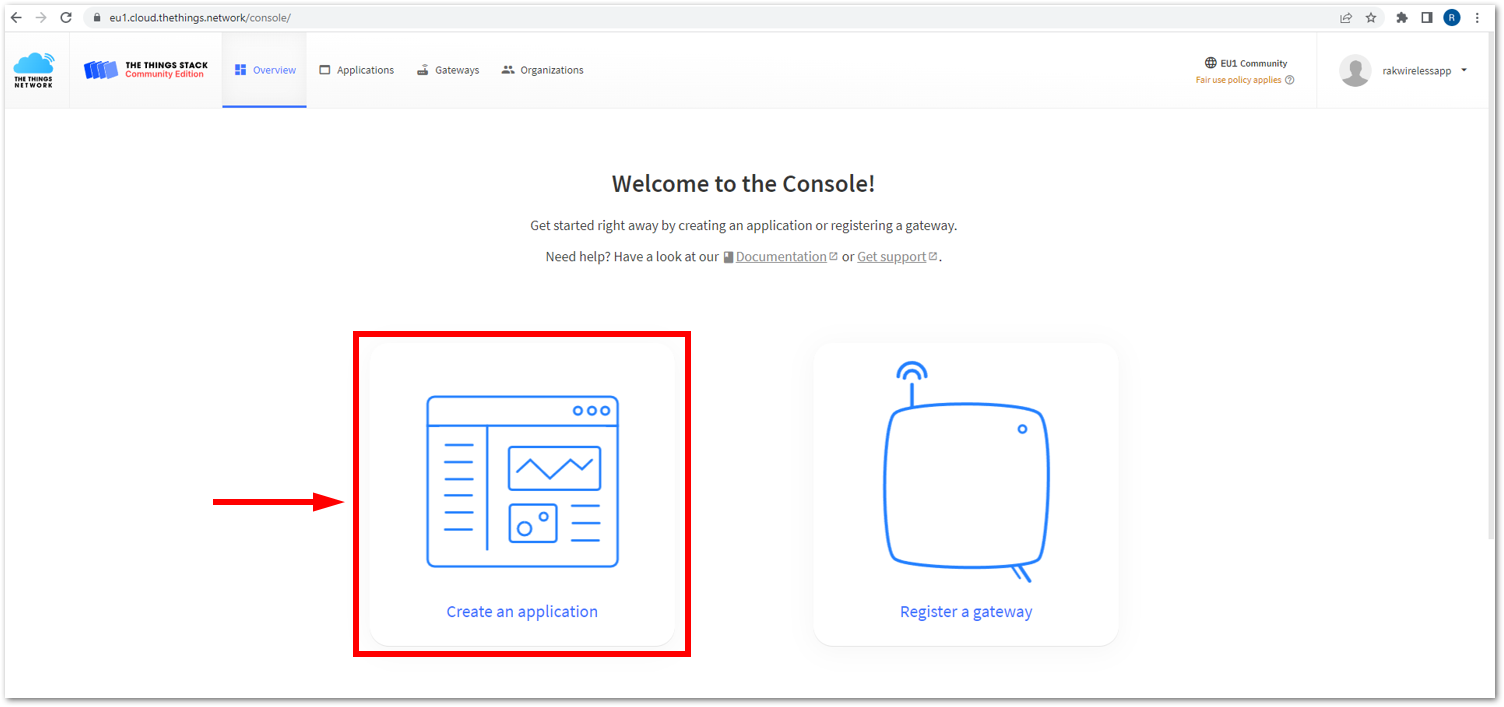 Figure 1: Creating TTN application for your LoRaWAN devices
Figure 1: Creating TTN application for your LoRaWAN devices- To have an application registered, input first the specific details and necessary information about your application then click Create application.
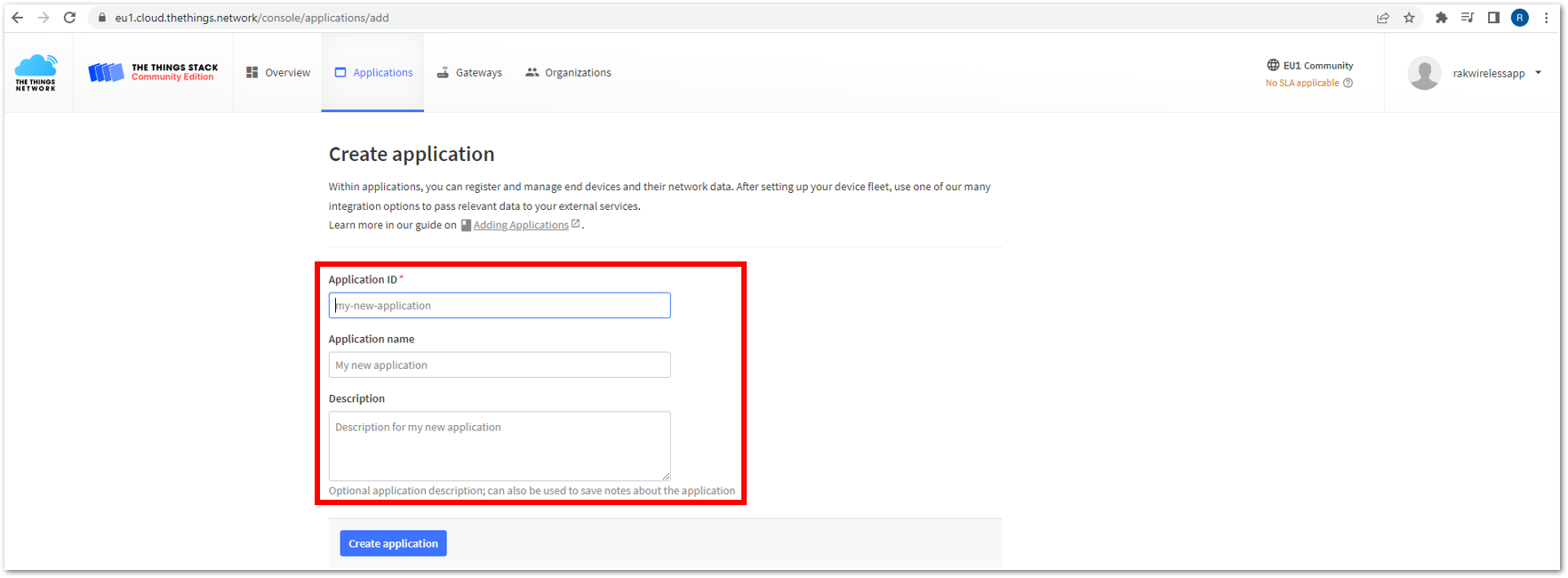 Figure 1: Details of the TTN application
Figure 1: Details of the TTN application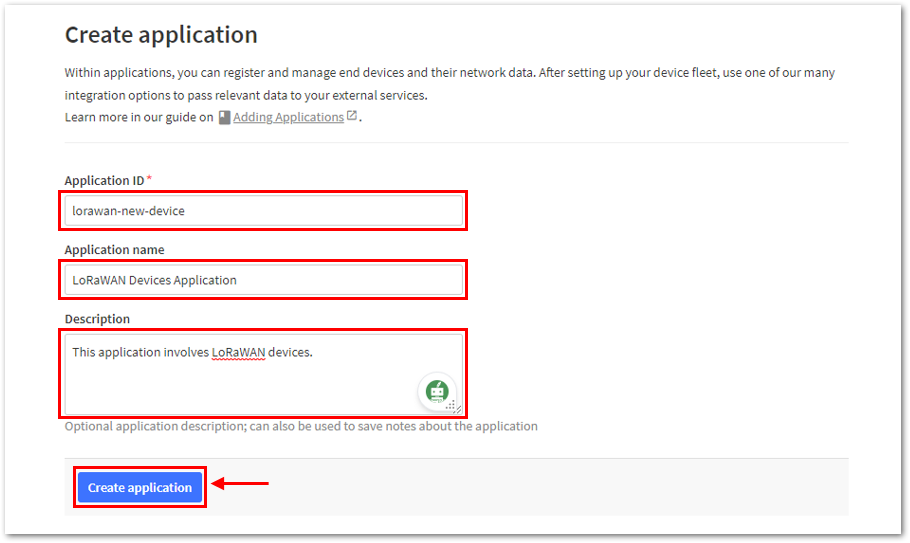 Figure 1: Details of the TTN application
Figure 1: Details of the TTN application- If you have no error on the previous step, you should now be on the application console page. The next step is to add end-devices to your TTN application.
LoRaWAN specifications enforce that each end-device has to be personalized and activated. There are two options in registering devices depending on the activation mode selected. Activation can be done either via Over-The-Air-Activation (OTAA) or Activation-By-Personalization (ABP).
TTN OTAA Device Registration
- Go to your application console to register a device. To start adding an OTAA end-device, click + Register end device, as shown in Figure 38.
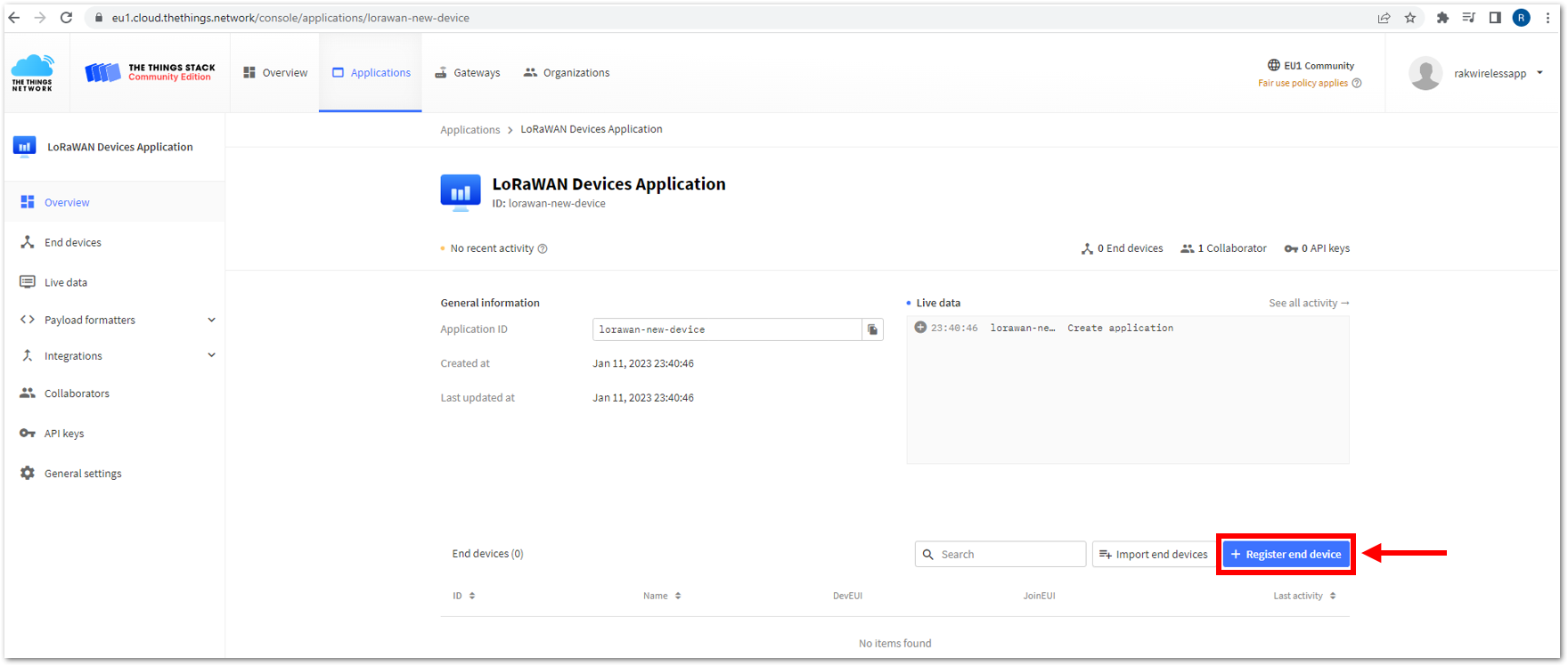 Figure 1: Register end device
Figure 1: Register end device- To register the board, click the Enter end device specifics manually.
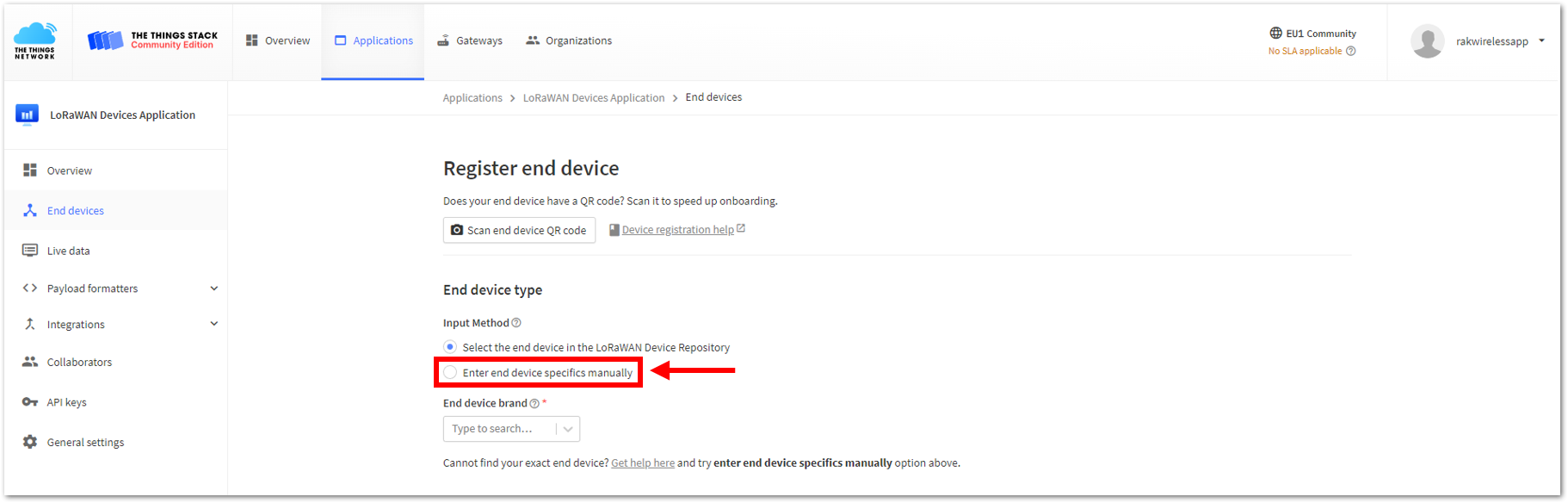 Figure 1: Enter end device specifics manually
Figure 1: Enter end device specifics manually- Next step is to set up Frequency plan, compatible LoRaWAN version, and Regional Parameters version supported. Then provide the JoinEUI credentials by entering zeroes into it.
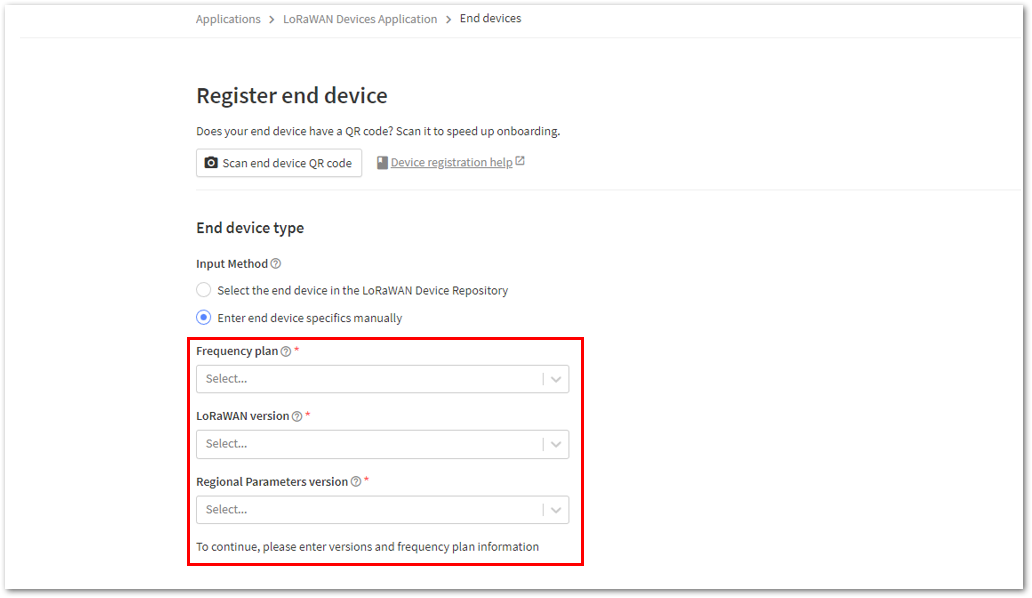 Figure 1: Setting up for your device
Figure 1: Setting up for your device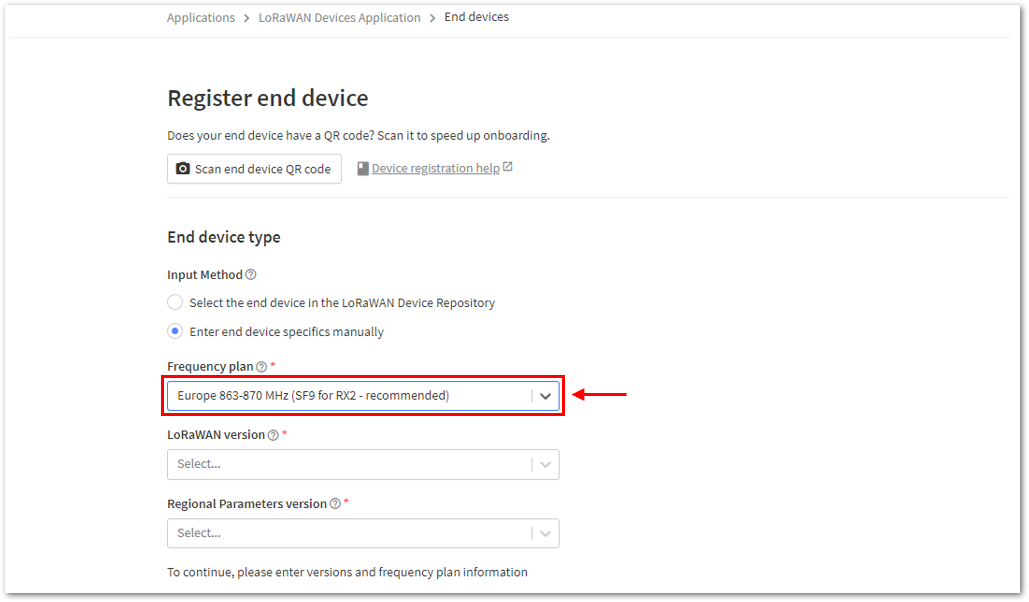 Figure 1: Setting up for your device
Figure 1: Setting up for your device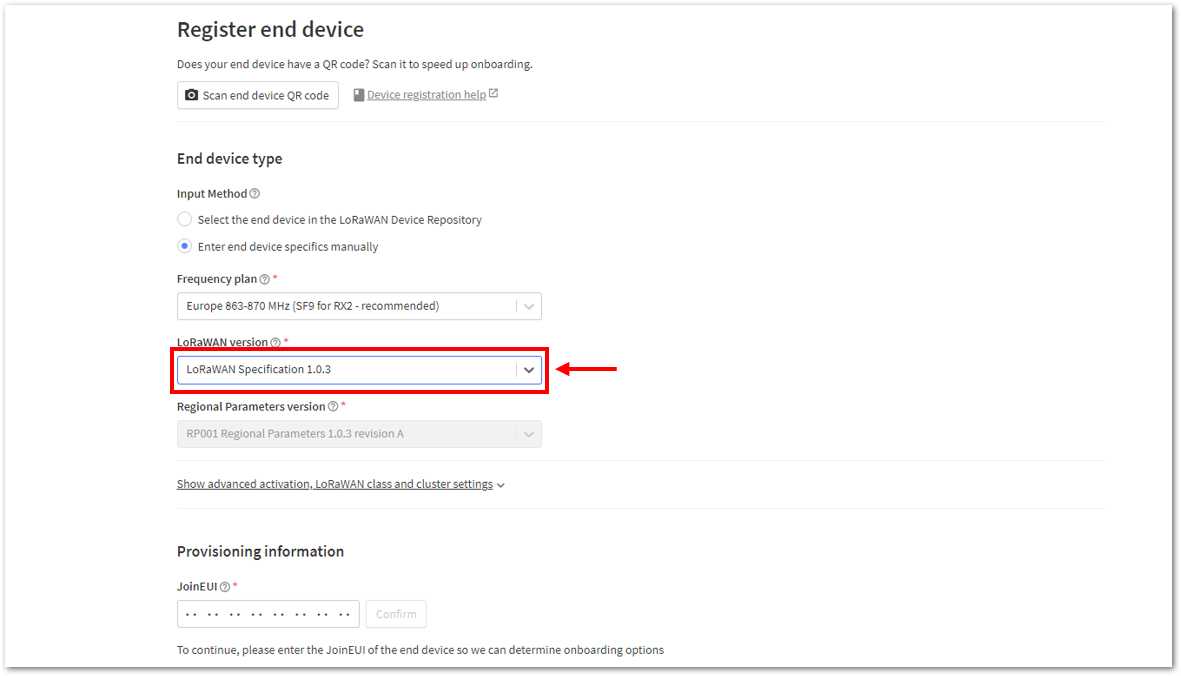 Figure 1: Setting up for your device
Figure 1: Setting up for your device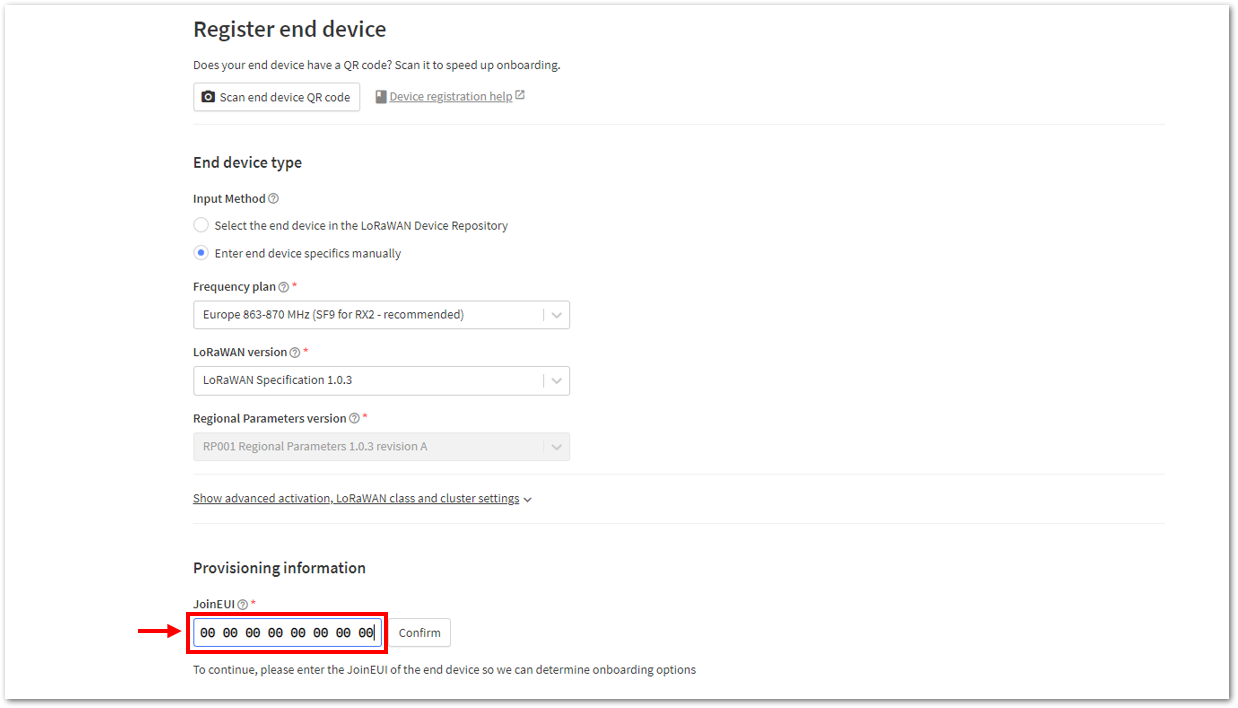 Figure 1: Setting up for your device
Figure 1: Setting up for your device- Then click Show advanced activation, LoRaWAN class and cluster settings. Configure the activation mode by selecting Over the air activation (OTAA) and Additional LoRaWAN class capabilities to class A only. Then click Confirm.
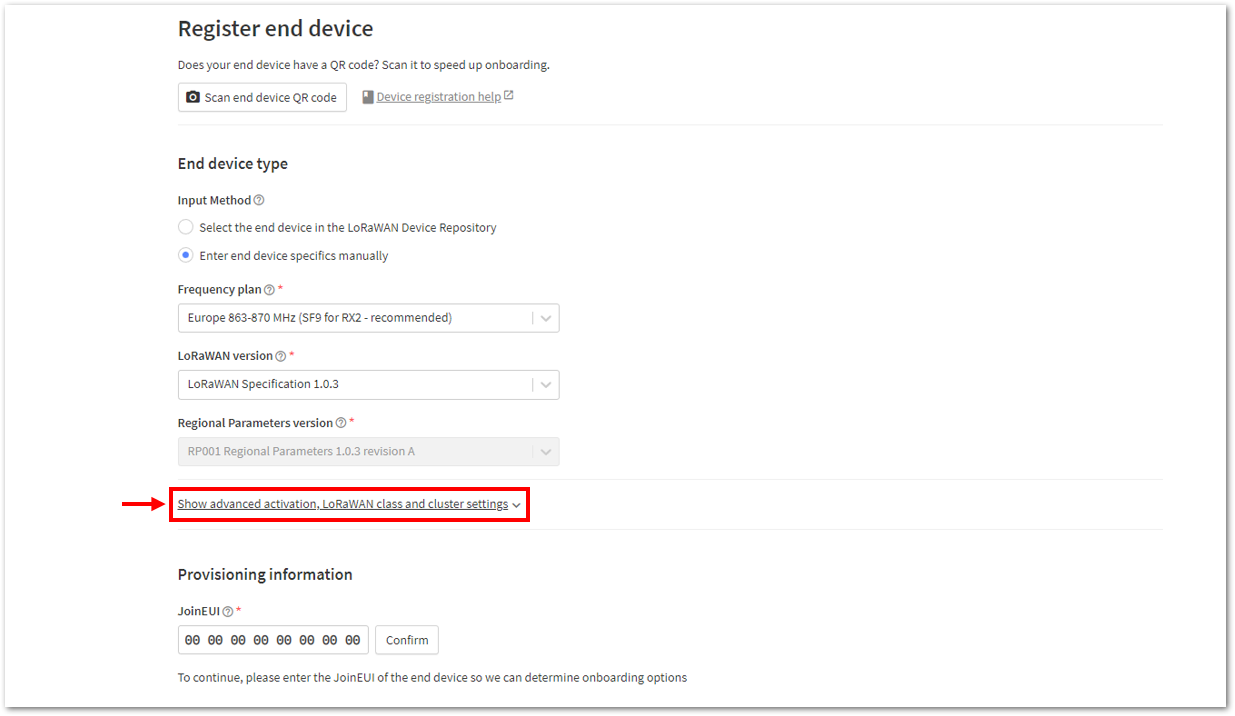 Figure 1: Setting up for your device
Figure 1: Setting up for your device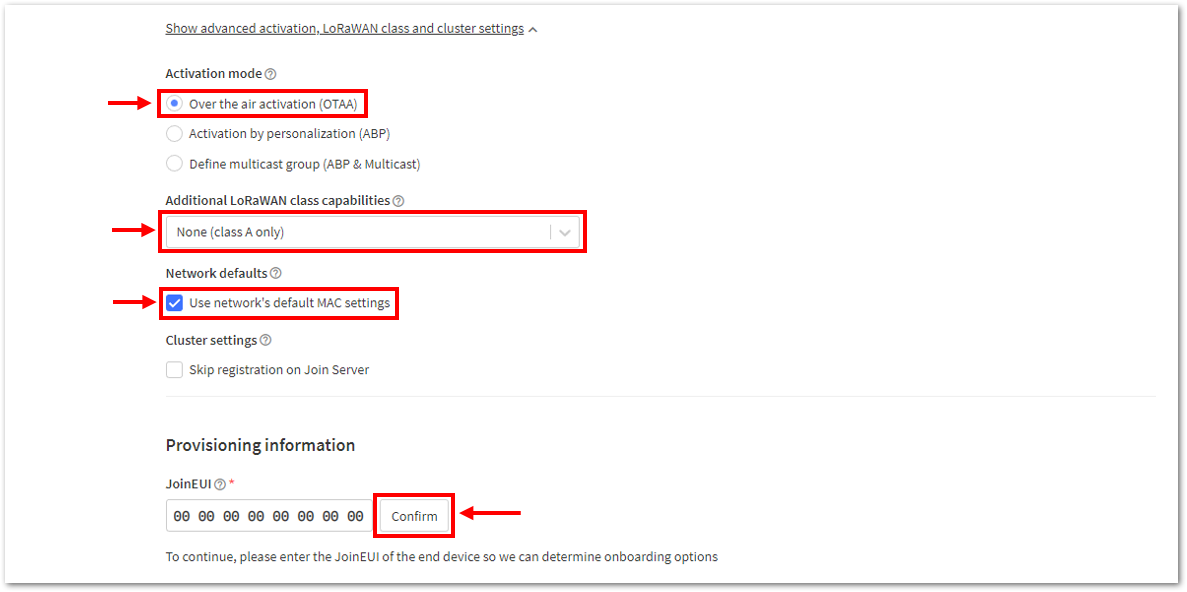 Figure 1: Setting up for your device
Figure 1: Setting up for your device- Once done, provide the DevEUI credentials of your device into the DevEUI portion. This will automatically generate the specific End device ID of your board. Then click Generate under AppKey under the Provisioning information section. Then click Register end device.
- The AppEUI, DevEUI, and AppKey are hidden in this section as these are unique from a specific device. The DevEUI credential is unique to every RAK3172-SiP device. Also, you should generate your own AppEUI and AppKey credentials for your specific device and application.
- The AppEUI is the same as JoinEUI.
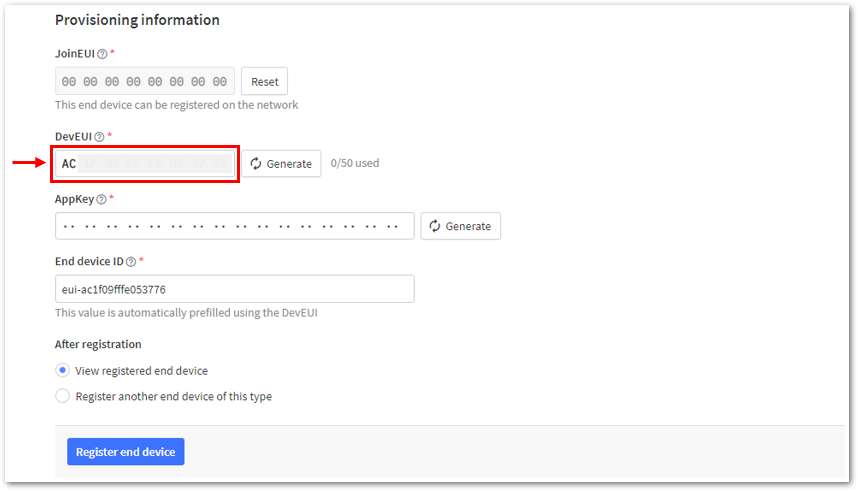 Figure 1: Setting up for your device
Figure 1: Setting up for your device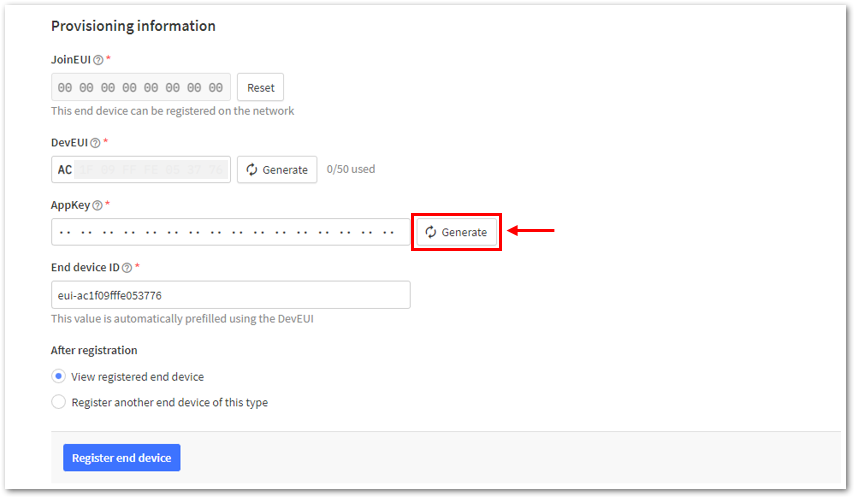 Figure 1: Setting up for your device
Figure 1: Setting up for your device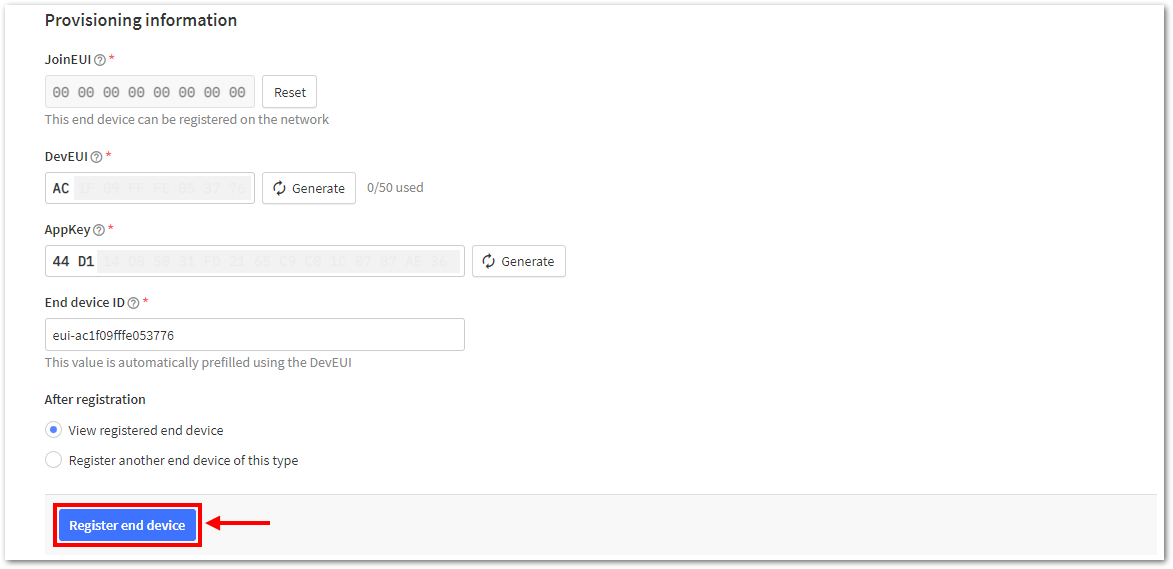 Figure 1: Register end device
Figure 1: Register end device- You should now be able to see the device on the TTN console after you fully register your device, as shown in Figure 49.
- The AppEUI, DevEUI, and AppKey are the parameters that you will need to activate your LoRaWAN end-device via OTAA. The AppKey is hidden by default for security reasons, but you can easily show it by clicking the show button. You can also copy the parameters quickly using the copy button.
- The three OTAA parameters on the TTN device console are MSB by default.
- These parameters are always accessible on the device console page, as shown in Figure 36.
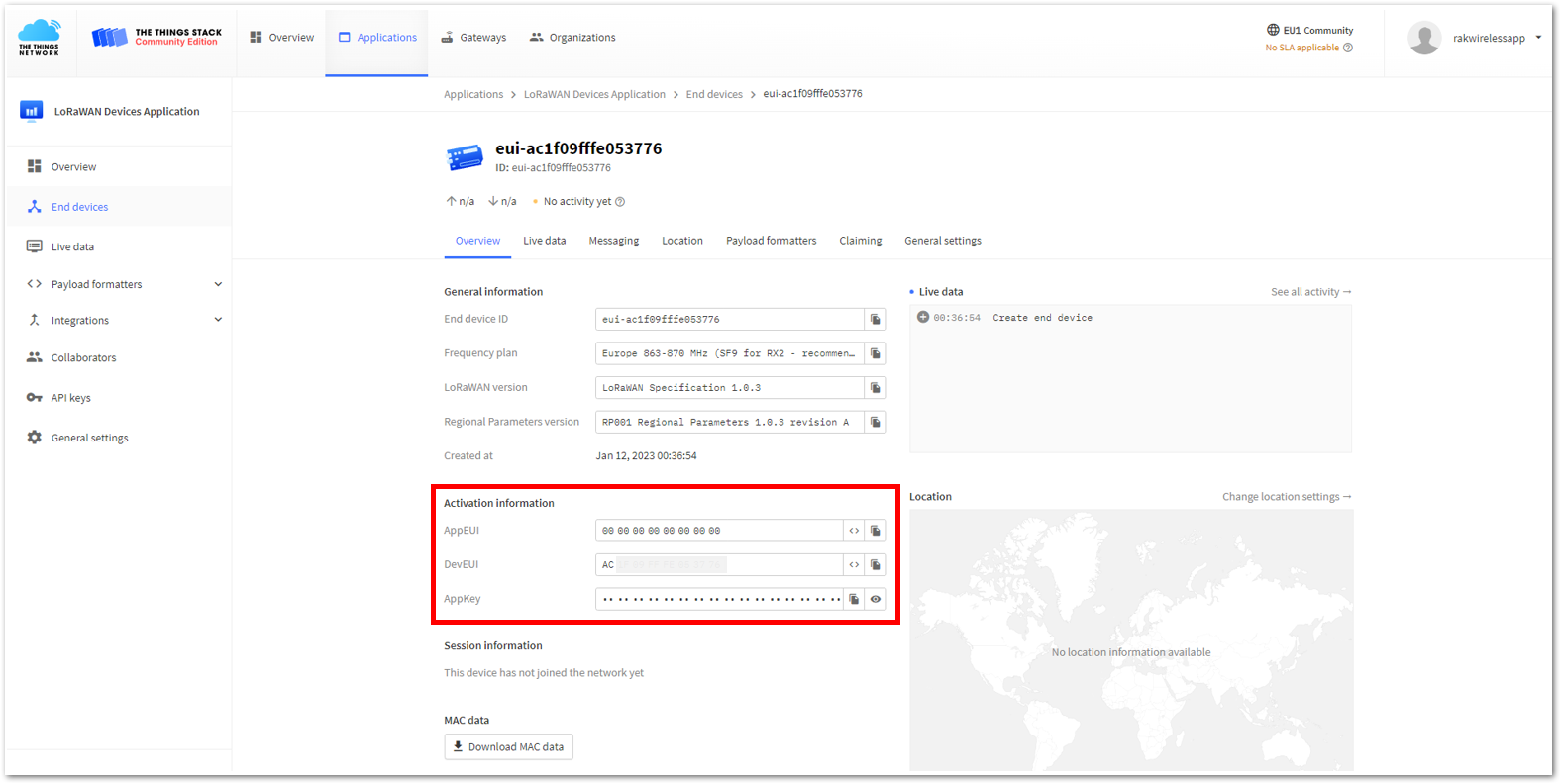 Figure 1: OTAA device successfully registered to TTN
Figure 1: OTAA device successfully registered to TTNOTAA Configuration for TTN
The RAK3172-SiP module can be configured using WisToolBox to do the OTAA configuration. WisToolBox is a software tool that supports RAK3172-SiP module. It automatically detects the RAK3172-SiP module once connected to the PC. Below are the options in WisToolBox that the OTAA configuration can be done.
OTAA Configuration for TTN via WisToolBox UI
The RAK3172-SiP should have the correct OTAA credentials to connect to TTN. This can be done using WisToolBox UI. Below are the steps on setting up your RAK3172-SiP using WisToolBox.
-
Connect your RAK3172-SiP with your chosen WisBlock base board to the PC via USB cable and open the WisToolBox application.
-
Click the CONNECT DEVICE button to launch the WisToolBox Dashboard.
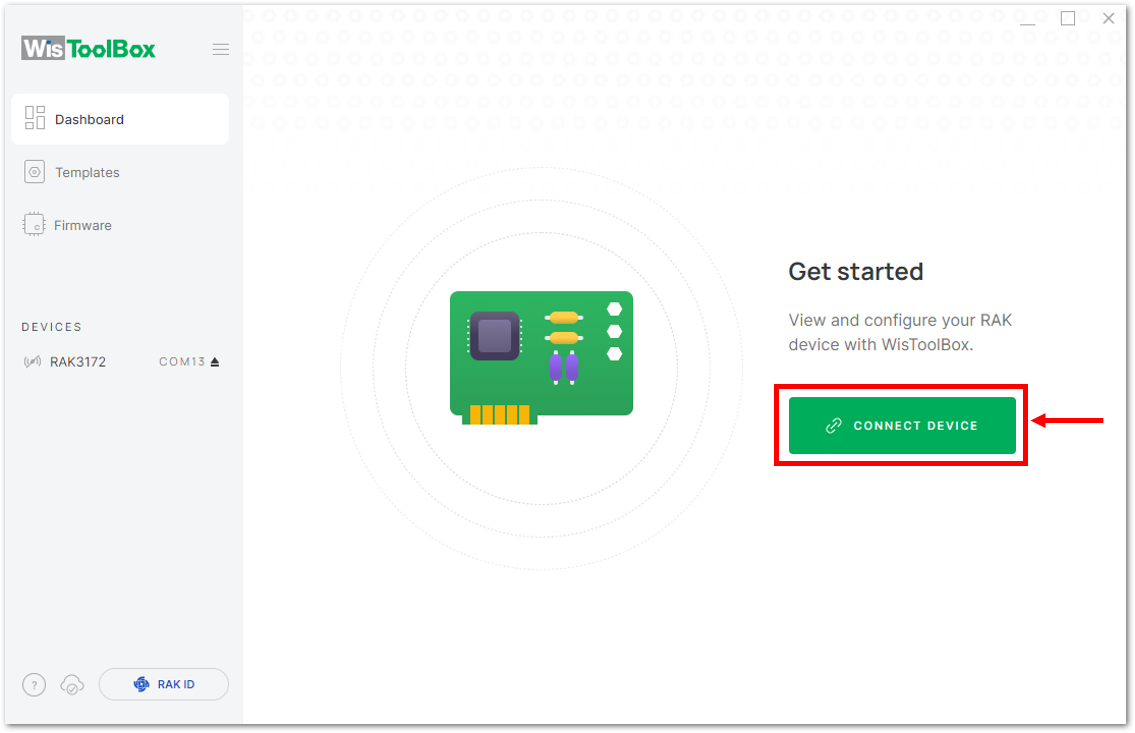 Figure 1: CONNECT DEVICE
Figure 1: CONNECT DEVICE- Then select your target port where your RAK3172-SiP is connected. Once recognized, click CONNECT as shown in Figure 52.
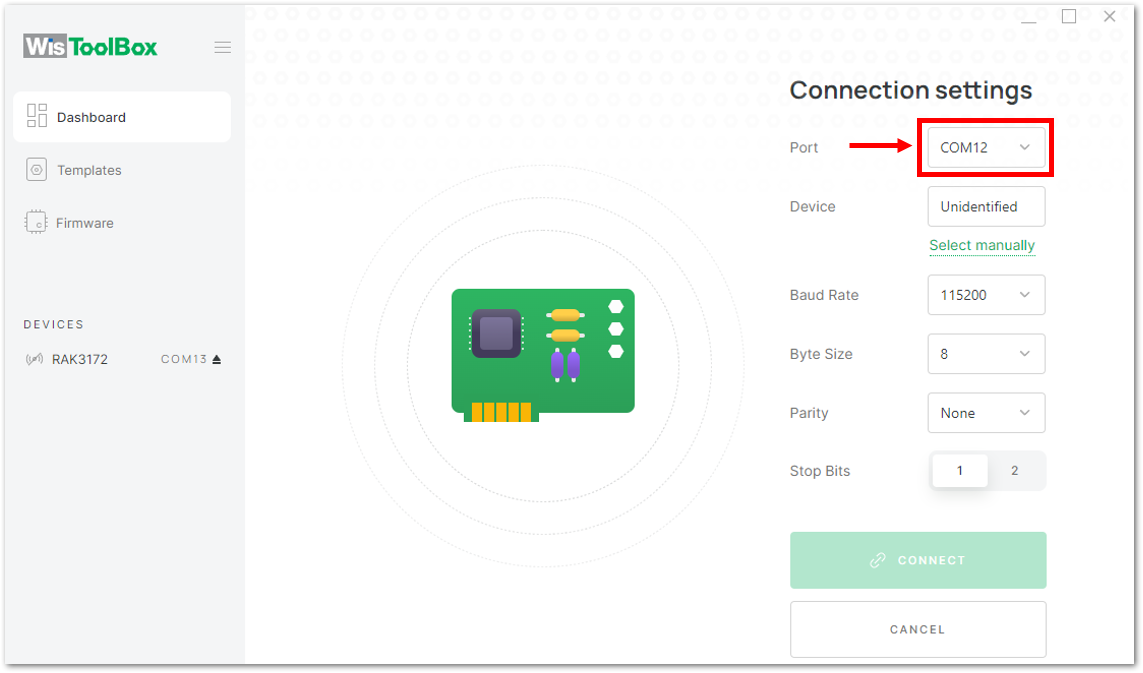 Figure 1: Setting up your device
Figure 1: Setting up your device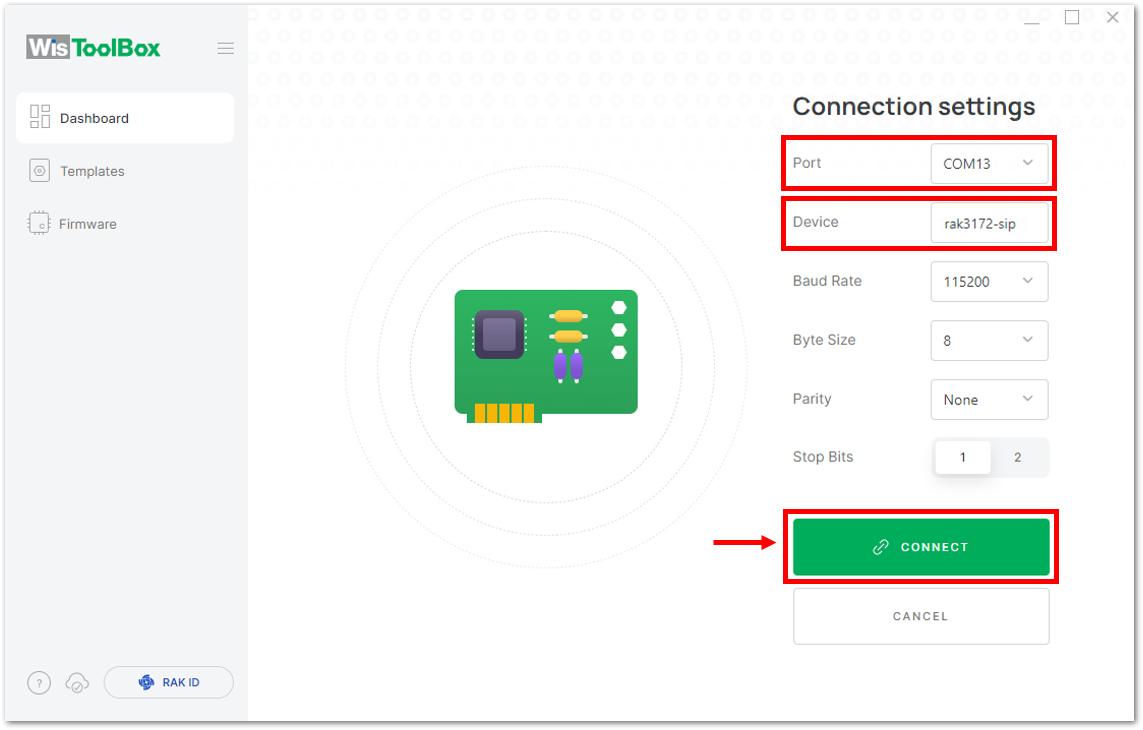 Figure 1: Setting up your device
Figure 1: Setting up your device- Once done, RAK3172-SiP will appear in the dashboard then select it.
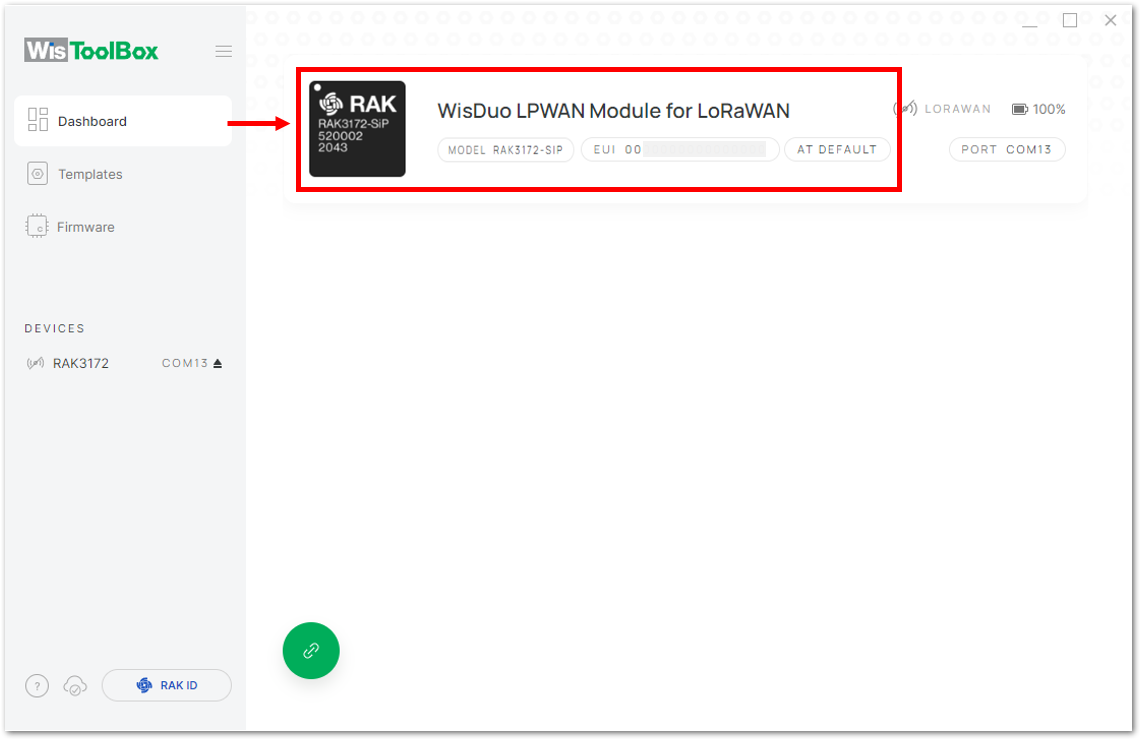 Figure 1: Device seen from WisToolBox dashboard
Figure 1: Device seen from WisToolBox dashboard- Then click PARAMETERS to do the configuration in your RAK3172.
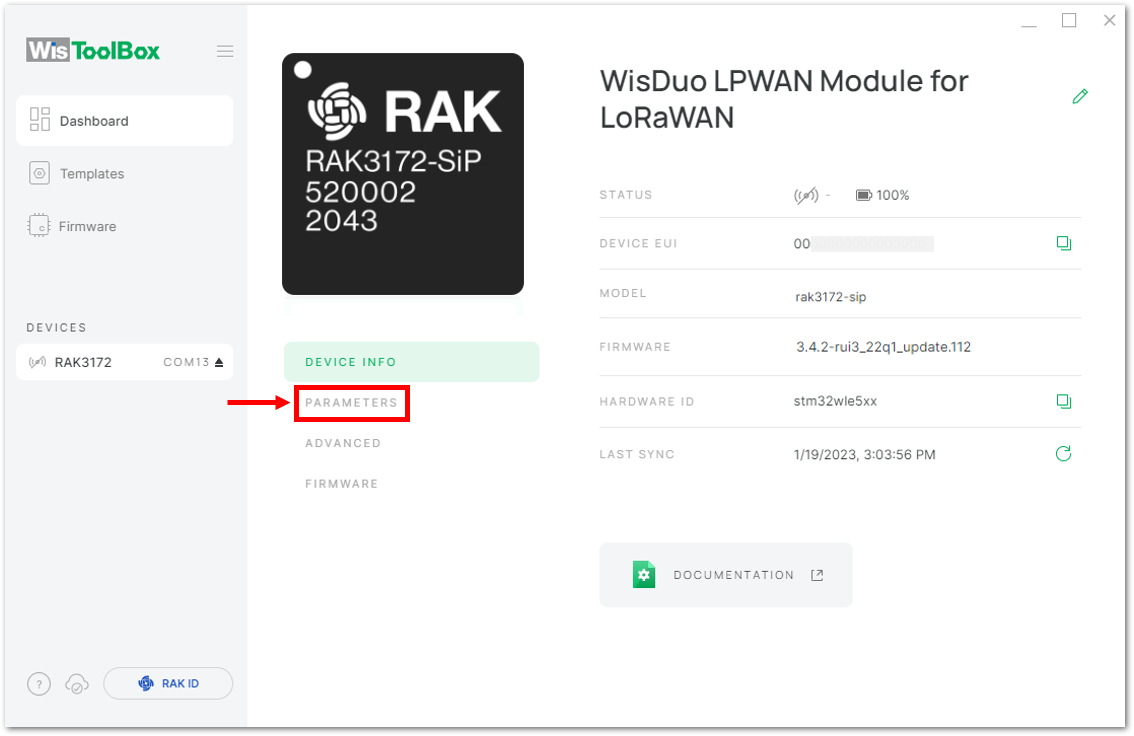 Figure 1: Setting up your device
Figure 1: Setting up your device- Click Global settings to set the network mode into LoRaWAN and join mode to OTAA. Make sure that the active region is using EU868 for this configuration. If you wish to work on other regional bands, you can choose among active regions based on your location.
- LoRa network mode: LoRaWAN
- LoRaWAN join mode: OTAA
- LoRaWAN region: EU868
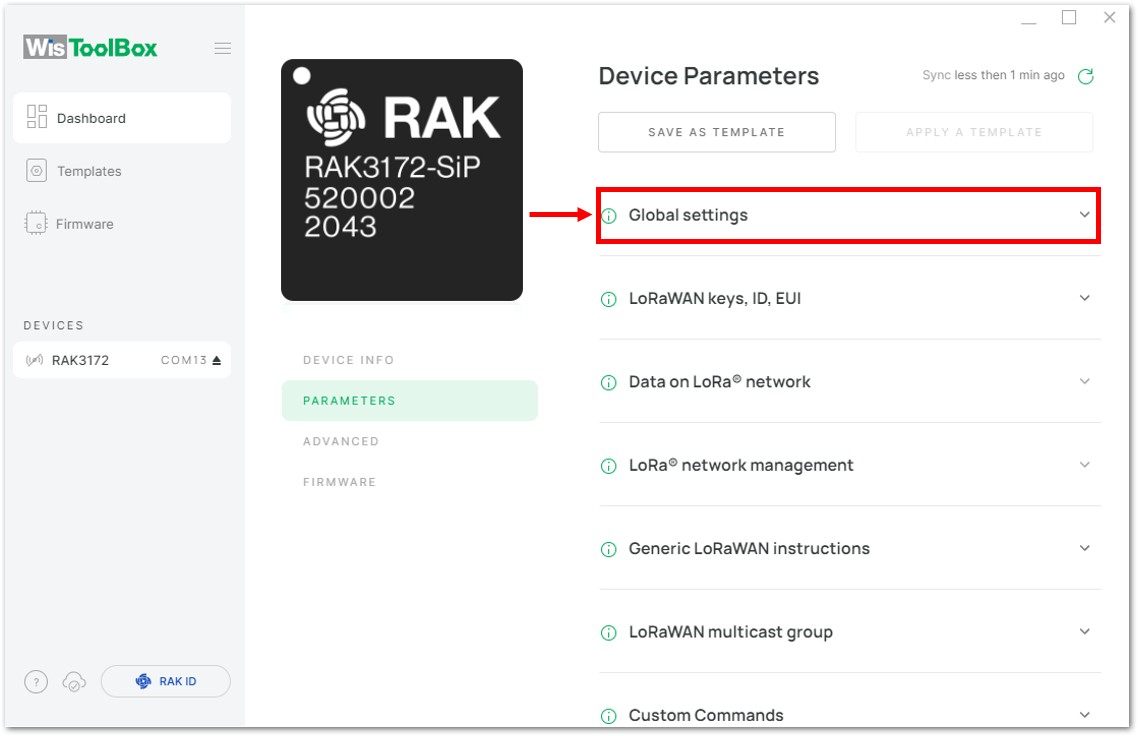 Figure 1: Global settings
Figure 1: Global settings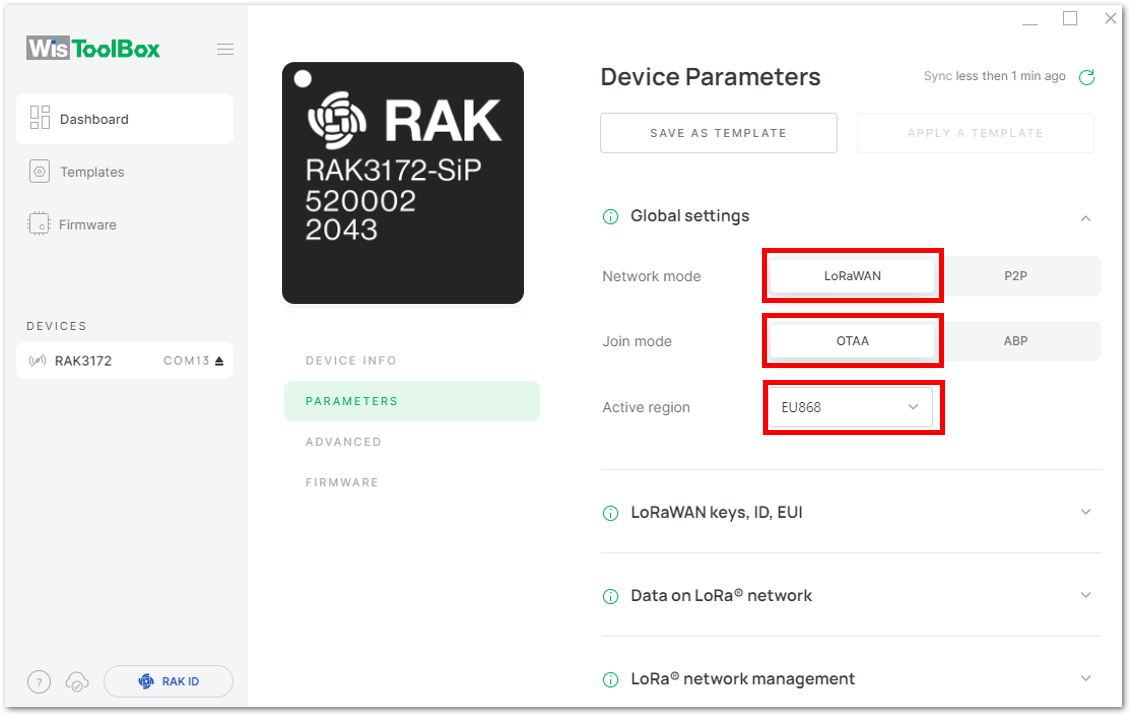 Figure 1: Global settings
Figure 1: Global settings- Then click LoRaWAN keys, ID, EUI to configure the Application EUI (AppEUI), Application key (AppKey) and Device EUI (DevEUI).
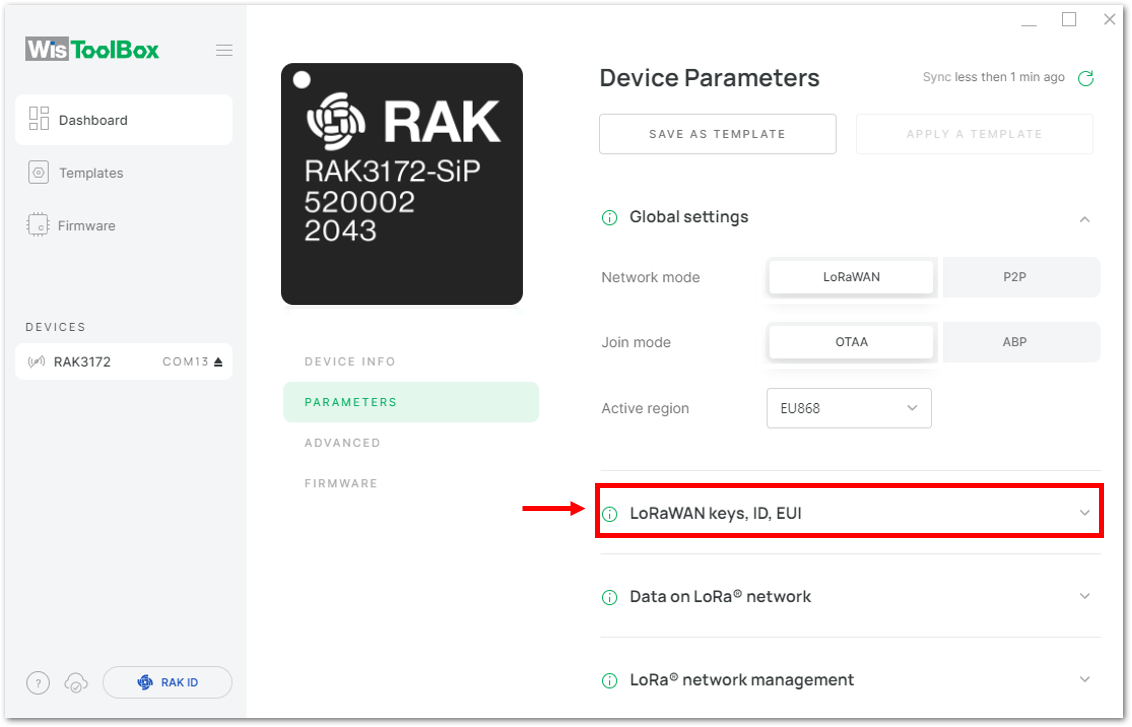 Figure 1: LoRaWAN keys, ID, EUI
Figure 1: LoRaWAN keys, ID, EUI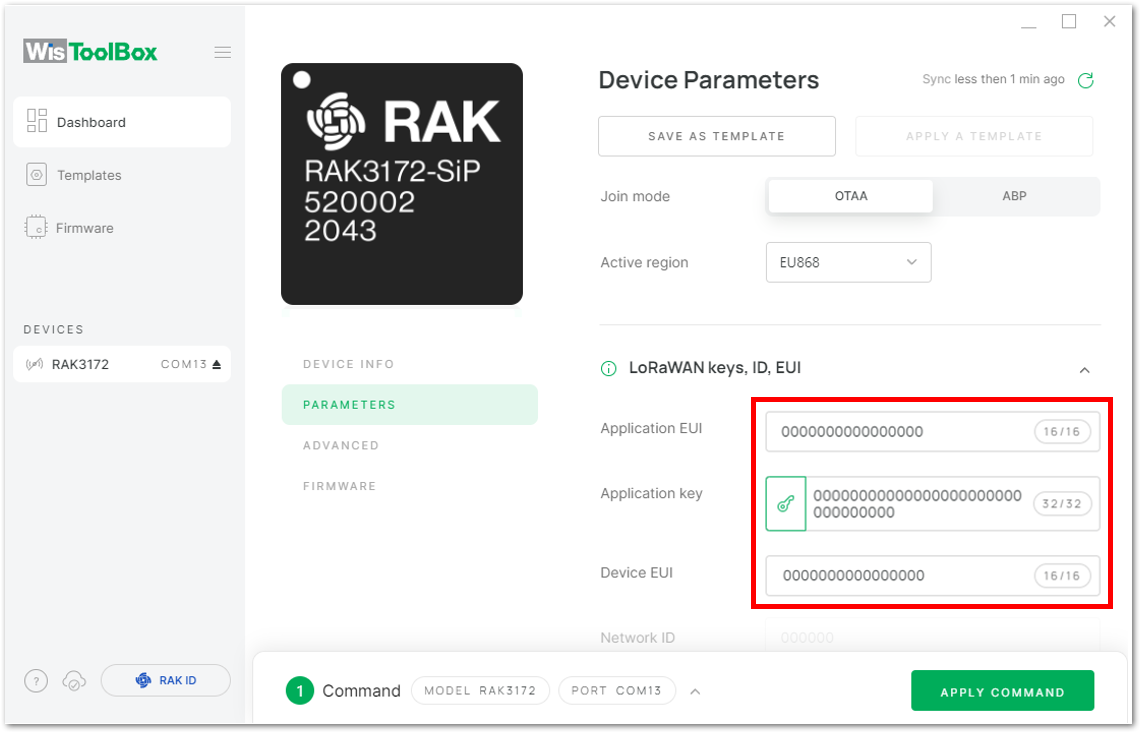 Figure 1: Setting up your device
Figure 1: Setting up your device- Then go back to the console where your RAK3172-SiP End device is created previously. Then copy all the credentials from there. Those will be the ones to be used also in the WisToolBox dashboard. Once encoded into the dashboard, click APPLY COMMAND to update your device as shown in Figure 66.
The AppEUI, DevEUI, and AppKey are hidden in this section as these are unique from a specific device.
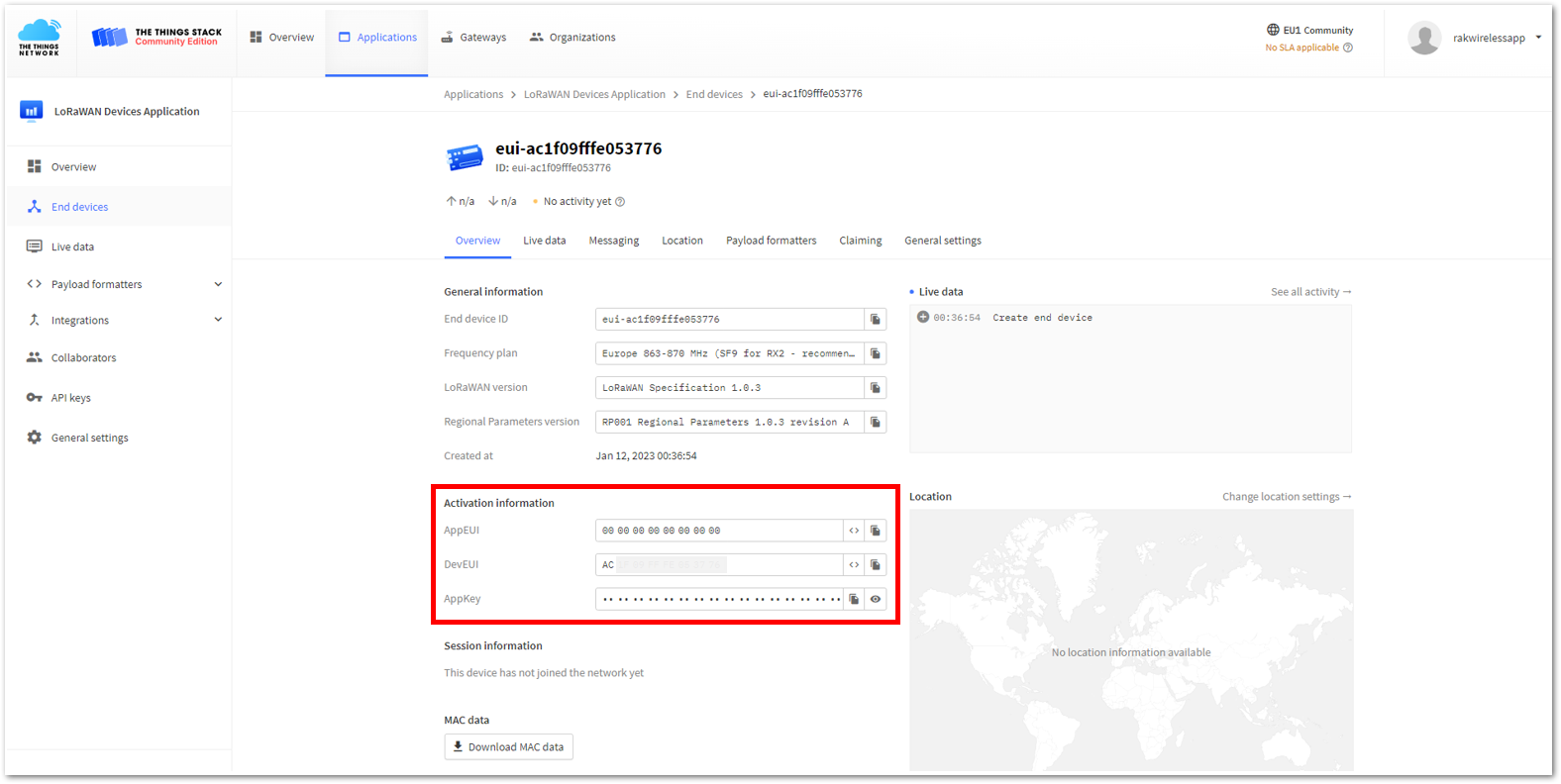 Figure 1: Your created an OTAA device from your console
Figure 1: Your created an OTAA device from your console- For Application EUI (AppEUI)
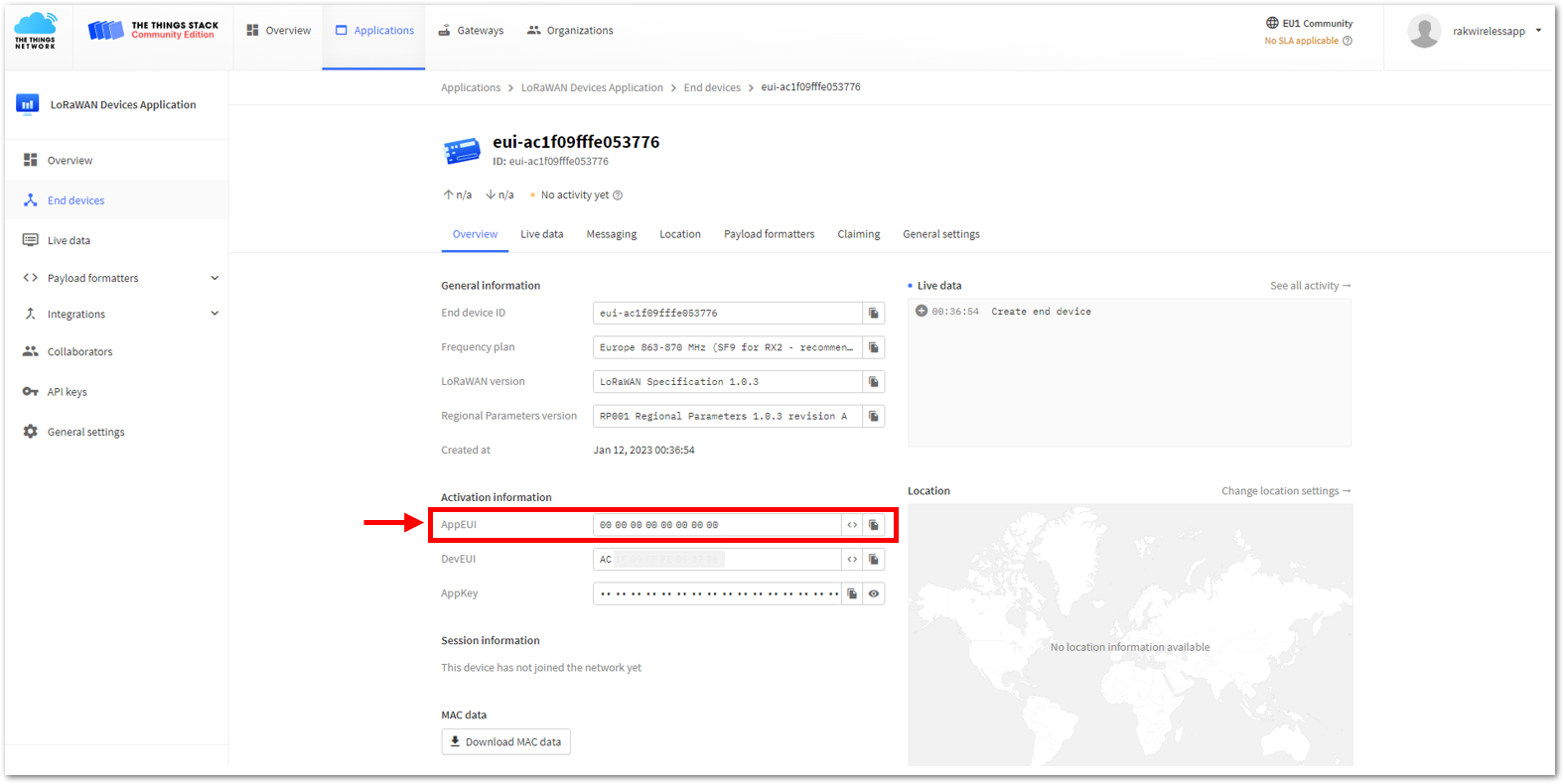 Figure 1: Copying the AppEUI credential from TTN to WisToolBox
Figure 1: Copying the AppEUI credential from TTN to WisToolBox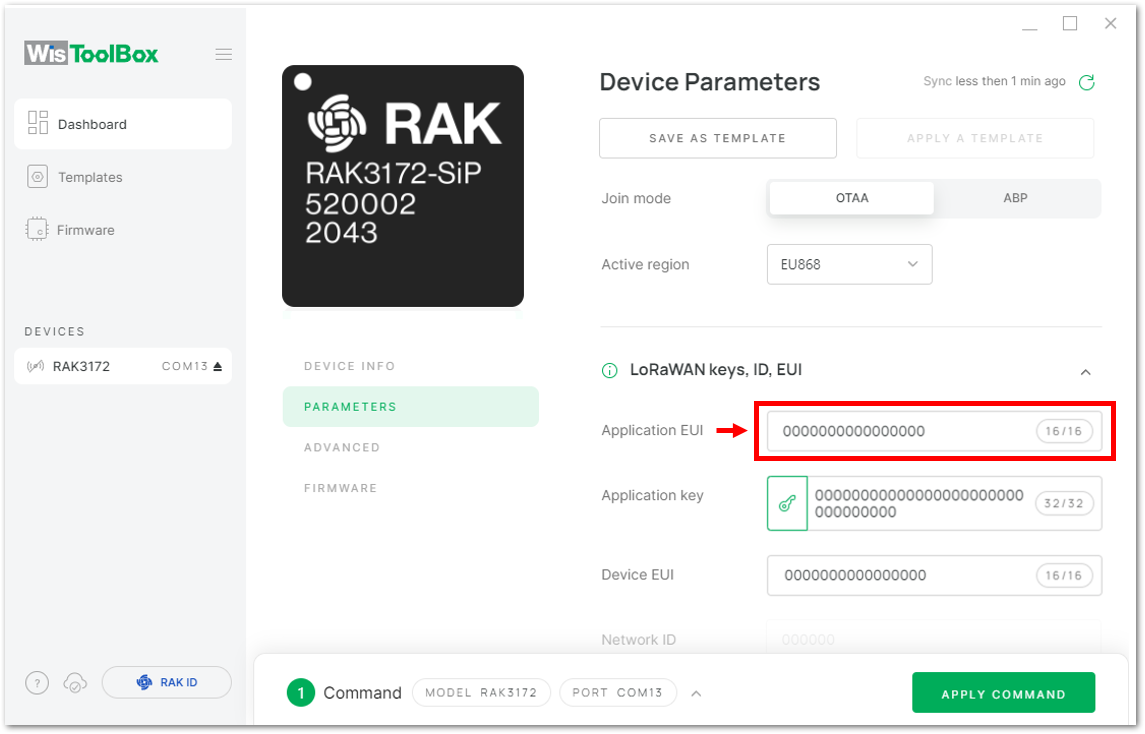 Figure 1: Copying the AppEUI credential from TTN to WisToolBox
Figure 1: Copying the AppEUI credential from TTN to WisToolBox- For Application key (AppKey)
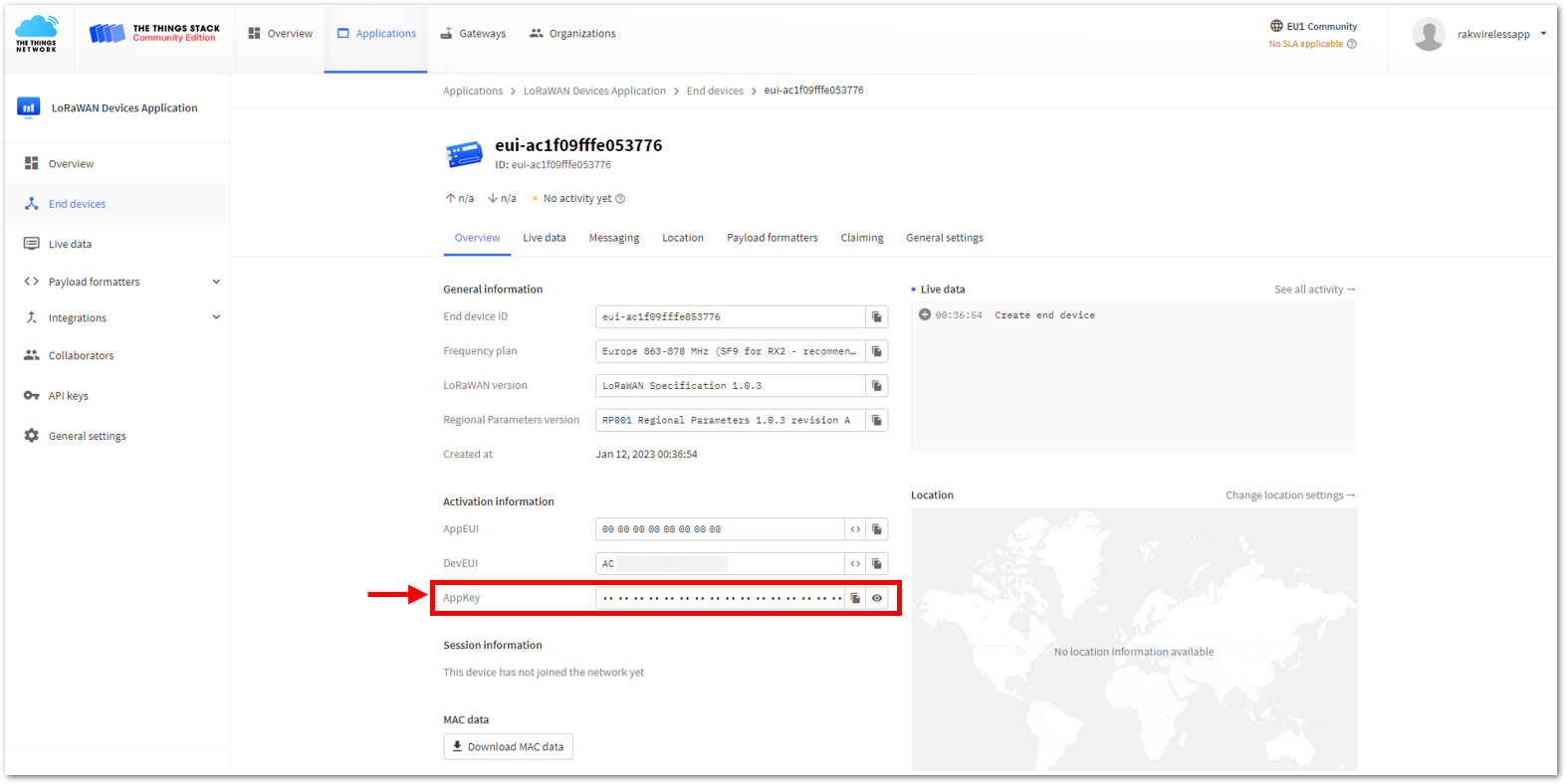 Figure 1: Copying the AppKey credential from TTN to WisToolBox
Figure 1: Copying the AppKey credential from TTN to WisToolBox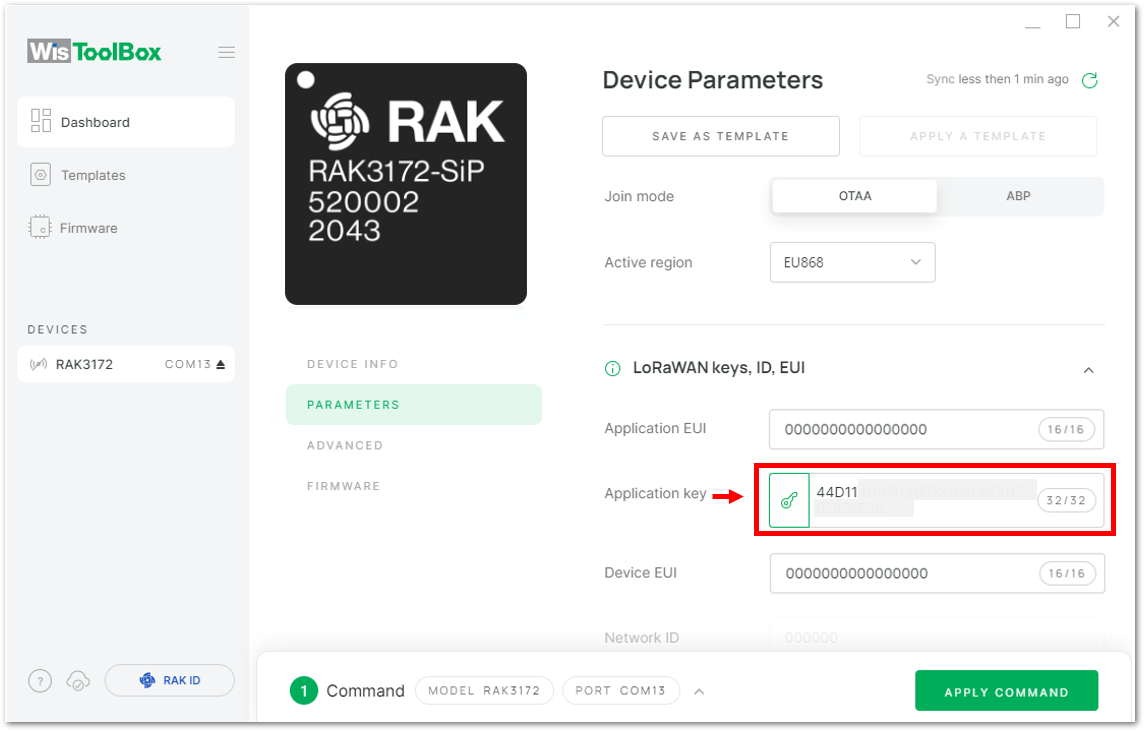 Figure 1: Copying the AppKey credential from TTN to WisToolBox
Figure 1: Copying the AppKey credential from TTN to WisToolBox- For Device EUI (DevEUI)
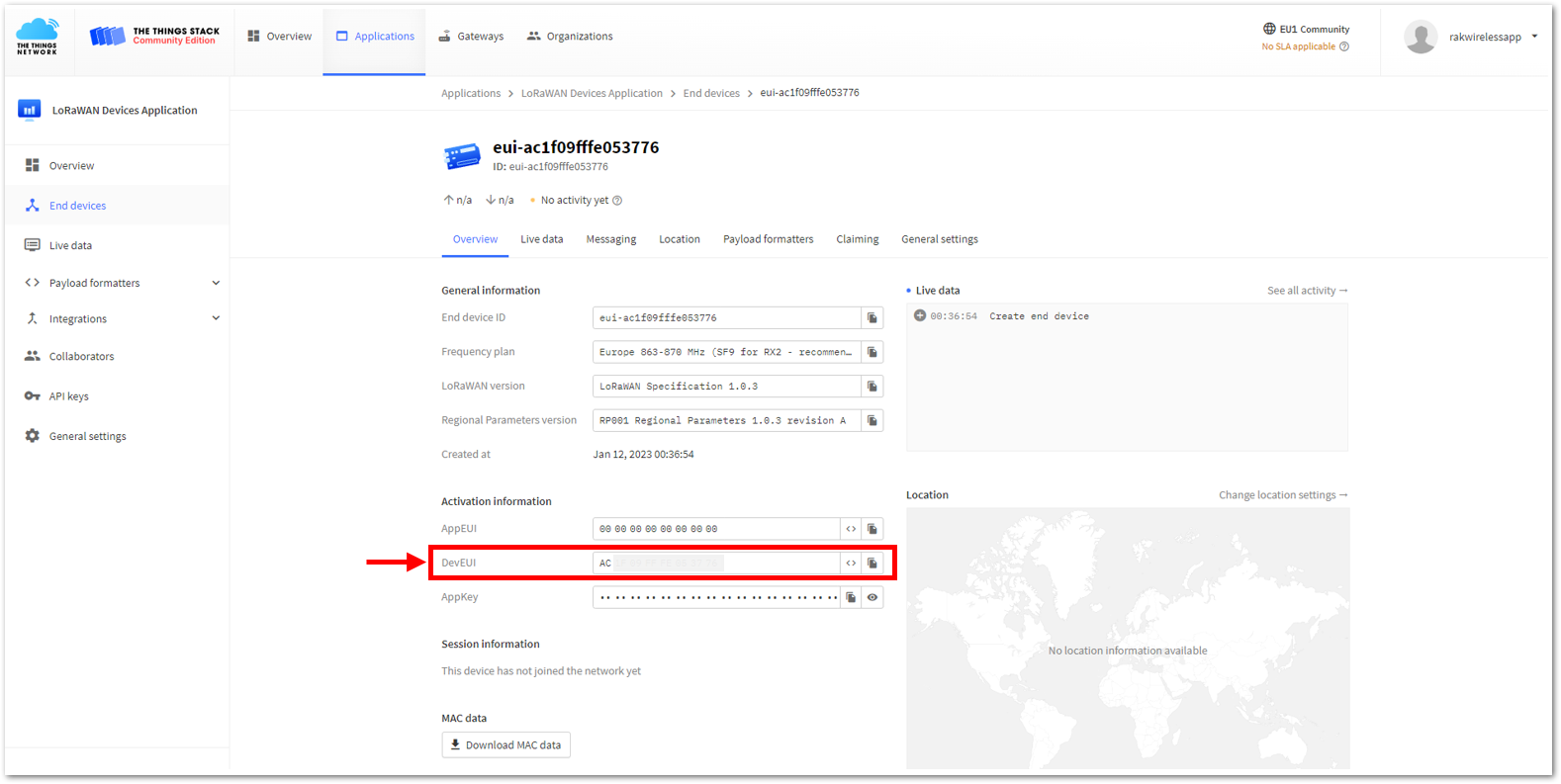 Figure 1: Copying the DevEUI credential from TTN to WisToolBox
Figure 1: Copying the DevEUI credential from TTN to WisToolBox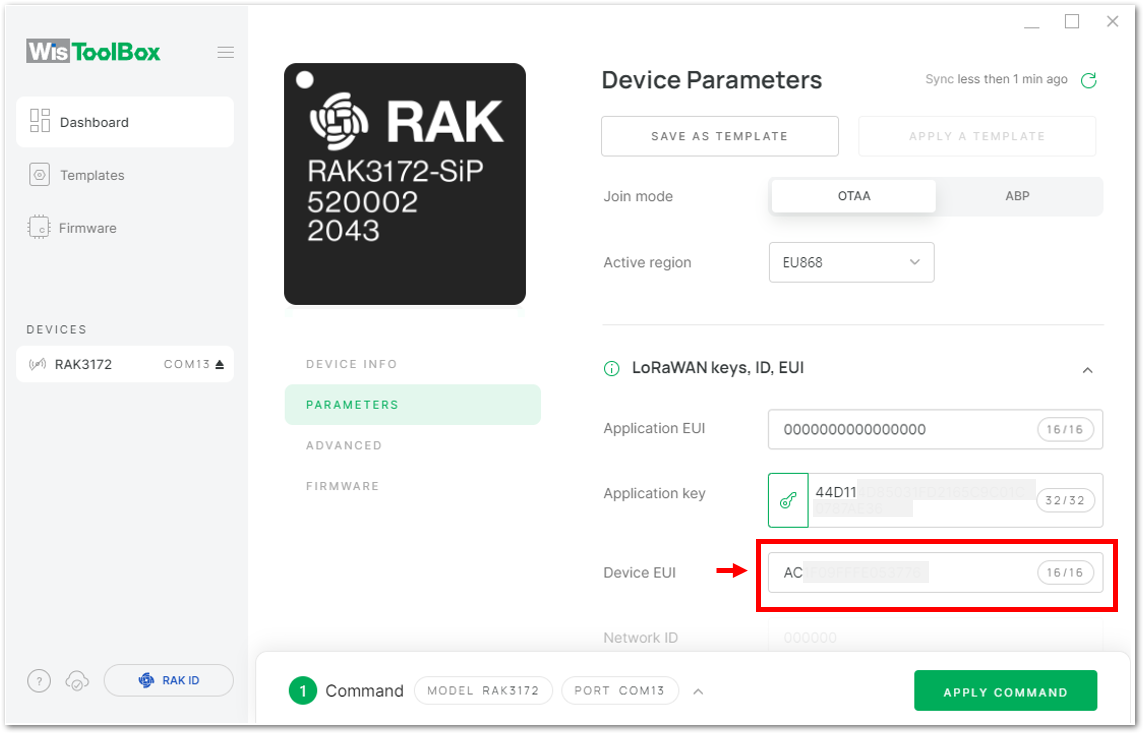 Figure 1: Copying the DevEUI credential from TTN to WisToolBox
Figure 1: Copying the DevEUI credential from TTN to WisToolBox- WisToolBox Dashboard
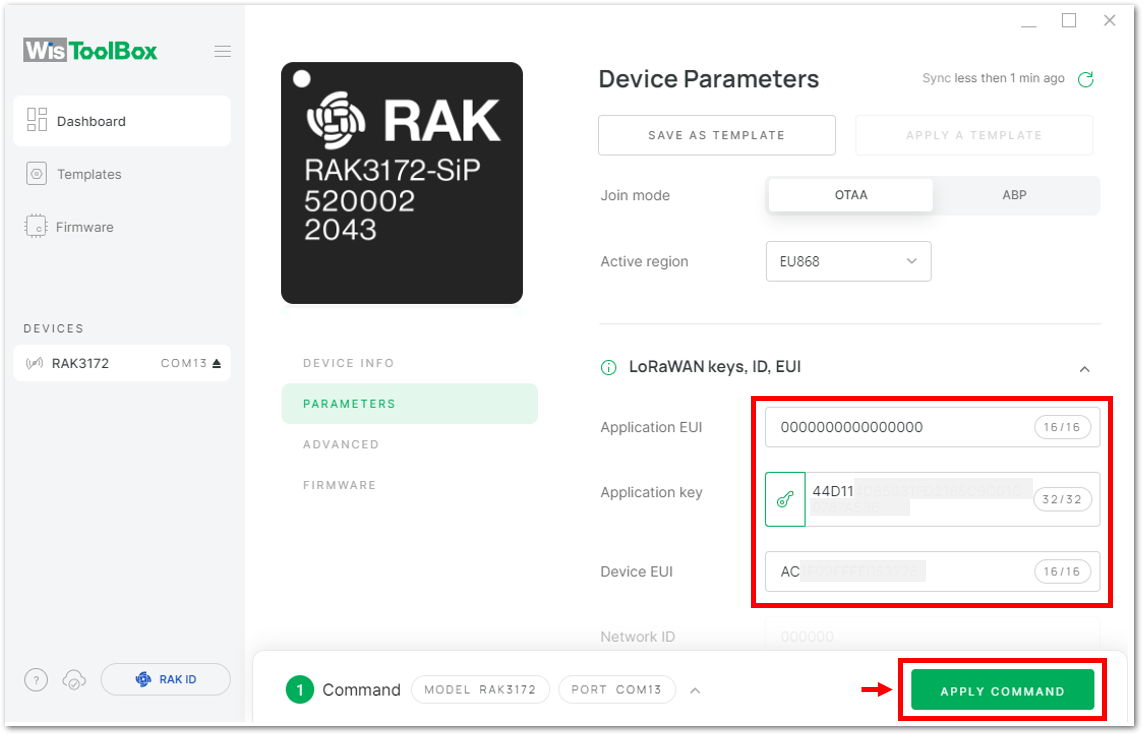 Figure 1: Used credentials from your console in WisToolBox dashboard
Figure 1: Used credentials from your console in WisToolBox dashboard- Once done, you will see the summary of commands that is applied to your device. Then click CLOSE.
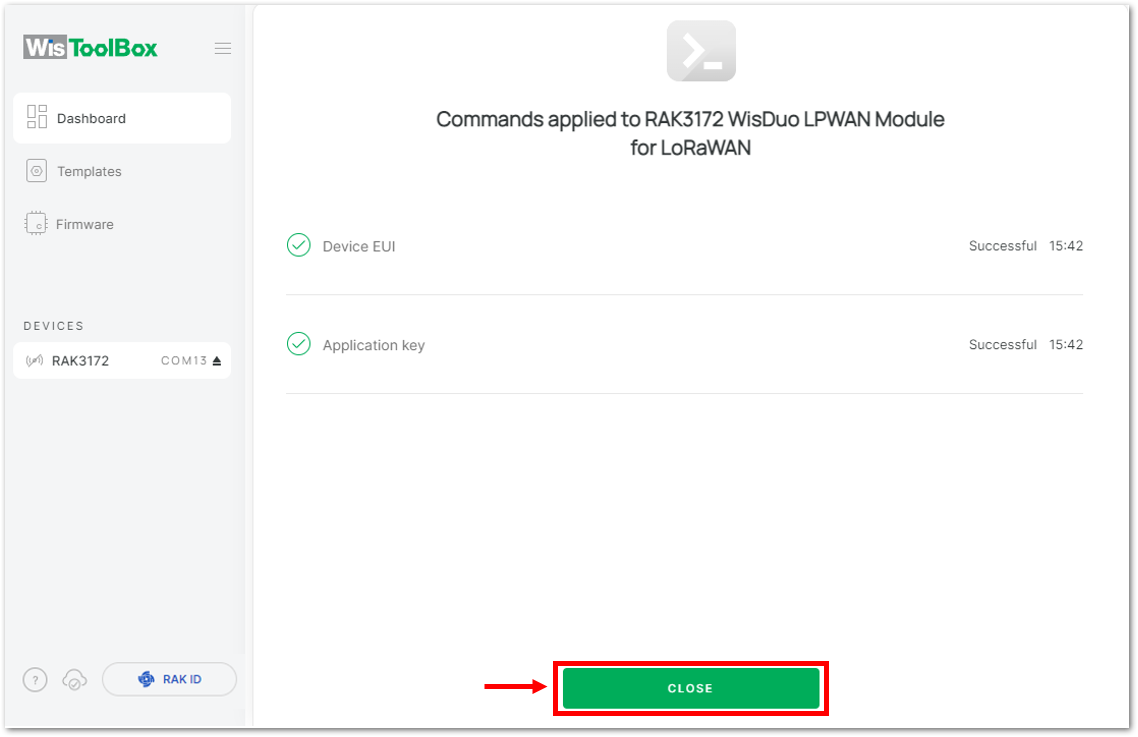 Figure 1: Summary of commands
Figure 1: Summary of commands- Now you will see it returns to the dashboard with updated credentials of your device.
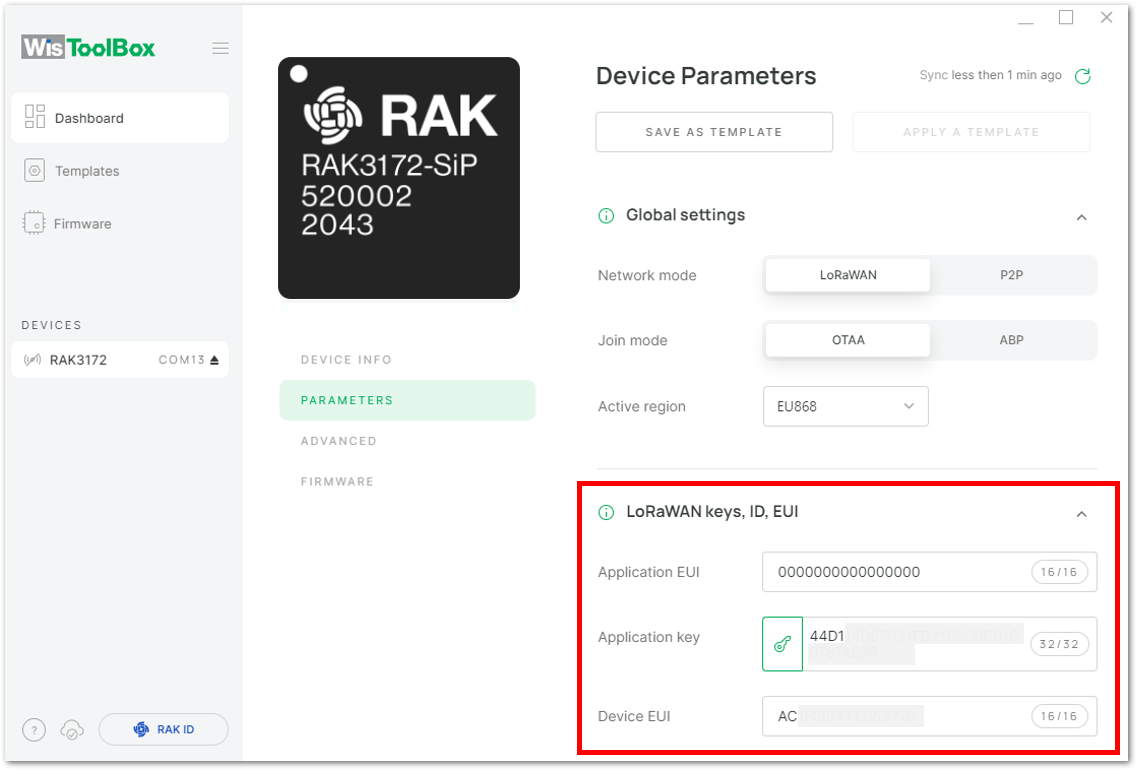 Figure 1: Successfully configured OTAA device via WisToolBox dashboard
Figure 1: Successfully configured OTAA device via WisToolBox dashboard- After your device's credentials update, it can now join the network. To do this, you need to go to Data on LoRa network under PARAMETERS. Then click the JOIN NETWORK under LoRaWAN join settings. After a few seconds, it will notify you that your OTAA device already joined the TTN server. You can also to your TTN console if your device has successfully joined the TTN.
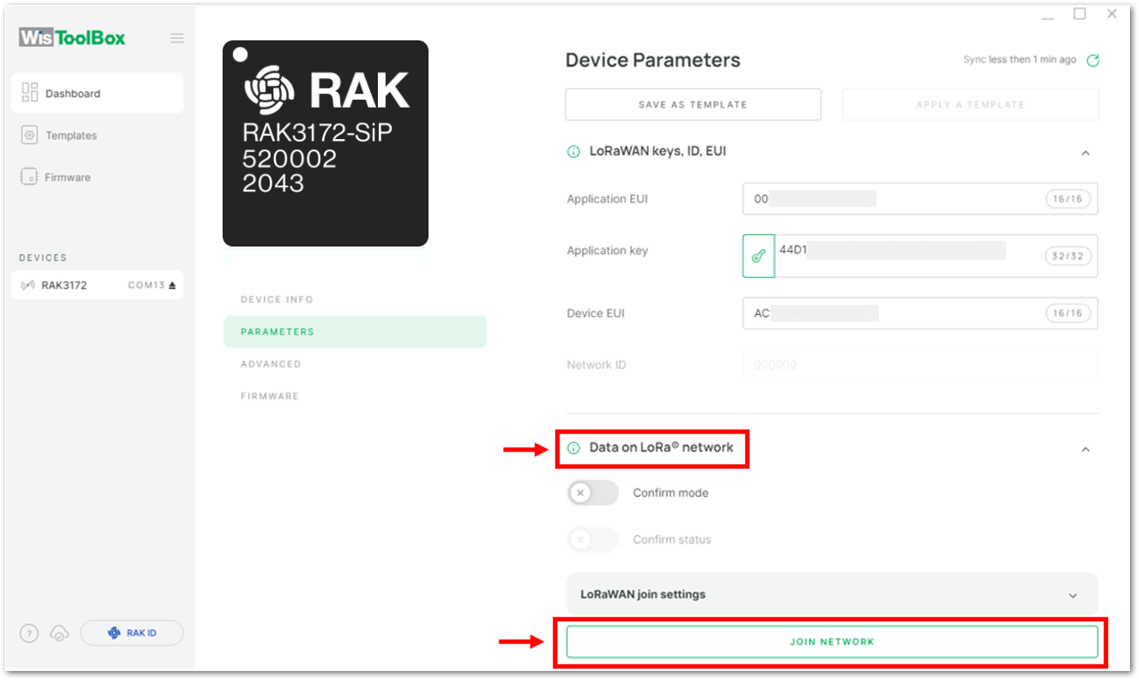 Figure 1: Joining mode of your OTAA device
Figure 1: Joining mode of your OTAA device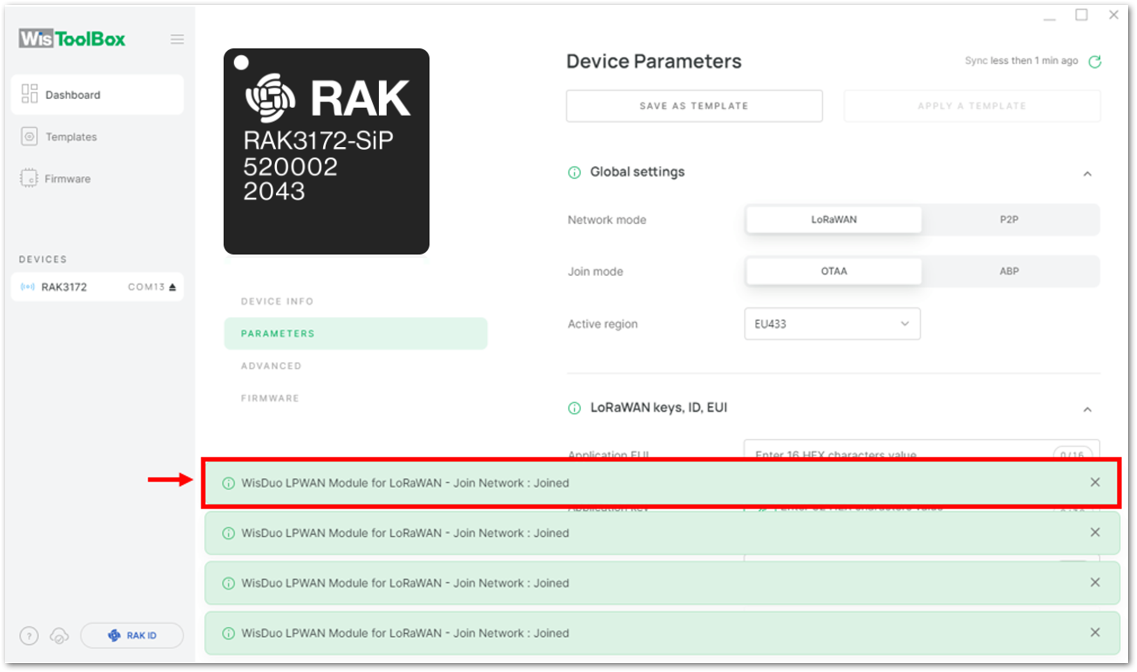 Figure 1: OTAA device successfully joined the TTN server
Figure 1: OTAA device successfully joined the TTN server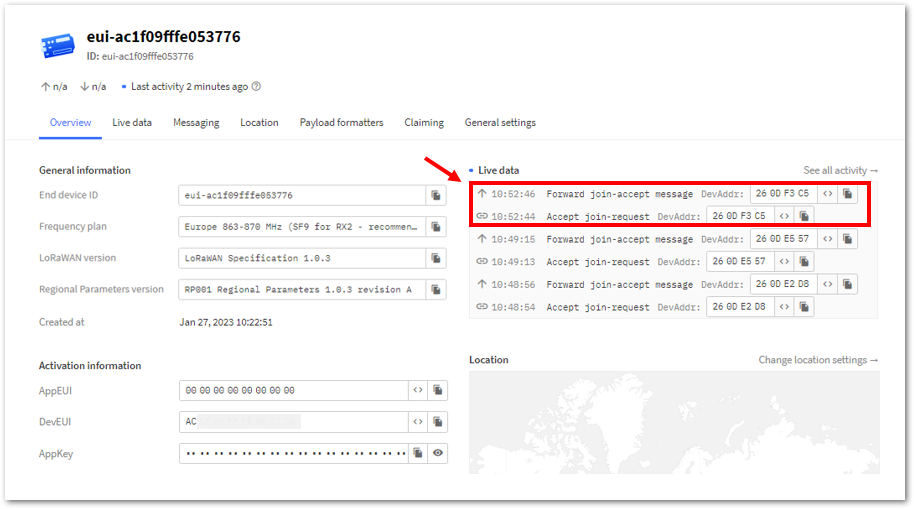 Figure 1: OTAA device successfully joined the TTN server
Figure 1: OTAA device successfully joined the TTN serverOTAA Configuration for TTN via WisToolBox Console
Here's another way of OTAA configuration using WisToolBox Console. Below are the steps on setting up your RAK3172-SiP using WisToolBox Console.
-
Connect your RAK3172-SiP with your chosen WisBlock base board to the PC via USB cable and open the WisToolBox application.
-
Click the CONNECT DEVICE button to launch the WisToolBox Dashboard.
 Figure 1: CONNECT DEVICE
Figure 1: CONNECT DEVICE- Then select your target port where your RAK3172-SiP is connected. Once recognized, click CONNECT as shown in Figure 74.
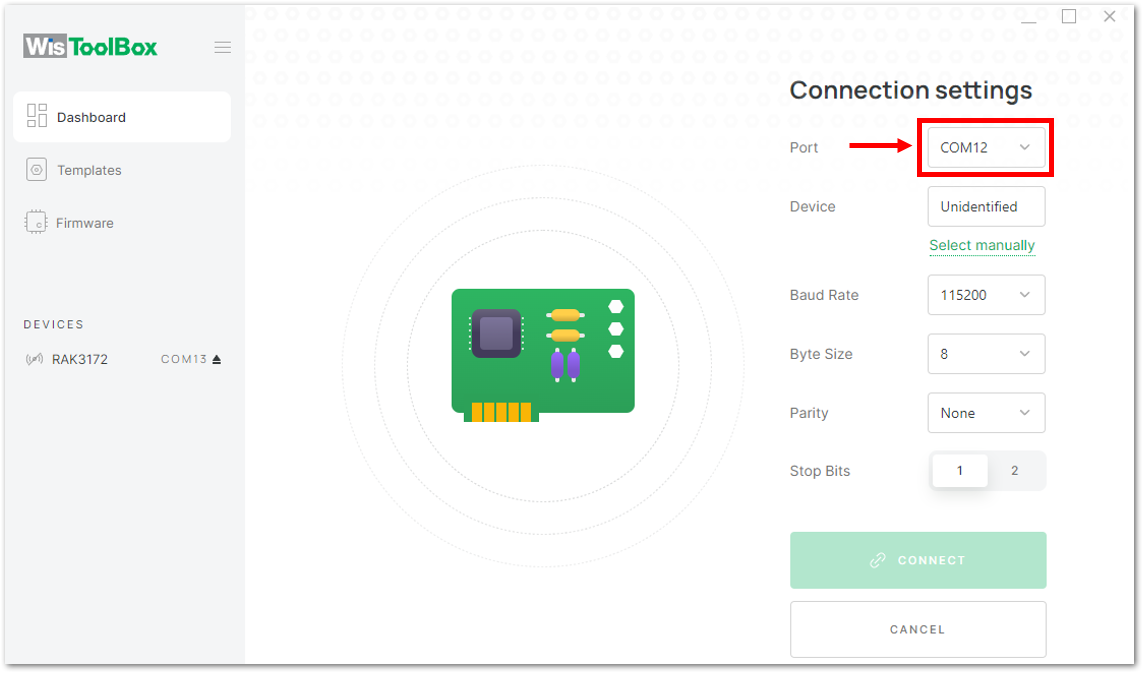 Figure 1: Setting up your device
Figure 1: Setting up your device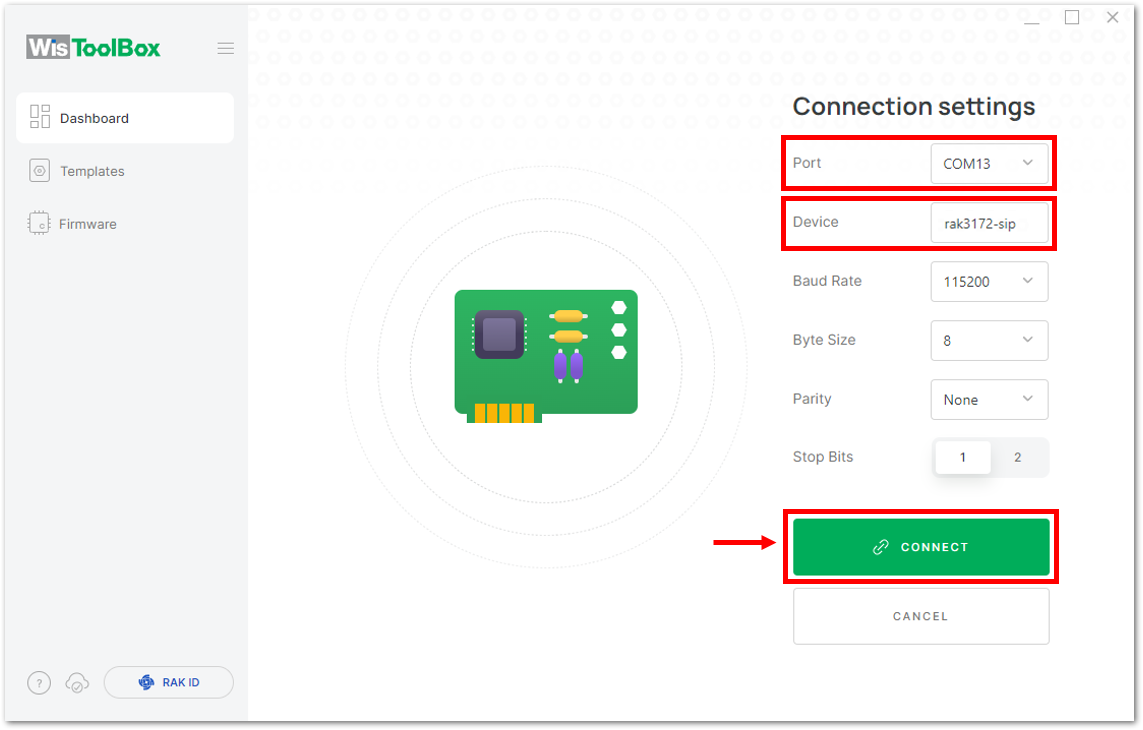 Figure 1: Setting up your device
Figure 1: Setting up your device- Once done, RAK3172-SiP will appear in the dashboard then select it.
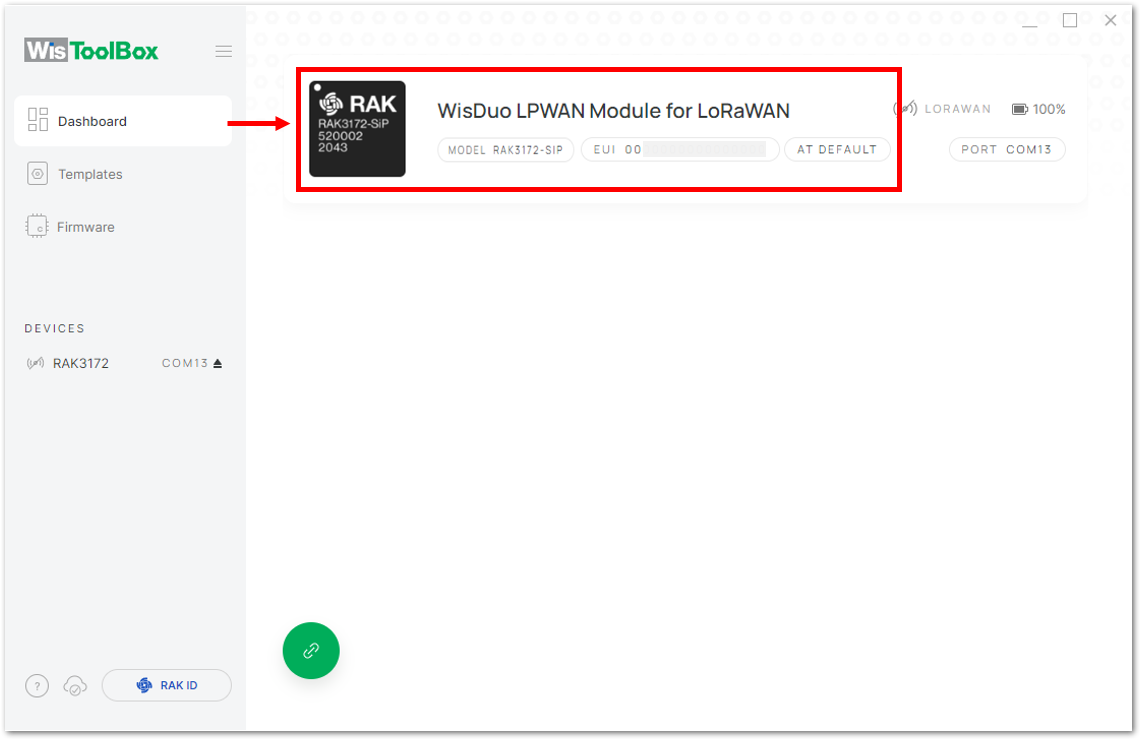 Figure 1: Device seen from WisToolBox dashboard
Figure 1: Device seen from WisToolBox dashboard- Then click ADVANCED.
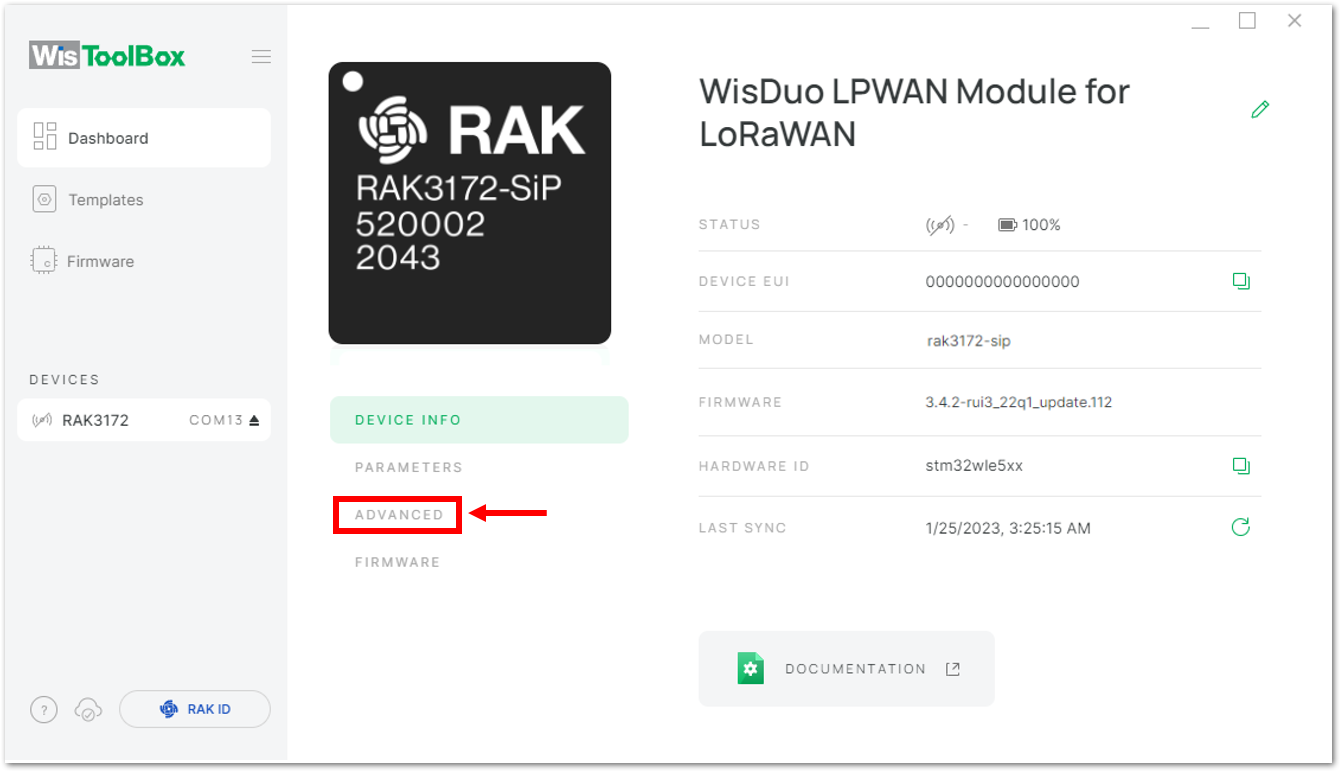 Figure 1: Setting up your device
Figure 1: Setting up your device- Once done, click OPEN CONSOLE to do the configuration.
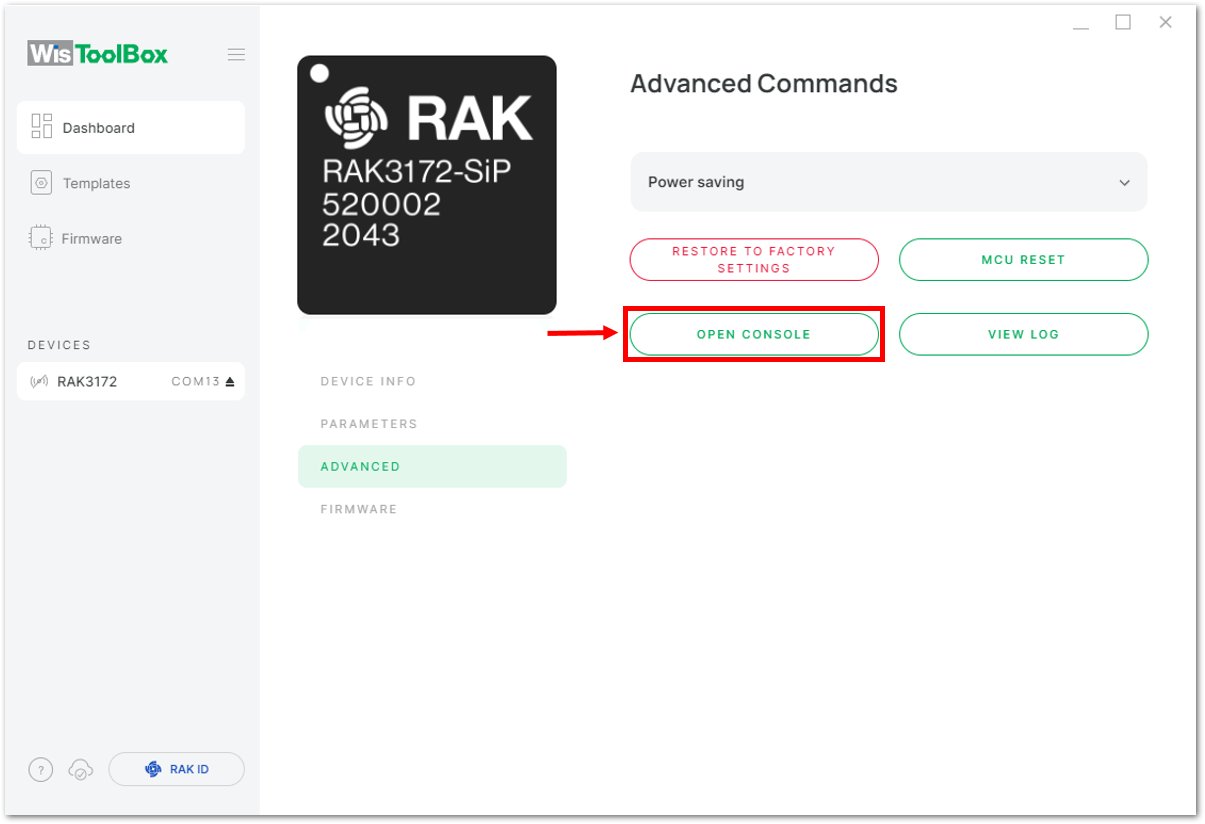 Figure 1: OPEN CONSOLE
Figure 1: OPEN CONSOLE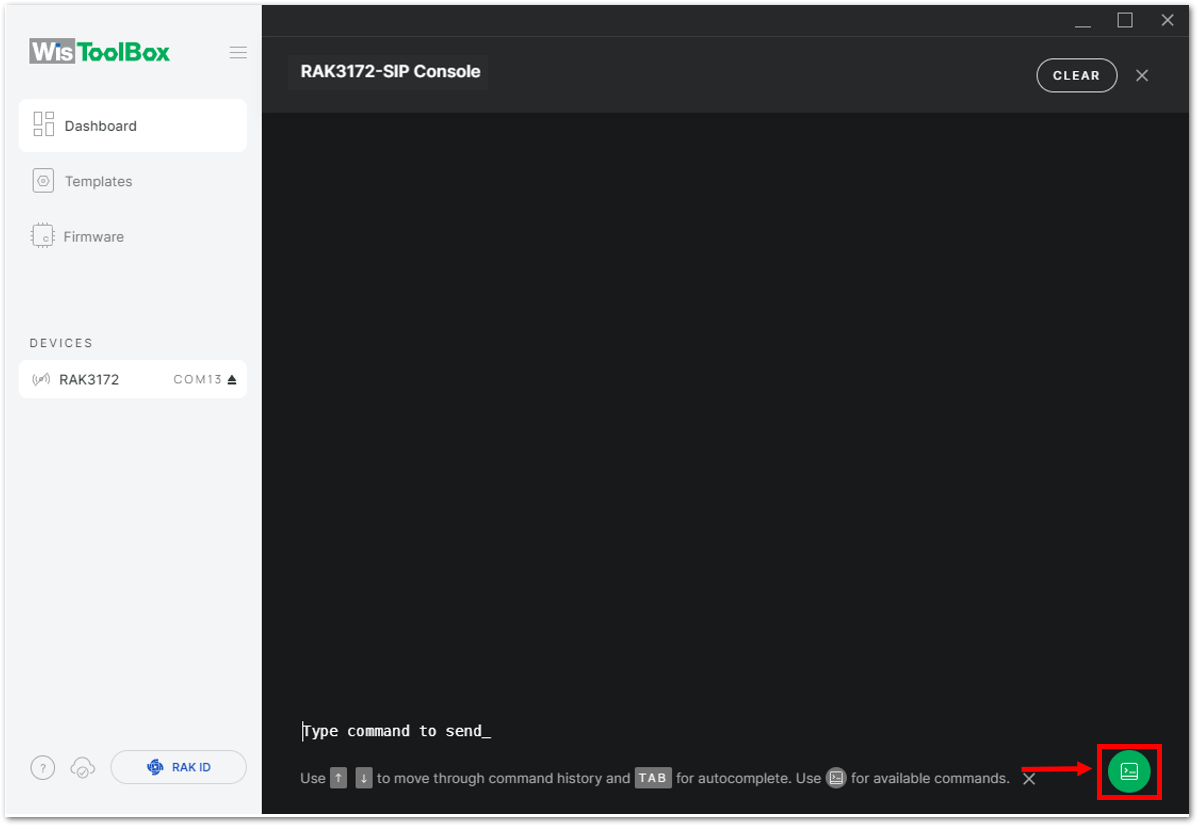 Figure 1: Opening the Console terminal of WisToolBox
Figure 1: Opening the Console terminal of WisToolBox Figure 1: Opening the Console terminal of WisToolBox
Figure 1: Opening the Console terminal of WisToolBox- To start the configuration, type ATE so you can echo the commands you input during your configuration. Then press Enter.
It is recommended to start by testing the console and verify that the current configuration is working by sending these two AT commands:
AT
ATE
ATE is useful for tracking the commands and troubleshooting.
You will receive OK when you input the two commands. After setting ATE, see all the commands you input together with the replies.
If there is no OK or any reply, check if the device is powered correctly. If you are getting power from a USB port, ensure that you have a good USB cable.
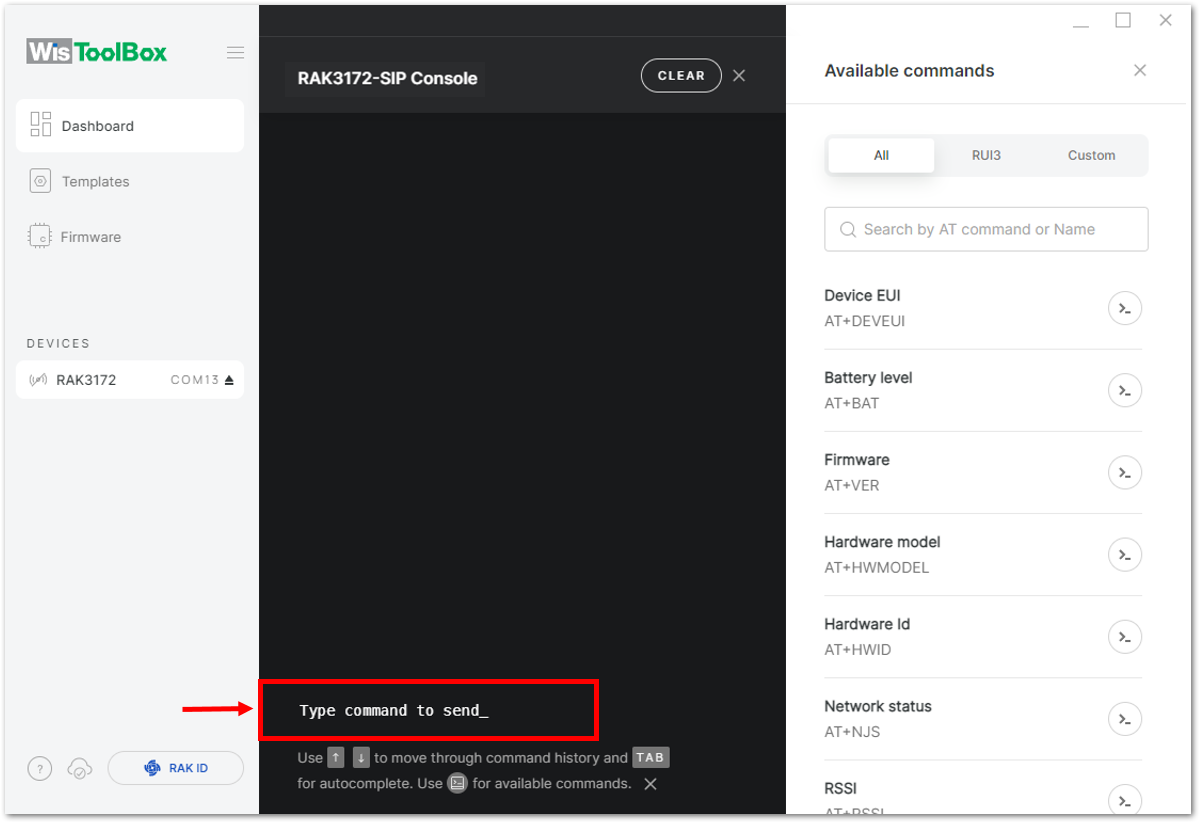 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console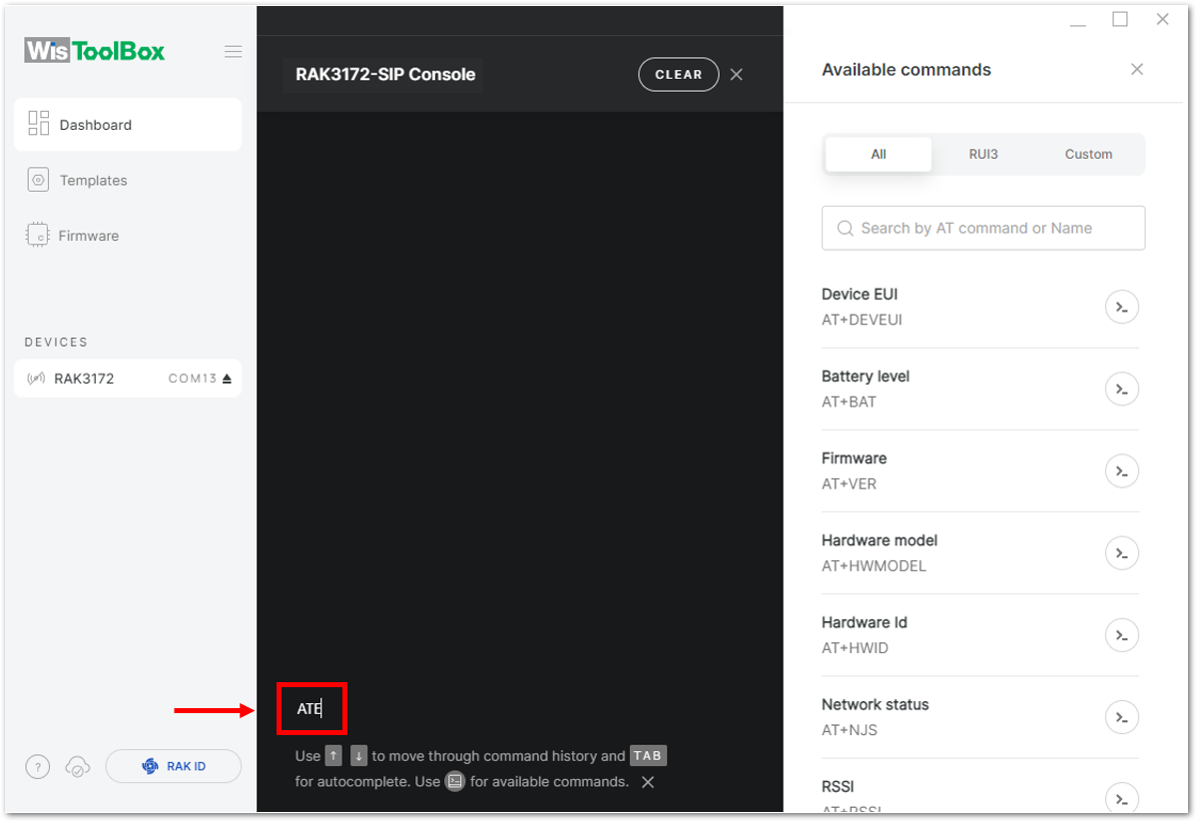 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console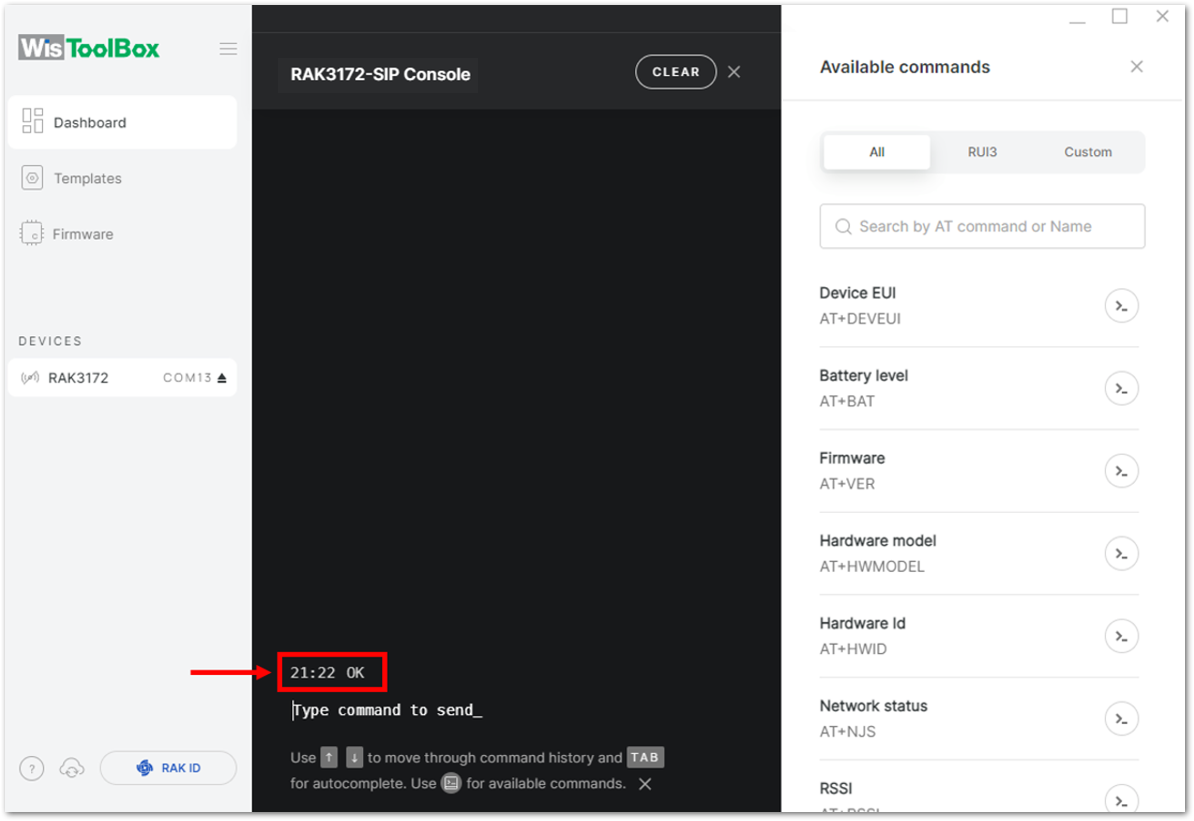 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console- Then configure the LoRaWAN join mode to OTAA. You can check what parameter you will input by typing AT+NJM? and then Enter into the console terminal. For OTAA, you should input AT+NJM=1 and then press Enter as shown in Figure 83.
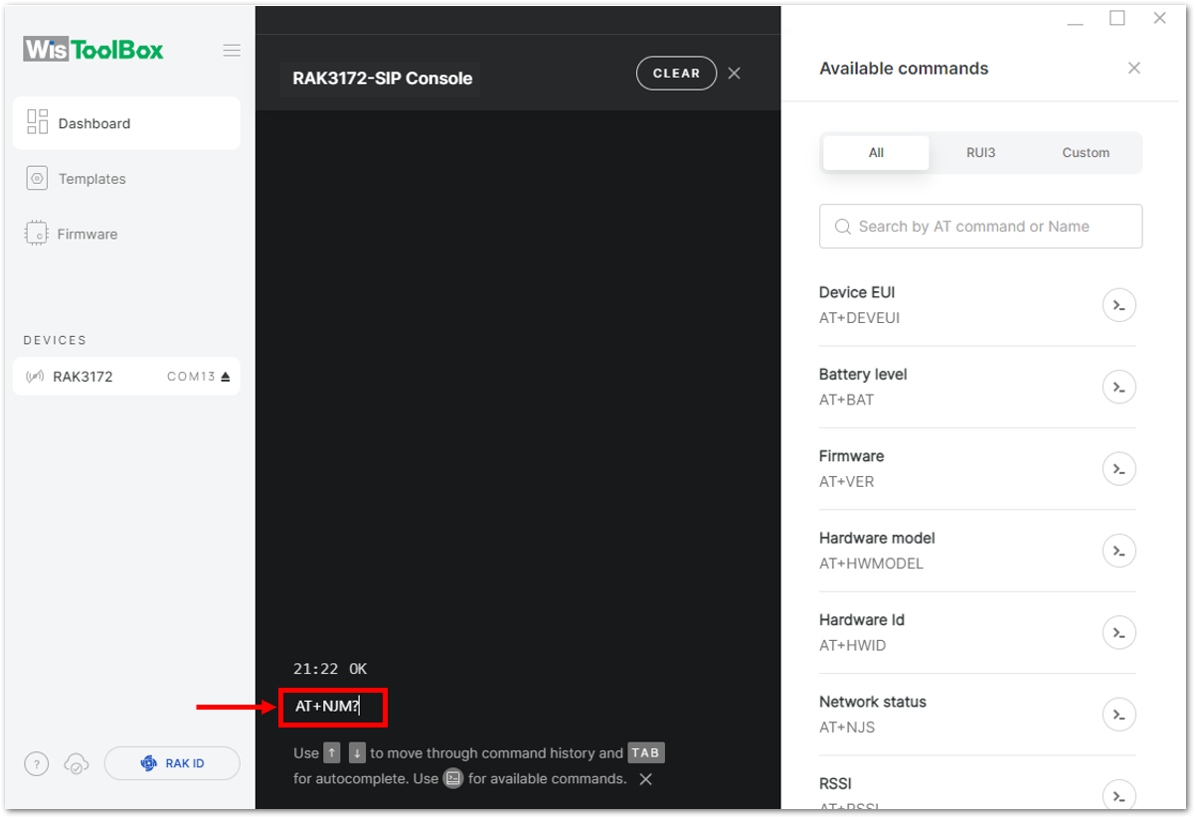 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console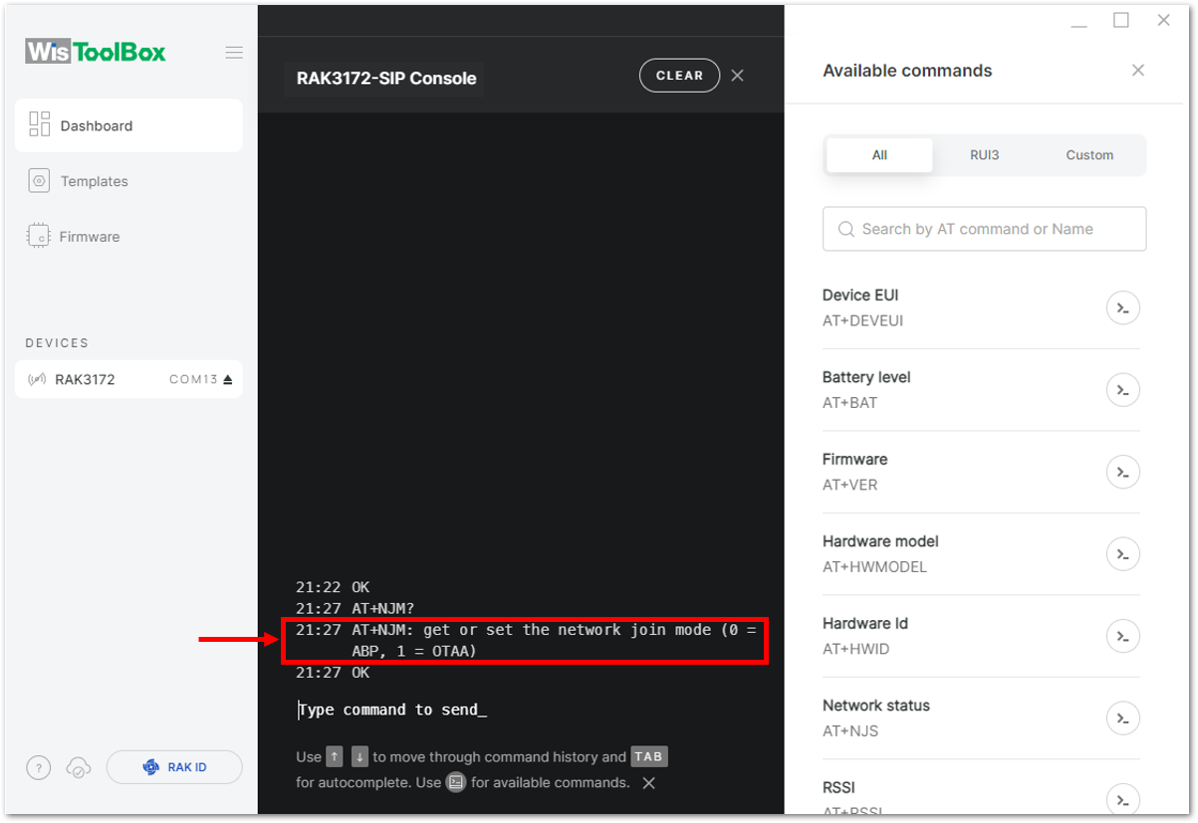 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console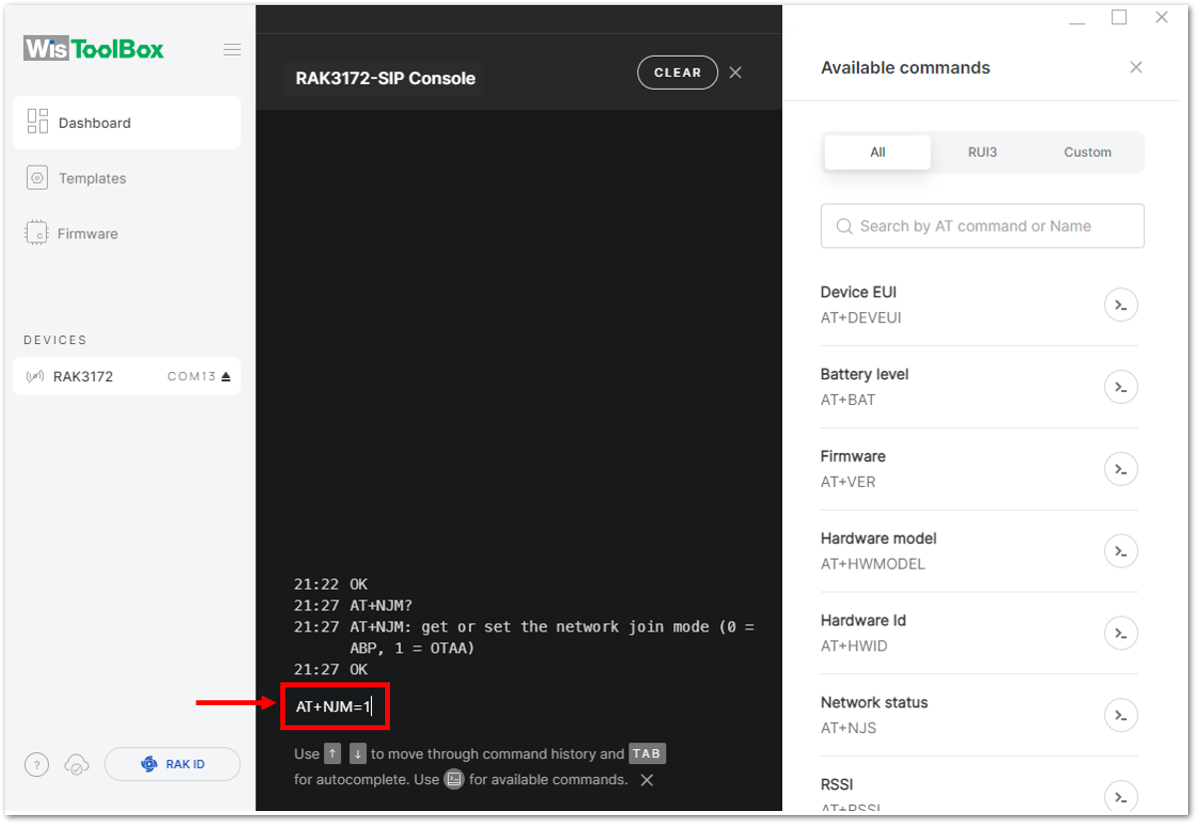 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console- Once done, set up your LoRaWAN region to EU868. You can check what parameter you will input by typing AT+BAND? and then Enter into the console terminal. For EU868, you should input AT+BAND=4 then press Enter. If you wish to work on other regional bands, you may check the list of band parameter options below.
Set the frequency/region to EU868.
AT+BAND=4
- Depending on the Regional Band you selected, you might need to configure the sub-band of your RAK3172 to match the gateway and LoRaWAN network server. This is especially important for Regional Bands like US915, AU915, and CN470.
- To configure the masking of channels for the sub-bands, you can use the
AT+MASKcommand that can be found on the AT Command Manual. - To illustrate, you can use sub-band 2 by sending the command
AT+MASK=0002.
List of band parameter options
| Code | Regional Band |
|---|---|
| 0 | EU433 |
| 1 | CN470 |
| 2 | RU864 |
| 3 | IN865 |
| 4 | EU868 |
| 5 | US915 |
| 6 | AU915 |
| 7 | KR920 |
| 8 | AS923-1 |
| 9 | AS923-2 |
| 10 | AS923-3 |
| 11 | AS923-4 |
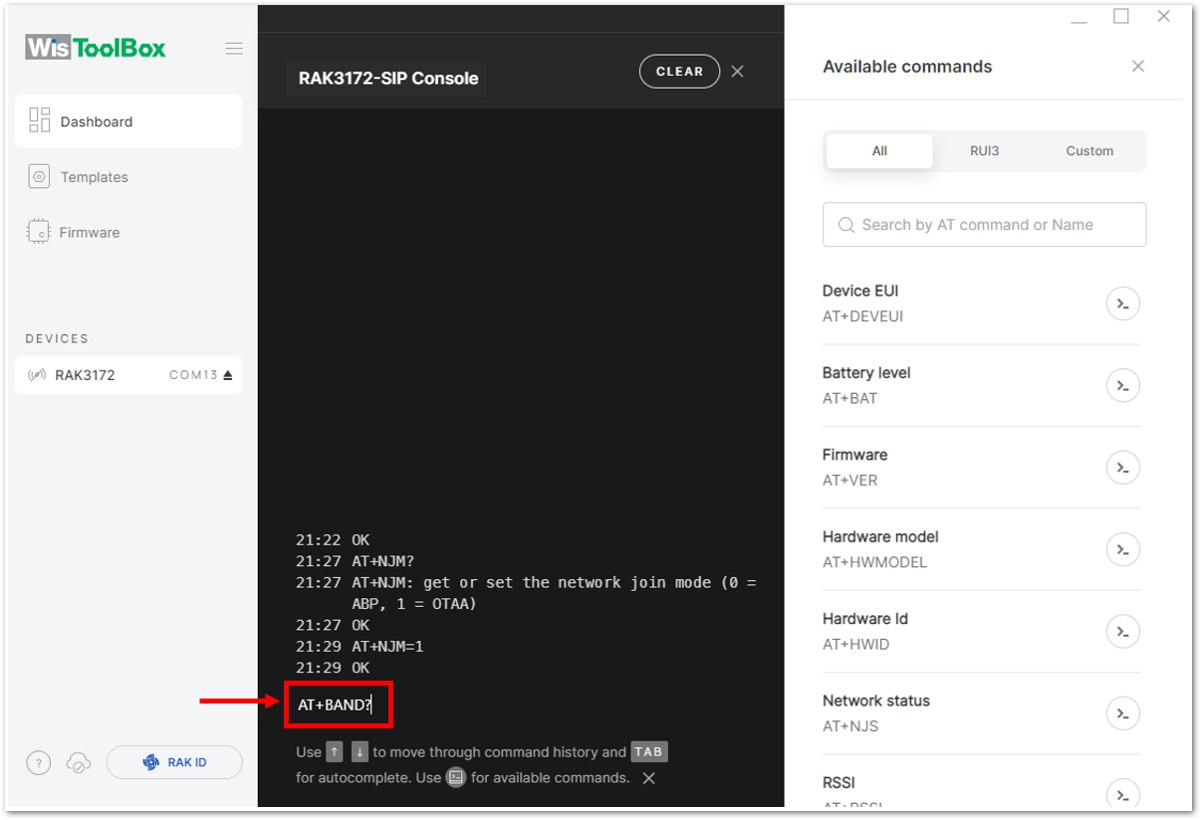 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console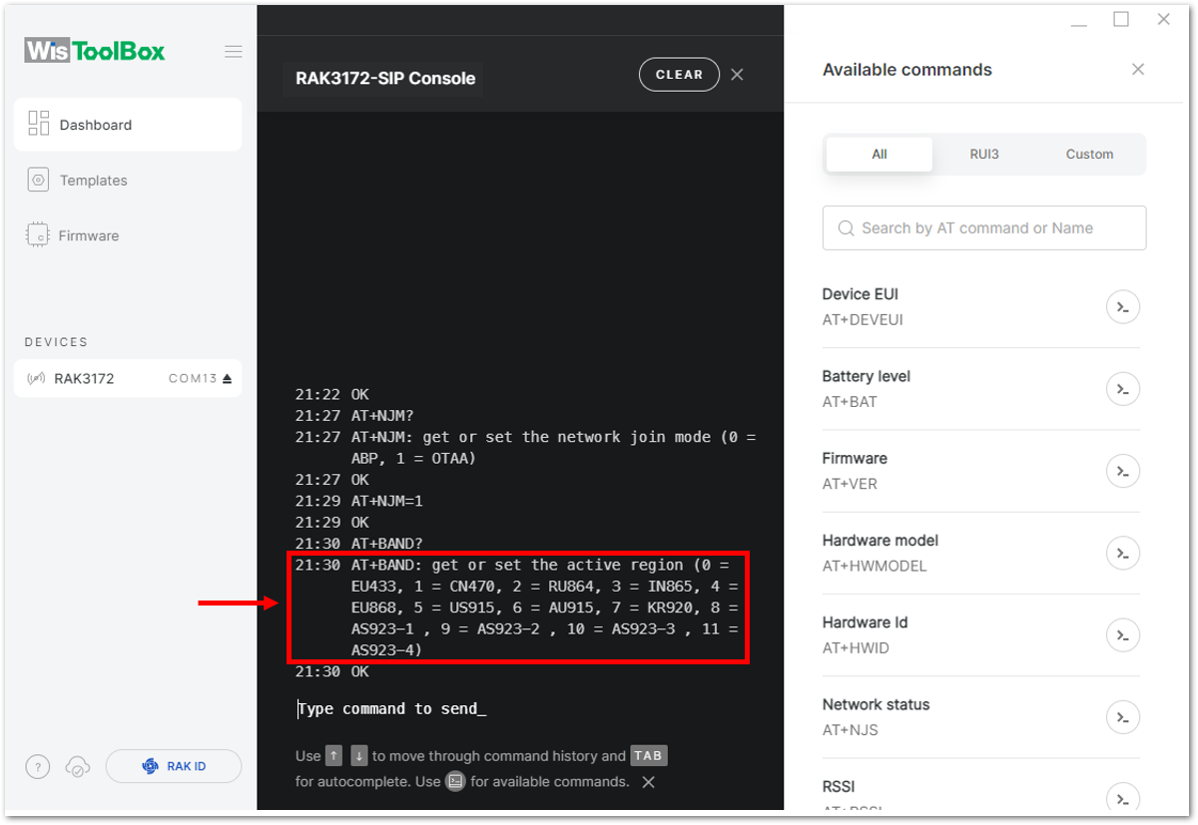 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console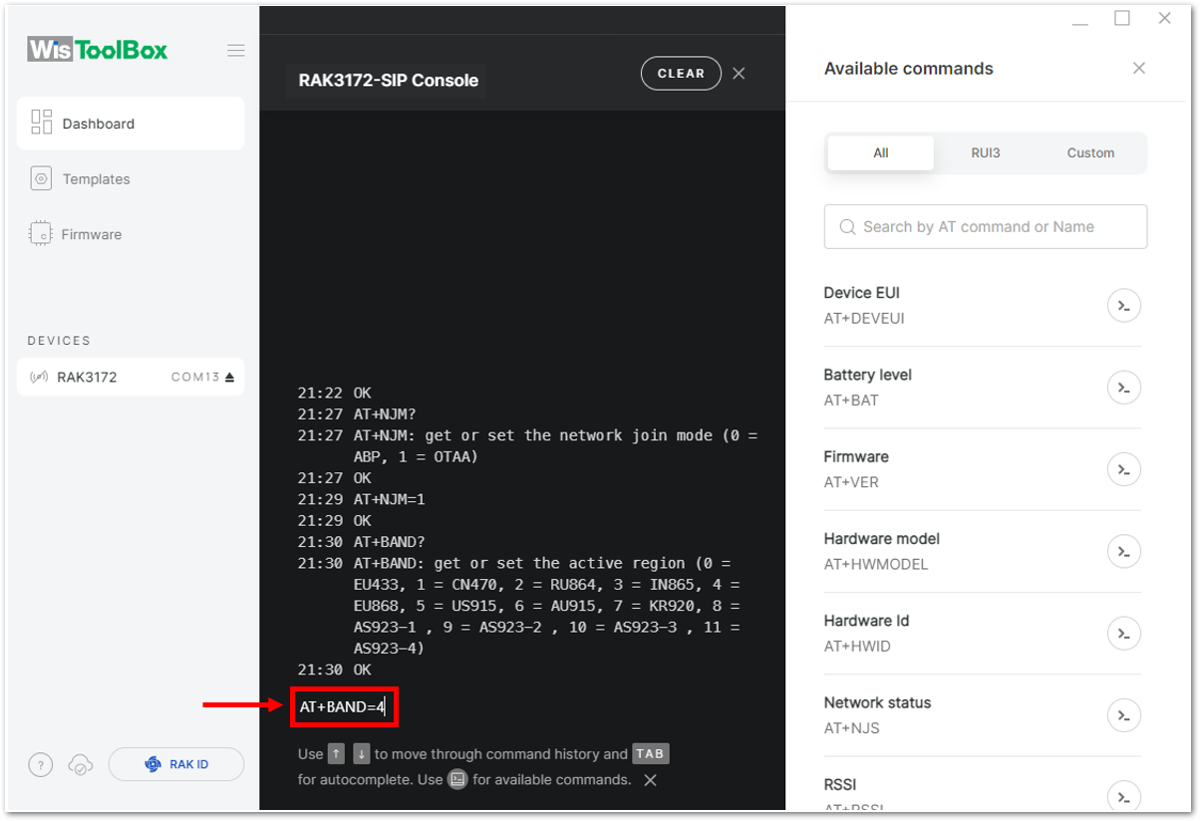 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console- Then next to this will be updating the OTAA credentials of your device. First to this will be the Application EUI (AppEUI). Go back to your console where your RAK3172 End device was created to copy the AppEUI credential then paste it to the WisToolBox Console then press Enter.
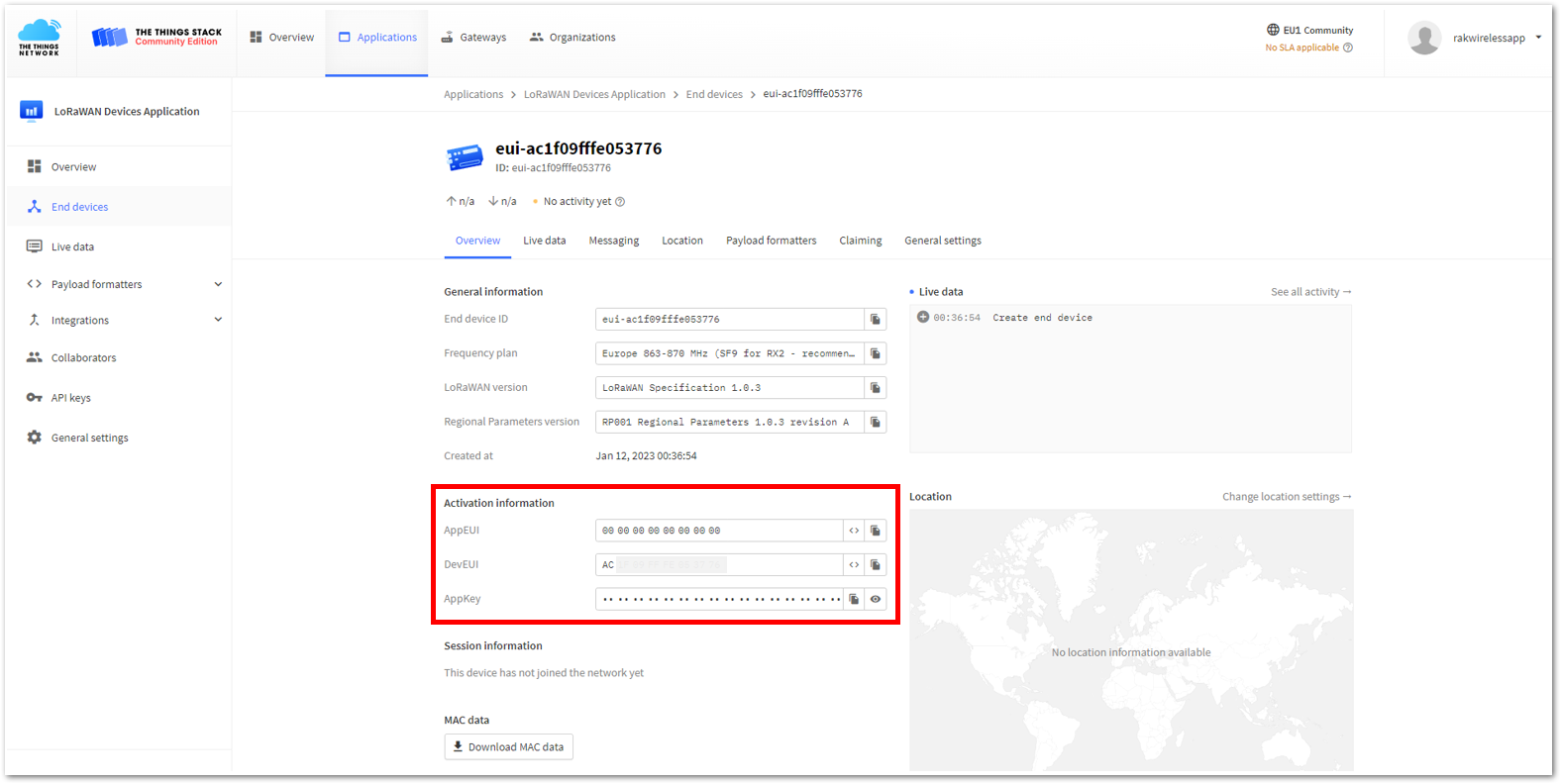 Figure 1: You created an OTAA device from your TTN console
Figure 1: You created an OTAA device from your TTN console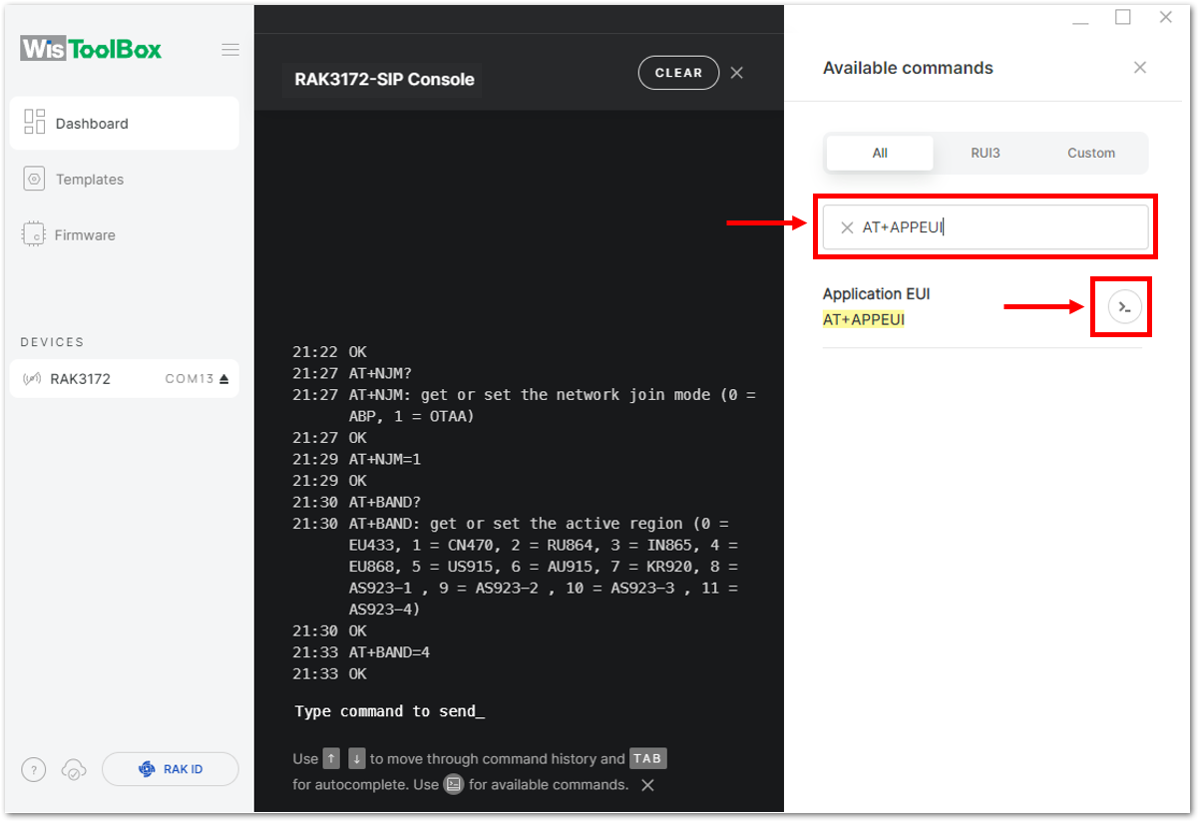 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console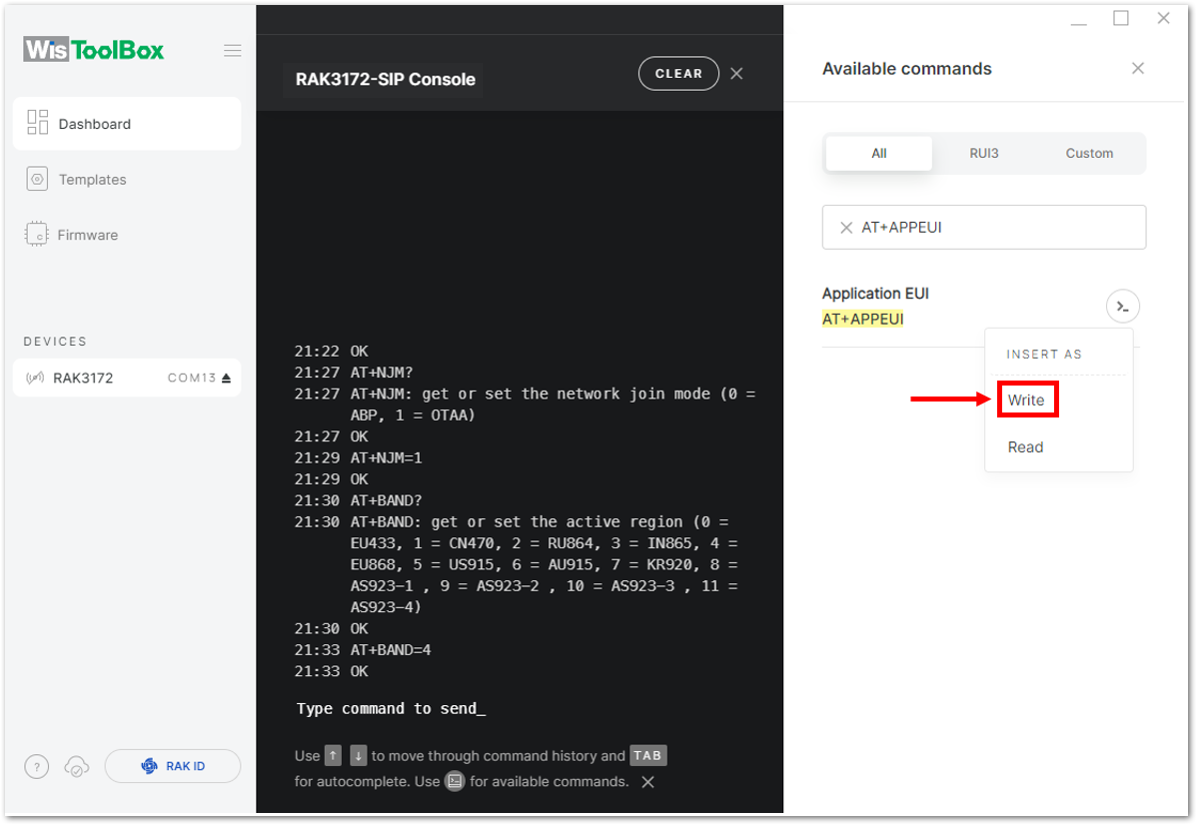 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console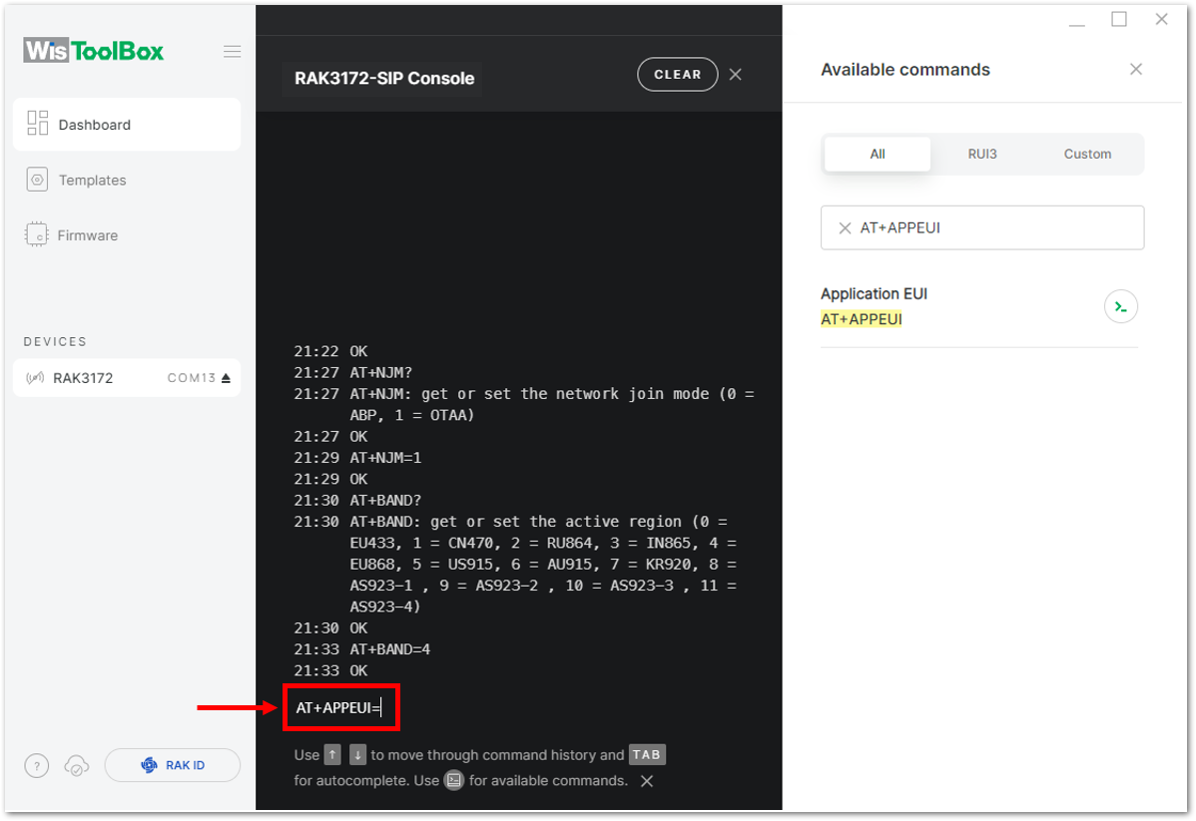 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console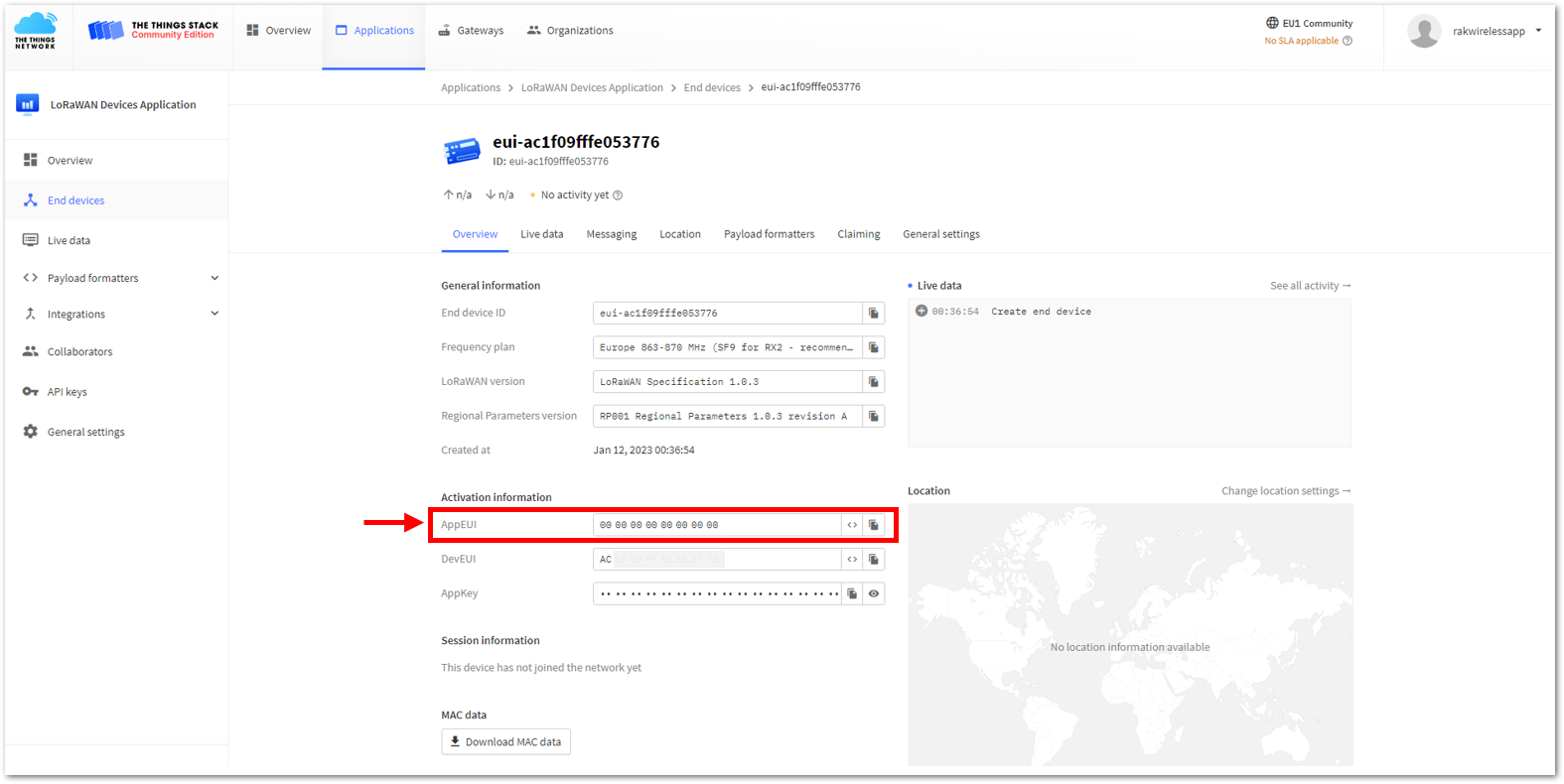 Figure 1: Copying the AppEUI credential from TTN to WisToolBox
Figure 1: Copying the AppEUI credential from TTN to WisToolBox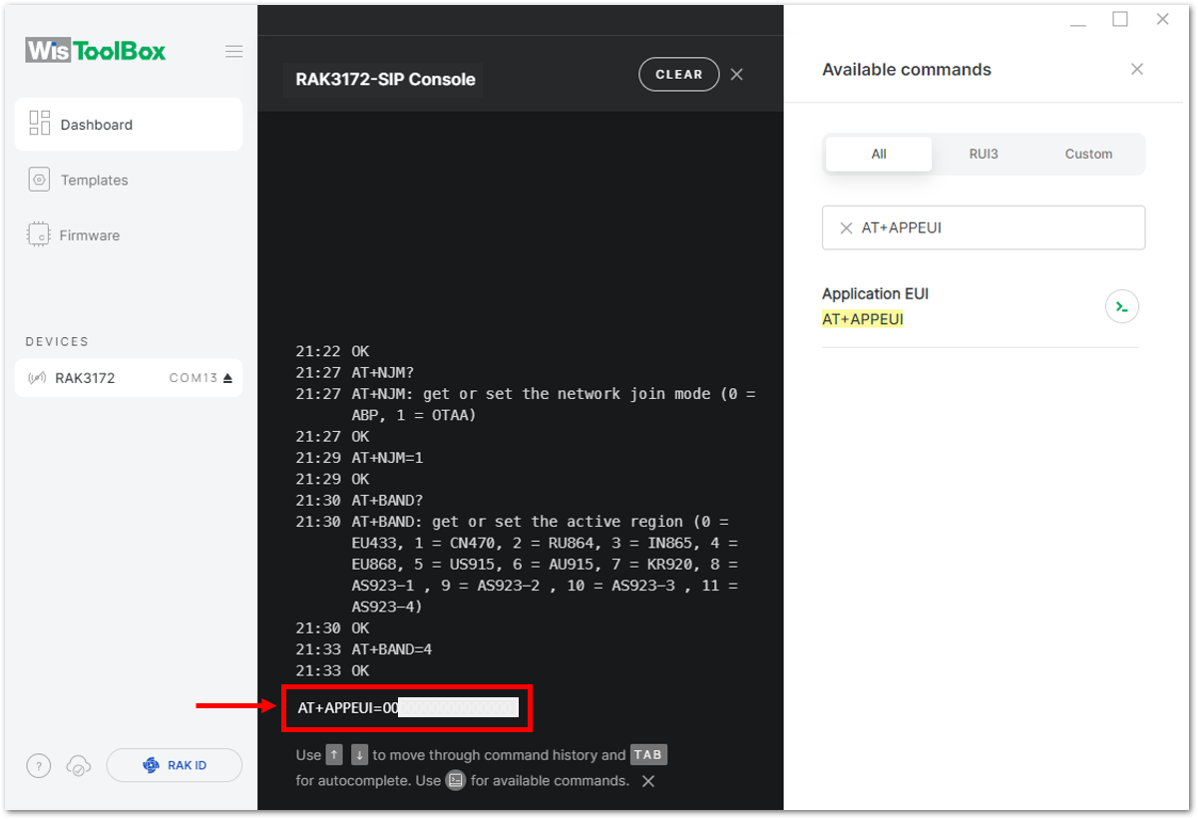 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console- Once done, do the same procedure to Application key (AppKey) and Device EUI (DevEUI).
- For Application key (AppKey)
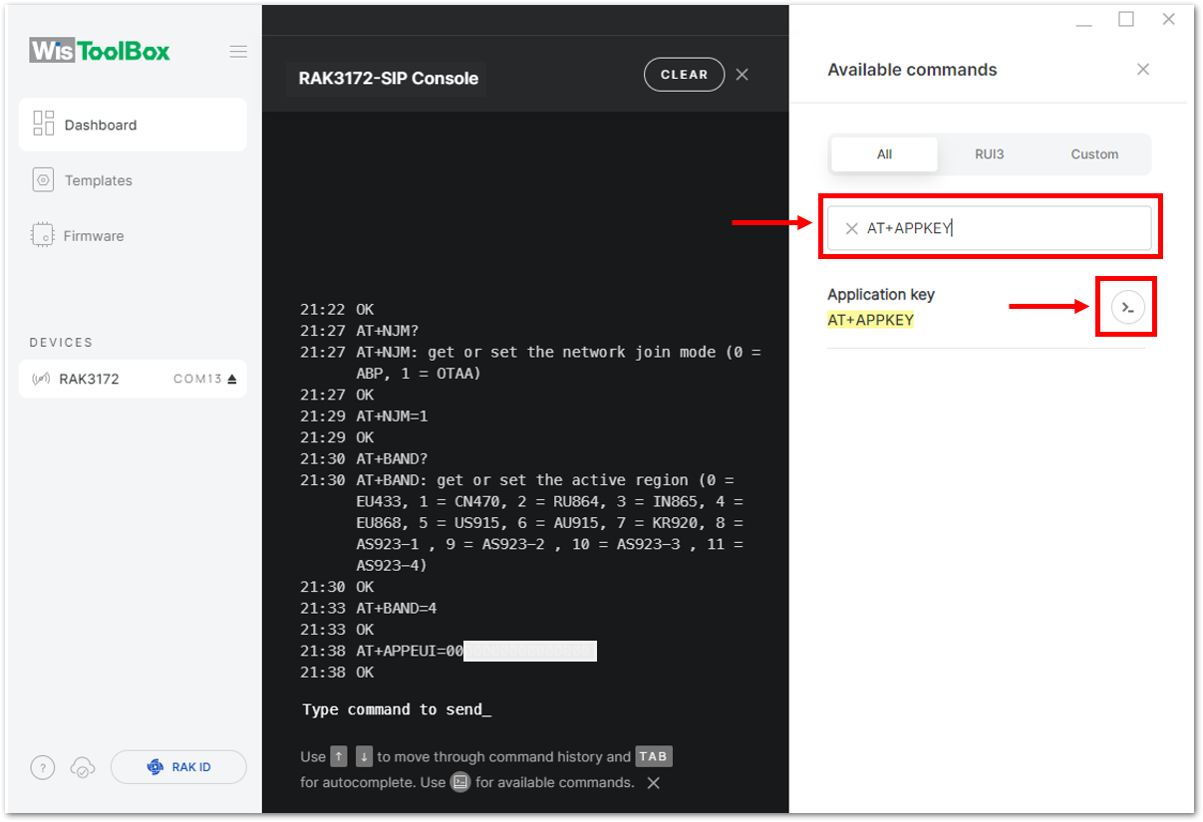 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console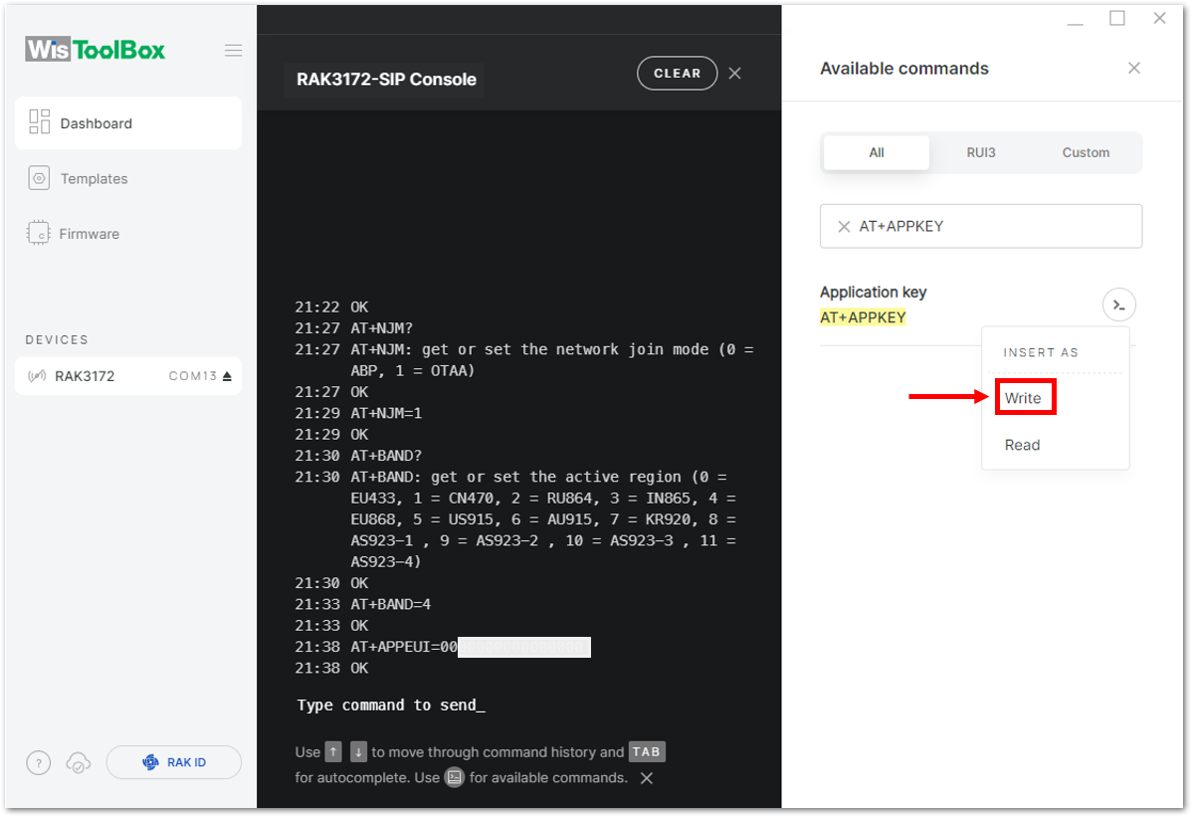 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console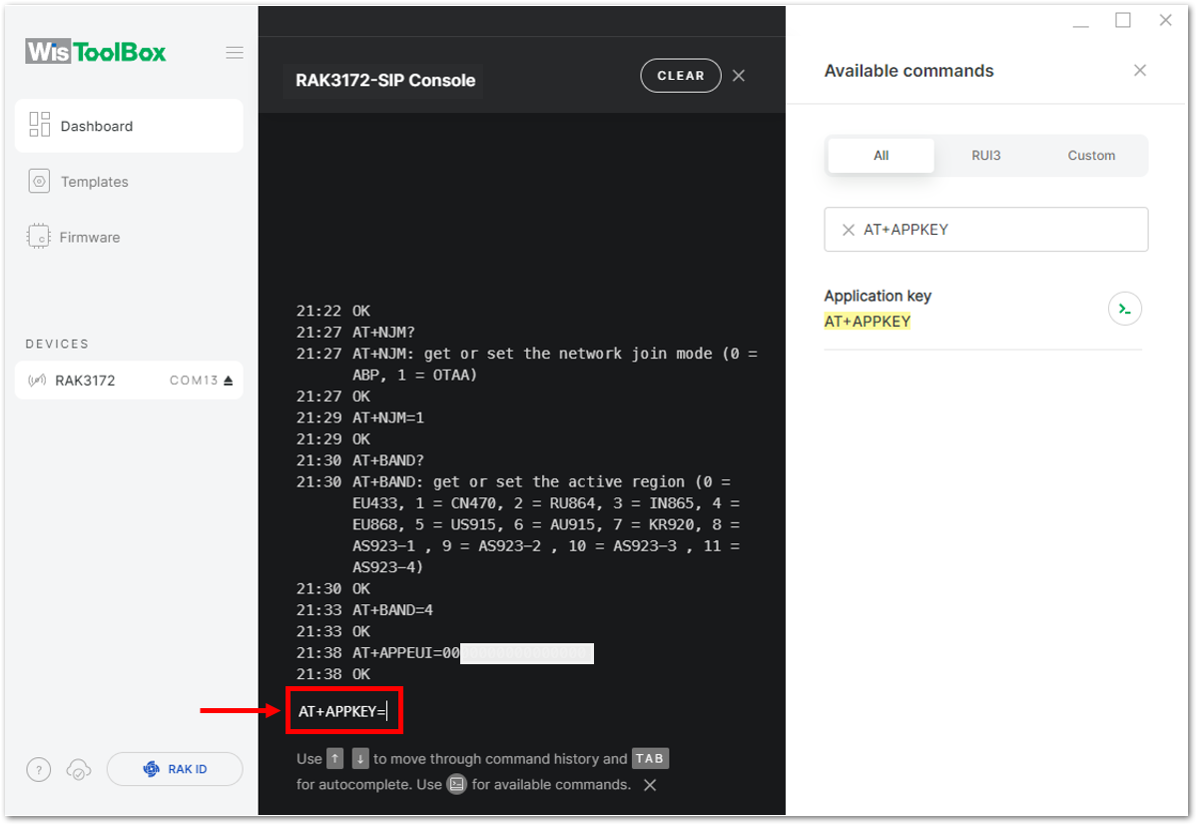 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console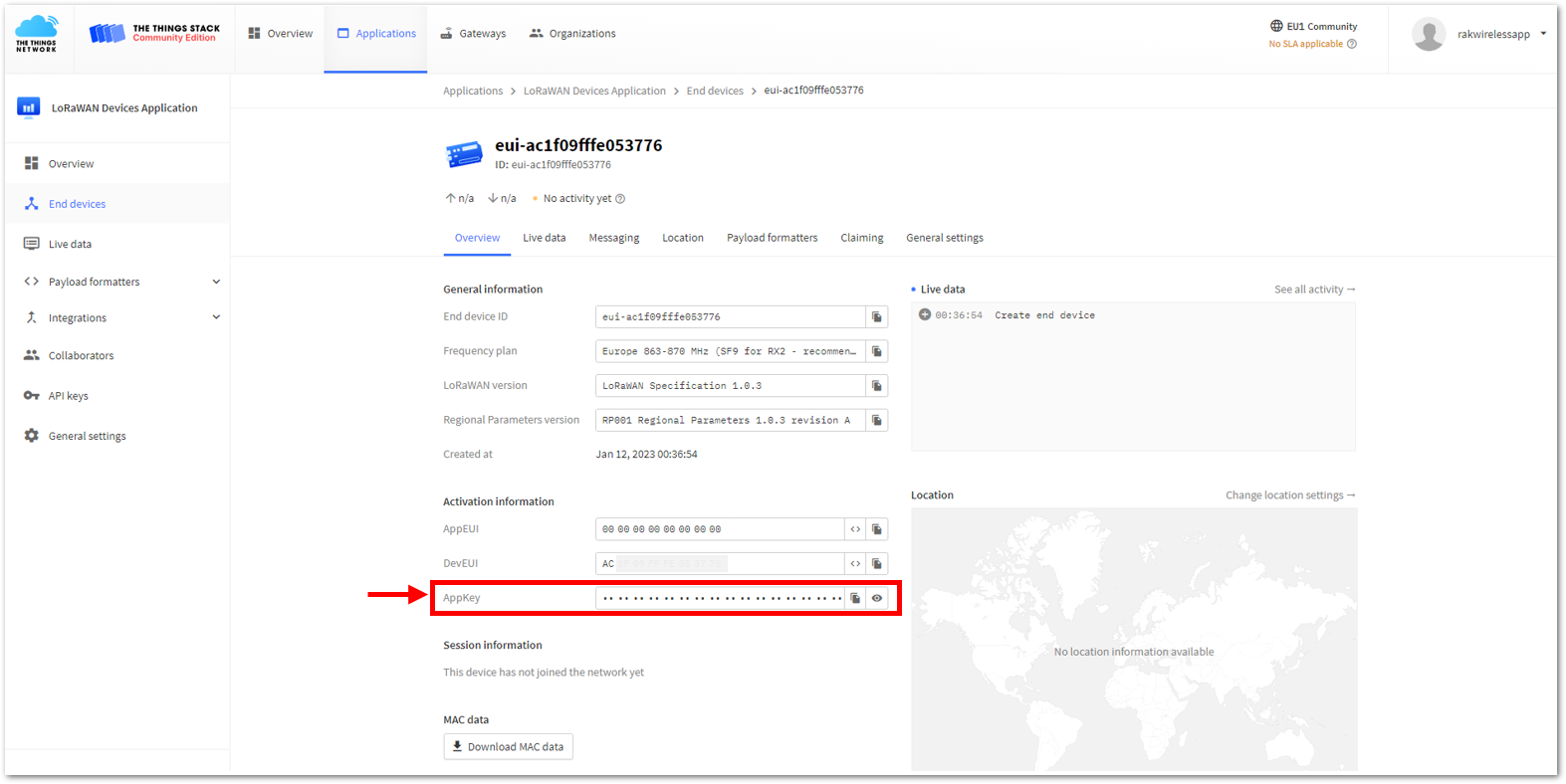 Figure 1: Copying the AppKey credential from TTN to WisToolBox
Figure 1: Copying the AppKey credential from TTN to WisToolBox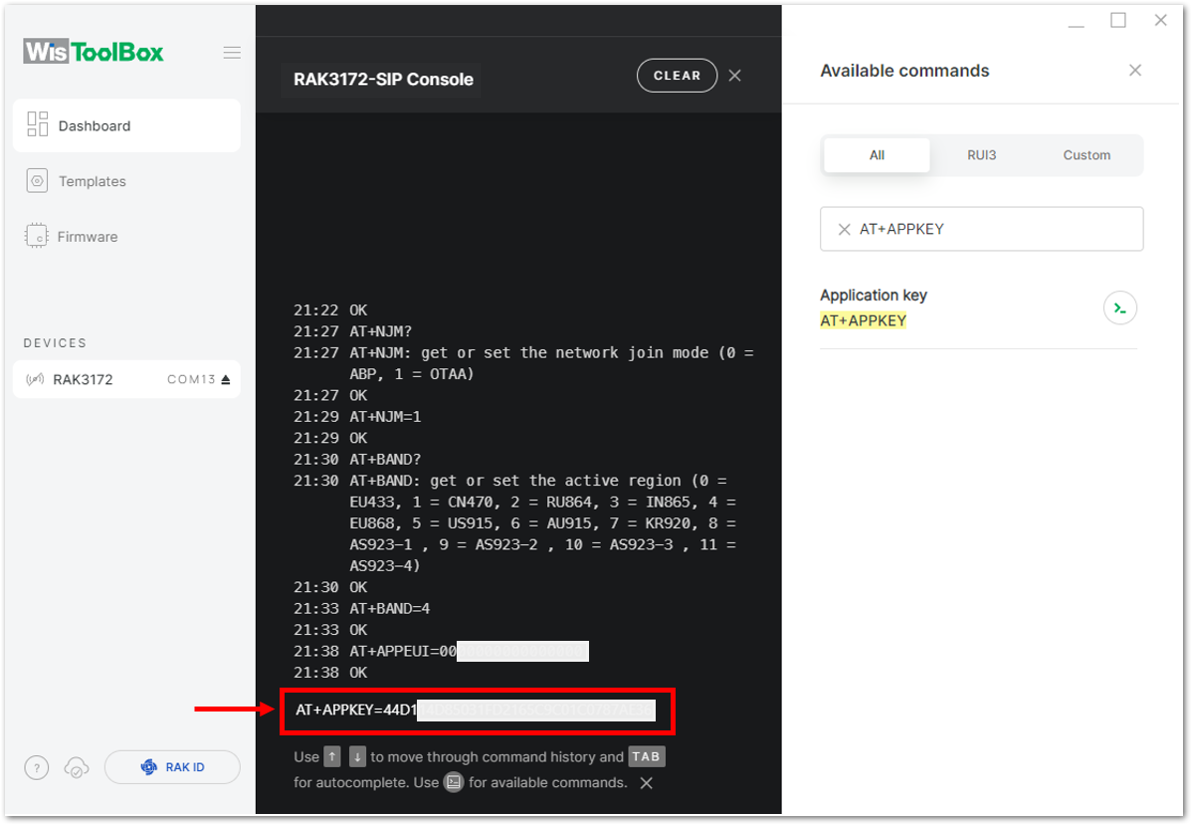 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console- For Device EUI (DevEUI)
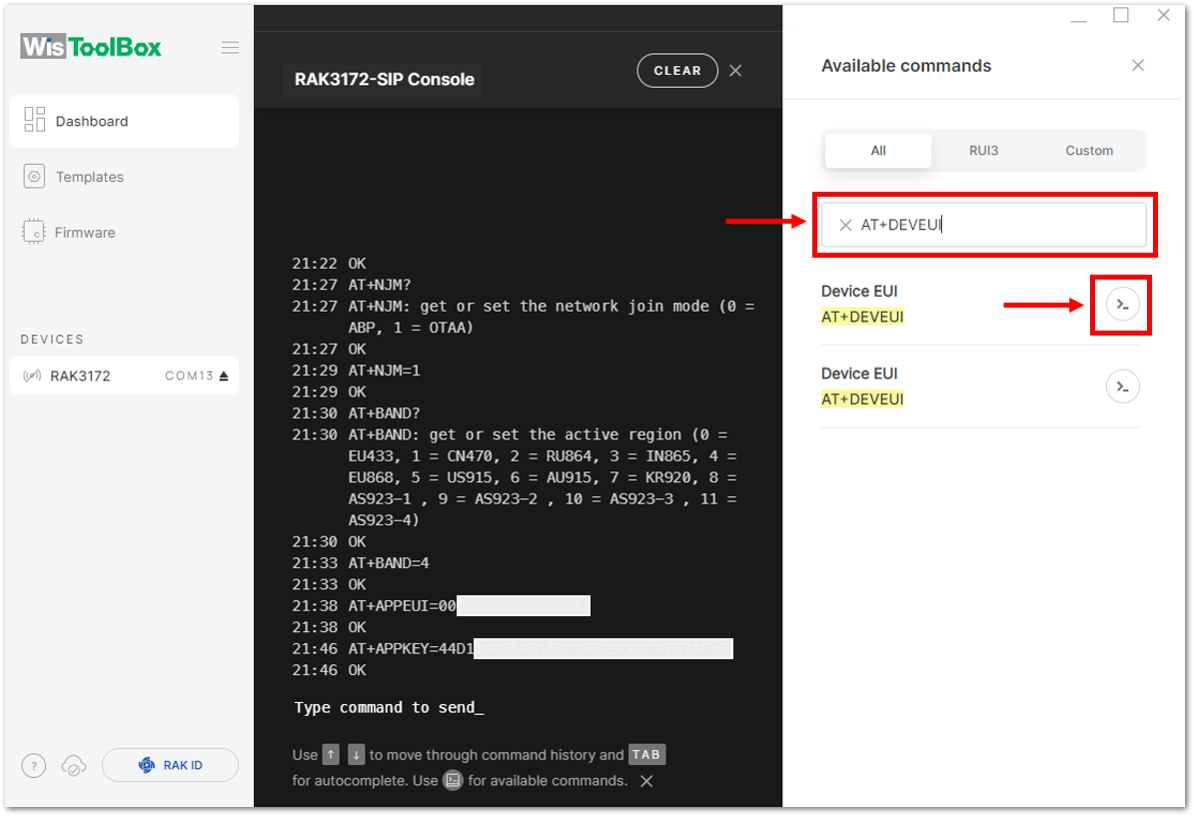 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console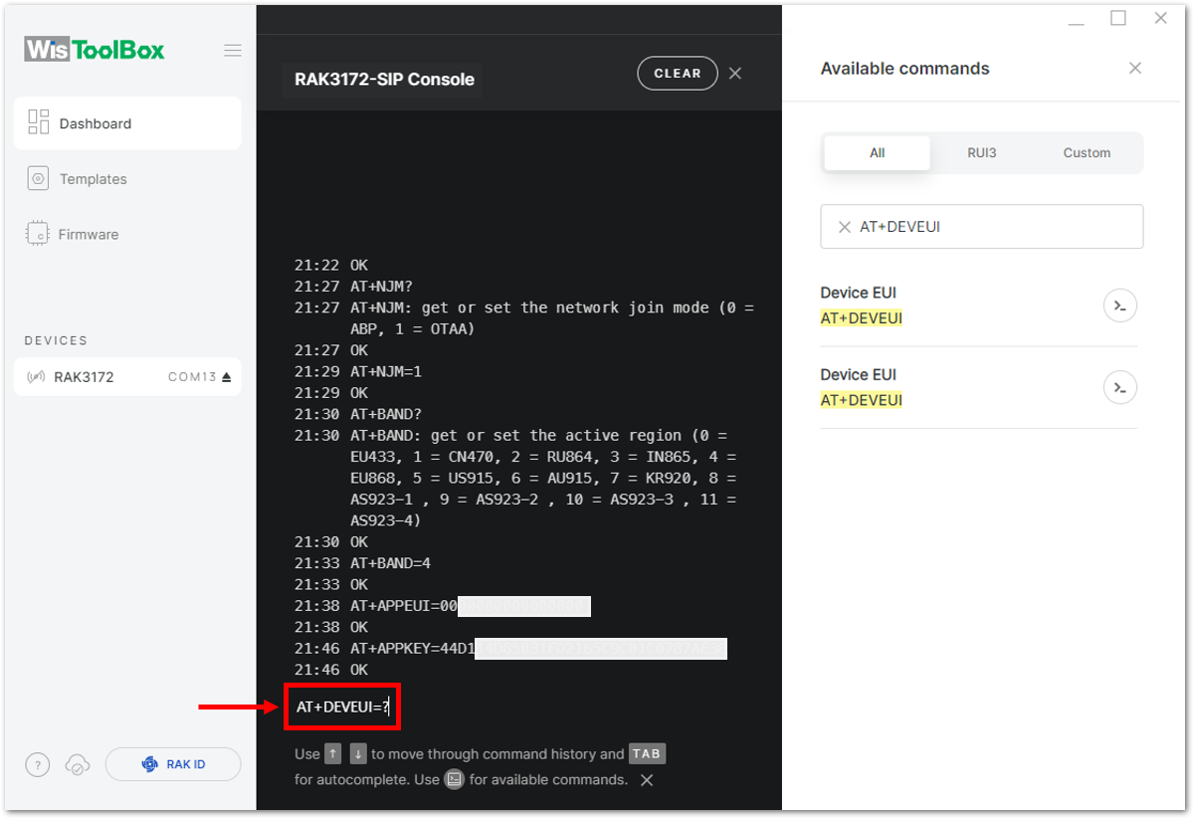 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console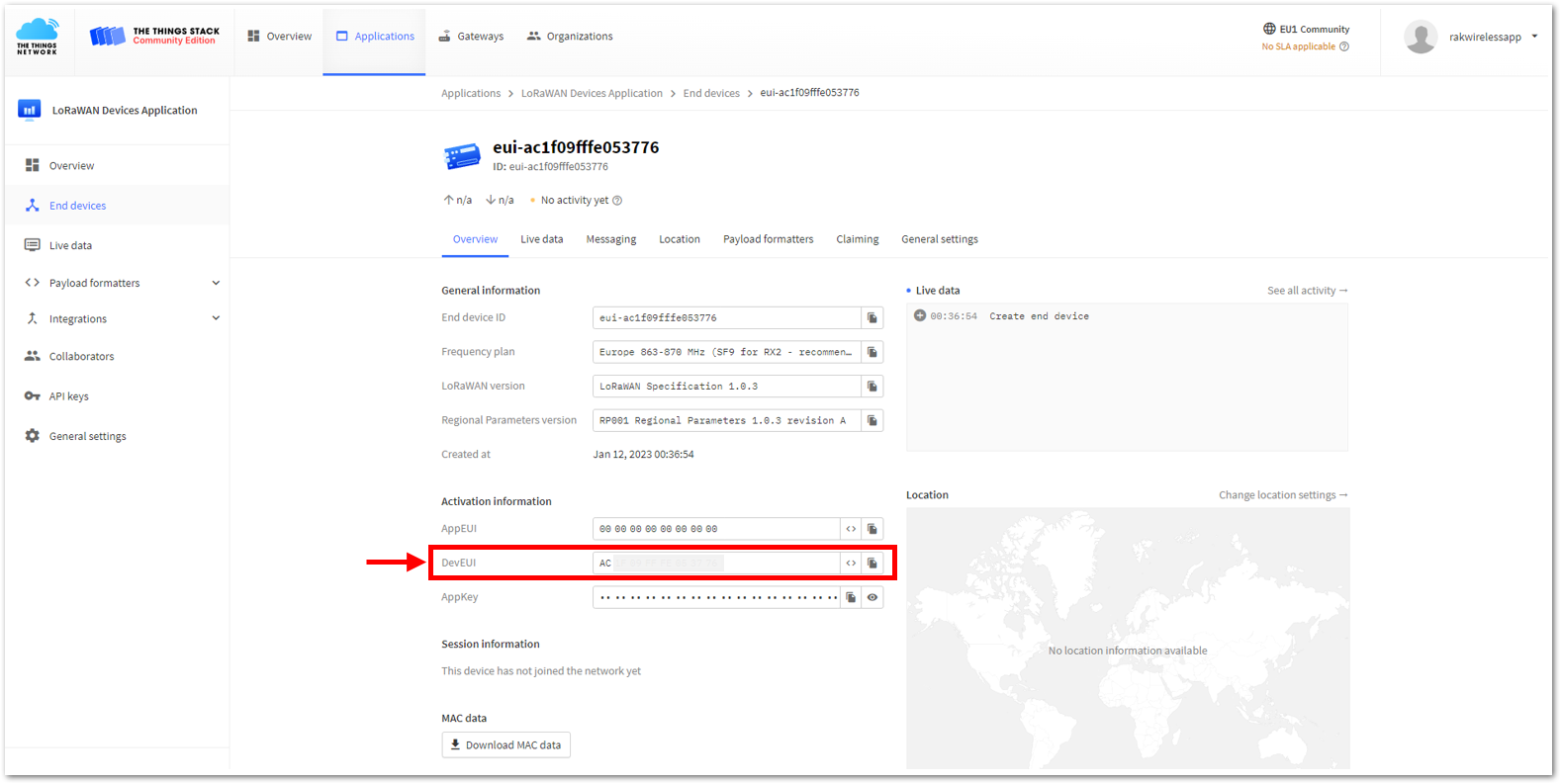 Figure 1: Copying the DevEUI credential from TTN to WisToolBox
Figure 1: Copying the DevEUI credential from TTN to WisToolBox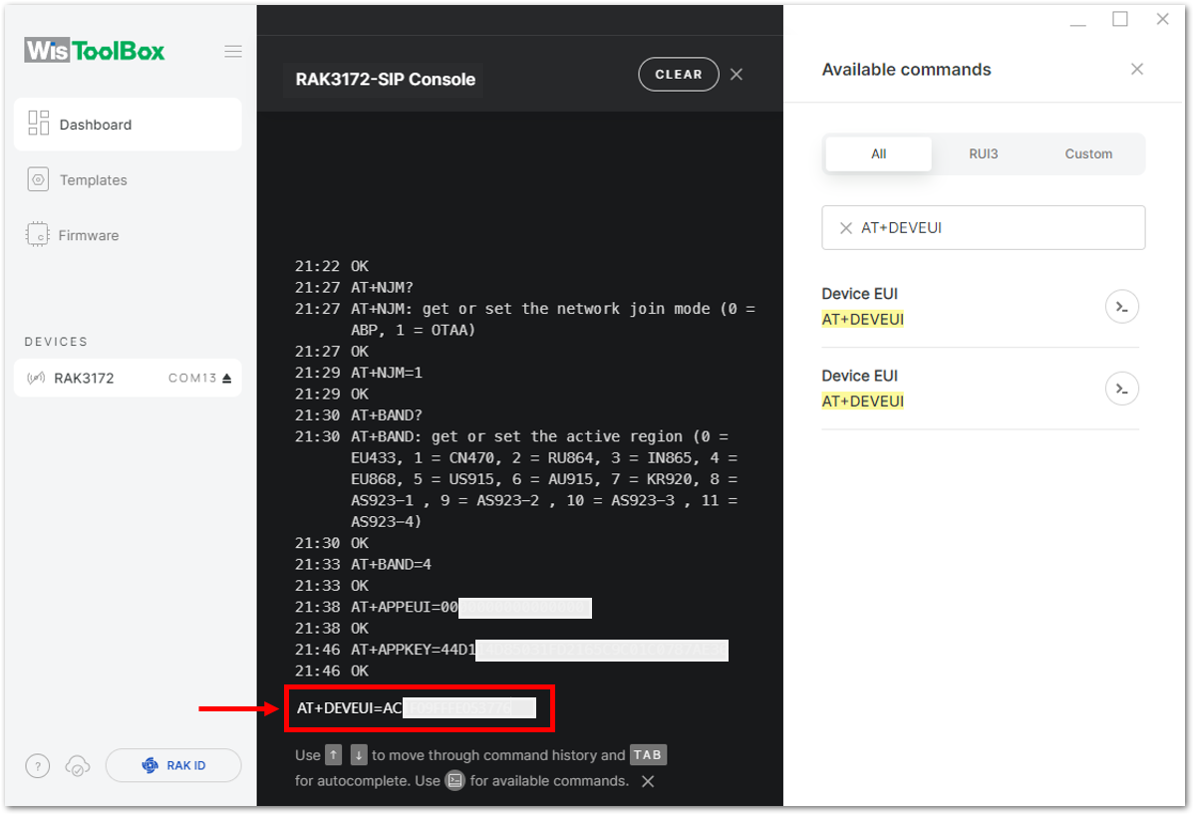 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console- Once done, click Dashboard to check the updated credentials of your OTAA device. Click PARAMETERS to open the Global Settings and LoRaWAN keys, ID, EUI and check whether these portions are updated.
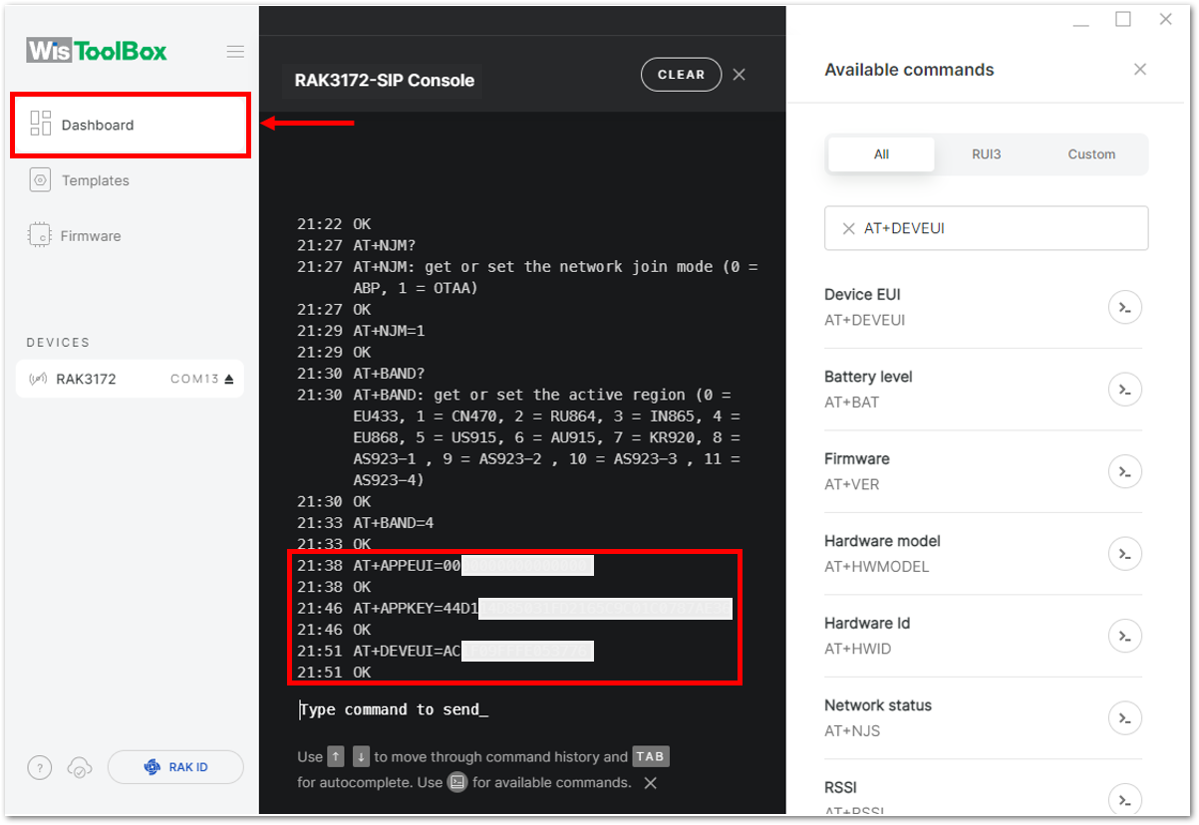 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console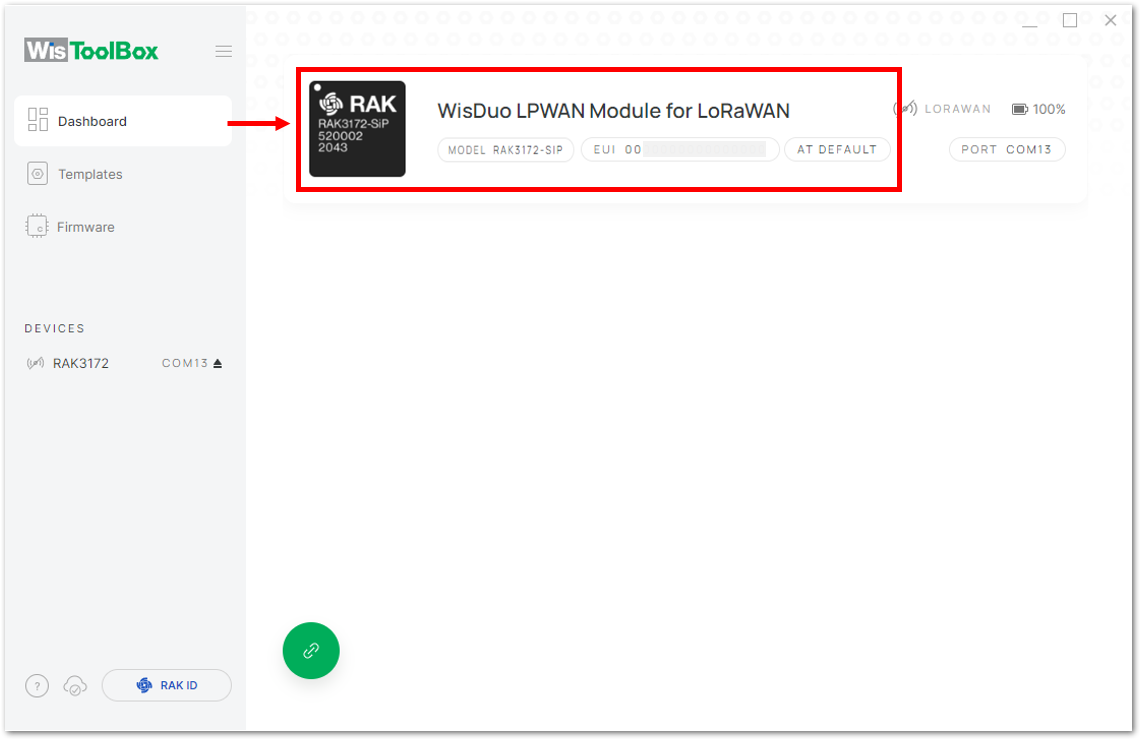 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console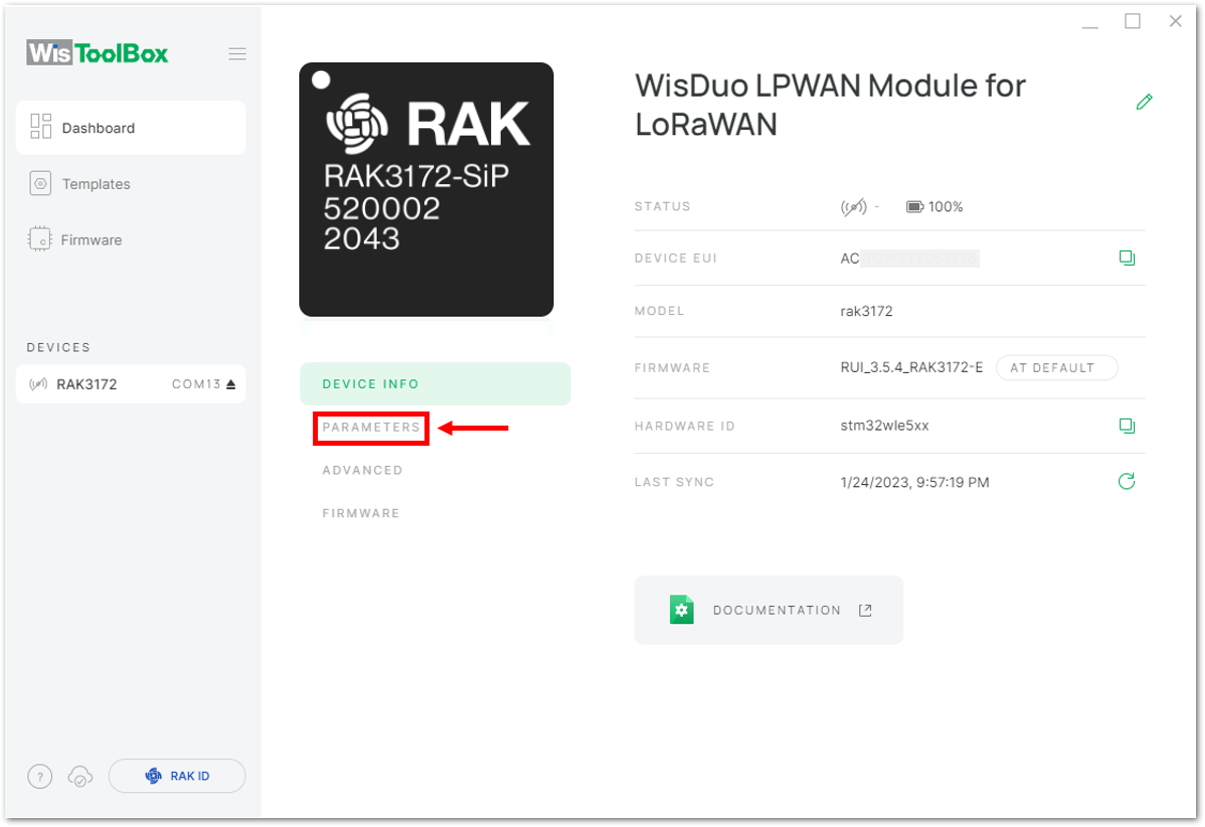 Figure 1: PARAMETERS
Figure 1: PARAMETERS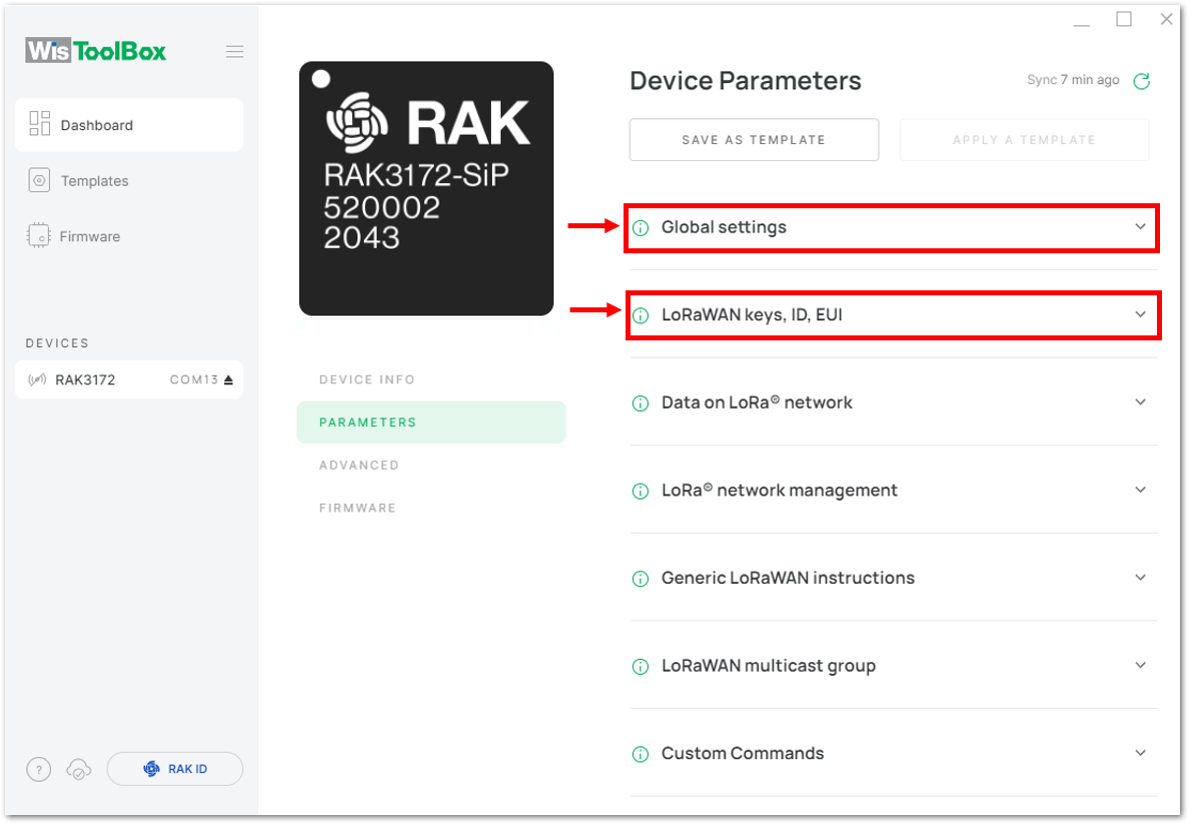 Figure 1: Global settings and LoRaWAN keys, ID, EUI
Figure 1: Global settings and LoRaWAN keys, ID, EUI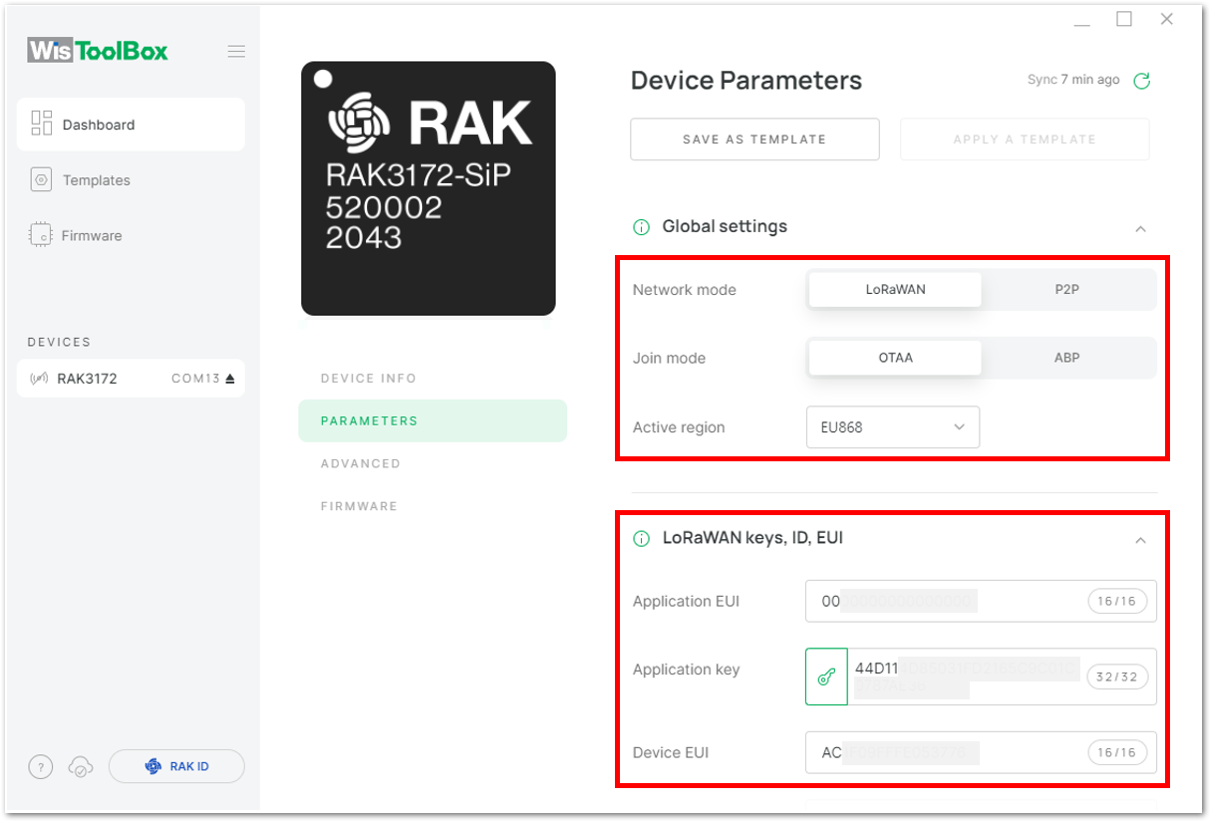 Figure 1: Global settings and LoRaWAN keys, ID, EUI details
Figure 1: Global settings and LoRaWAN keys, ID, EUI details-
Now you have a configured OTAA device using WisToolBox Console. You can now join the network using the WisToolBox console.
-
To do this, you need to go again to the WisToolBox console and type AT+JOIN. Then edit it to AT+JOIN=1 then press Enter to join the network.
AT+JOIN command parameters are optional. You can configure the settings for auto-join, reattempt interval, and the number of join attempts if your application needs it. If not configured, it will use the default parameter values.
AT+JOIN and AT+JOIN=1 also share the common functionality of trying to join the network.
Join command format: AT+JOIN=w:x:y:z
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| w | Join command - 1: joining, 0: stop joining. |
| x | Auto-join config - 1: auto-join on power-up, 0: no auto-join |
| y | Reattempt interval in seconds (7-255) - 8 is the default. |
| z | Number of join attempts (0-255) - 0 is the default. |
After 5 or 6 seconds, if the request is successfully received by a LoRa gateway, you should see a +EVT:JOINED status reply, as shown in the figure below:
If the OTAA device failed to join, you need to check if your device is within reach of a working LoRaWAN gateway that is configured to connect to TTN. It is also important to check that all your OTAA parameters (DEVEUI, APPEUI, and APPKEY) are correct using the AT+DEVEUI=?, AT+APPEUI=?, and AT+APPKEY=? commands. Lastly, ensure that the antenna of your device is properly connected.
After checking all the things above, try to join again.
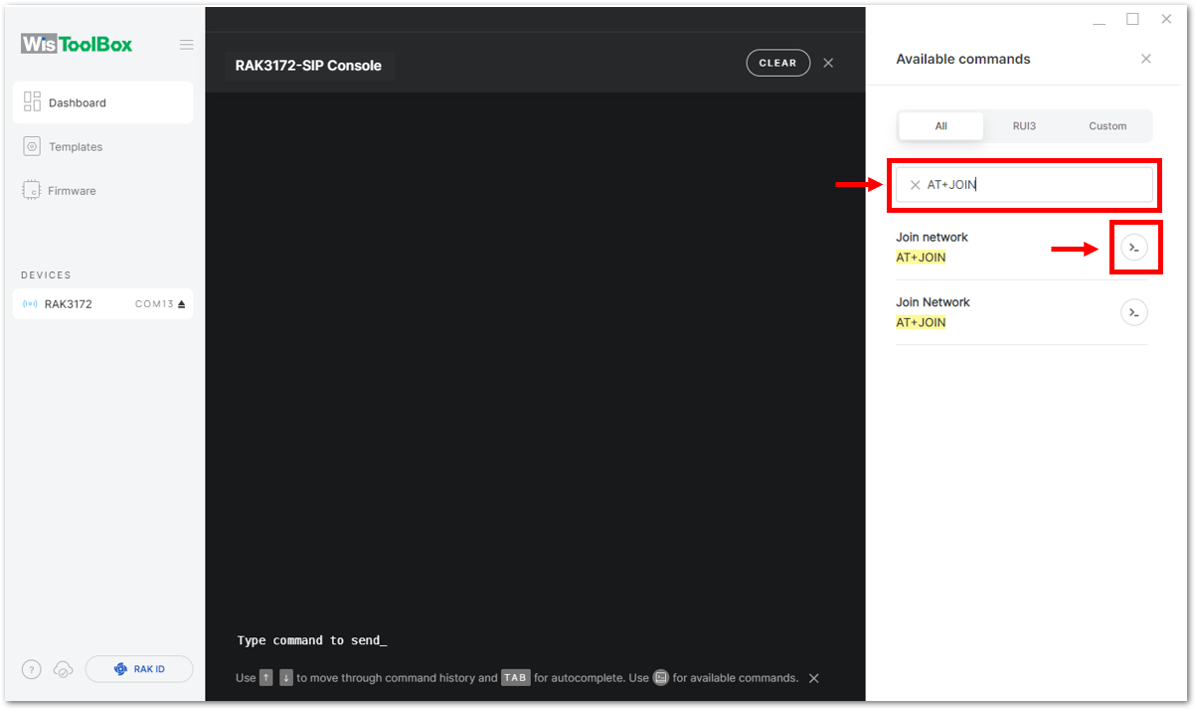 Figure 1: Joining mode using WisToolBox Console
Figure 1: Joining mode using WisToolBox Console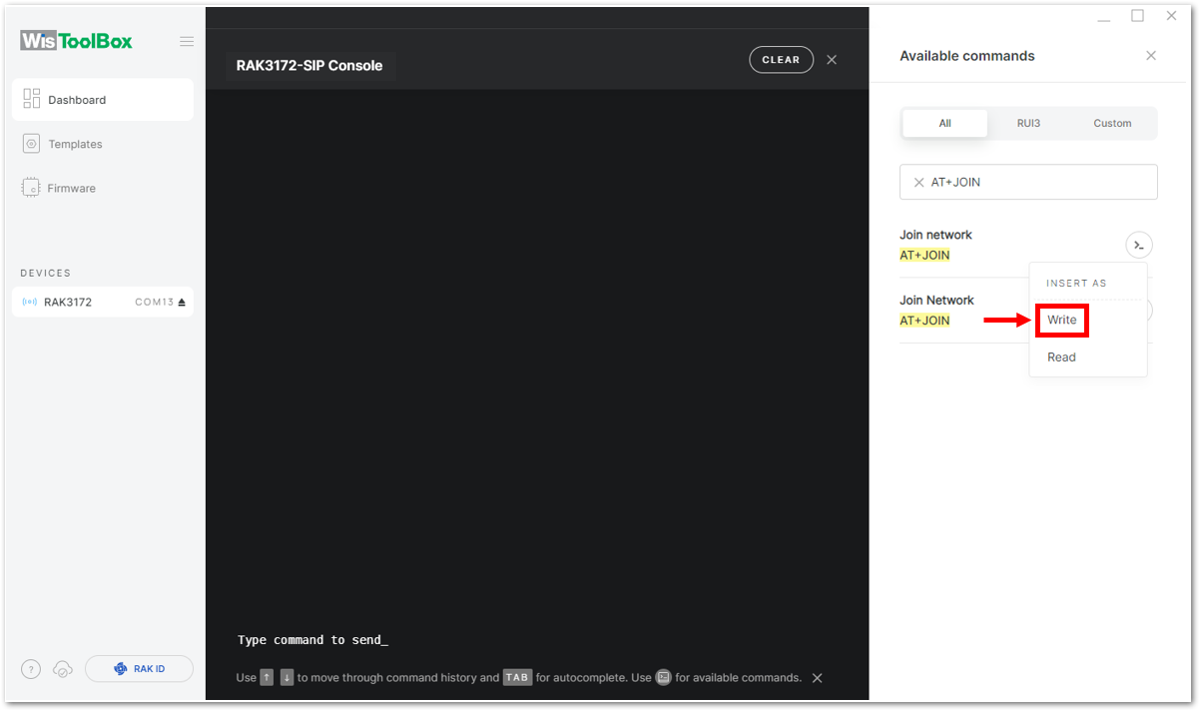 Figure 1: Joining mode using WisToolBox Console
Figure 1: Joining mode using WisToolBox Console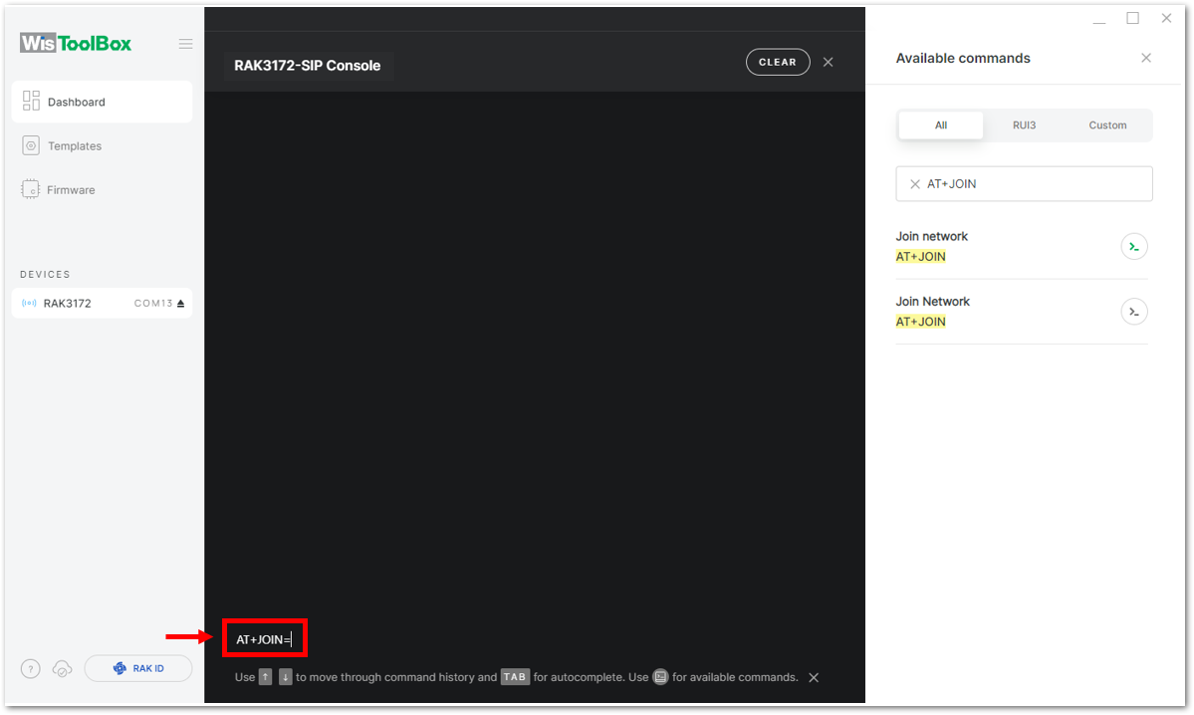 Figure 1: Joining mode using WisToolBox Console
Figure 1: Joining mode using WisToolBox Console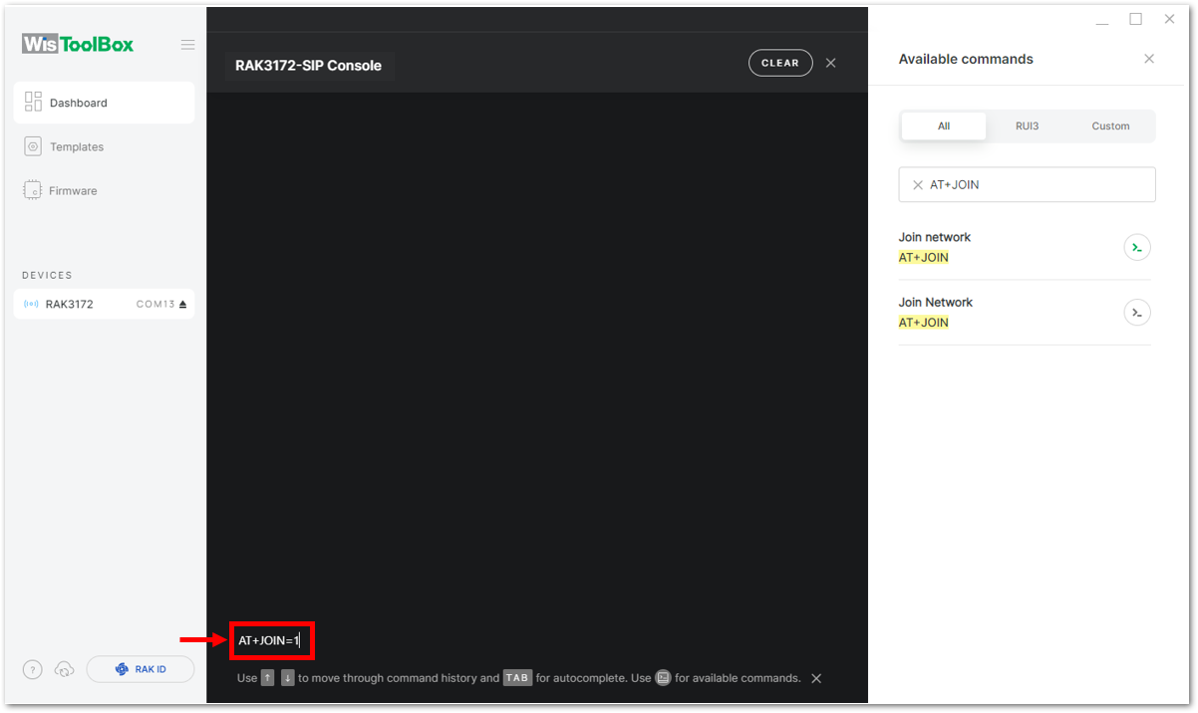 Figure 1: Joining mode using WisToolBox Console
Figure 1: Joining mode using WisToolBox Console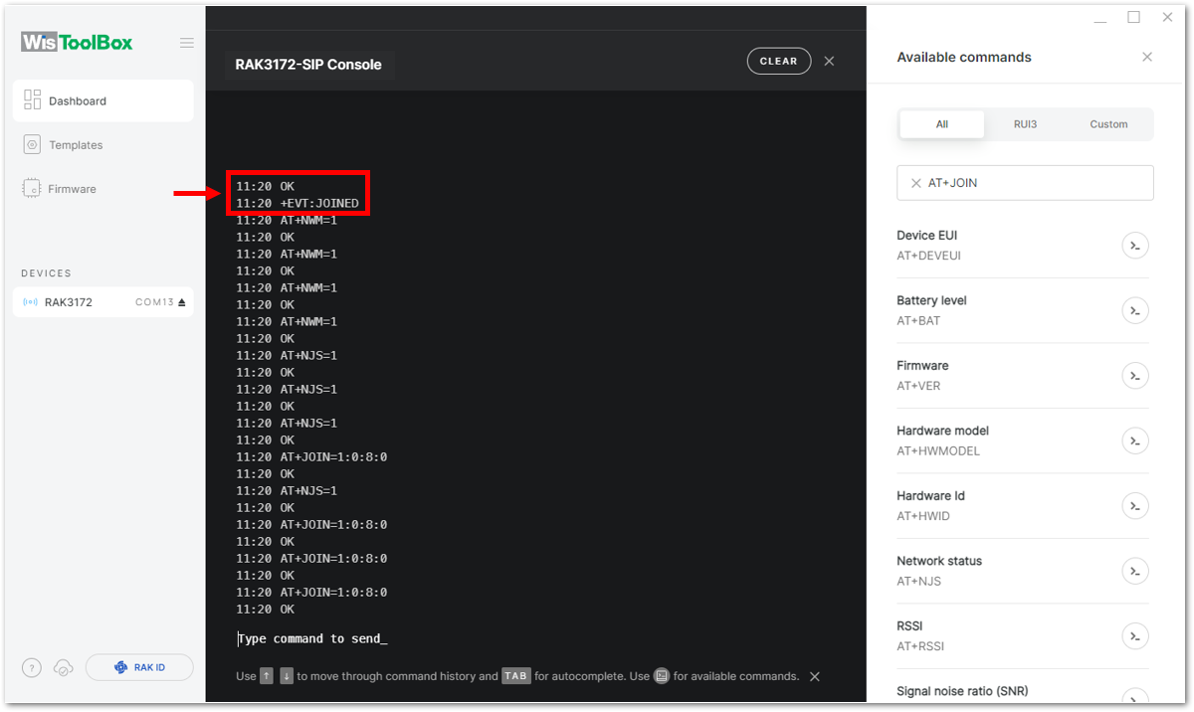 Figure 1: OTAA device successfully joined the network
Figure 1: OTAA device successfully joined the network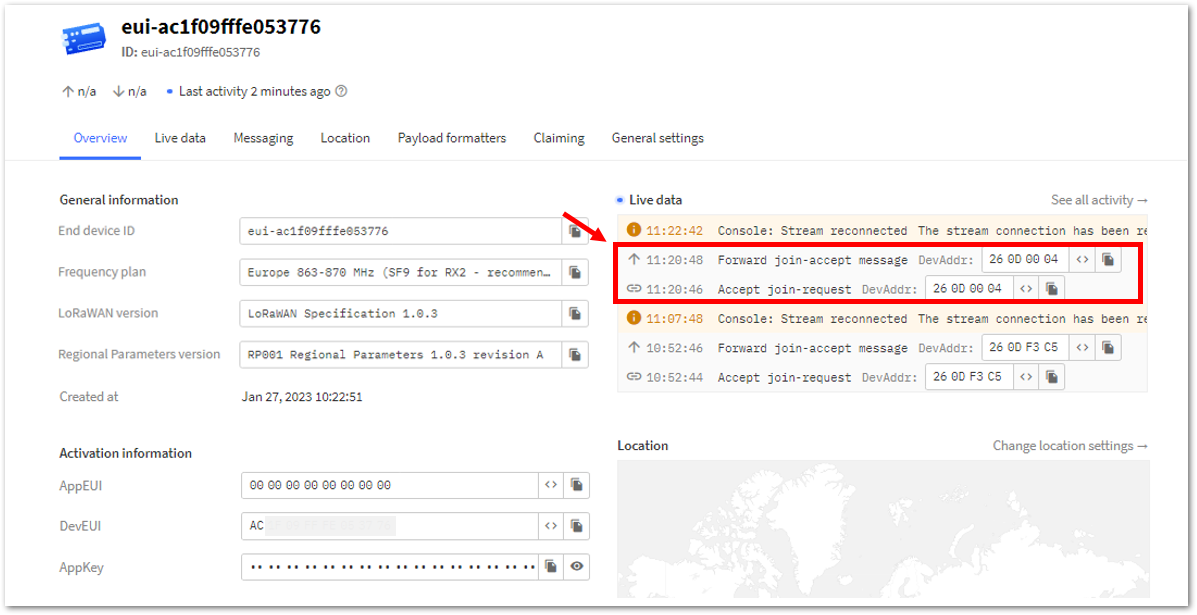 Figure 1: OTAA device successfully joined the network
Figure 1: OTAA device successfully joined the network- With the end-device properly joined to the TTN, try to send some payload after a successful join. Send command format:
AT+SEND=<port>:<payload>
AT+SEND=2:12345678
 Figure 1: OTAA device sending payload to the network
Figure 1: OTAA device sending payload to the network Figure 1: OTAA device sending payload to the network
Figure 1: OTAA device sending payload to the network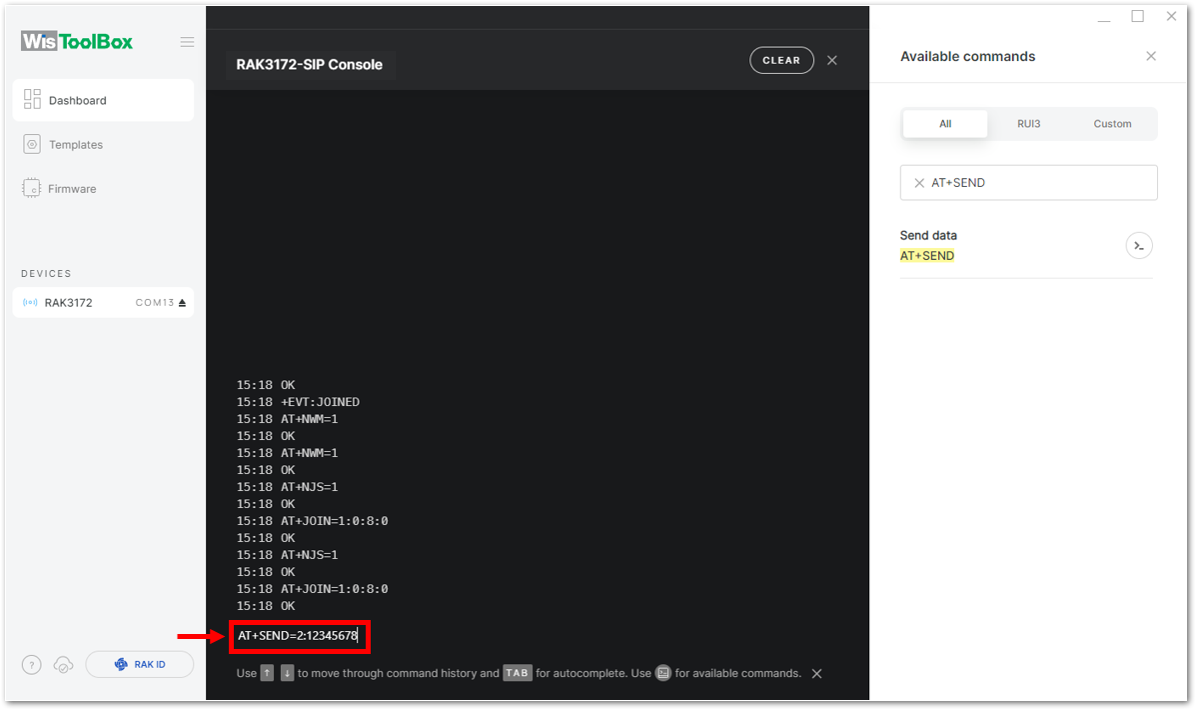 Figure 1: OTAA device sending payload to the network
Figure 1: OTAA device sending payload to the network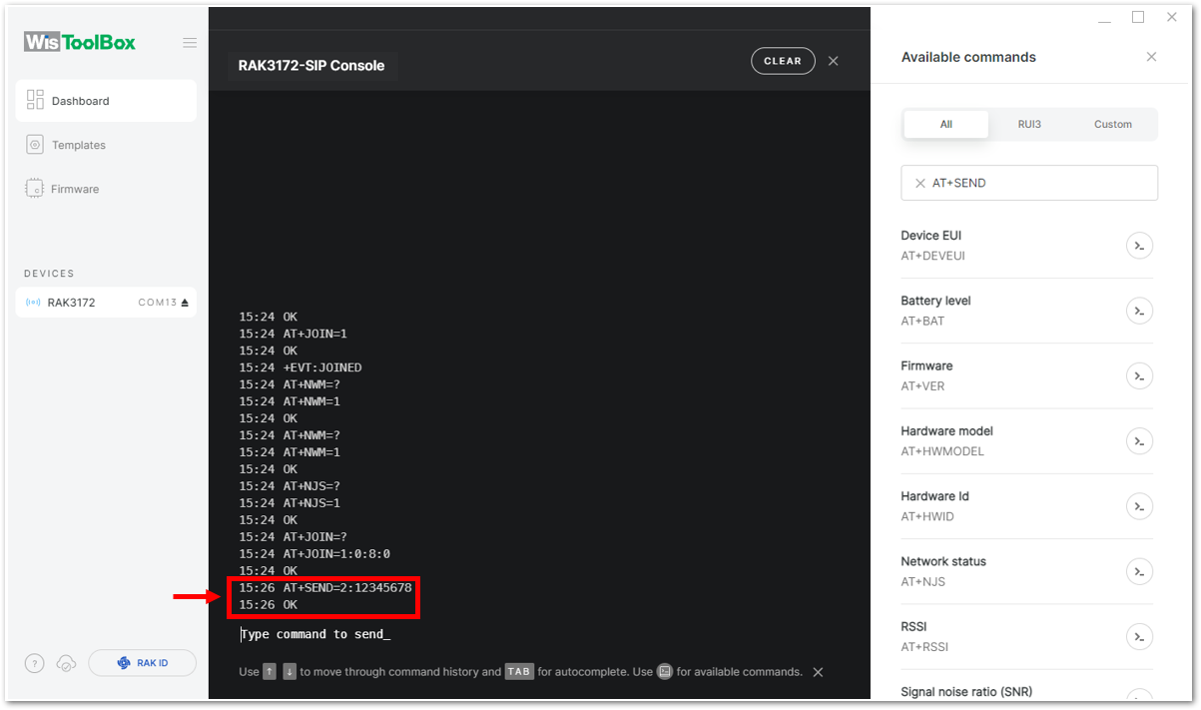 Figure 1: OTAA device sending payload to the network
Figure 1: OTAA device sending payload to the network- You can see the data sent by the RAK3172-SiP module on the TTN device console Live data section. Also, the Last seen info should be a few seconds or minutes ago.
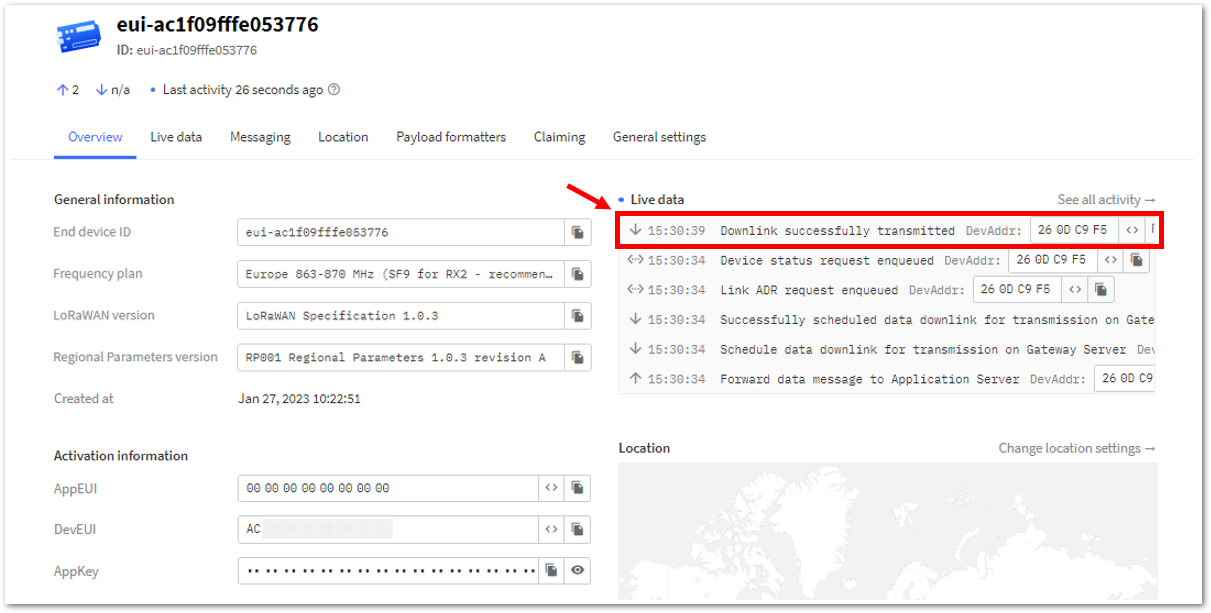 Figure 1: OTAA Test Sample Data Sent Viewed in TTN
Figure 1: OTAA Test Sample Data Sent Viewed in TTNTTN ABP Device Registration
- To register an ABP device, go to your application console and select the application to which you want your device to be added. Then click + Register end device, as shown in Figure 120.
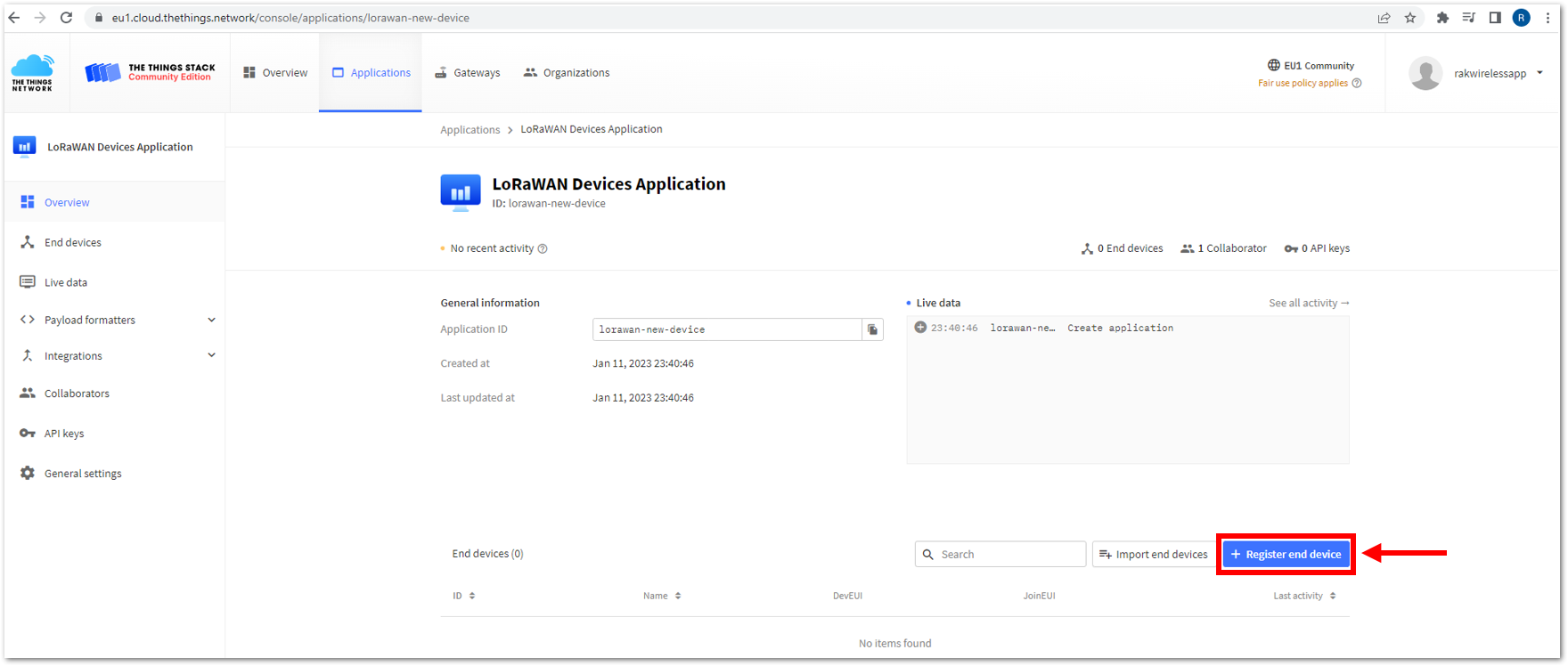 Figure 1: Adding ABP Device
Figure 1: Adding ABP Device- To register the board, click the Enter end device specifics manually.
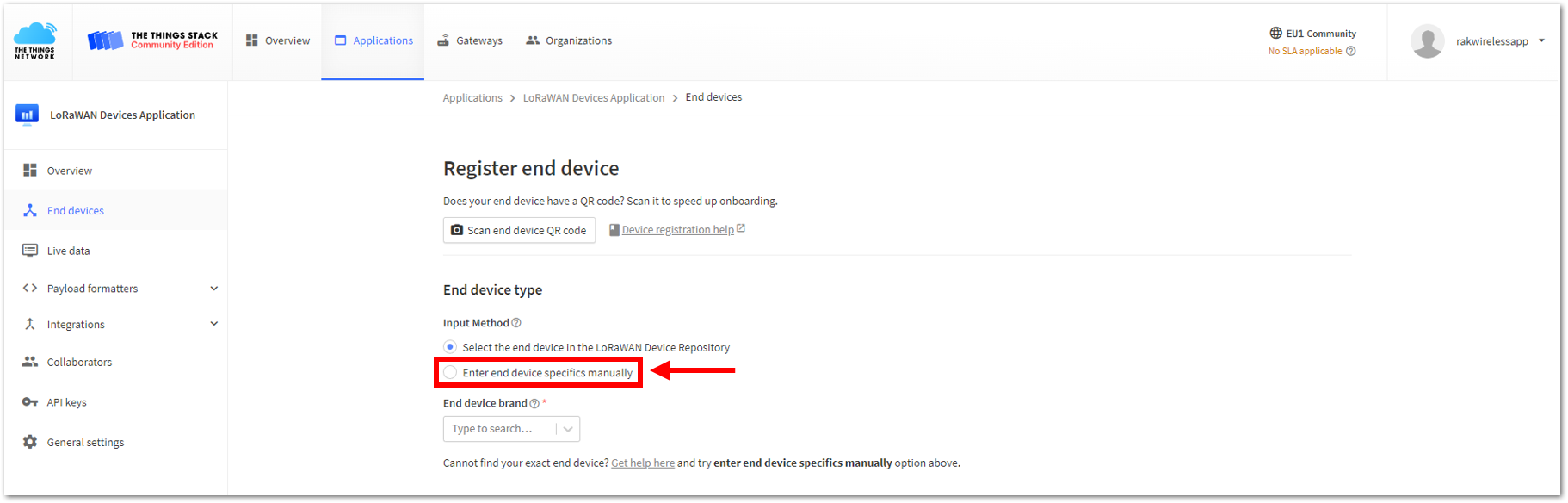 Figure 1: Enter end device specifics manually
Figure 1: Enter end device specifics manually- Next step is to set up Frequency plan, compatible LoRaWAN version, and Regional Parameters version supported.
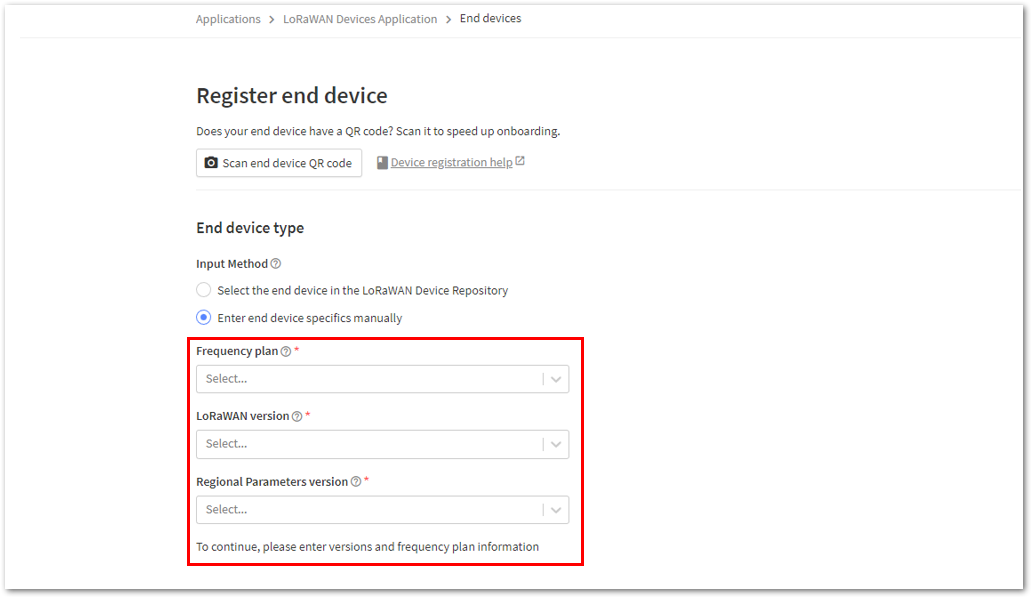 Figure 1: Setting up for your device
Figure 1: Setting up for your device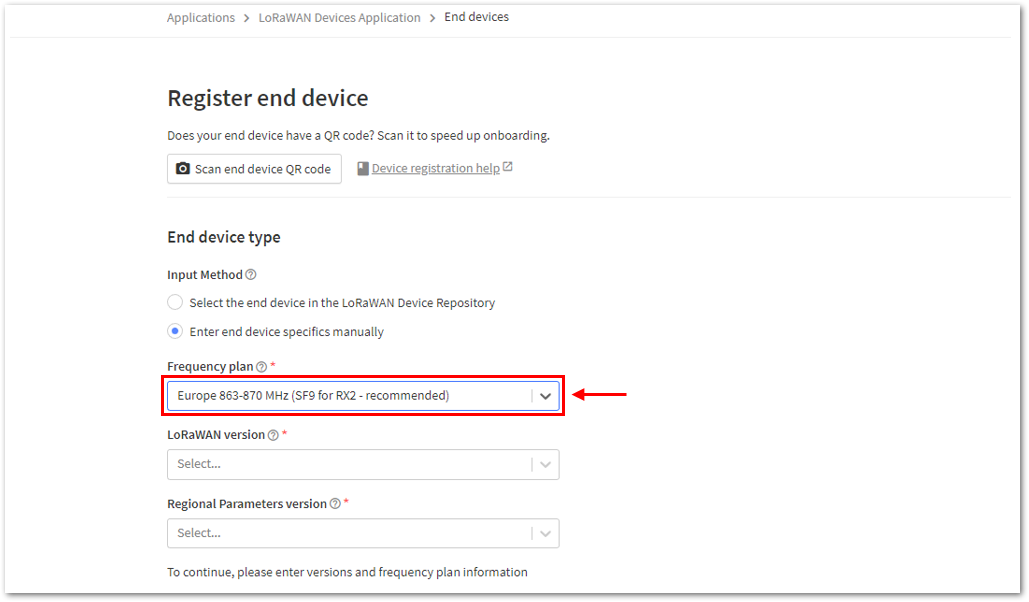 Figure 1: Setting up for your device
Figure 1: Setting up for your device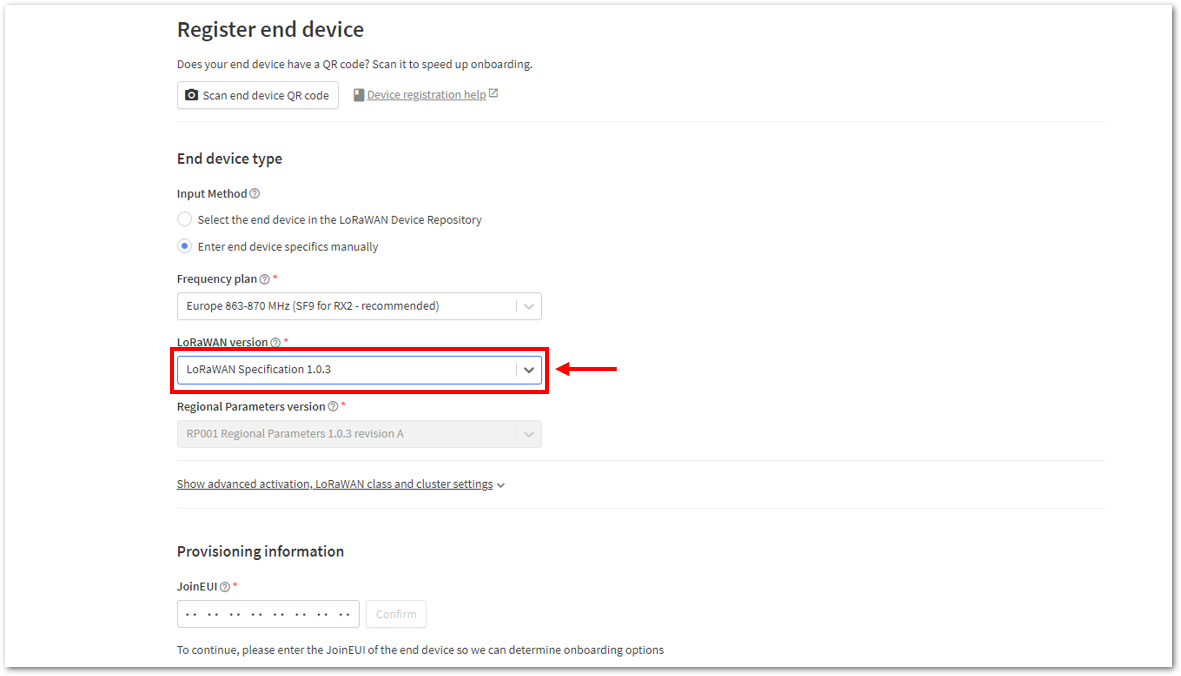 Figure 1: Setting up for your device
Figure 1: Setting up for your device- Then click Show advanced activation, LoRaWAN class and cluster settings. Configure the activation mode by selecting Activation by personalization (ABP) and Additional LoRaWAN class capabilities to class A only.
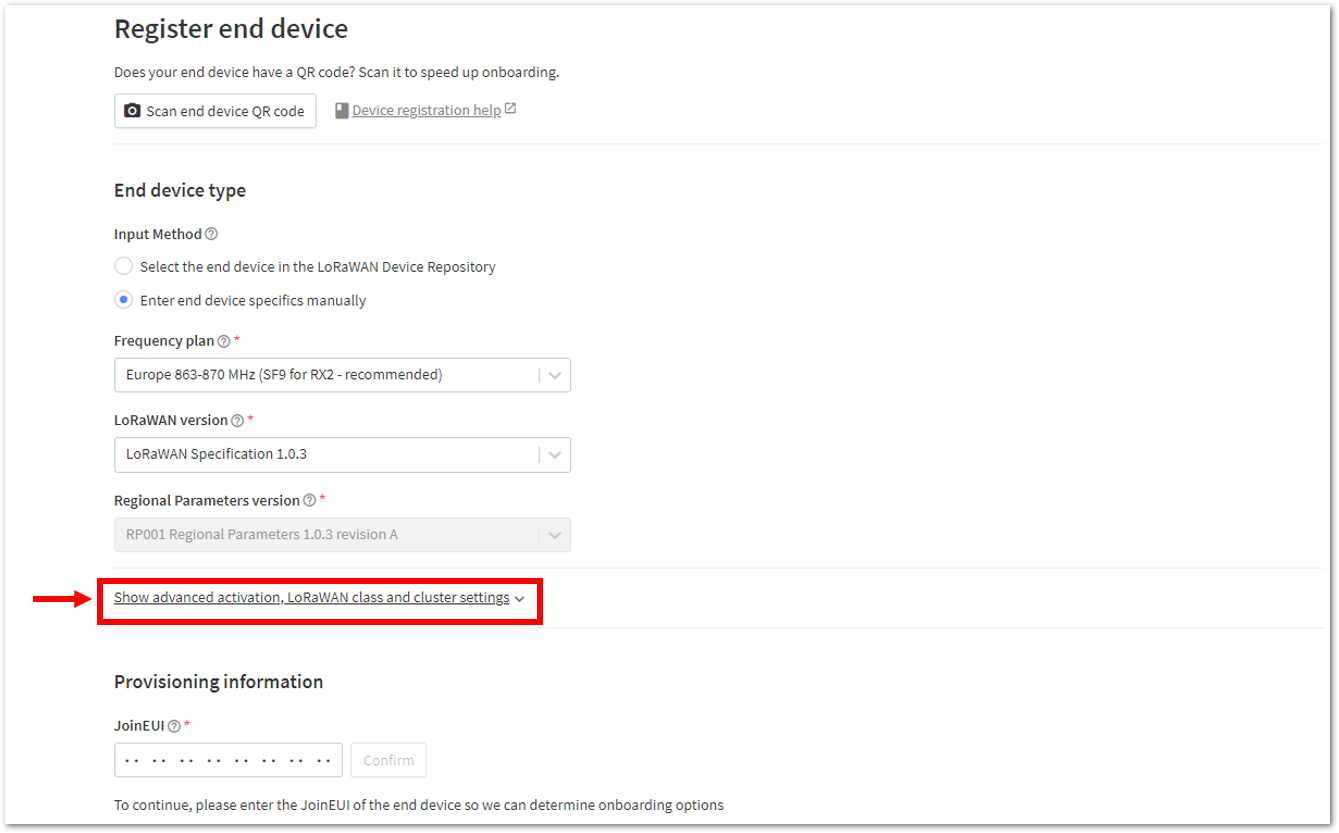 Figure 1: Setting up for your device
Figure 1: Setting up for your device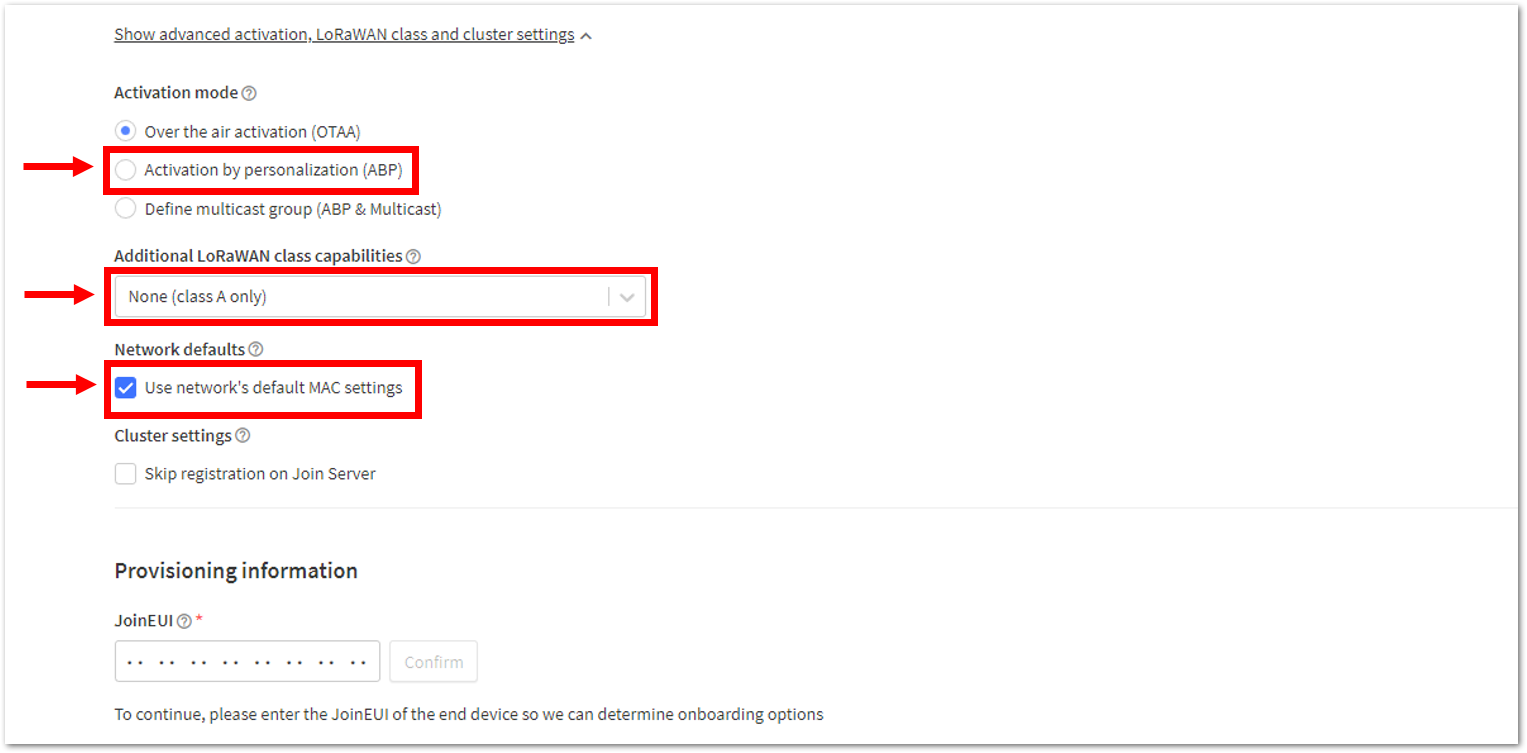 Figure 1: Setting up for your device
Figure 1: Setting up for your device- Once done, provide the DevEUI credentials of your device into the DevEUI portion. This will automatically generate the specific End device ID of your board. Then click Generate under Device address, AppSKey, and NwkSKey under the Provisioning information section. Then click Register end device.
The DevEUI, Device address, AppSKey, and NwkSKey are hidden in this section as these are unique from a specific device. The DevEUI credential is unique to every RAK3172-SiP device. Also, you should generate your own Device address, AppSKey, and NwkSKey credentials for your specific device and application.
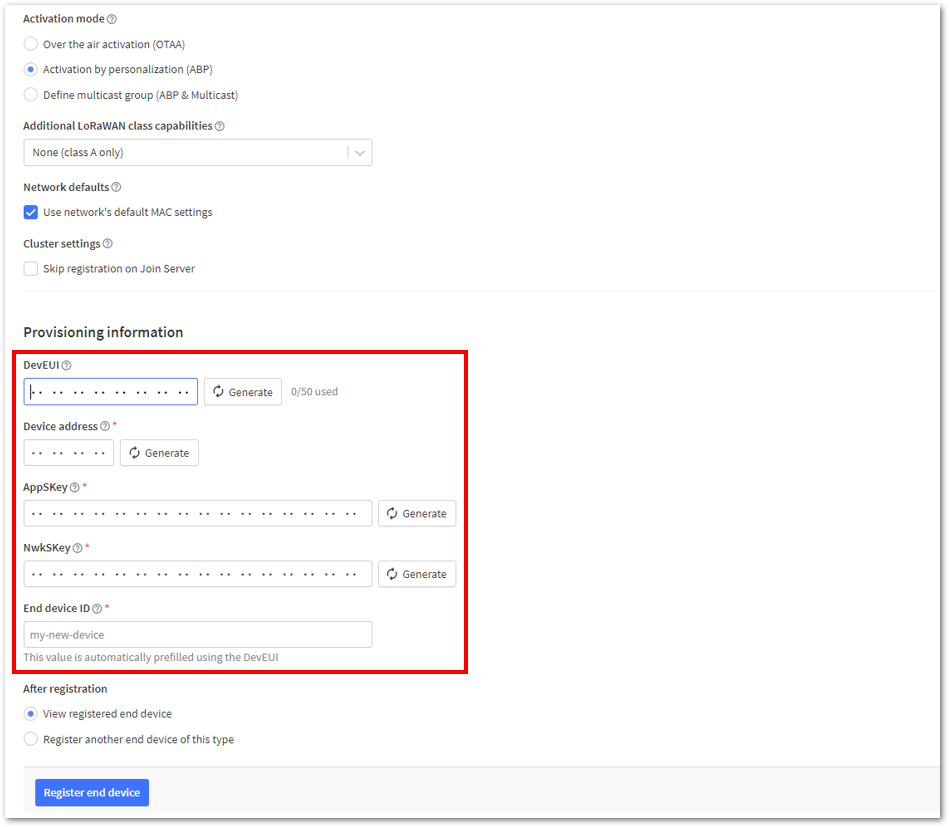 Figure 1: Setting up for your device
Figure 1: Setting up for your device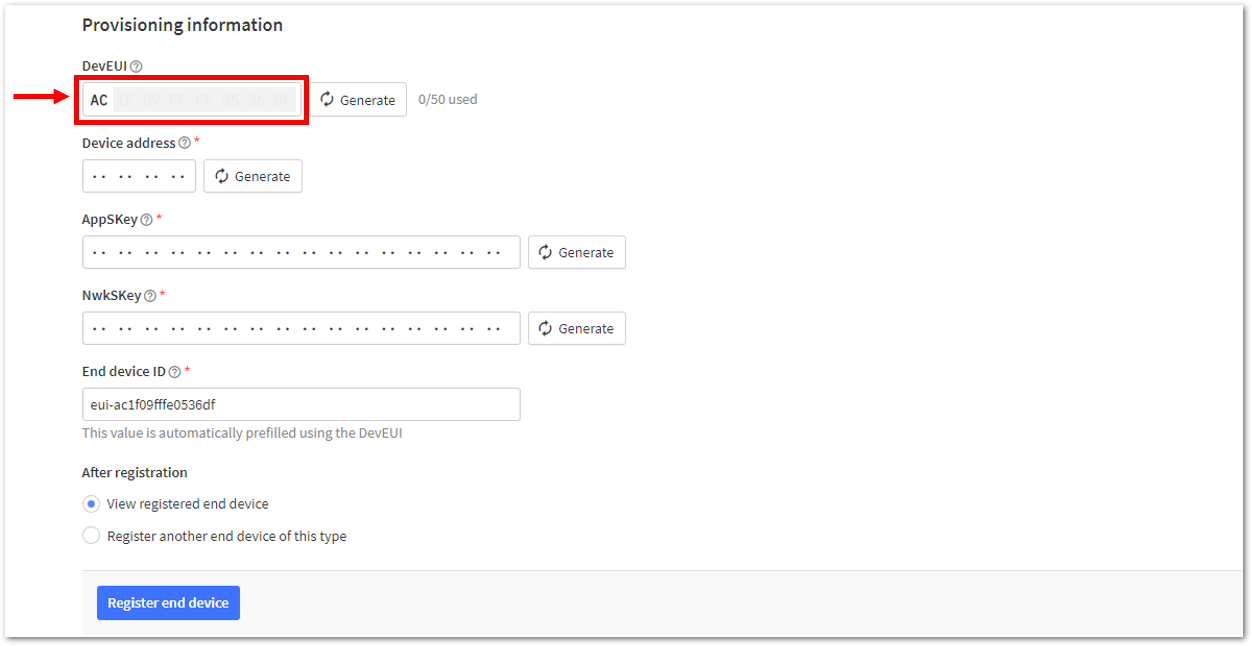 Figure 1: Setting up for your device
Figure 1: Setting up for your device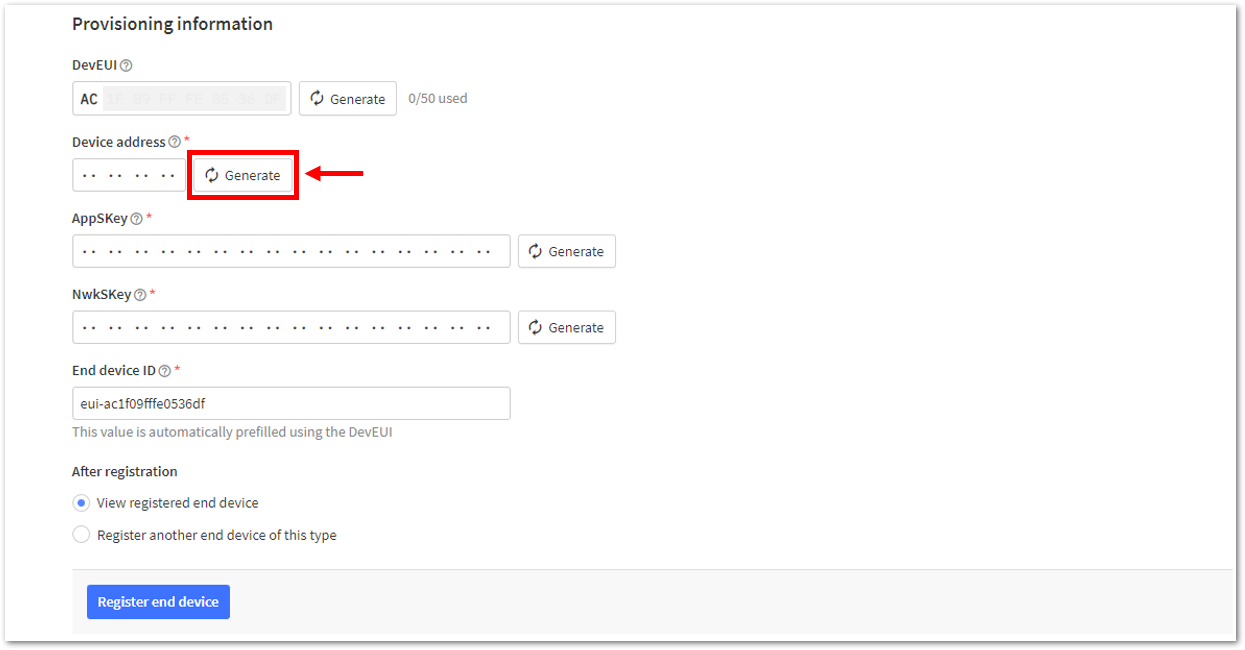 Figure 1: Setting up for your device
Figure 1: Setting up for your device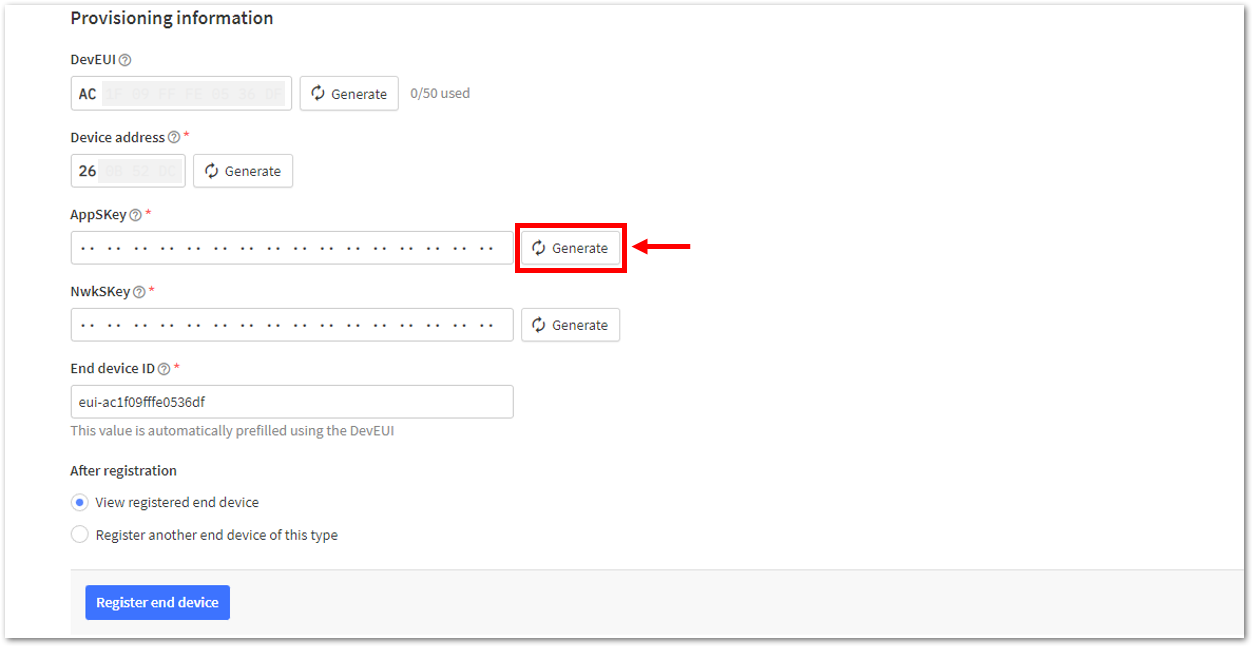 Figure 1: Setting up for your device
Figure 1: Setting up for your device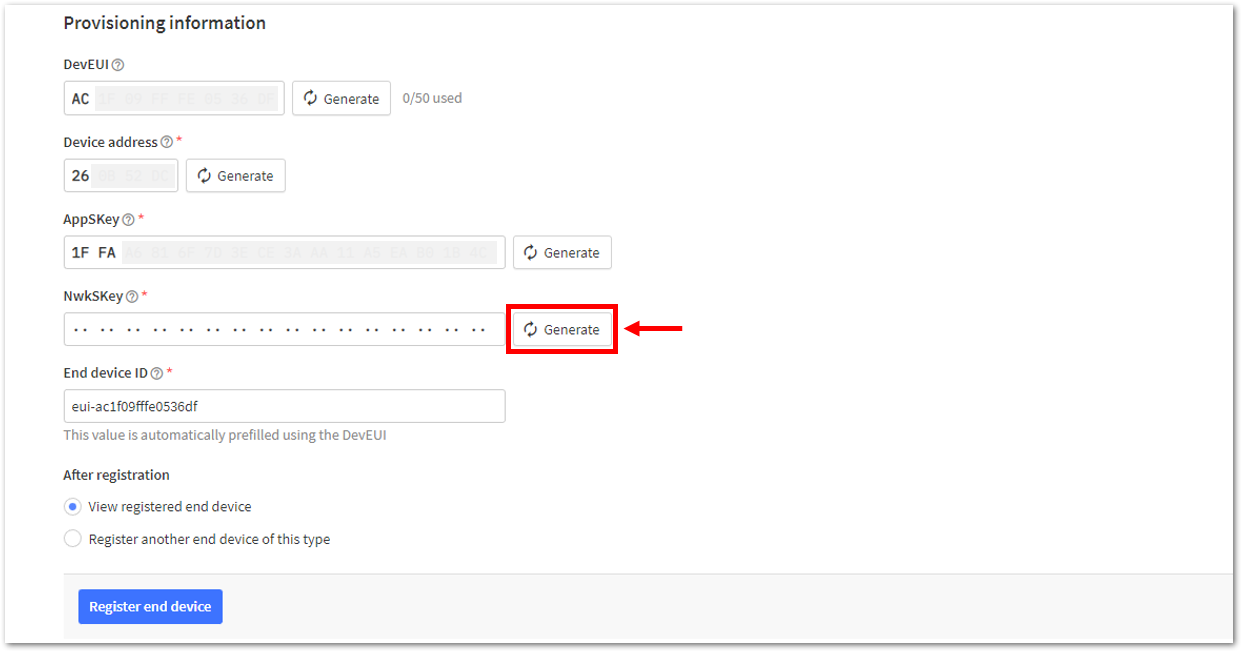 Figure 1: Setting up for your device
Figure 1: Setting up for your device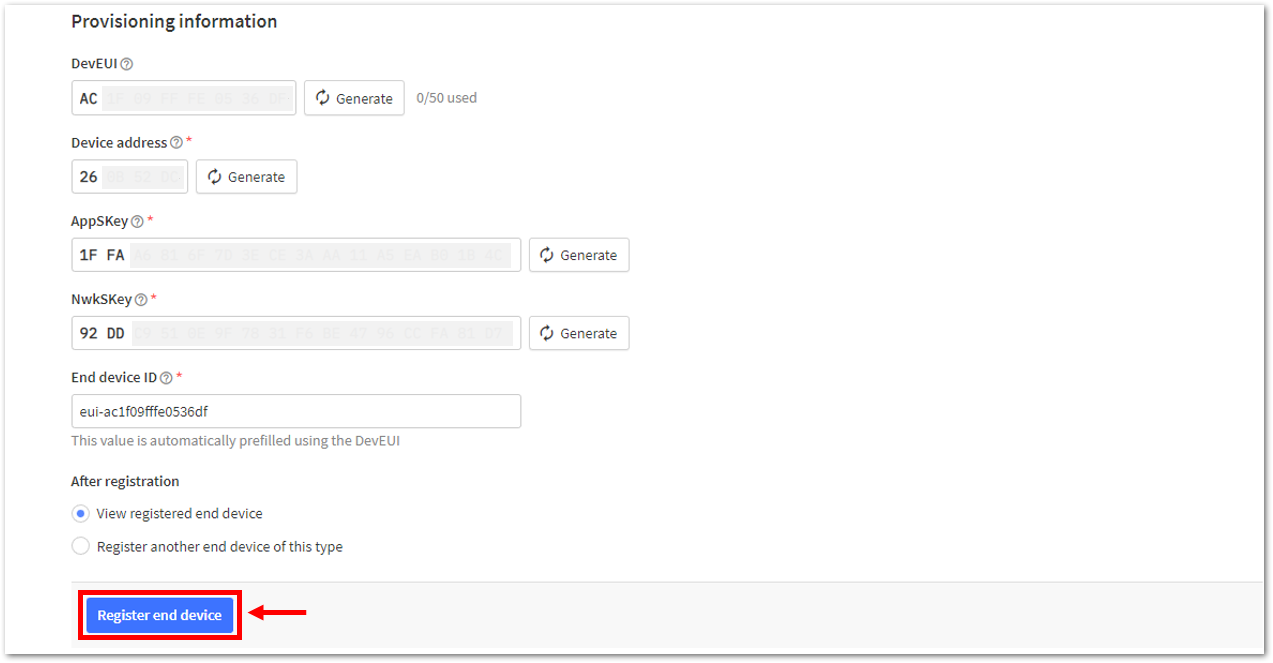 Figure 1: Register end device
Figure 1: Register end device- You should now be able to see the device on the TTN console after you fully register your device, as shown in Figure 133.
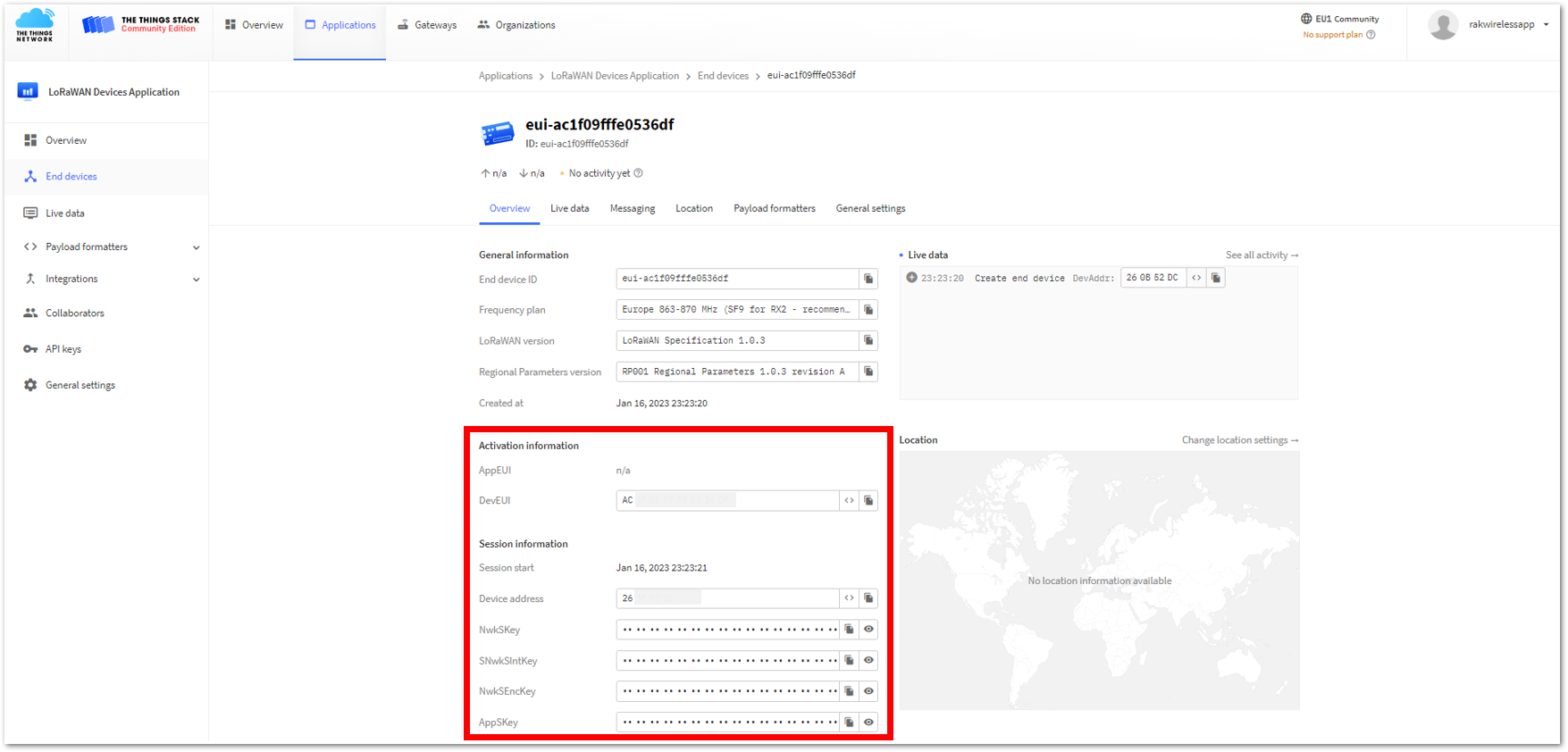 Figure 1: ABP device successfully registered to TTN
Figure 1: ABP device successfully registered to TTNABP Configuration for TTN
The RAK3172-SiP module can be configured using WisToolBox to do the ABP configuration. WisToolBox is a software tool that supports RAK3172-SiP module. It automatically detects the RAK3172-SiP module once connected to the PC. Below are the options in WisToolBox that the ABP configuration can be done.
ABP Configuration for TTN via WisToolBox UI
The RAK3172-SiP should have the correct ABP credentials to connect to TTN. This can be done using WisToolBox. Below are the steps on setting up your RAK3172-SiP using WisToolBox.
-
Connect your RAK3172-SiP with your chosen WisBlock base board to the PC via USB cable and open the WisToolBox application.
-
Click the CONNECT DEVICE button to launch the WisToolBox Dashboard.
 Figure 1: CONNECT DEVICE
Figure 1: CONNECT DEVICE- Then select your target port where your RAK3172-SiP is connected. Once recognized, click CONNECT as shown in Figure 136.
 Figure 1: Setting up your device
Figure 1: Setting up your device Figure 1: Setting up your device
Figure 1: Setting up your device- Once done, RAK3172-SiP will appear in the dashboard then select it.
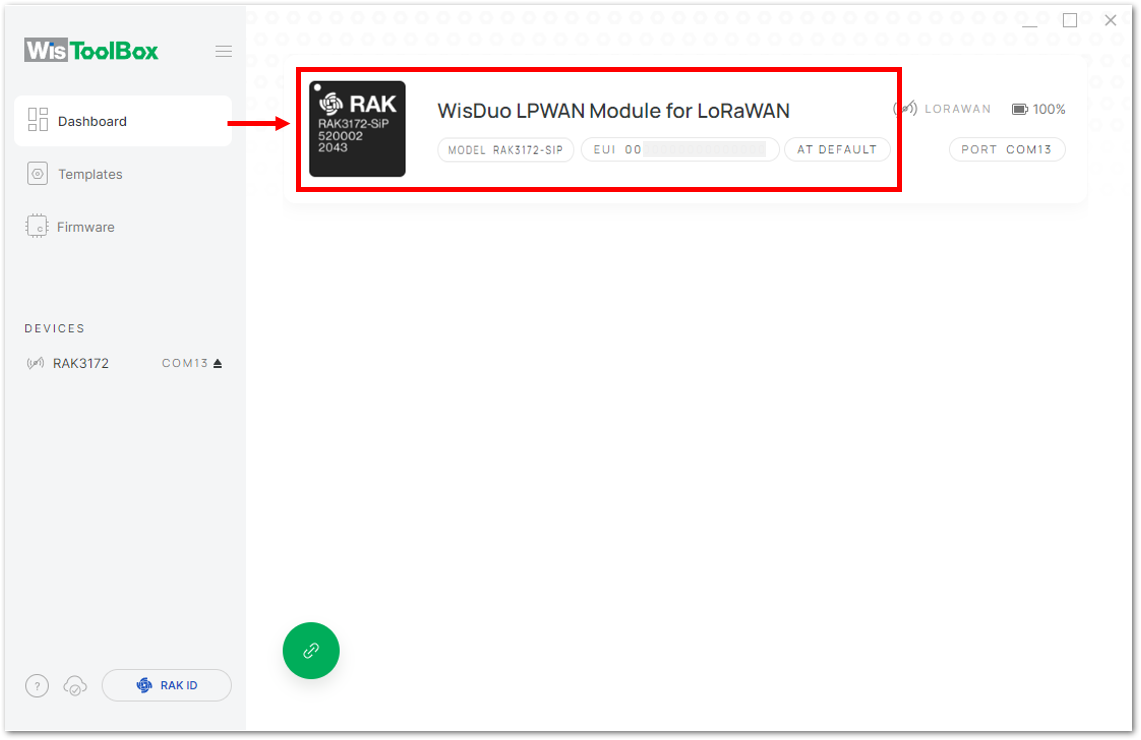 Figure 1: Device seen from WisToolBox dashboard
Figure 1: Device seen from WisToolBox dashboard- Then click PARAMETERS to do the configuration in your RAK3172-SiP.
The AppSKey, Device address, and NwkSKey are hidden in this section as these are unique from a specific device.
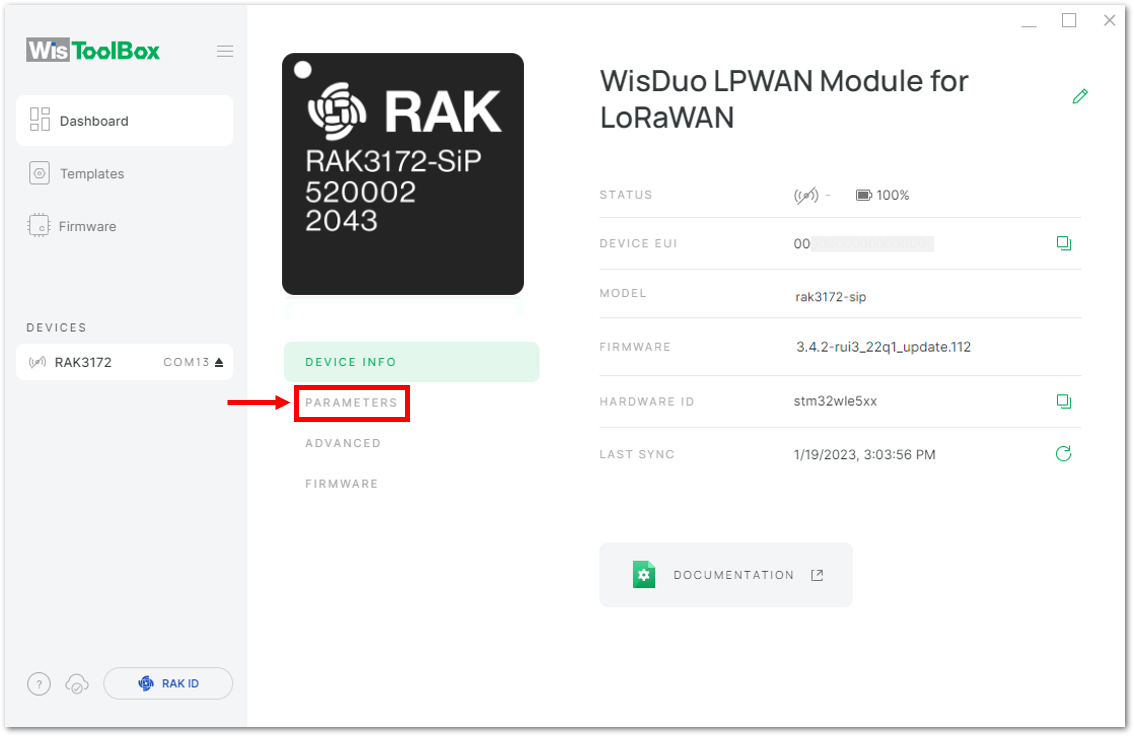 Figure 1: Setting up your device
Figure 1: Setting up your device- Click Global settings to set the network mode into LoRaWAN and join mode to ABP. Make sure that the active region is using EU868 for this configuration. If you wish to work on other regional bands, you can choose among active regions based on your location.
- LoRa network mode: LoRaWAN
- LoRaWAN join mode: ABP
- LoRaWAN region: EU868
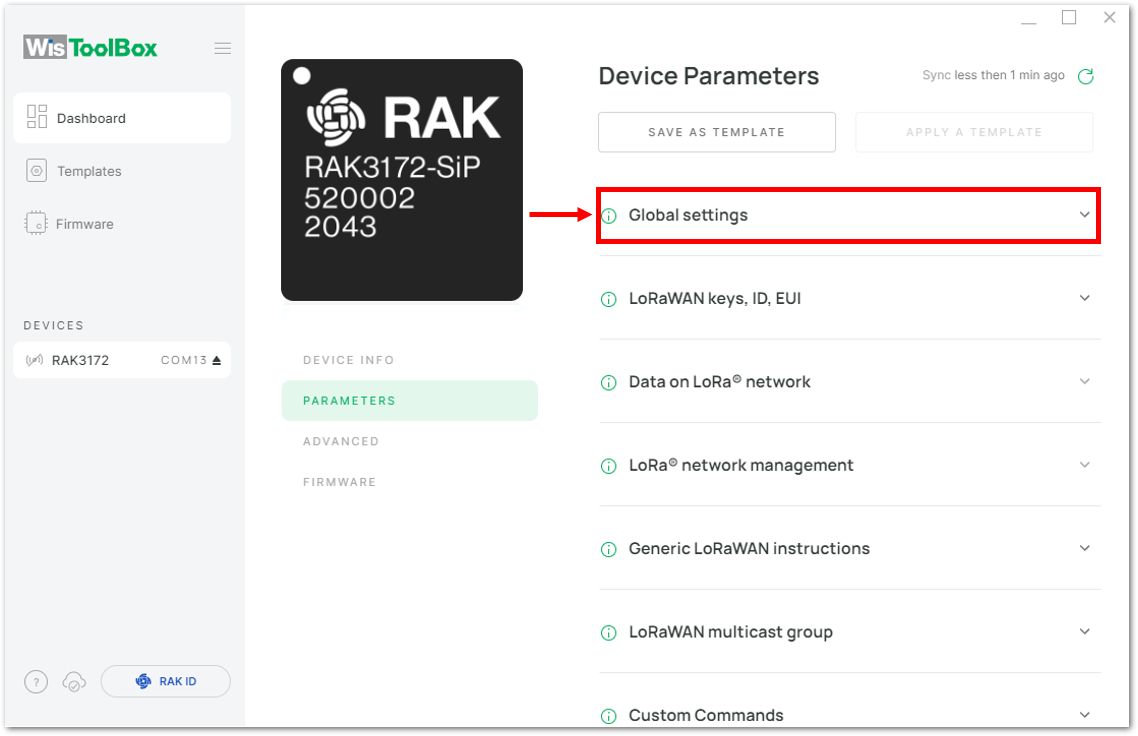 Figure 1: Global settings
Figure 1: Global settings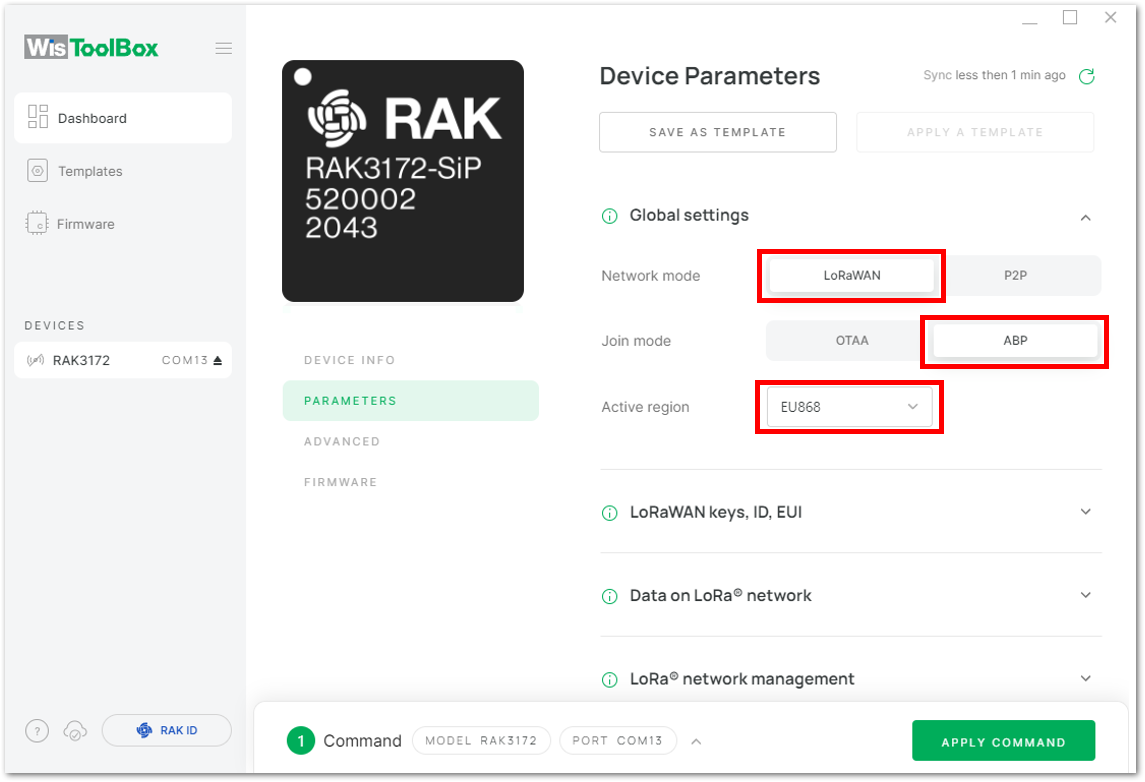 Figure 1: Global settings
Figure 1: Global settings- Then click LoRaWAN keys, ID, EUI to configure the Application session key (AppSKey), Device address and Network session key (NwkSKey).
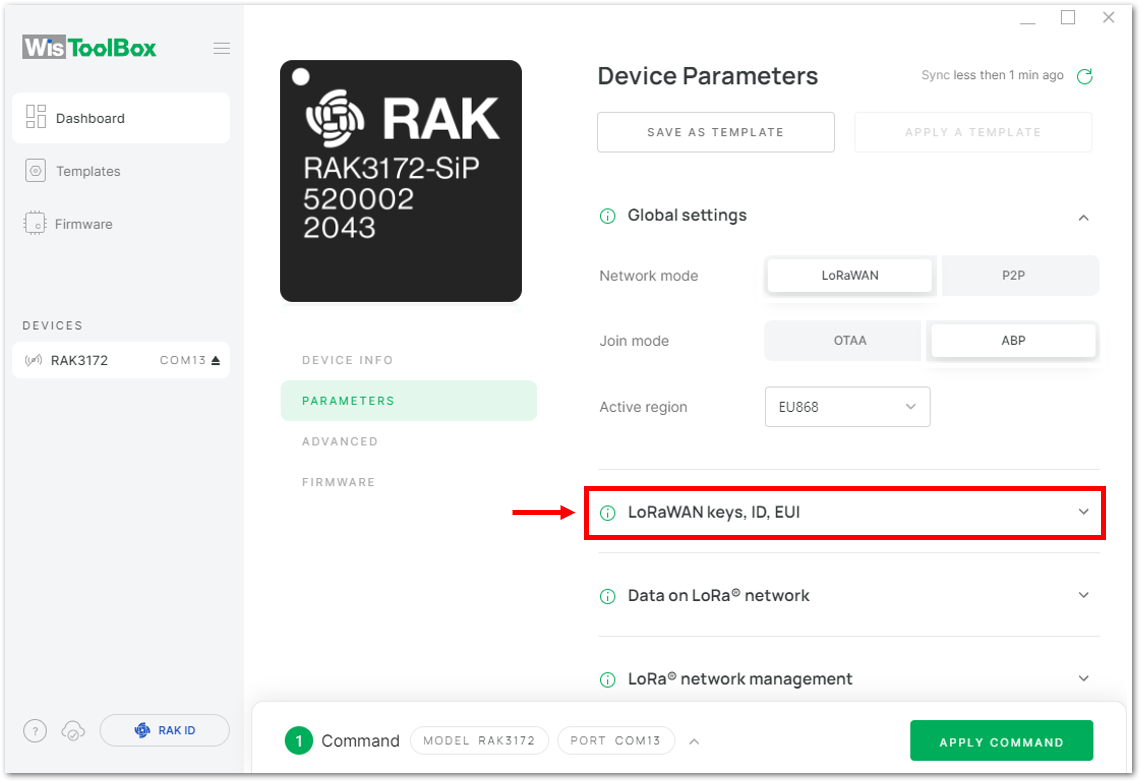 Figure 1: LoRaWAN keys, ID, EUI
Figure 1: LoRaWAN keys, ID, EUI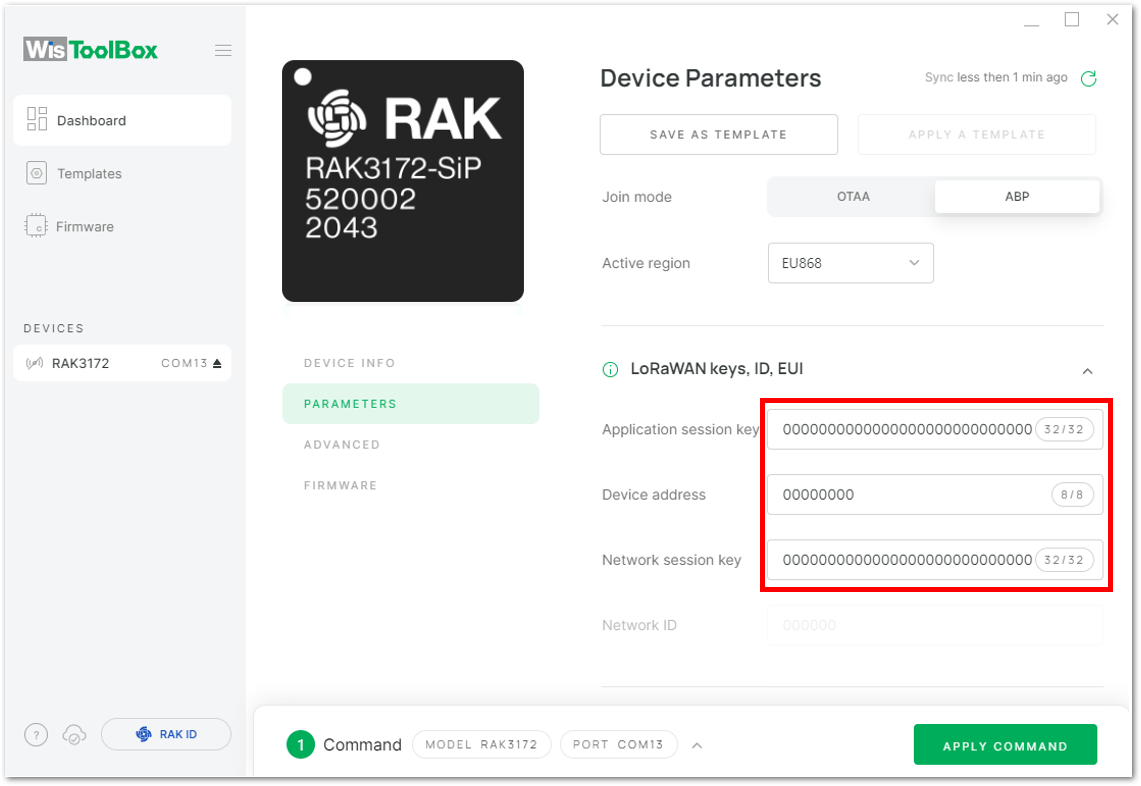 Figure 1: Setting up your device
Figure 1: Setting up your device- Then go back to the console where your RAK3172-SiP End device is created previously. Then copy all the credentials from there. Those will be the ones to be used also in the WisToolBox dashboard. Once encoded into the dashboard, click APPLY COMMANDS to update your device as shown in Figure 150.
The AppSKey, Device address, and NwkSKey are hidden in this section as these are unique from a specific device.
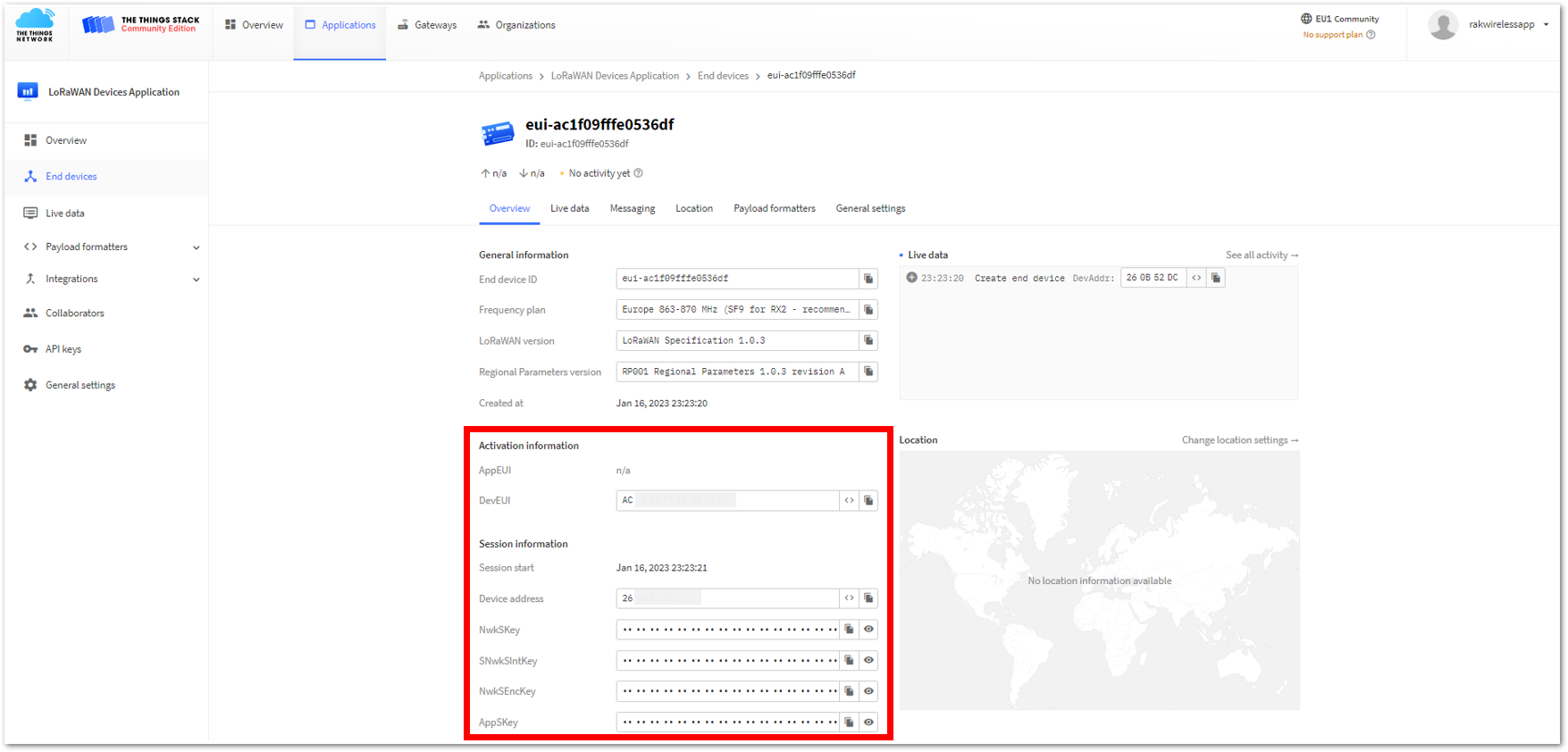 Figure 1: Your created ABP device from your console
Figure 1: Your created ABP device from your console- For Application session key (AppSKey)
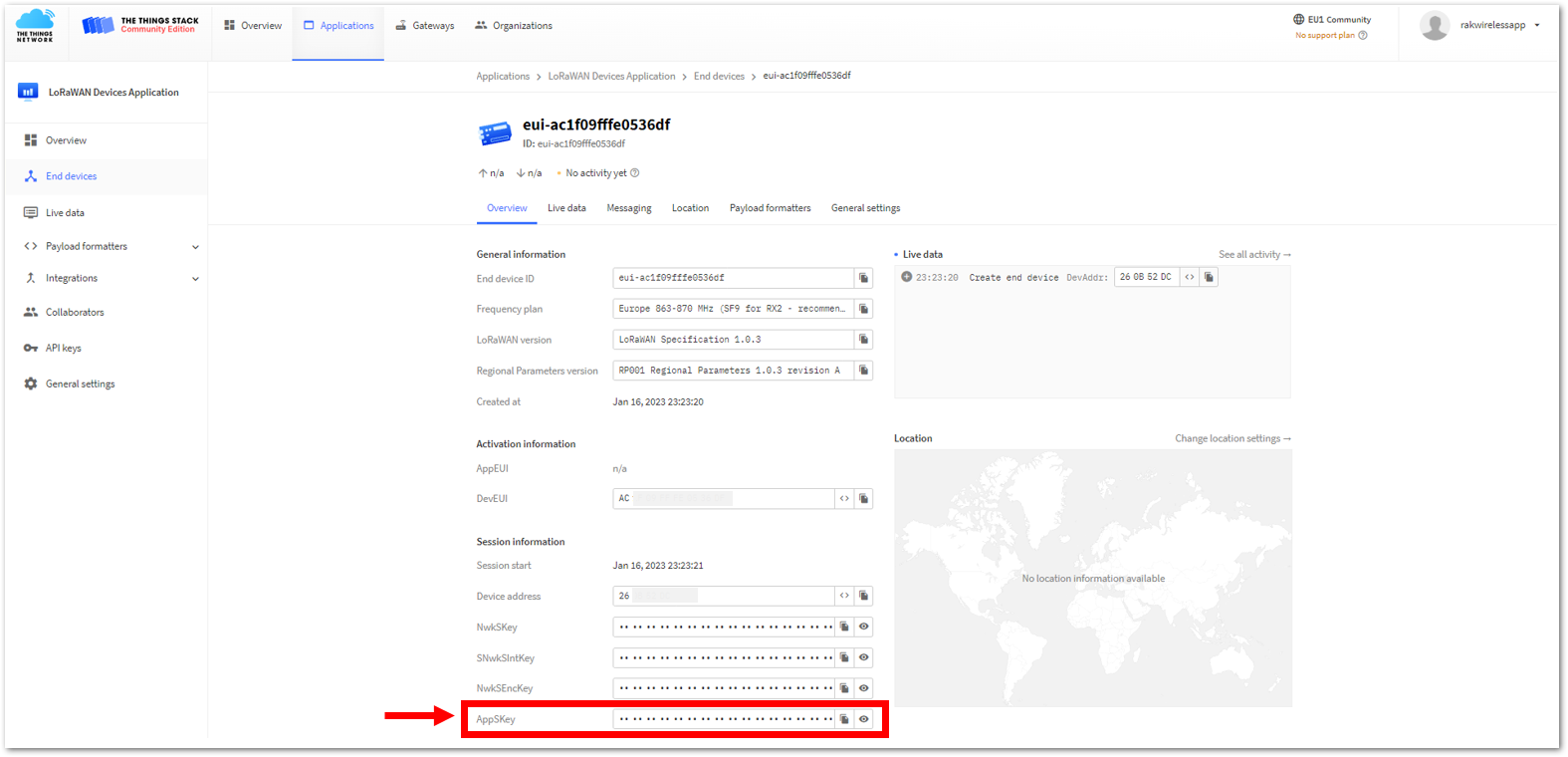 Figure 1: Copying the AppSKey credential from TTN to WisToolBox
Figure 1: Copying the AppSKey credential from TTN to WisToolBox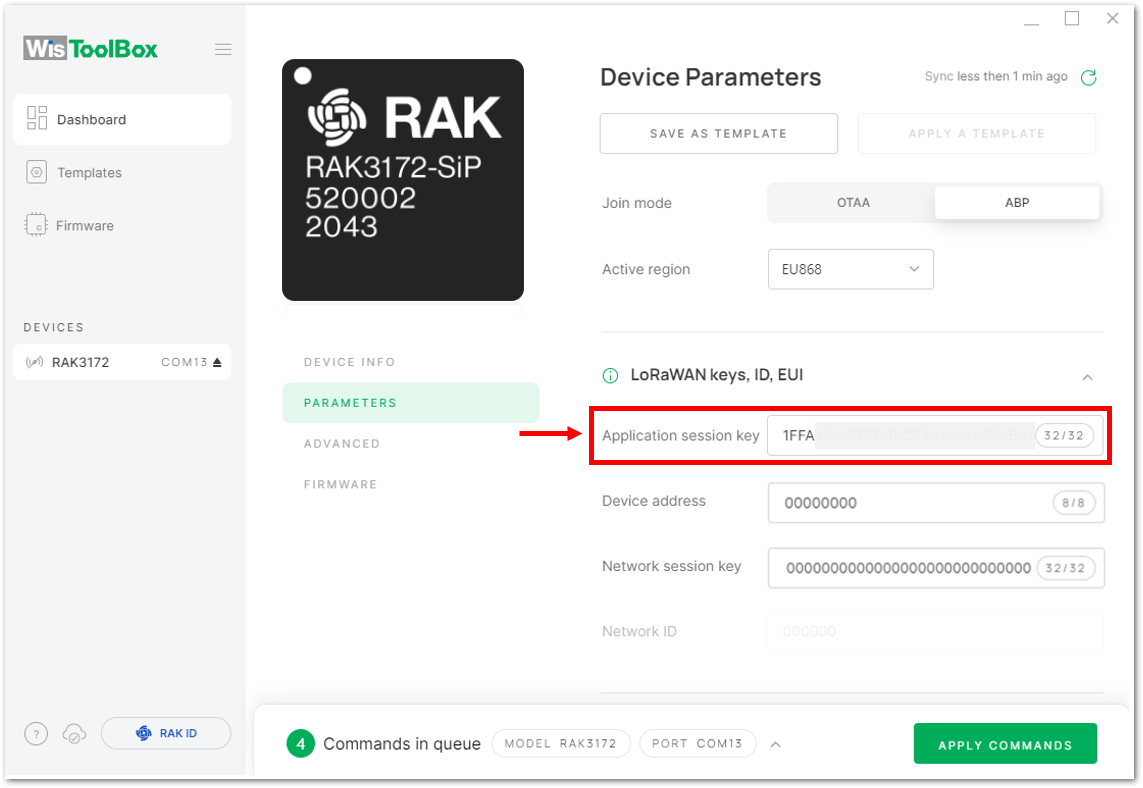 Figure 1: Copying the AppSKey credential from TTN to WisToolBox
Figure 1: Copying the AppSKey credential from TTN to WisToolBox- For Device address
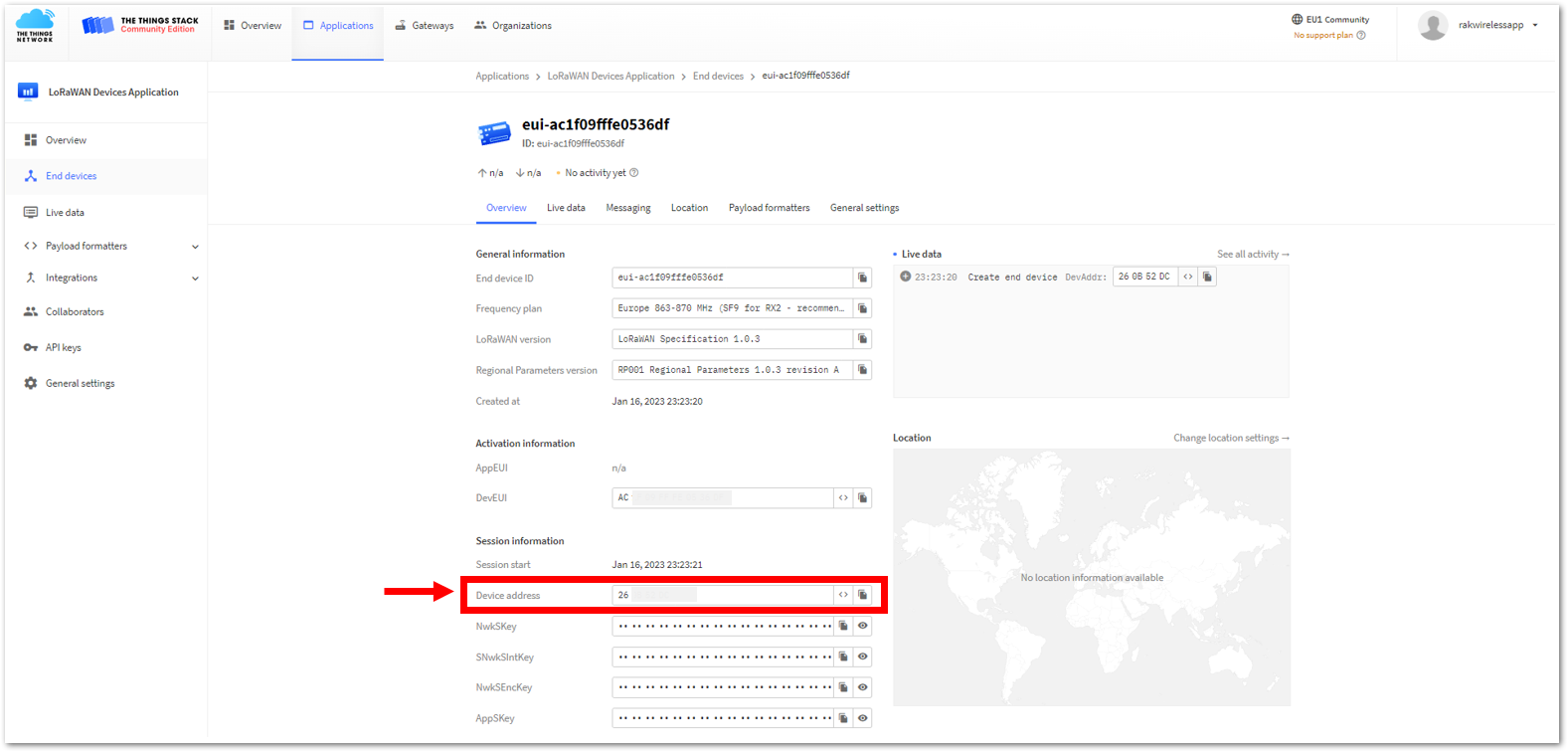 Figure 1: Copying the Device address credential from TTN to WisToolBox
Figure 1: Copying the Device address credential from TTN to WisToolBox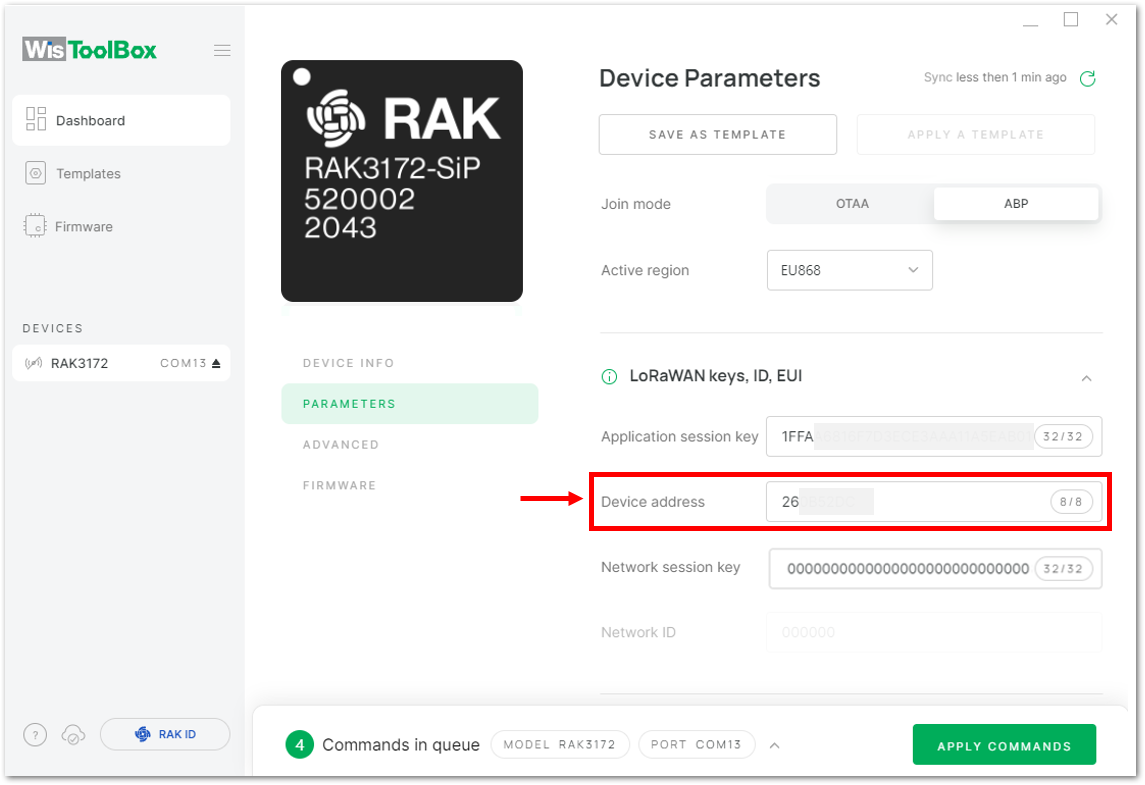 Figure 1: Copying the Device address credential from TTN to WisToolBox
Figure 1: Copying the Device address credential from TTN to WisToolBox- For Network session key (NwkSKey)
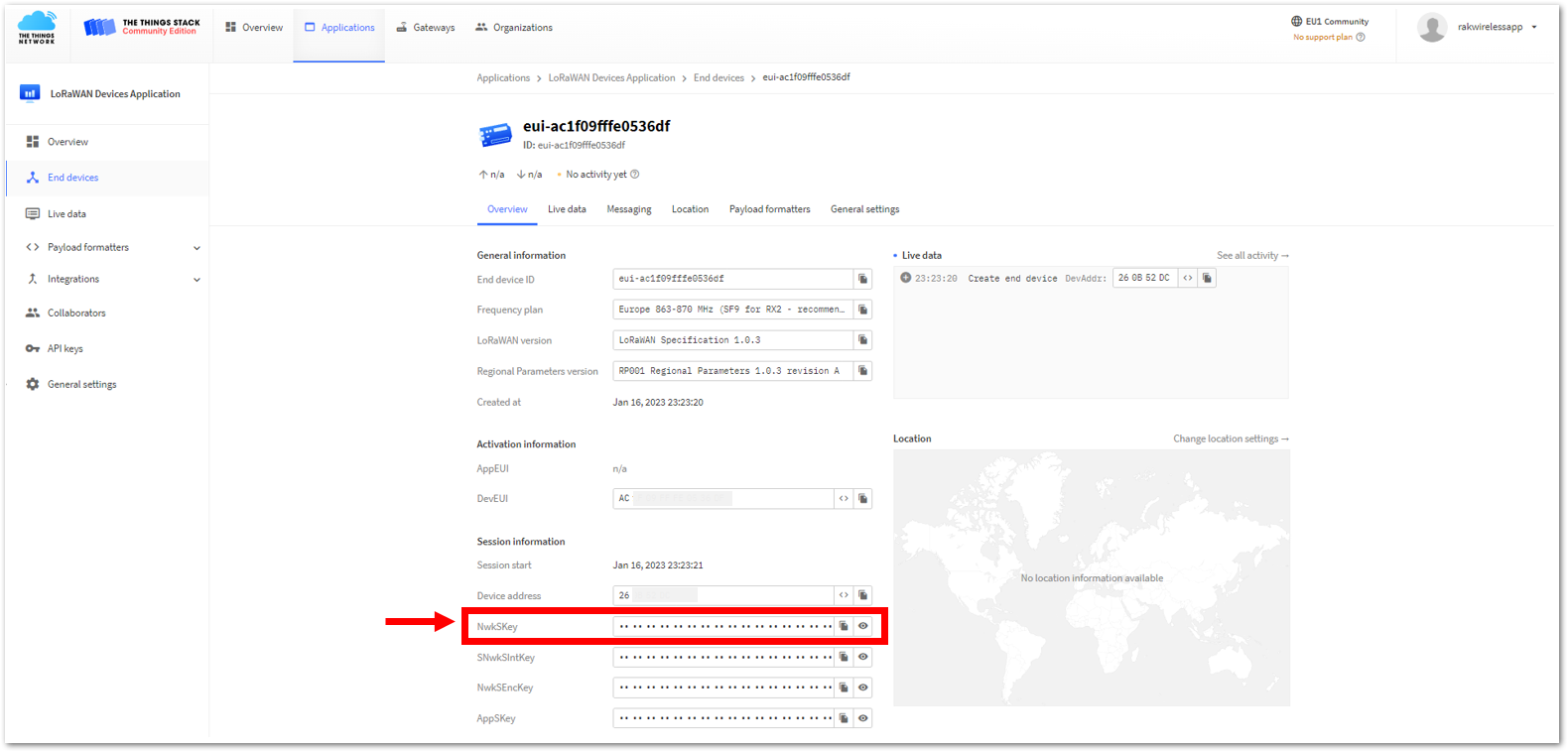 Figure 1: Copying the NwkSKey credential from TTN to WisToolBox
Figure 1: Copying the NwkSKey credential from TTN to WisToolBox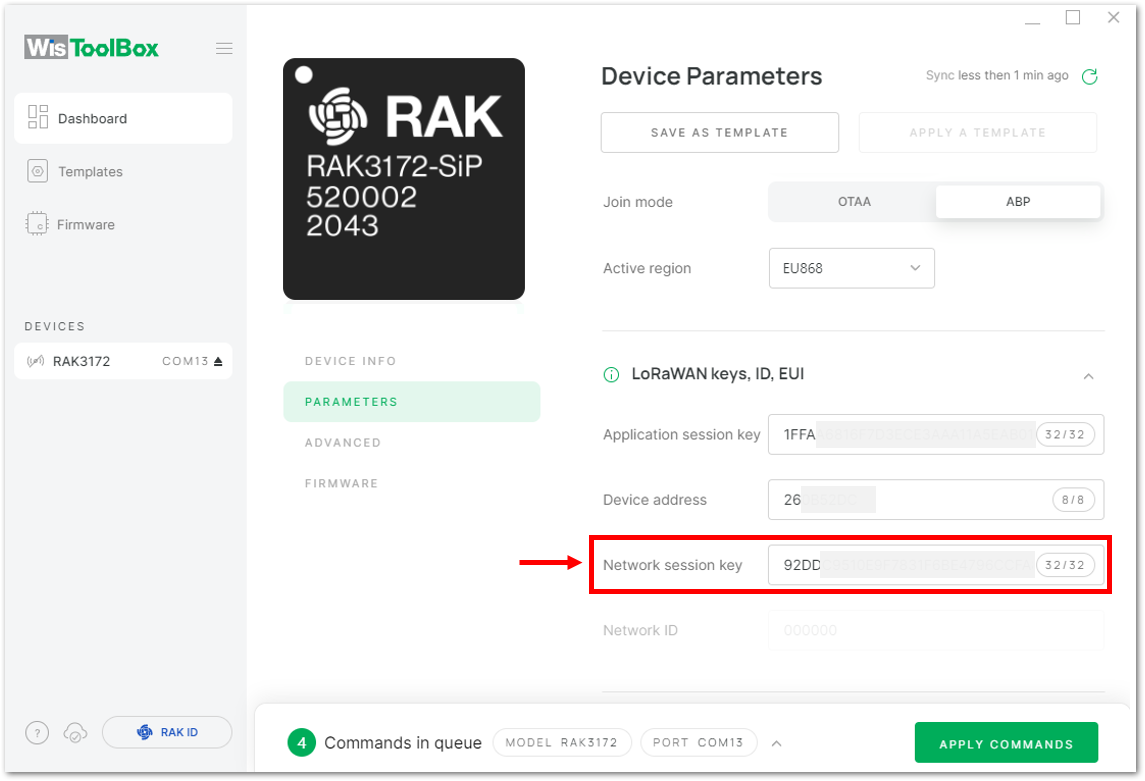 Figure 1: Copying the NwkSKey credential from TTN to WisToolBox
Figure 1: Copying the NwkSKey credential from TTN to WisToolBox- WisToolBox Dashboard
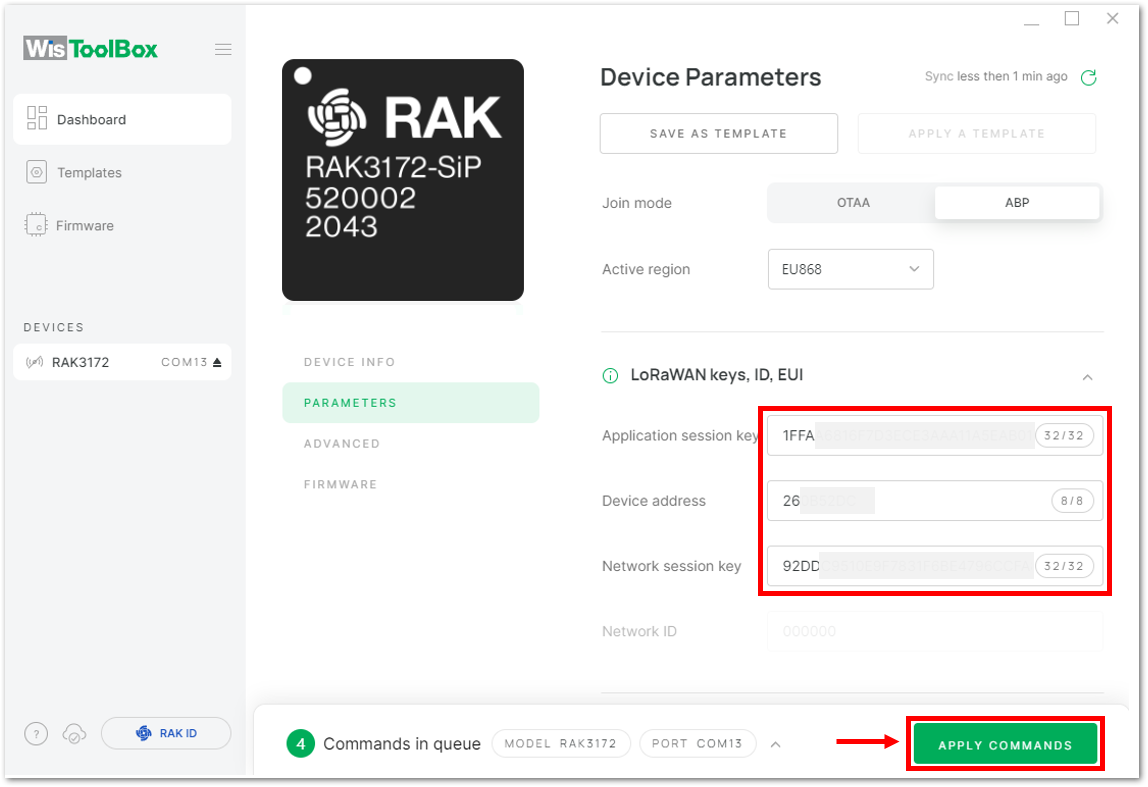 Figure 1: Used credentials from your console in WisToolBox dashboard
Figure 1: Used credentials from your console in WisToolBox dashboard- Once done, you will see the summary of commands that is applied to your device. Then click CLOSE.
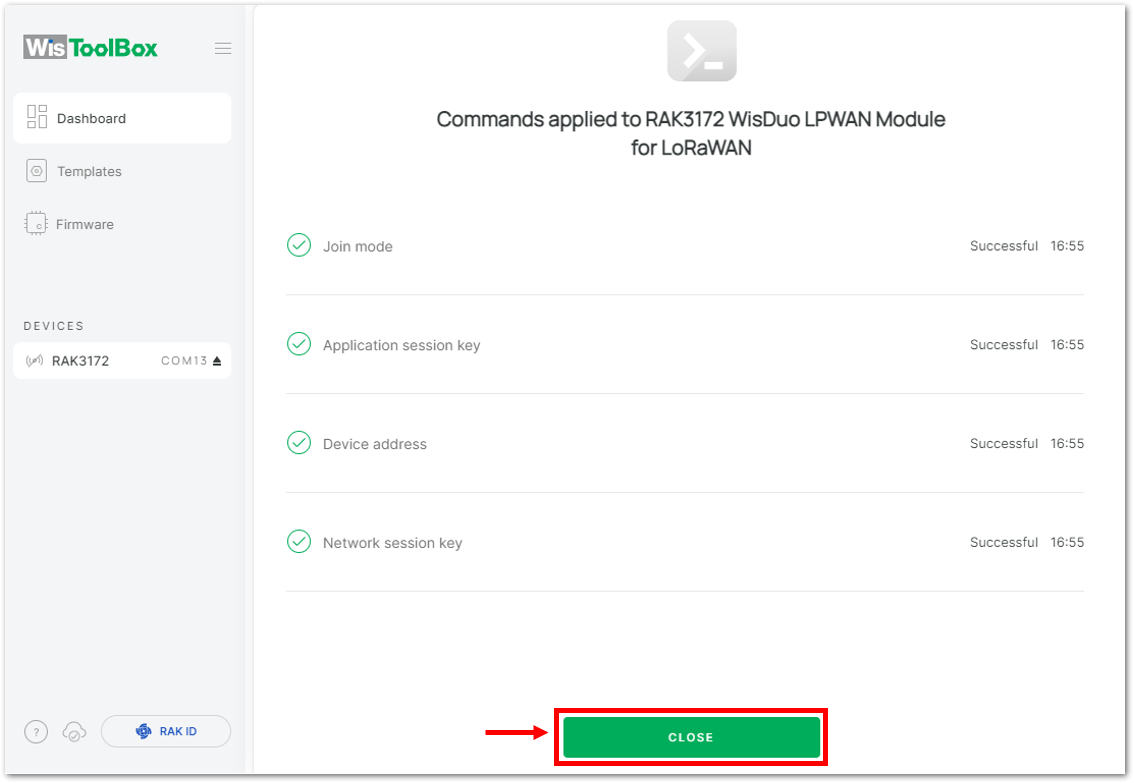 Figure 1: Summary of commands
Figure 1: Summary of commands- Now you will see it returns to the dashboard with updated credentials of your device.
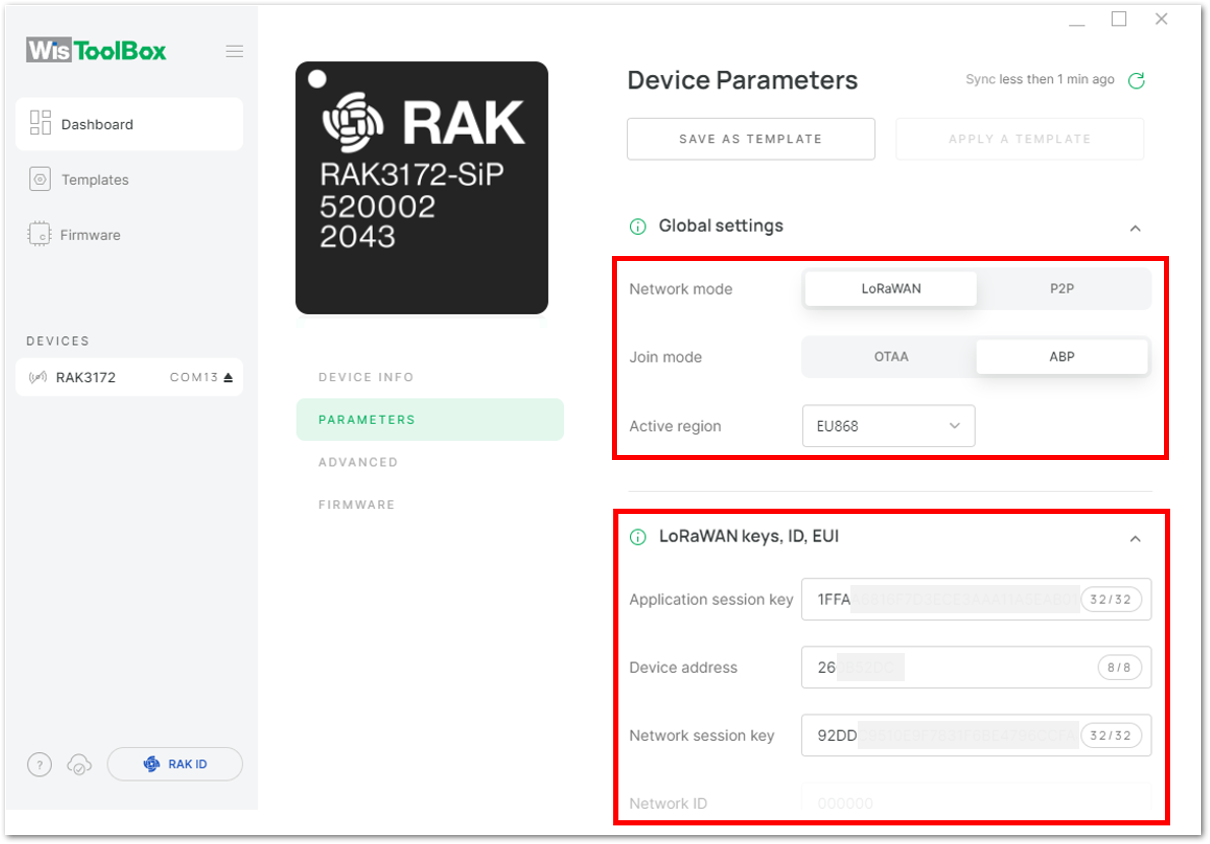 Figure 1: Successfully configured ABP device via WisToolBox dashboard
Figure 1: Successfully configured ABP device via WisToolBox dashboardABP Configuration for TTN via WisToolBox Console
Here's another way of ABP configuration using WisToolBox Console. Below are the steps on setting up your RAK3172-SiP using WisToolBox Console.
-
Connect your RAK3172-SiP with your chosen WisBlock base board to the PC via USB cable and open the WisToolBox application.
-
Click the CONNECT DEVICE button to launch the WisToolBox Dashboard.
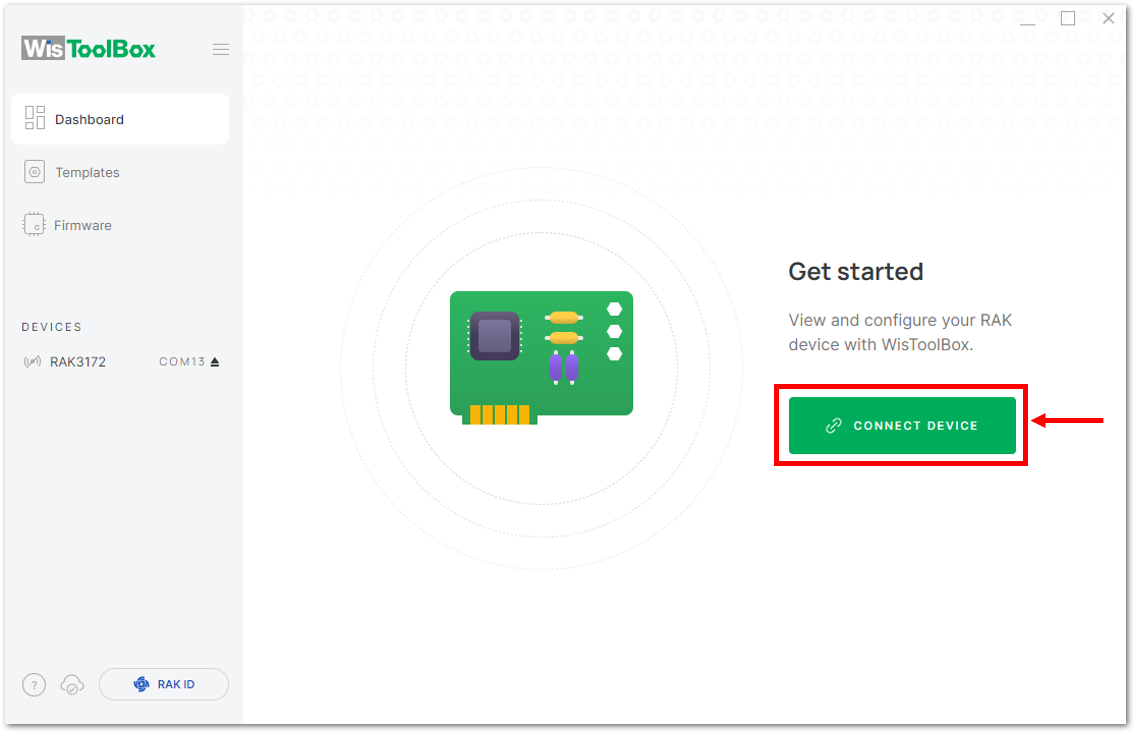 Figure 1: CONNECT DEVICE
Figure 1: CONNECT DEVICE- Then select your target port where your RAK3172-SiP is connected. Once recognized, click CONNECT as shown in Figure 155.
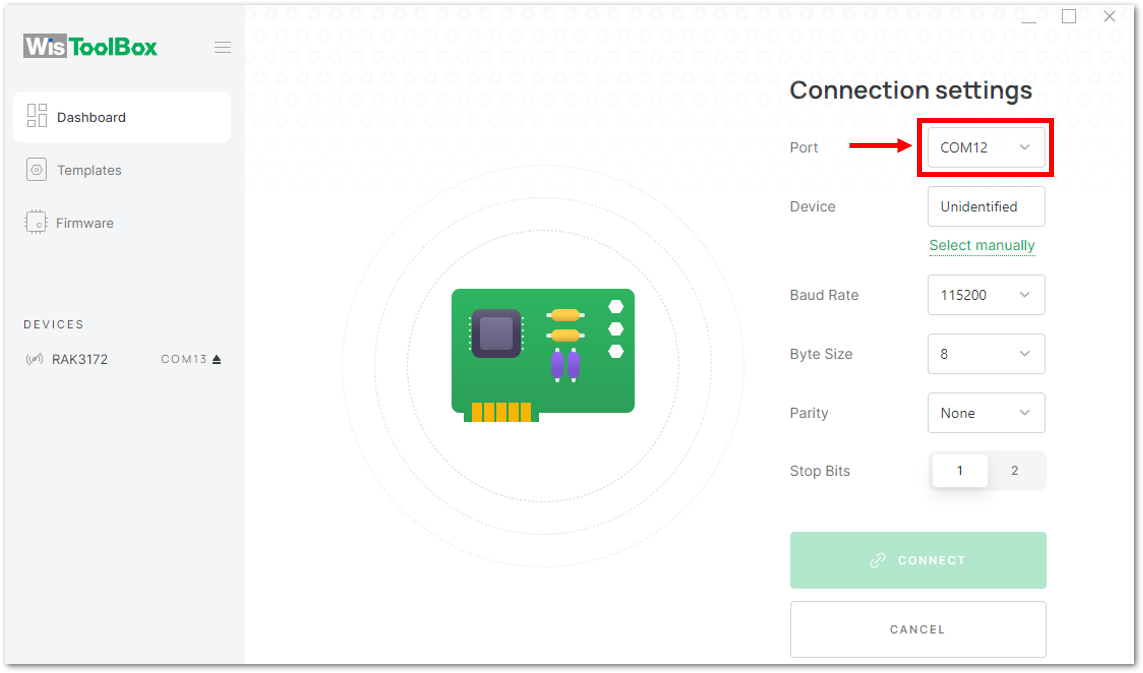 Figure 1: Setting up your device
Figure 1: Setting up your device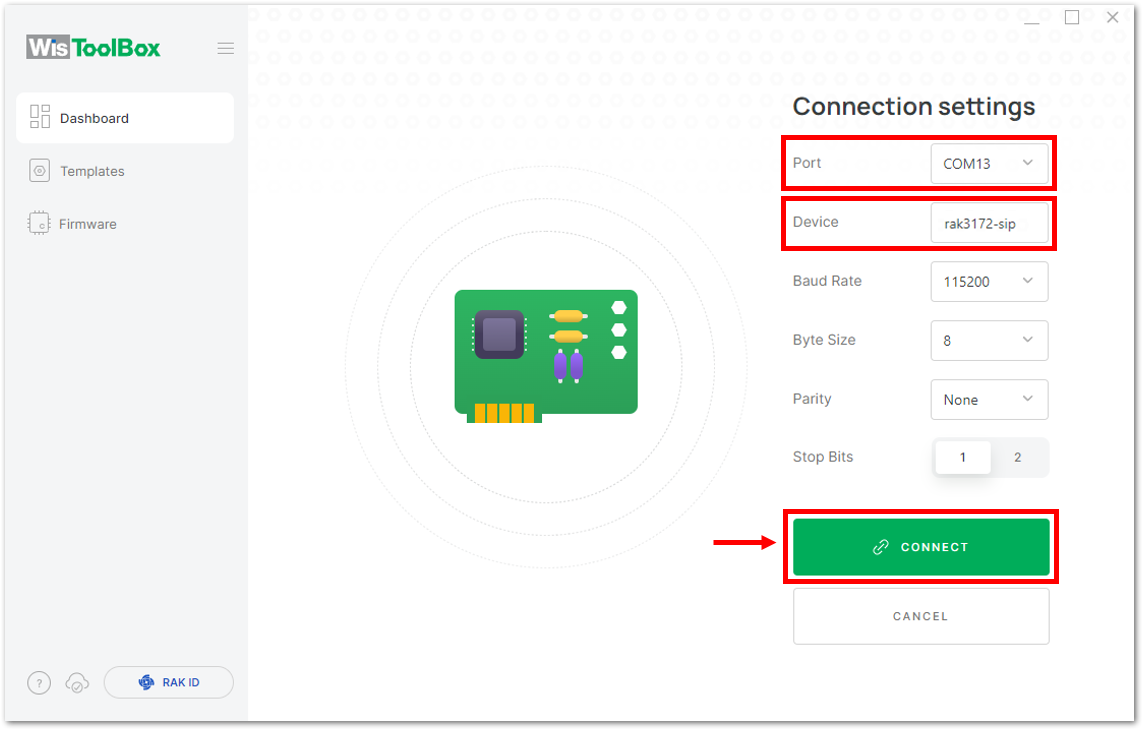 Figure 1: Setting up your device
Figure 1: Setting up your device- Once done, RAK3172-SiP will appear in the dashboard then select it.
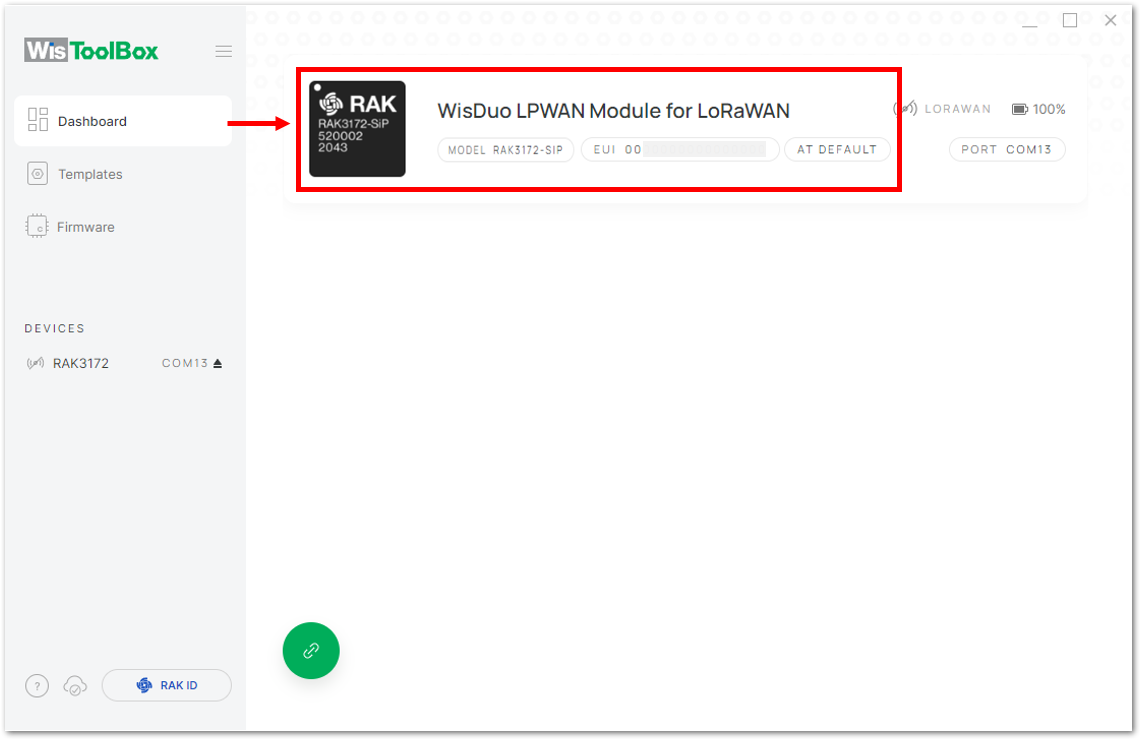 Figure 1: Device seen from WisToolBox dashboard
Figure 1: Device seen from WisToolBox dashboard- Then click ADVANCED.
 Figure 1: Setting up your device
Figure 1: Setting up your device- Once done, click OPEN CONSOLE to do the configuration.
 Figure 1: OPEN CONSOLE
Figure 1: OPEN CONSOLE Figure 1: Opening the Console terminal of WisToolBox
Figure 1: Opening the Console terminal of WisToolBox Figure 1: Opening the Console terminal of WisToolBox
Figure 1: Opening the Console terminal of WisToolBox- To start the configuration, type ATE so you can echo the commands you input during your configuration. Then press Enter.
It is recommended to start by testing the console and verify that the current configuration is working by sending these two AT commands:
AT
ATE
ATE is useful for tracking the commands and troubleshooting.
You will receive OK when you input the two commands. After setting ATE, see all the commands you input together with the replies.
If there is no OK or any reply, check if the device is powered correctly. If you are getting power from a USB port, ensure that you have a good USB cable.
 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console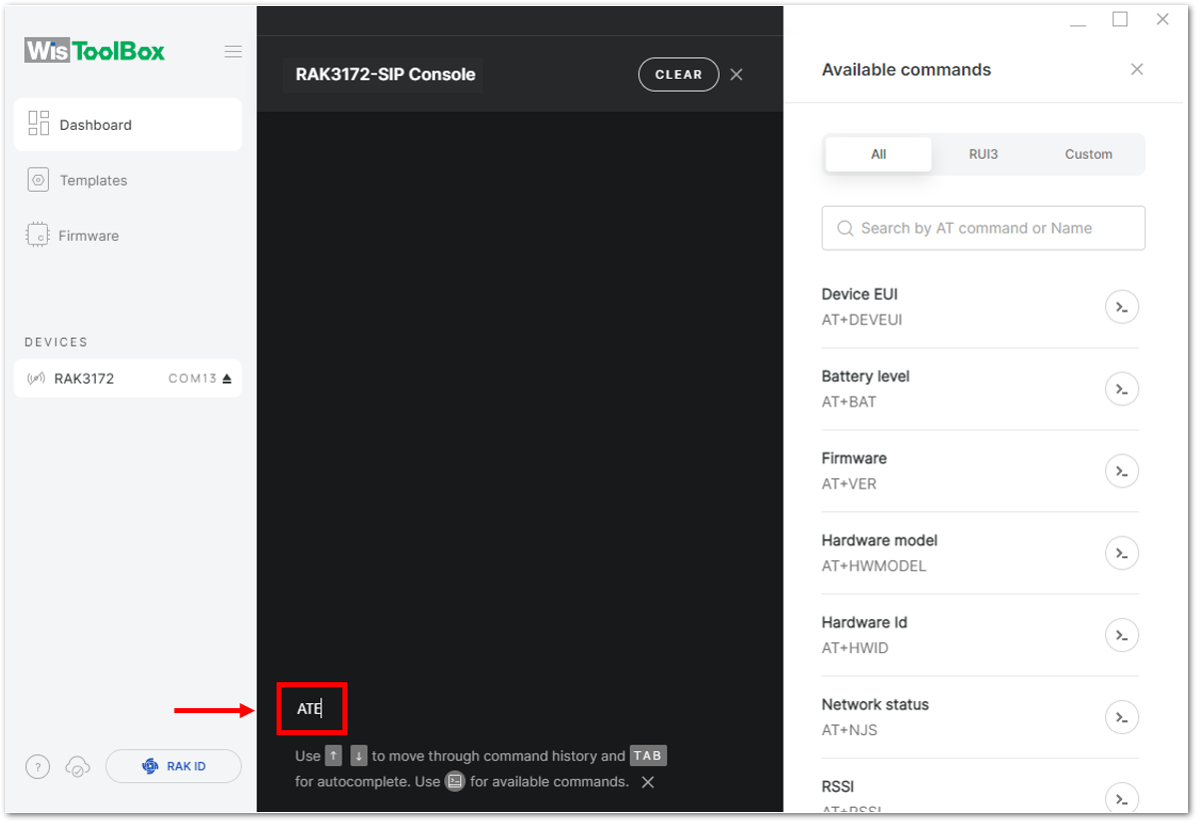 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console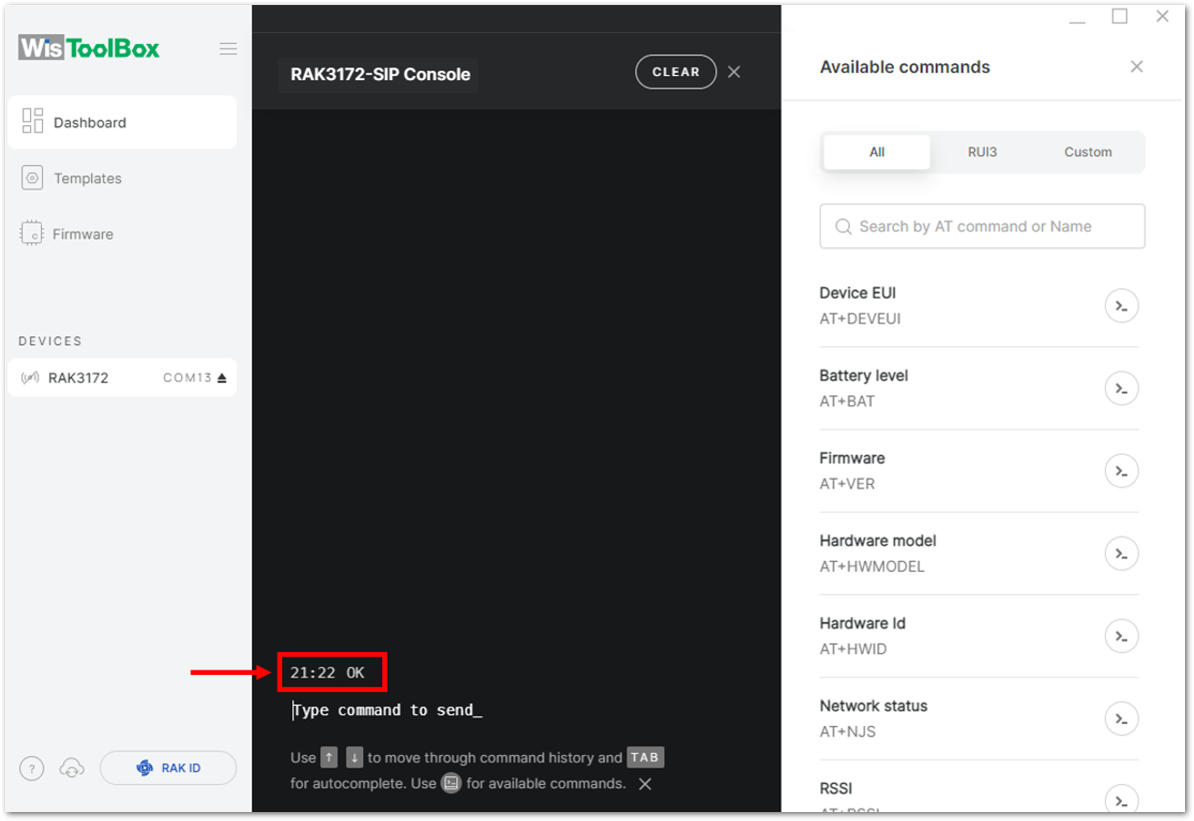 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console- Then configure the LoRaWAN join mode to ABP. You can check what parameter you will input by typing AT+NJM? and then Enter into the console terminal. For ABP, you should input AT+NJM=0 and then press Enter as shown in Figure 164.
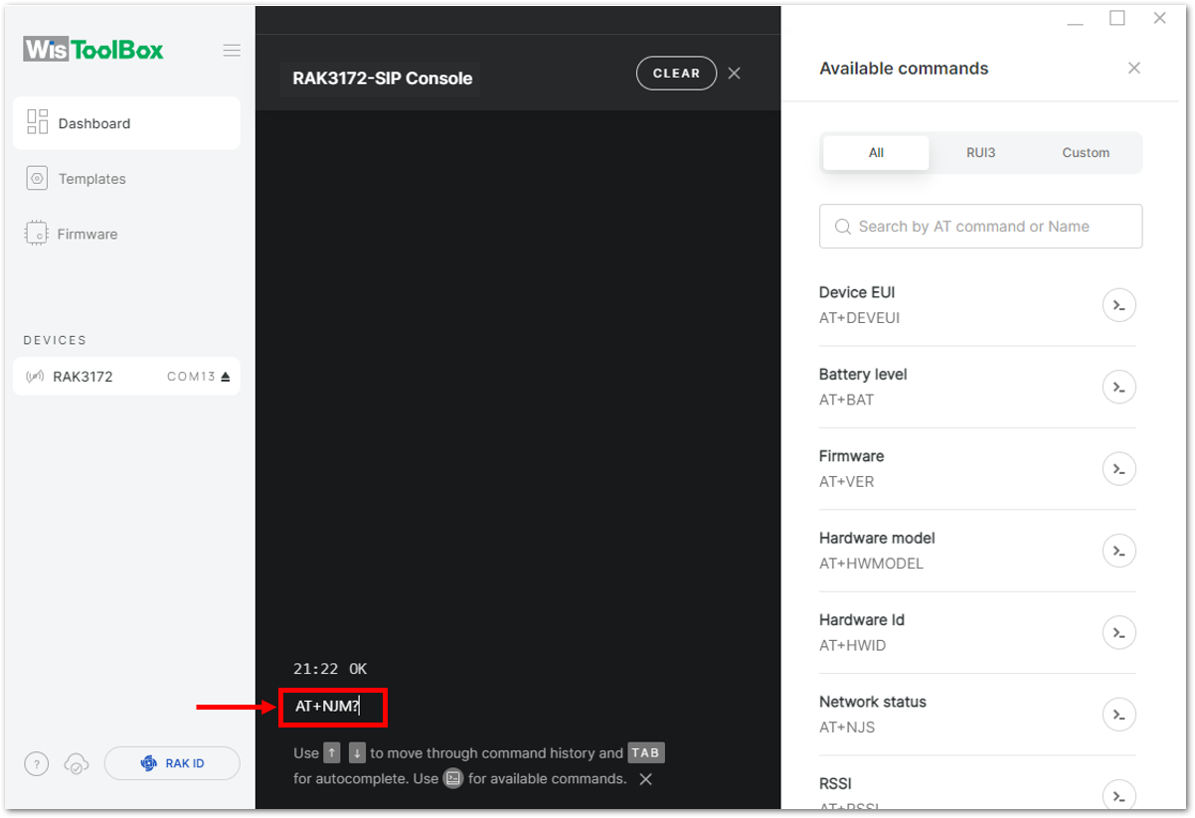 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console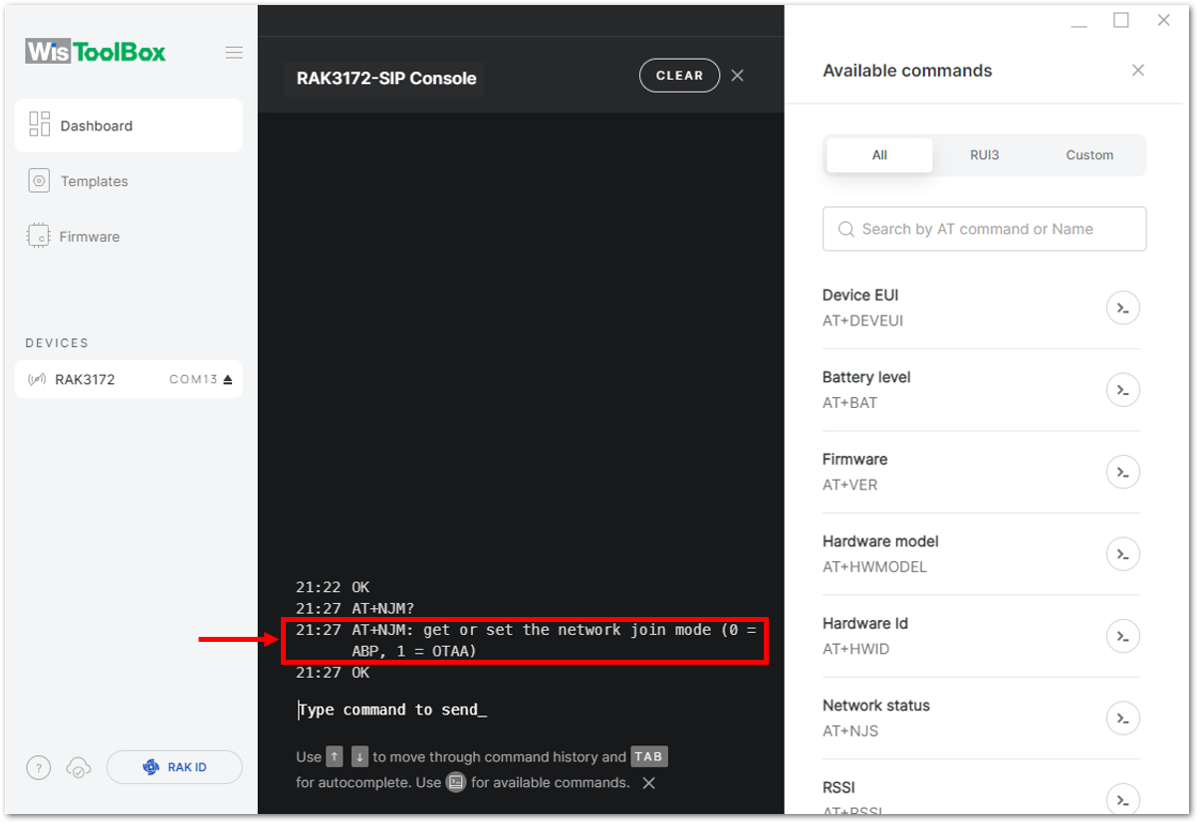 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console- Once done, set up your LoRaWAN region to EU868. You can check what parameter you will input by typing AT+BAND? and then Enter into the console terminal. For EU868, you should input AT+BAND=4 then press Enter. If you wish to work on other regional bands, you may check the list of band parameter options below.
Set the frequency/region to EU868.
AT+BAND=4
- Depending on the Regional Band you selected, you might need to configure the sub-band of your RAK3172 to match the gateway and LoRaWAN network server. This is especially important for Regional Bands like US915, AU915, and CN470.
- To configure the masking of channels for the sub-bands, you can use the
AT+MASKcommand that can be found on the AT Command Manual. - To illustrate, you can use sub-band 2 by sending the command
AT+MASK=0002.
List of band parameter options
| Code | Regional Band |
|---|---|
| 0 | EU433 |
| 1 | CN470 |
| 2 | RU864 |
| 3 | IN865 |
| 4 | EU868 |
| 5 | US915 |
| 6 | AU915 |
| 7 | KR920 |
| 8 | AS923-1 |
| 9 | AS923-2 |
| 10 | AS923-3 |
| 11 | AS923-4 |
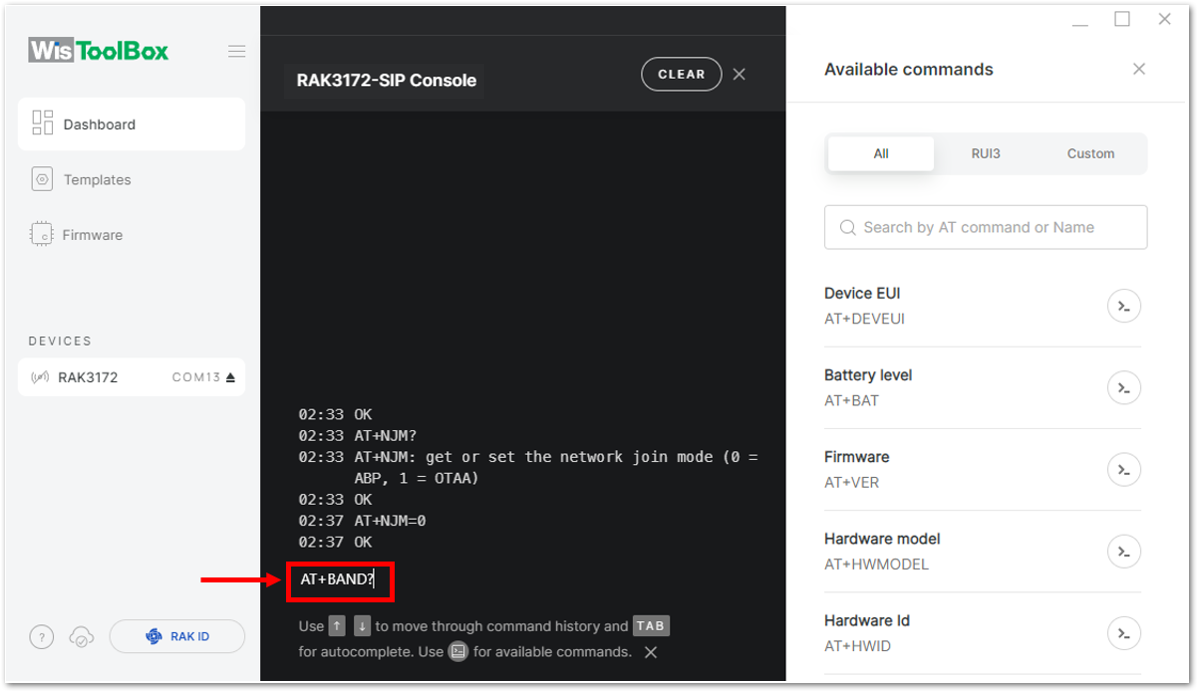 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console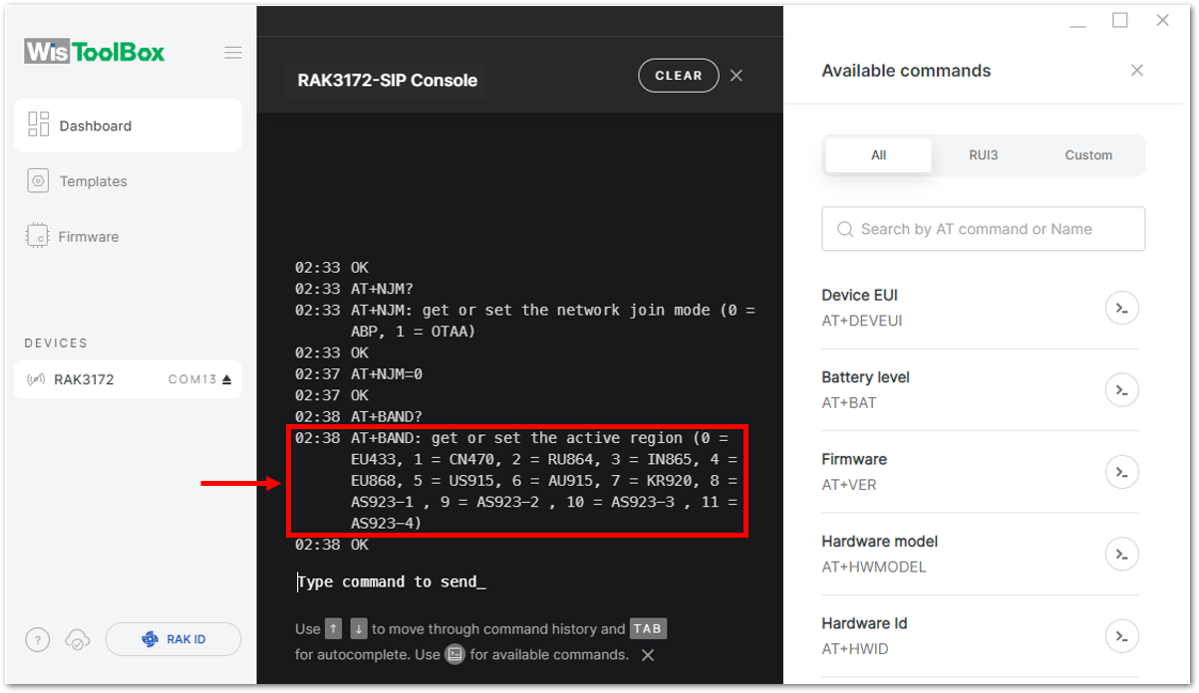 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console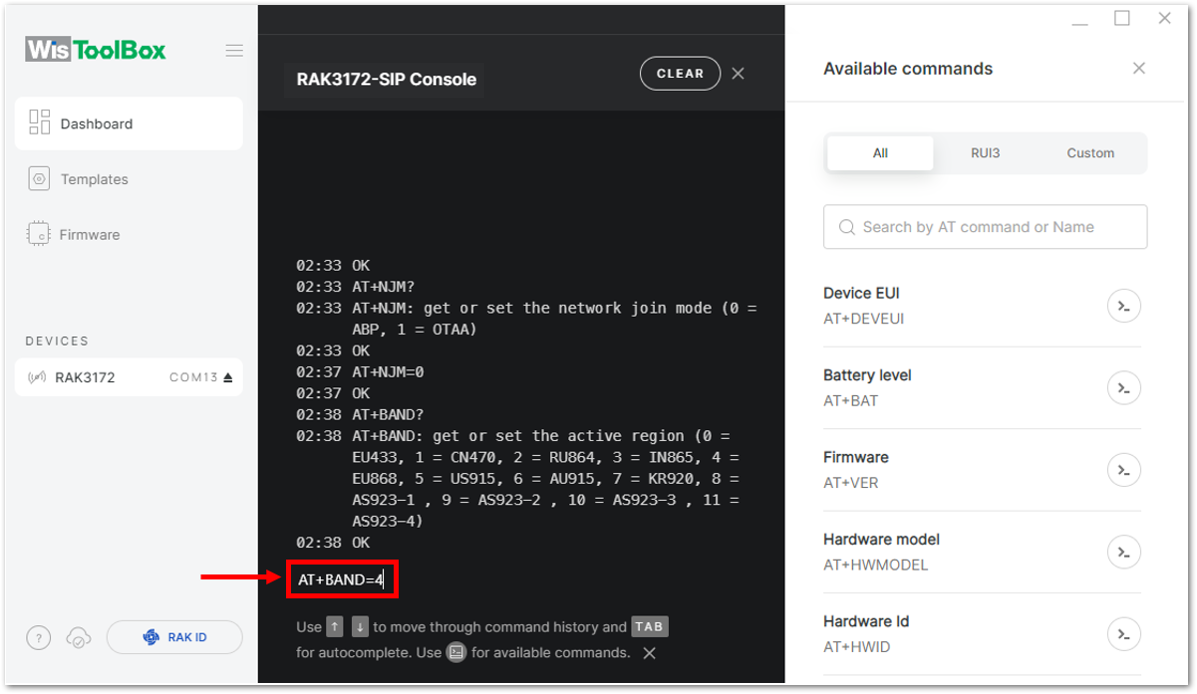 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console- Then next to this will be updating the ABP credentials of your device. First to this will be the Application session key (AppSKey). Go back to your console where your RAK3172-SiP End device was created to copy the AppSKey credential then paste it to the WisToolBox Console then press Enter.
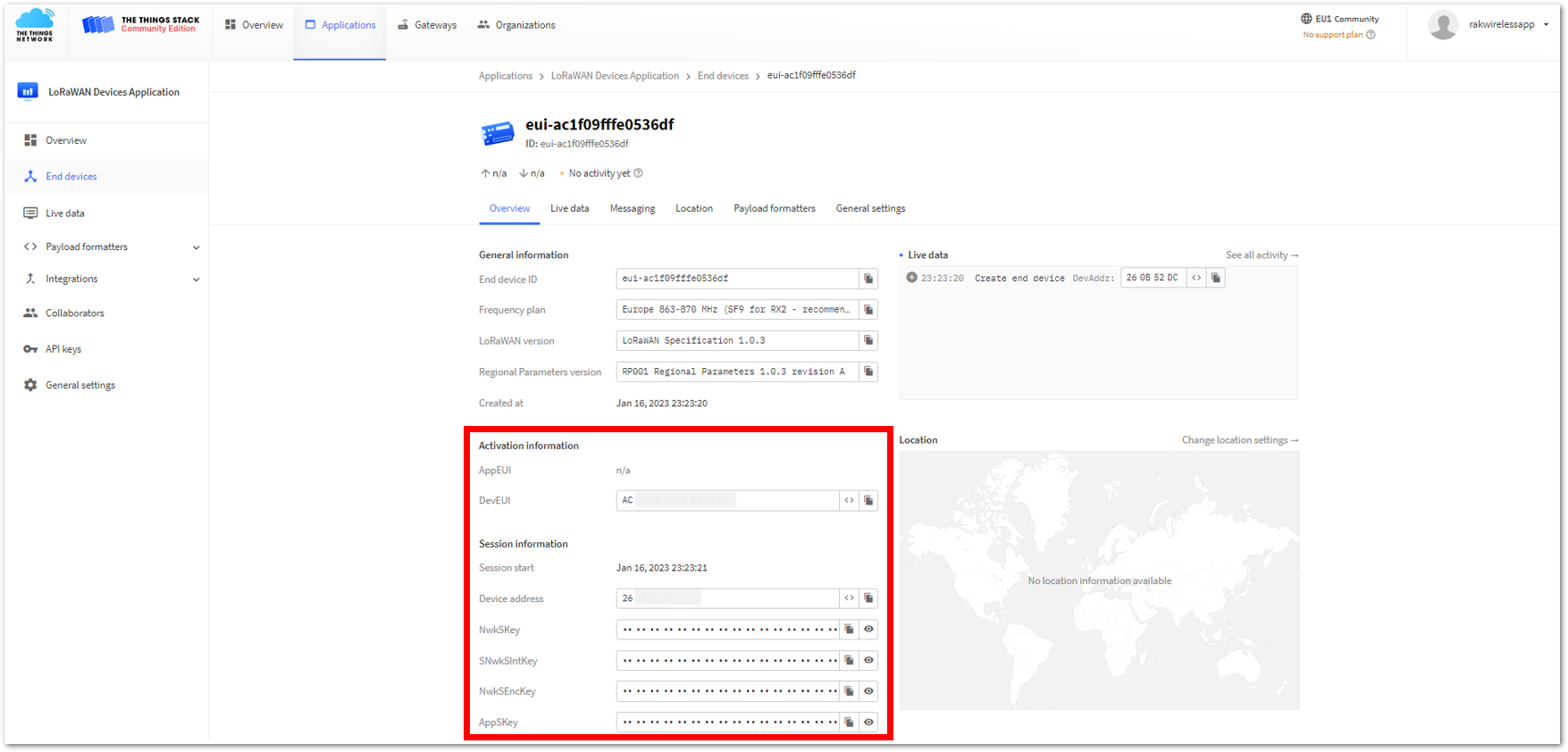 Figure 1: Your created ABP device from your TTN console
Figure 1: Your created ABP device from your TTN console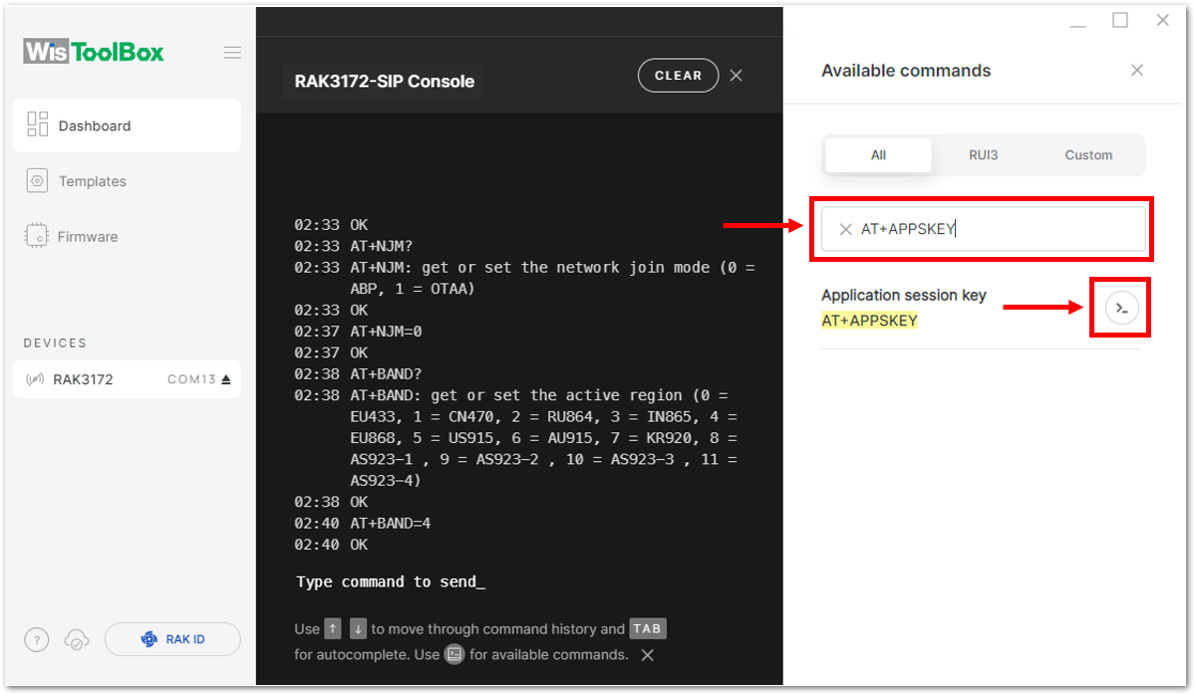 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console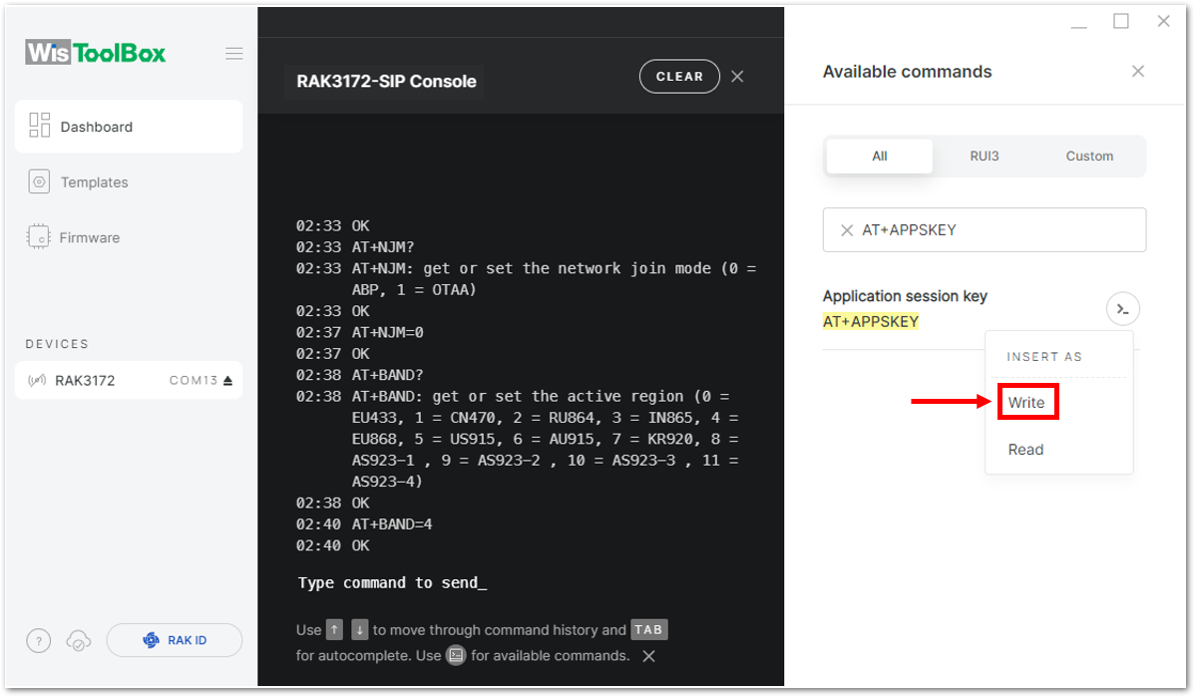 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console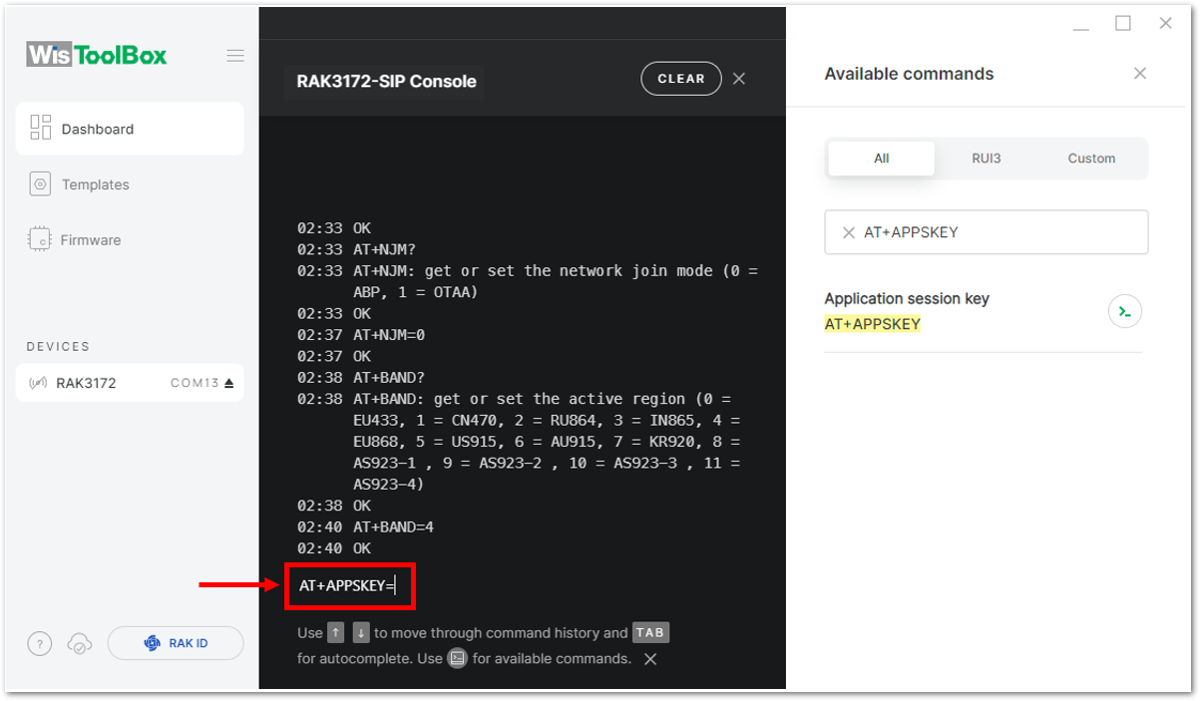 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console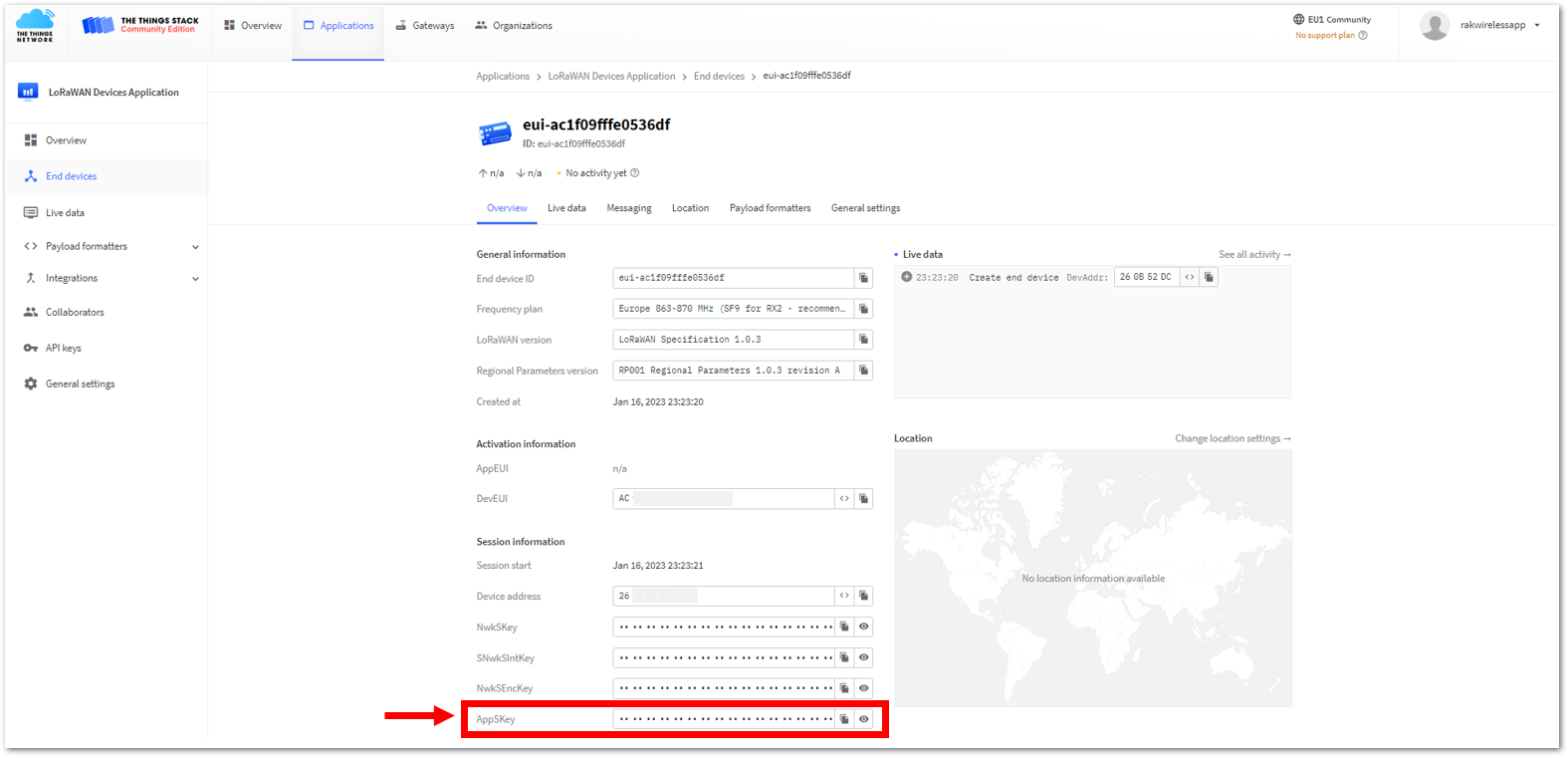 Figure 1: Copying the AppSKey credential from TTN to WisToolBox
Figure 1: Copying the AppSKey credential from TTN to WisToolBox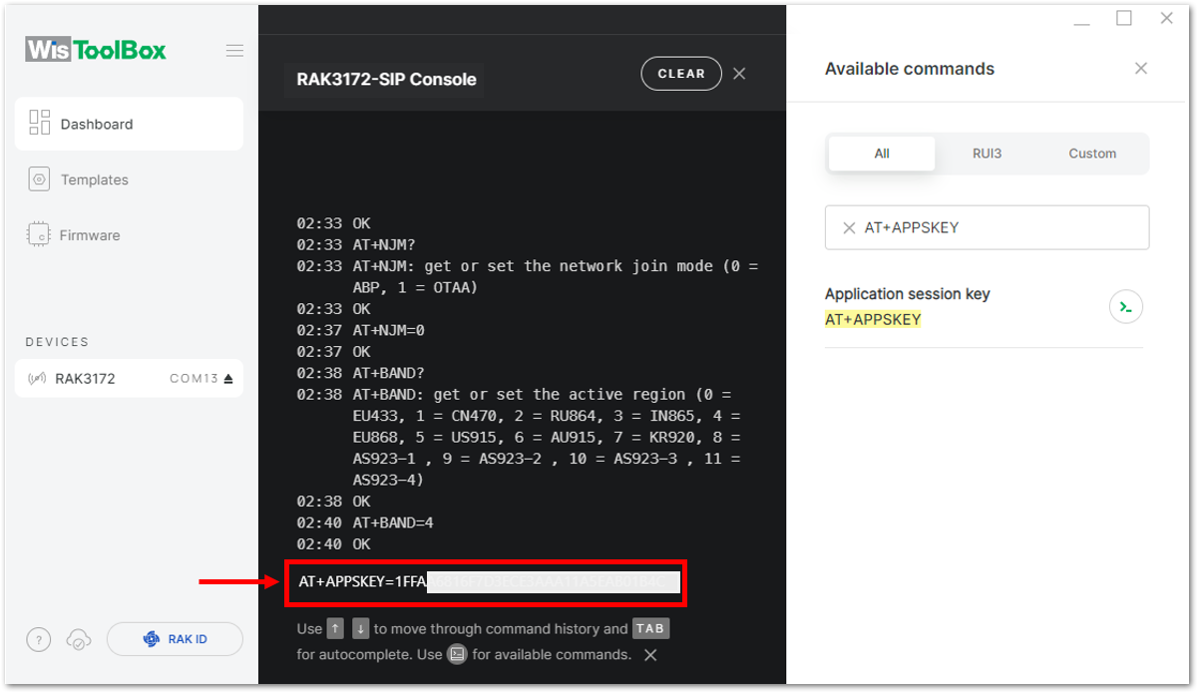 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console- Once done, do the same procedure to Device address and Network session key (NwkSKey).
- For Device address
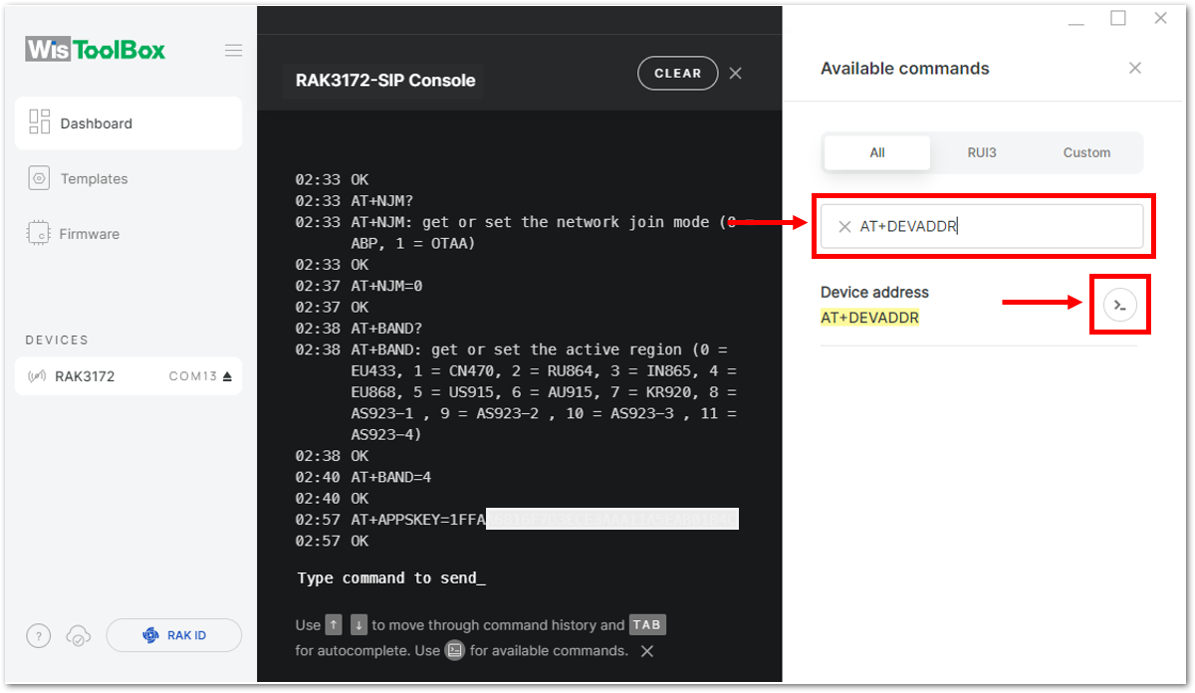 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console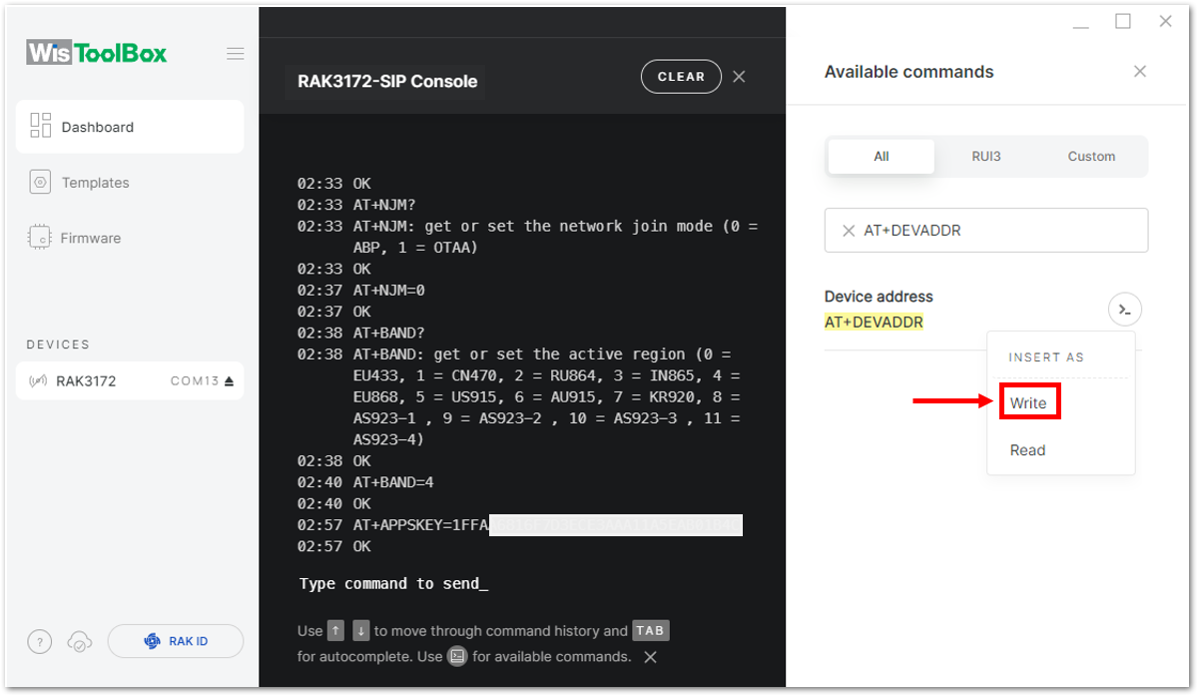 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console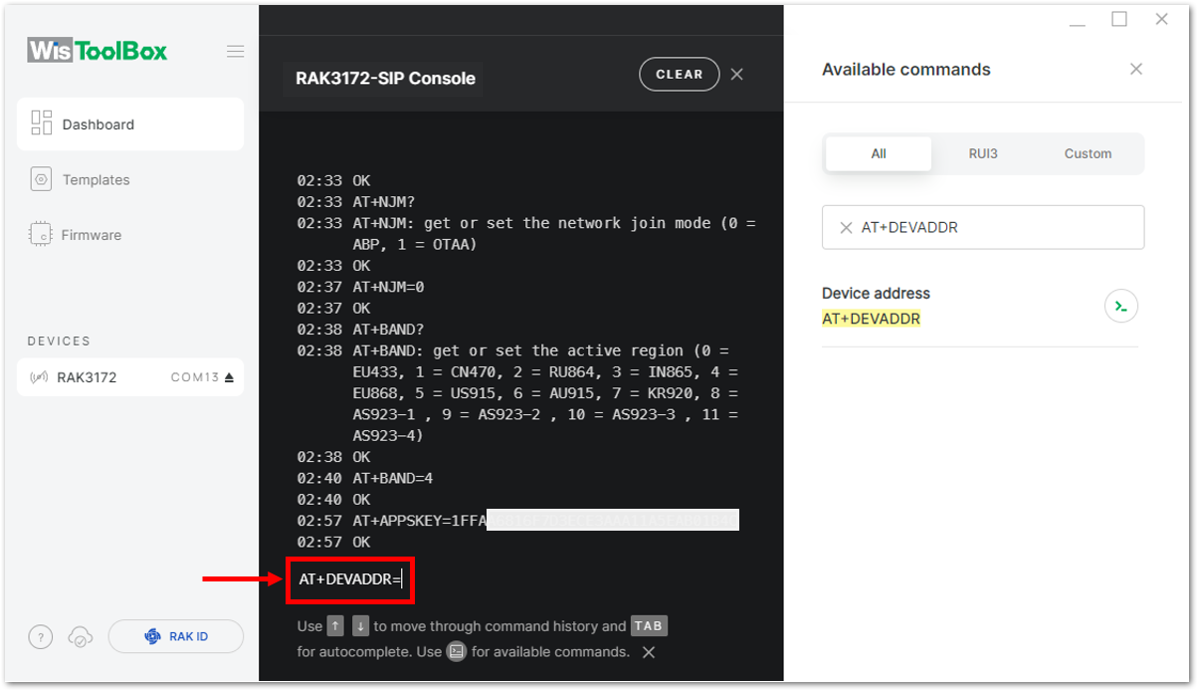 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console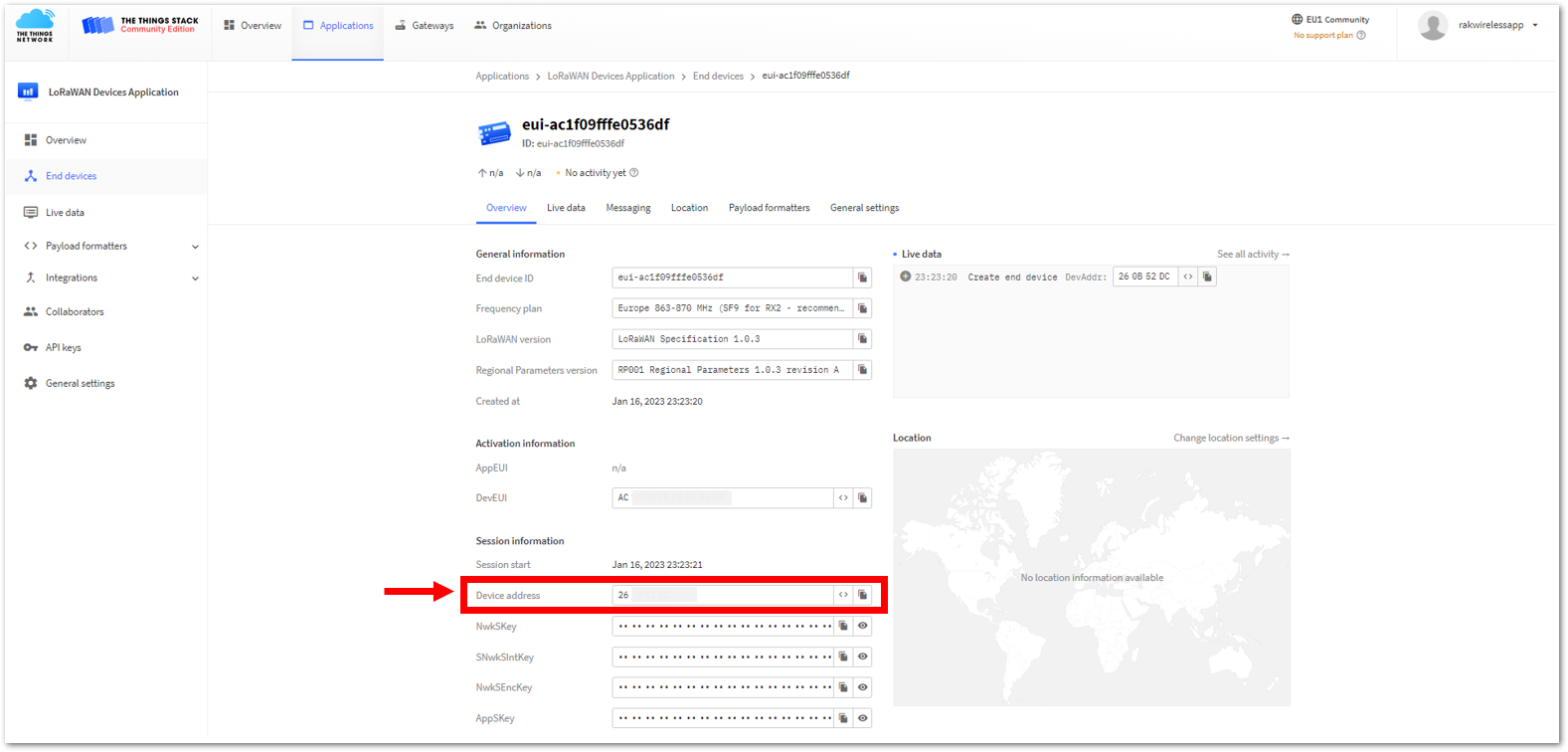 Figure 1: Copying the Device address credential from TTN to WisToolBox
Figure 1: Copying the Device address credential from TTN to WisToolBox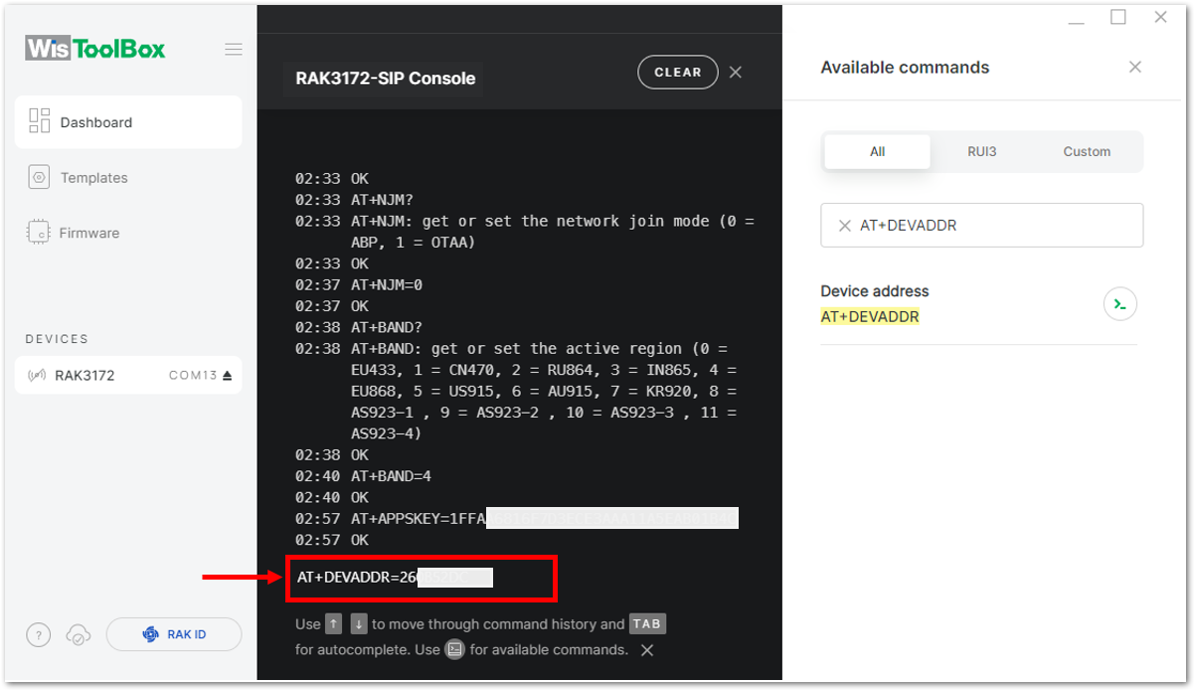 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console- For Network session key (NwkSKey)
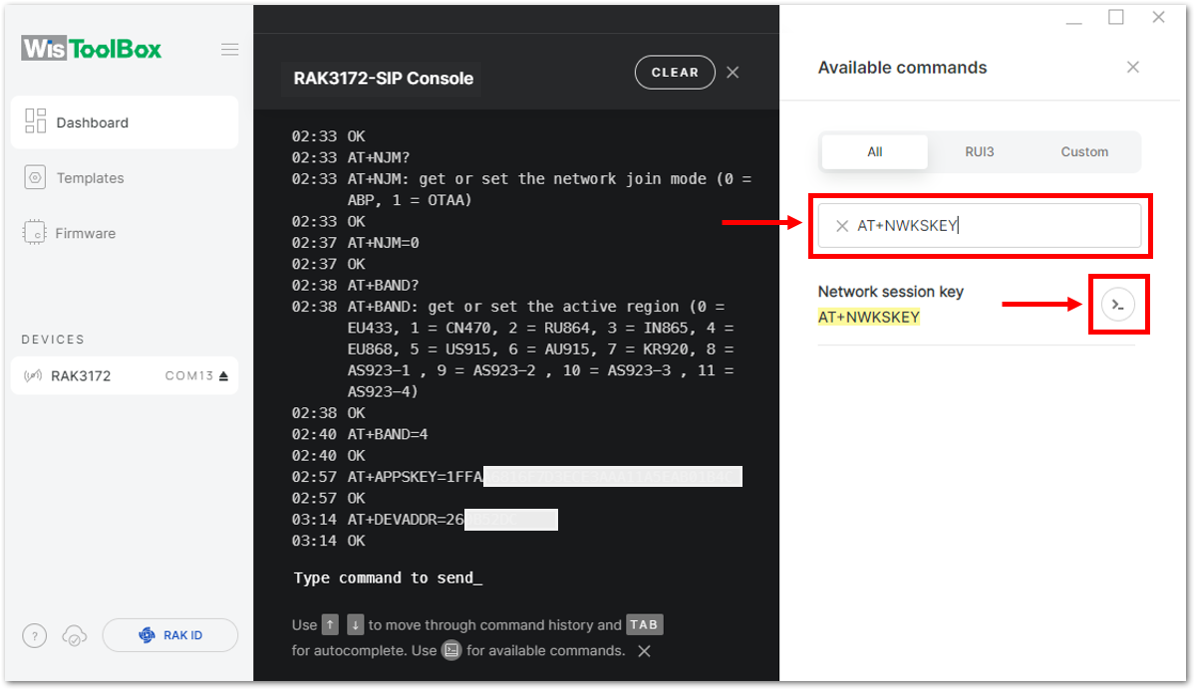 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console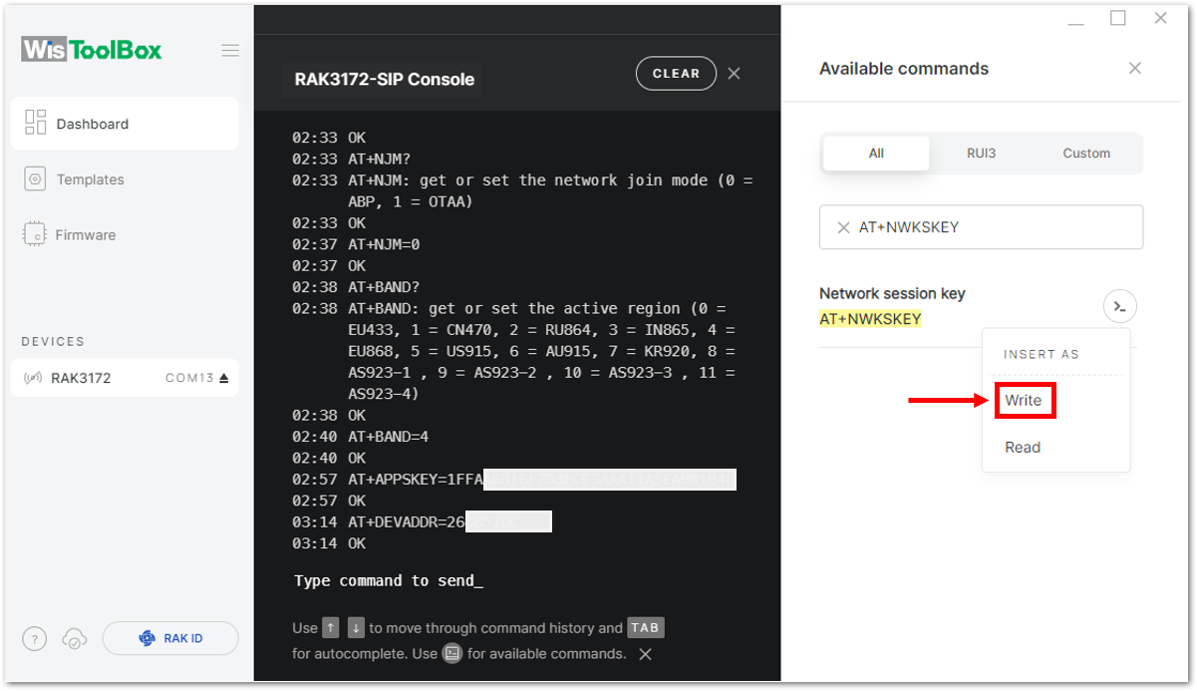 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console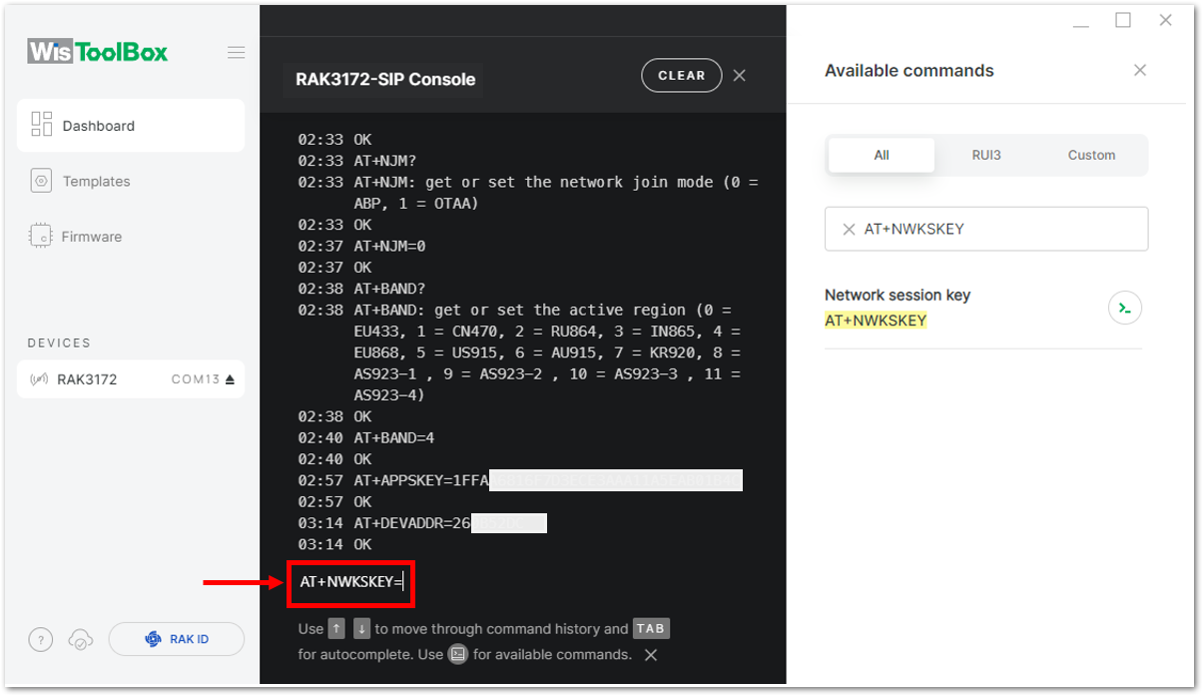 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console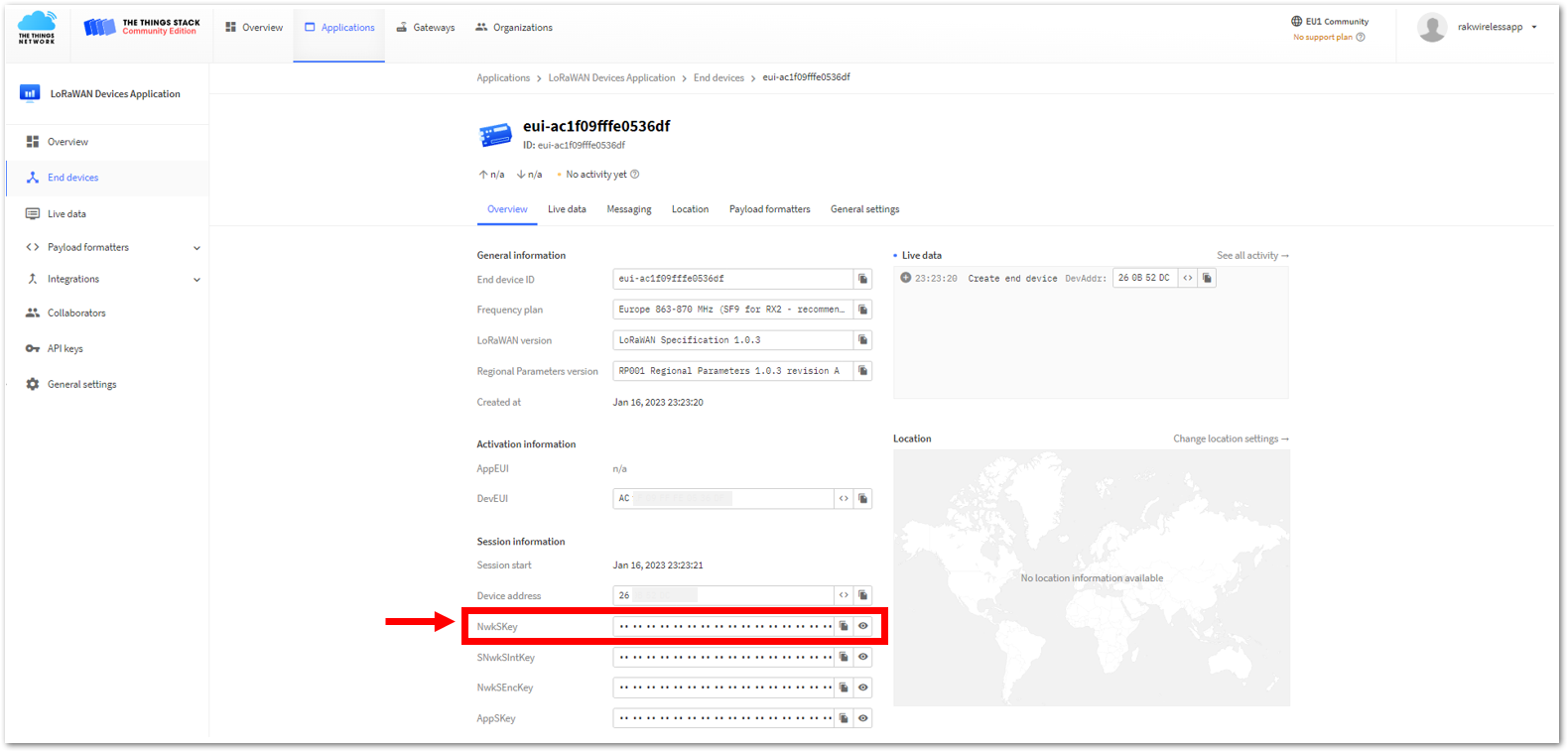 Figure 1: Copying the NwkSKey credential from TTN to WisToolBox
Figure 1: Copying the NwkSKey credential from TTN to WisToolBox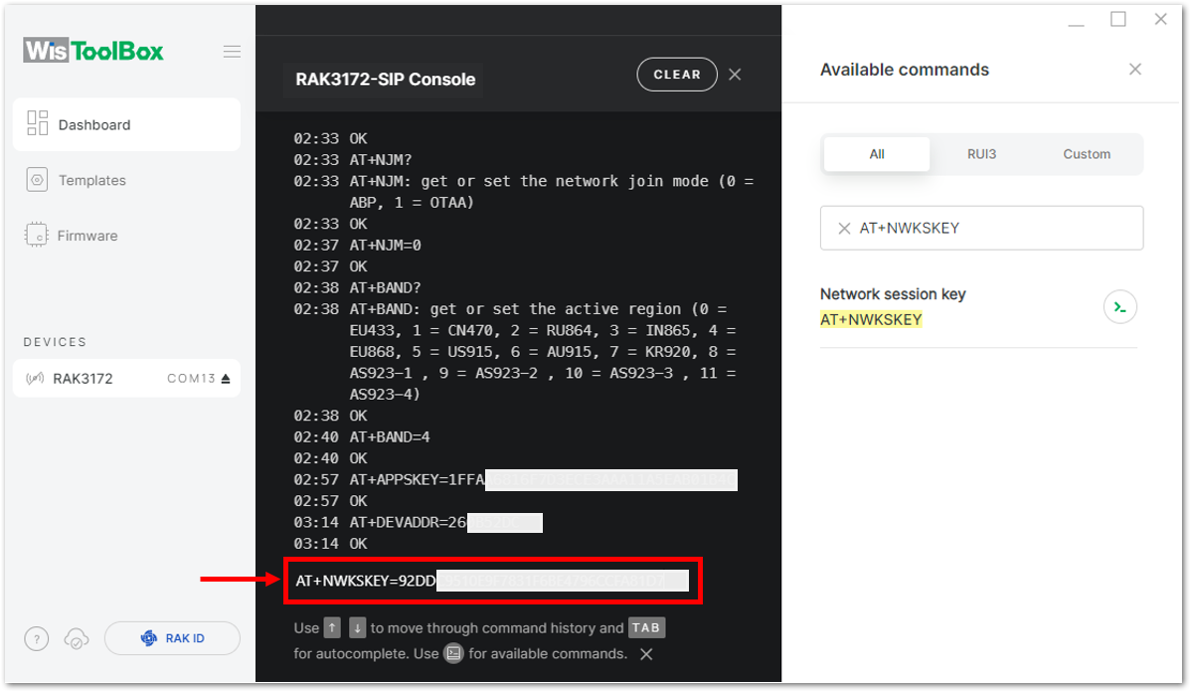 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console- Once done, click Dashboard to check the updated credentials of your ABP device. Click PARAMETERS to open the Global Settings and LoRaWAN keys, ID, EUI and check whether these portions are updated.
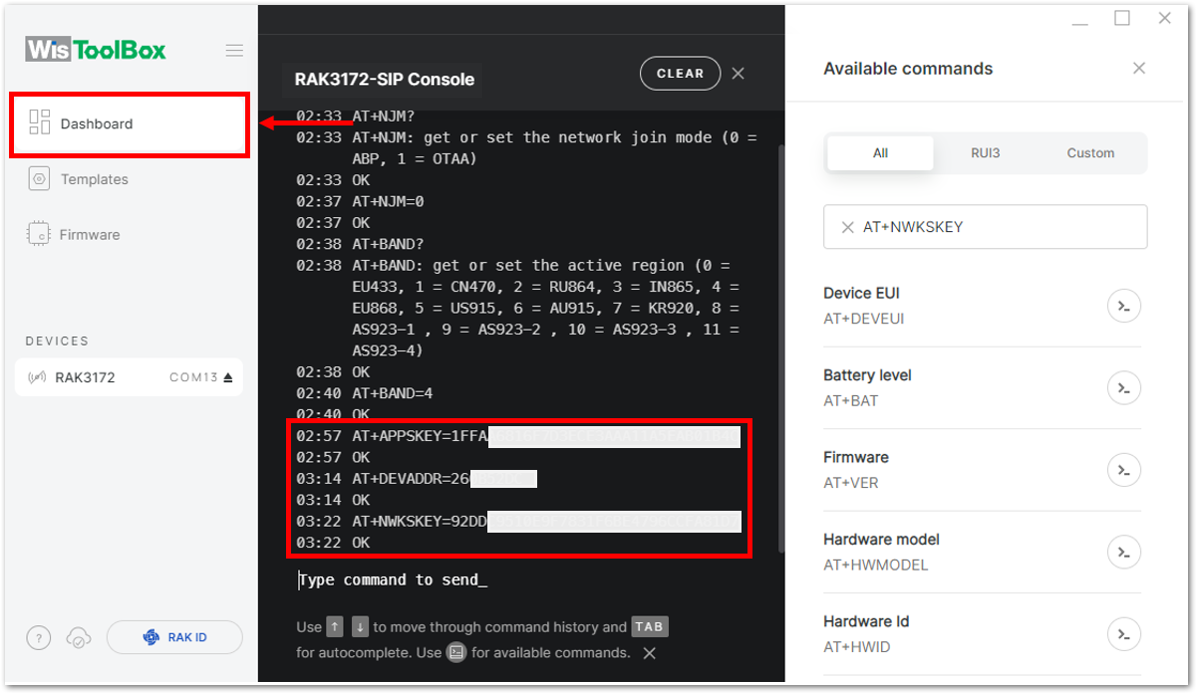 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console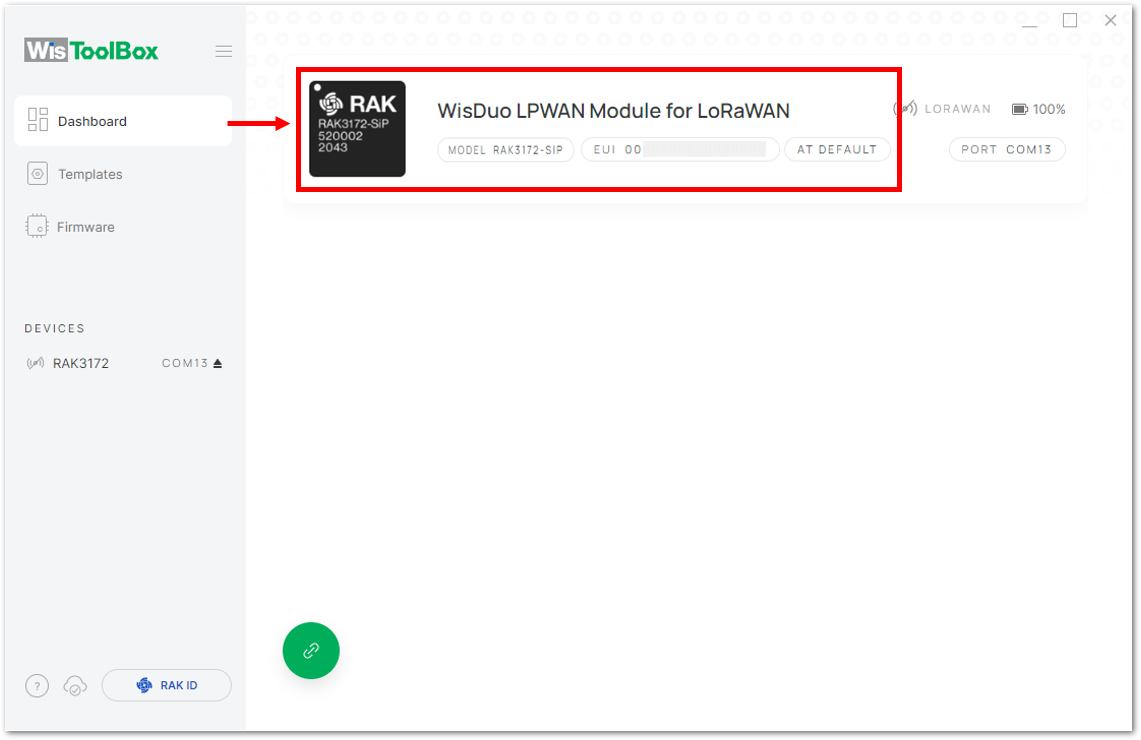 Figure 1: Setting up your Console
Figure 1: Setting up your Console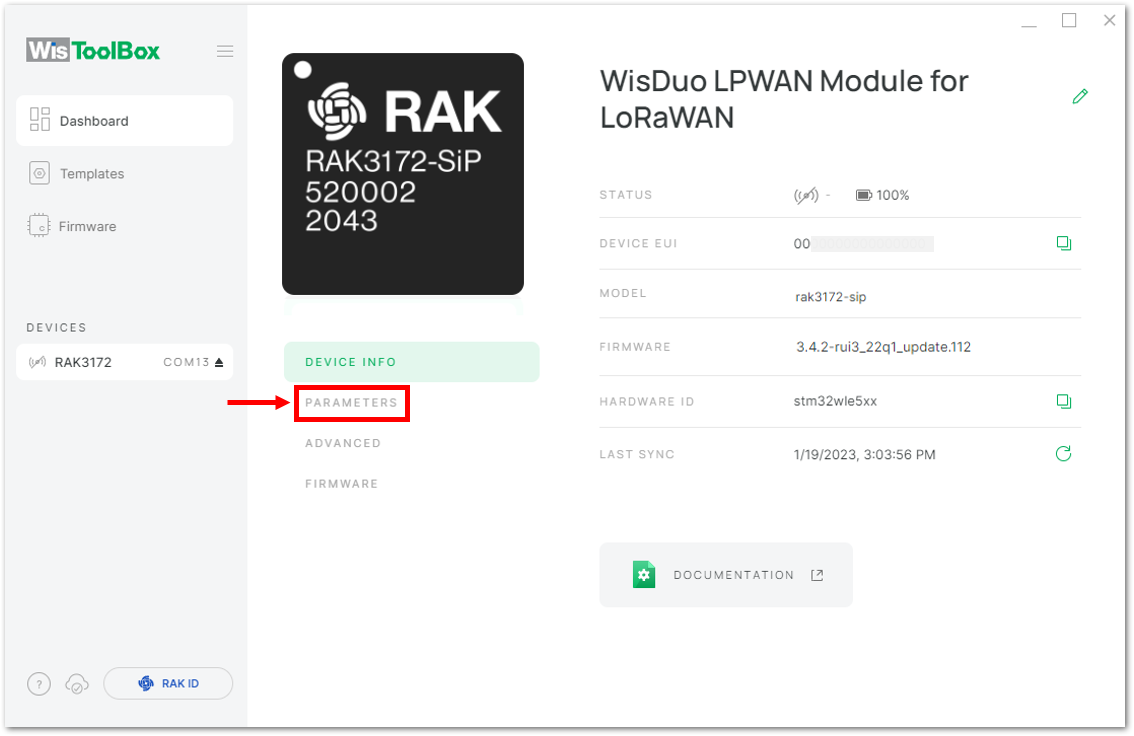 Figure 1: PARAMETERS
Figure 1: PARAMETERS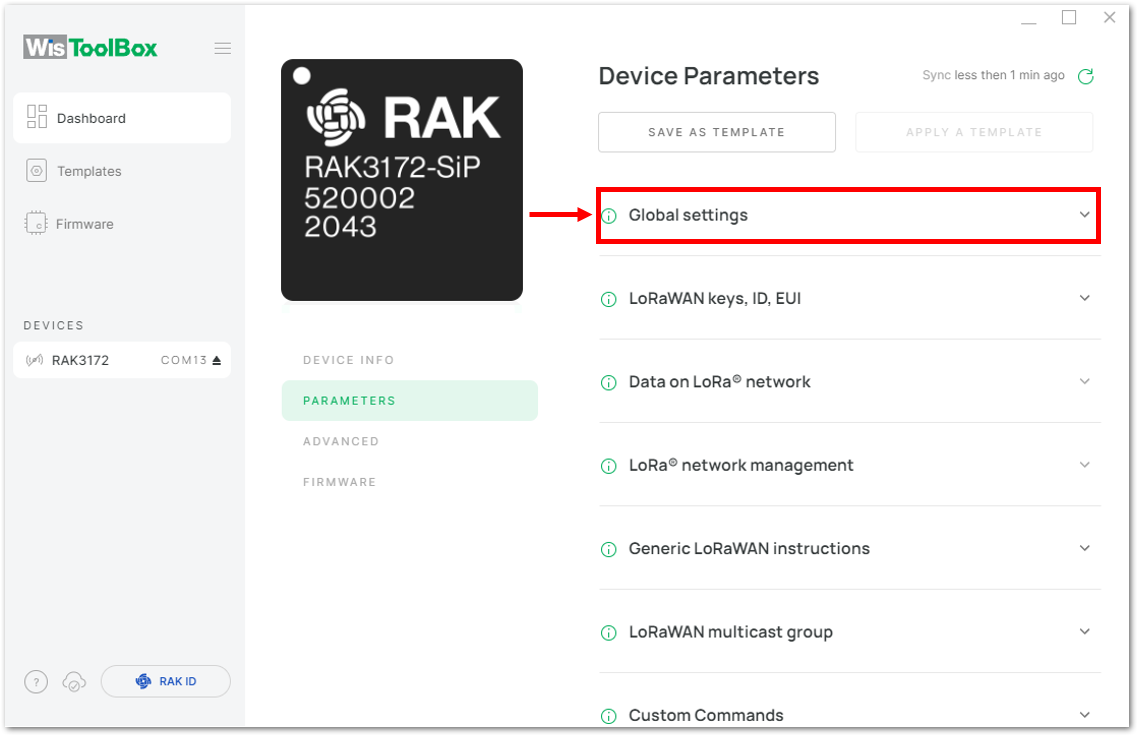 Figure 1: Global settings and LoRaWAN keys, ID, EUI
Figure 1: Global settings and LoRaWAN keys, ID, EUI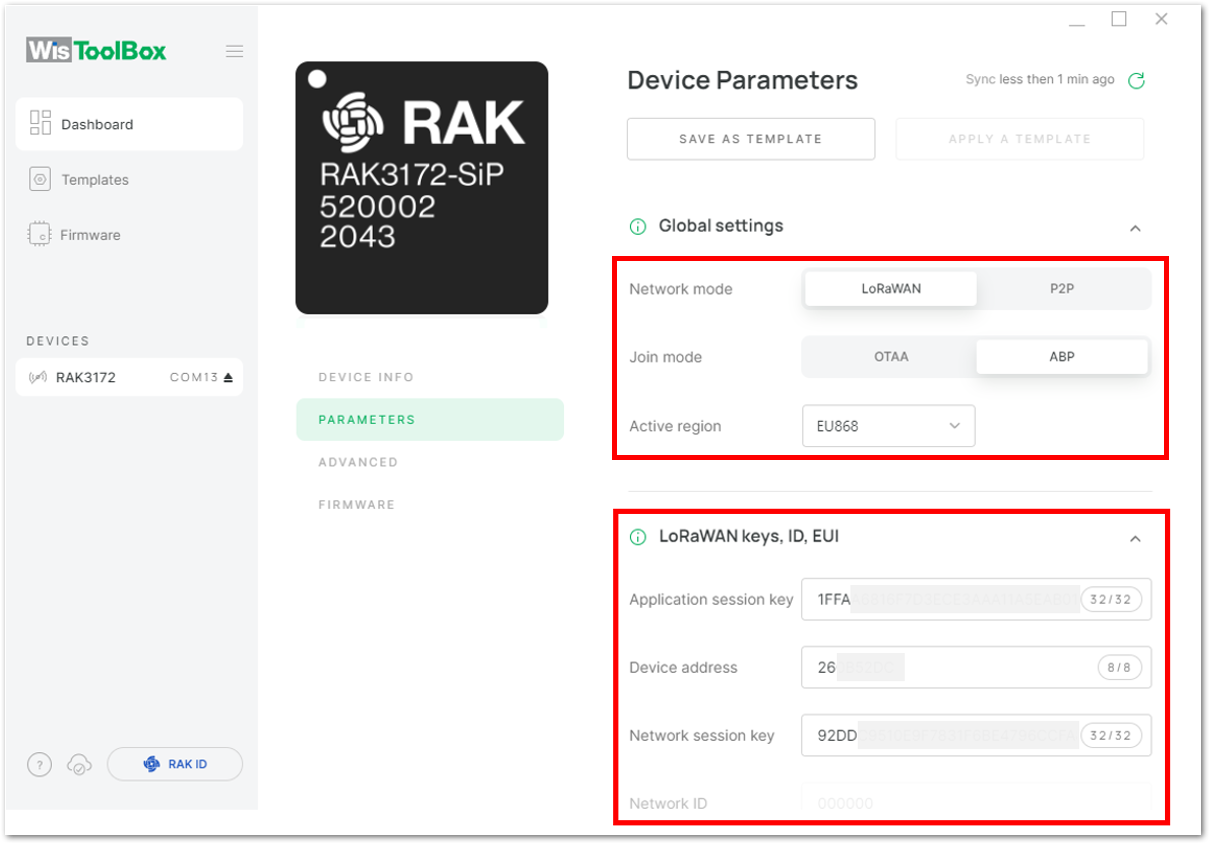 Figure 1: Global settings and LoRaWAN keys, ID, EUI details
Figure 1: Global settings and LoRaWAN keys, ID, EUI details- Now you have a configured ABP device using WisToolBox Console. ABP-configured devices are directly tied to the network once done with the above procedures so the joining procedure is not needed.
- Now you can try sending the payload to TTN. Open again the terminal console of WisToolBox to send some payload using it. Send command format:
AT+SEND=<port>:<payload>
AT+SEND=2:12345678
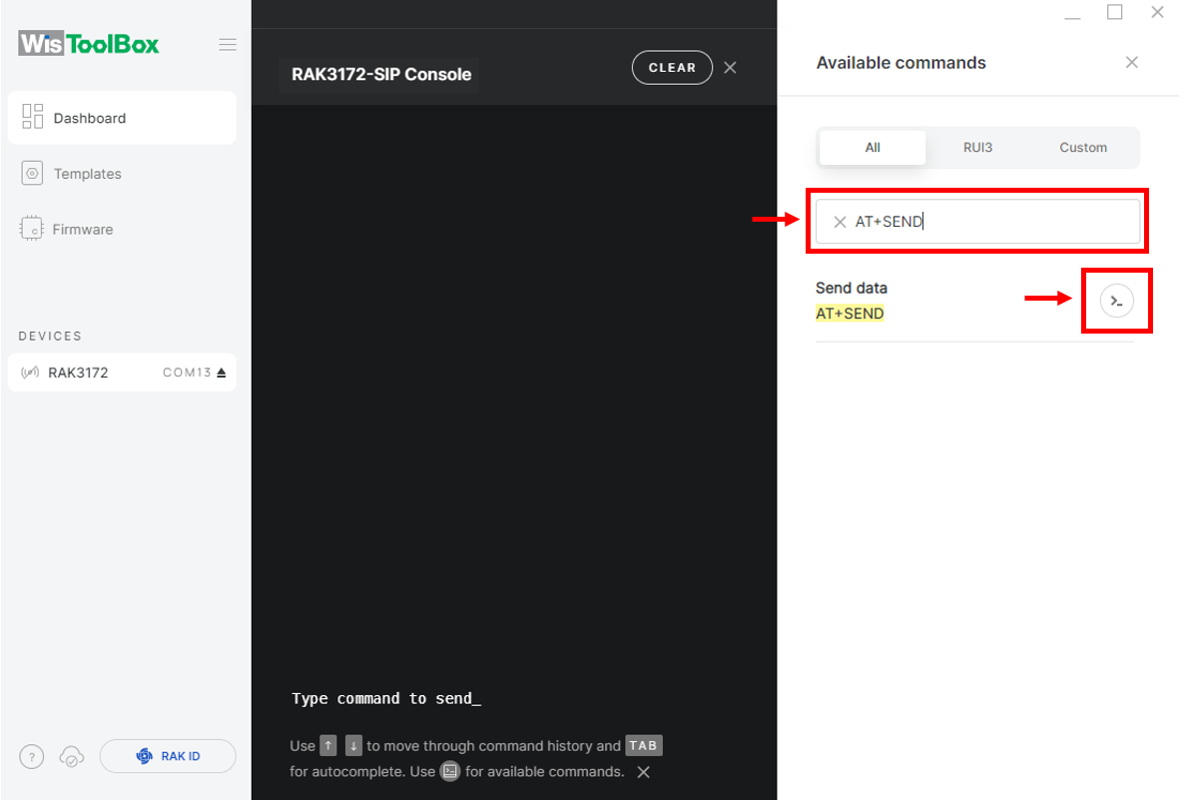 Figure 1: ABP device sending payload to the network
Figure 1: ABP device sending payload to the network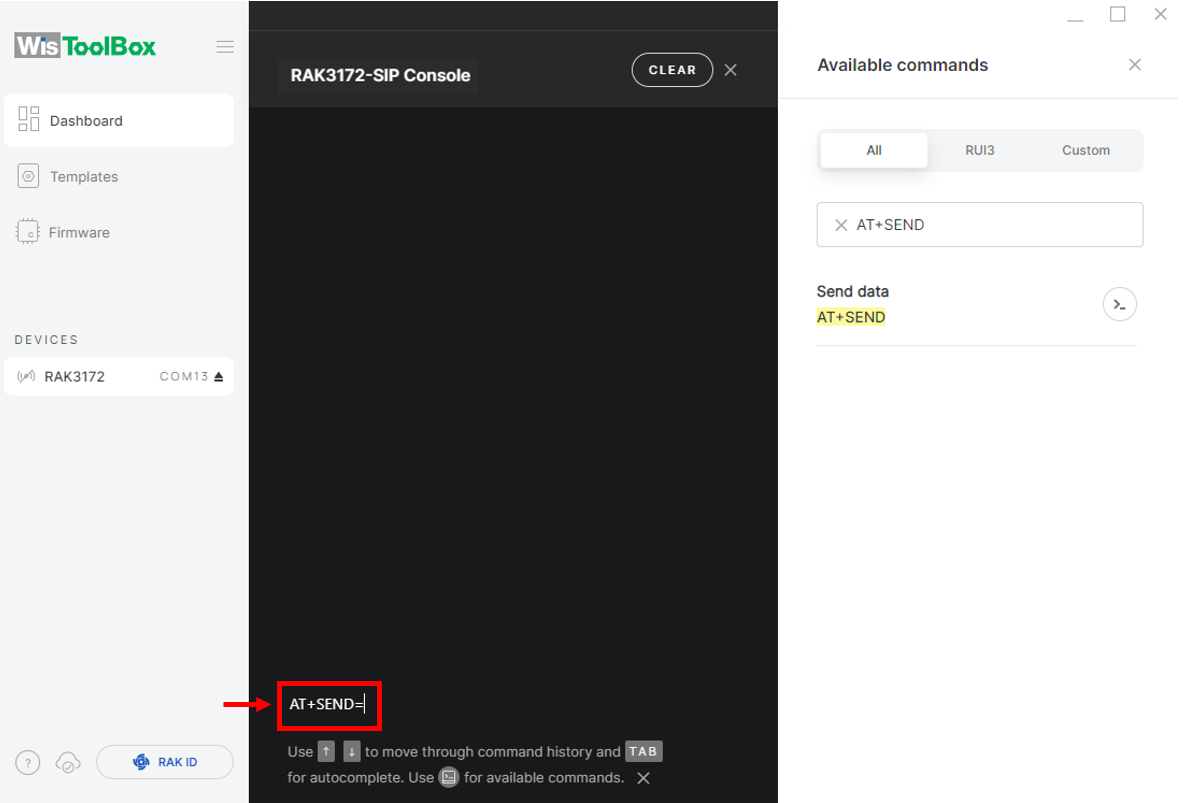 Figure 1: ABP device sending payload to the network
Figure 1: ABP device sending payload to the network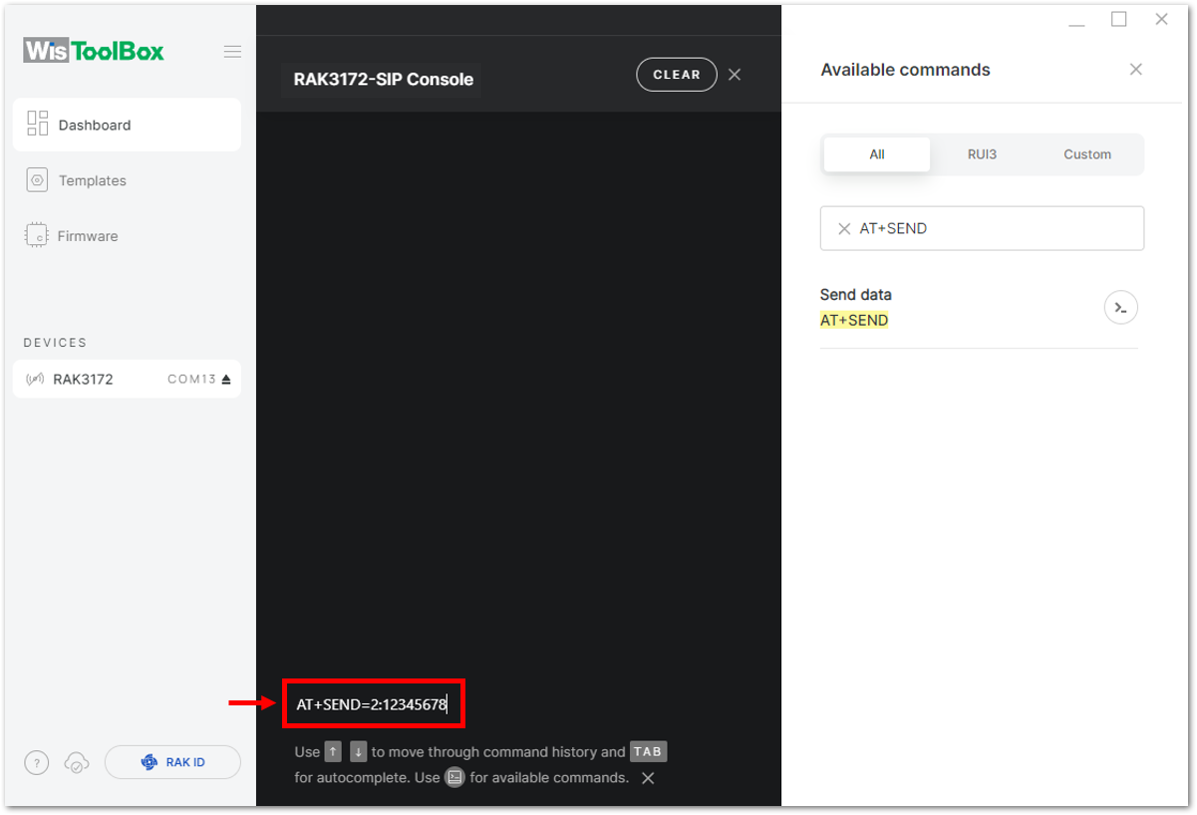 Figure 1: ABP device sending payload to the network
Figure 1: ABP device sending payload to the network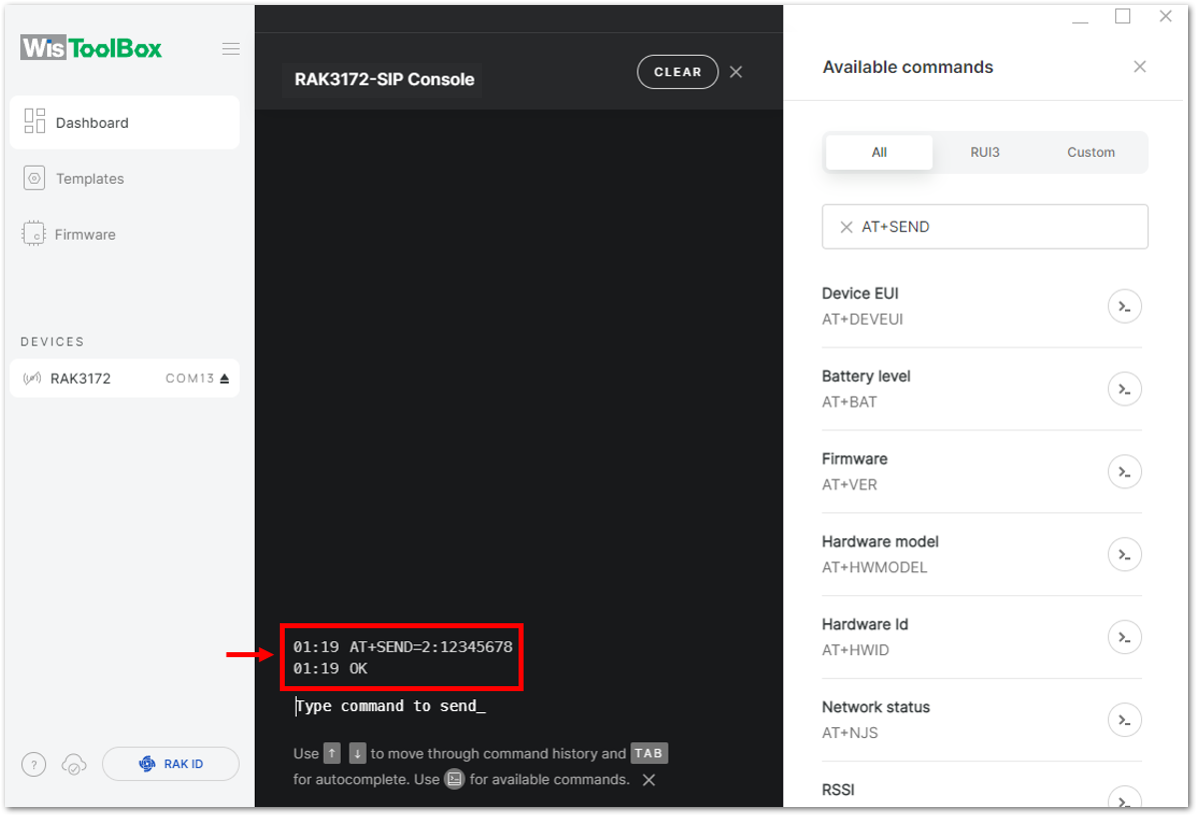 Figure 1: ABP device sending payload to the network
Figure 1: ABP device sending payload to the network- You can see the data sent by the RAK3172-SiP module on the TTN device console Live data section. Also, the Last seen info should be a few seconds or minutes ago.
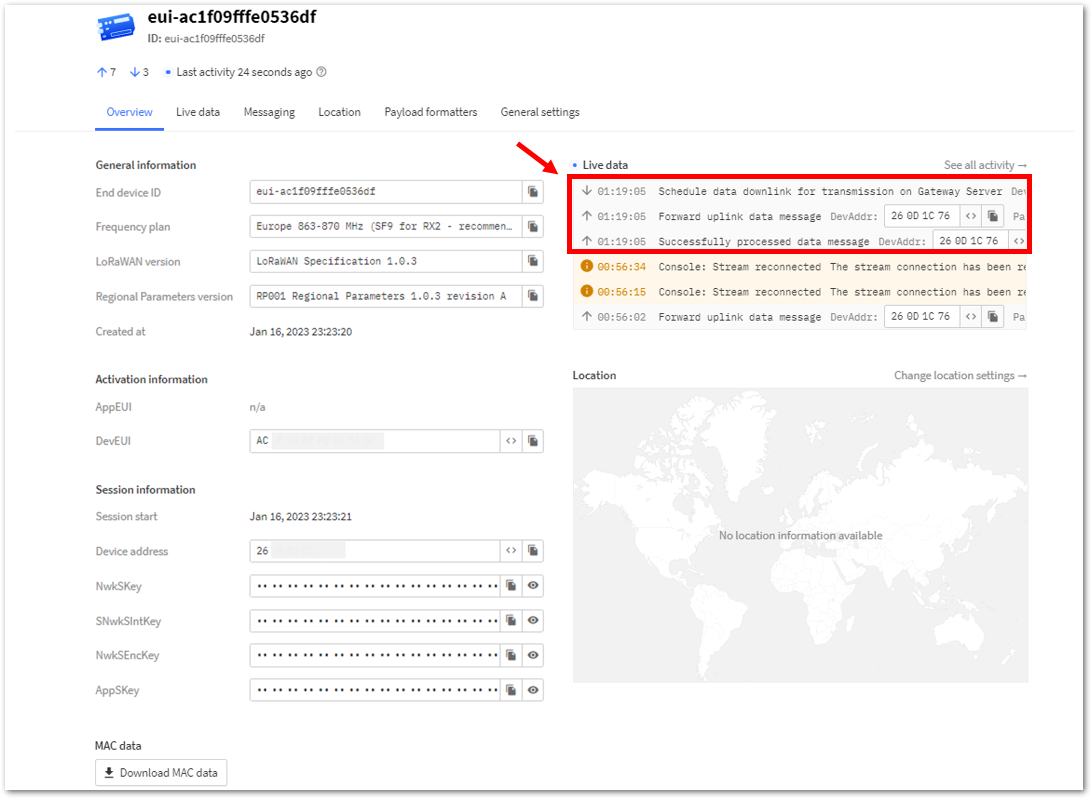 Figure 1: ABP Test Sample Data Sent Viewed in TTN
Figure 1: ABP Test Sample Data Sent Viewed in TTNConnecting with ChirpStack
This section shows how to connect the RAK3172-SiP to the ChirpStack platform.
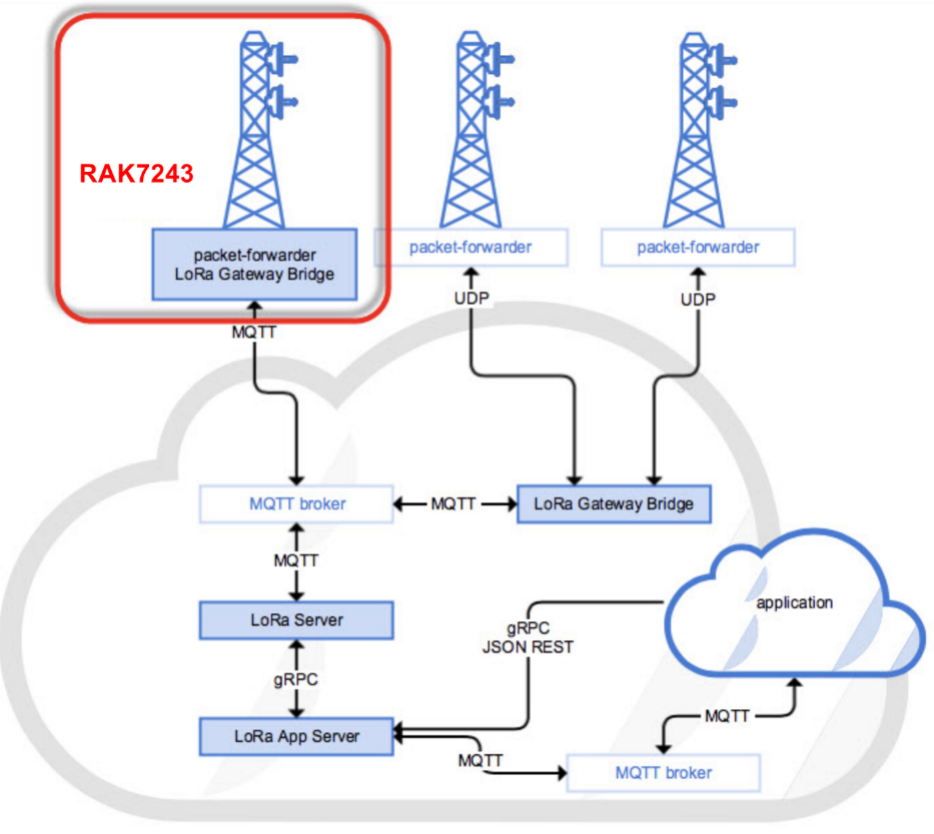 Figure 1: RAK3172-SiP in the context of the ChirpStack platform
Figure 1: RAK3172-SiP in the context of the ChirpStack platformThe ChirpStack, previously known as the LoRaServer project, provides open-source components for building LoRaWAN networks. Like in the case of TTN, the RAK3172-SiP is located in the periphery and will transmit the data to the backend servers through a LoRaWAN gateway. Learn more about ChirpStack.
It is assumed that you are using a RAK Gateway and its built-in ChirpStack. Also, the gateway with the ChirpStack must be configured successfully. For further information, check the RAK documents for more details.
-
In summary, these are the requirements:
- In a ChirpStack online gateway, the frequency band of the nodes should be consistent with the frequency band of the gateway in use.
- RAK Serial Port Tool provided by RAK
- RAK3172-SiP module
The frequency band used in the demonstration is EU868.
Create a New Application
- Log in to the ChirpStack server using your account and password.
- Go to the Application section, as shown in Figure 197.
 Figure 1: Application section
Figure 1: Application section- By default, you should create a new application, although you can reuse existing ones. For this setup, create a new Application by clicking on the CREATE button and filling in the required parameters, as shown in Figure 198 and Figure 199.
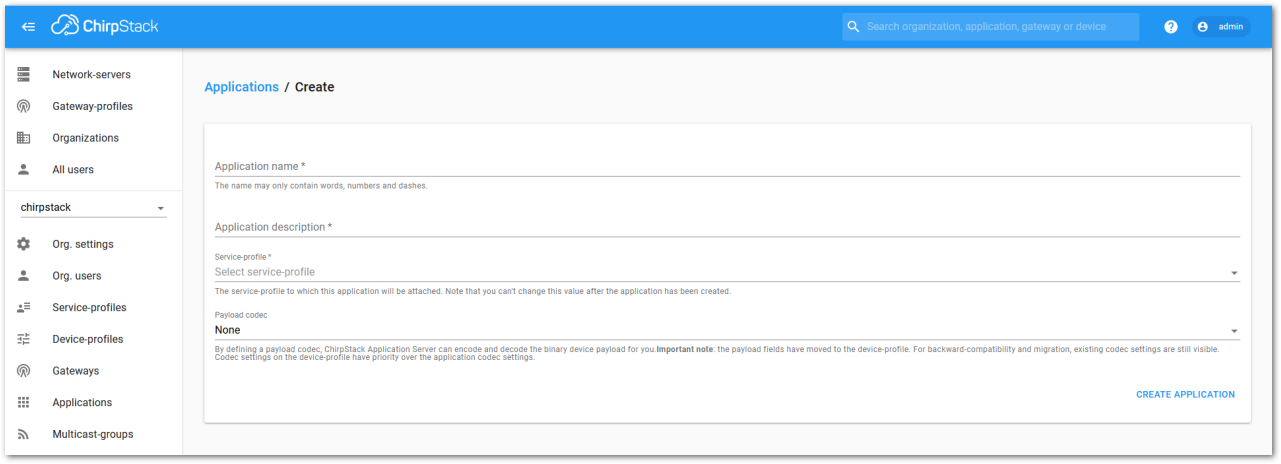 Figure 1: Creating a new application
Figure 1: Creating a new application- For this setup, create an Application named rak_node_test.
ChirpStack LoraServer supports multiple system configurations, with only one by default.
- Service profile: Field is to select the system profile.
- Payload codec: It is the parsing method for selecting load data such as parsing LPP format data.
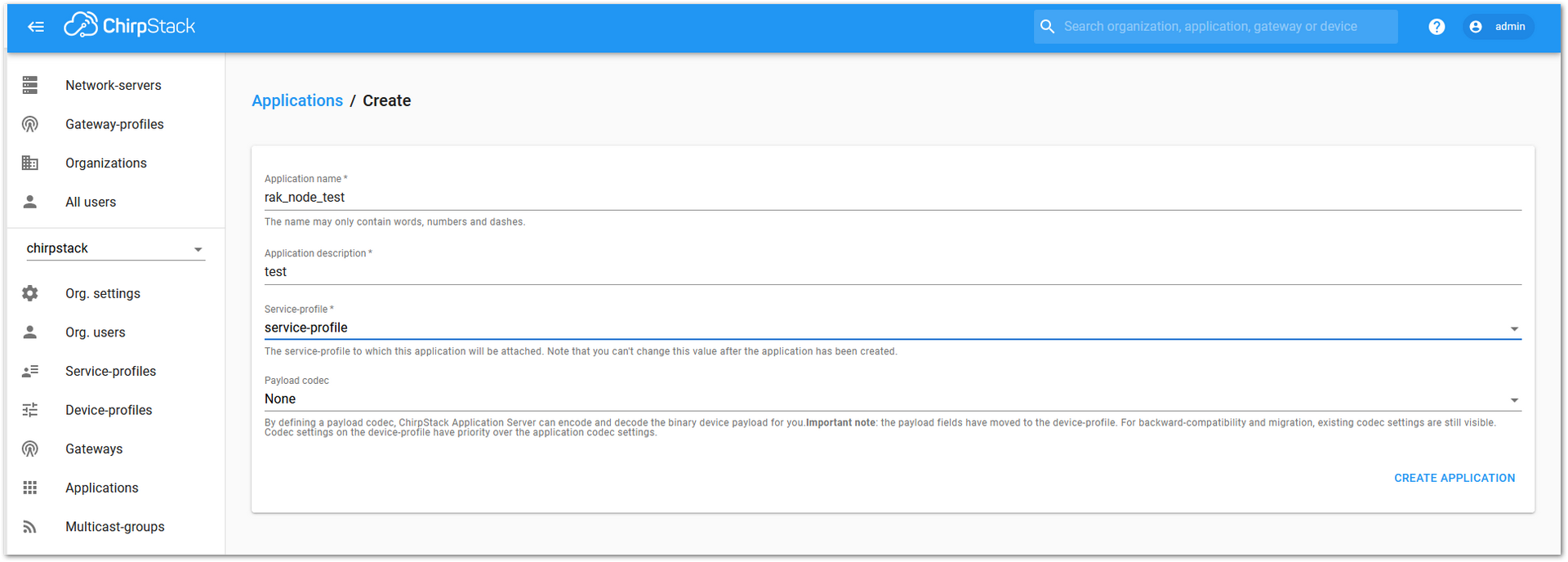 Figure 1: Filling in the parameters of an application
Figure 1: Filling in the parameters of an application-
Choose the Application created in the previous step, then select the DEVICES tab, as shown in Figure 200 and Figure 201.
-
Once done, click “+ CREATE”.
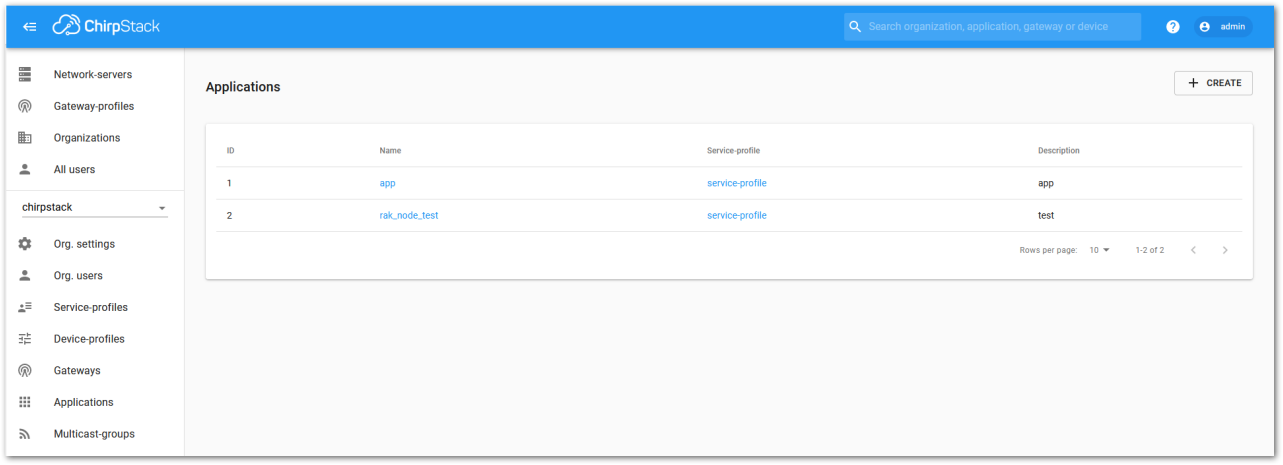 Figure 1: List of applications created
Figure 1: List of applications created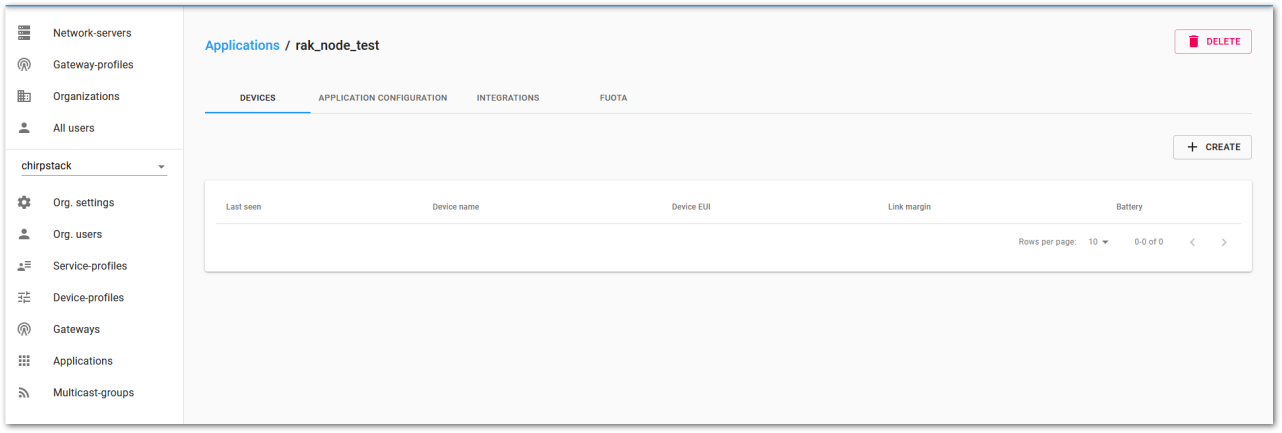 Figure 1: Device tab of an application
Figure 1: Device tab of an application- Once inside the DEVICE tab, create a new device (LoRaWAN node) by clicking on the “+ CREATE” button.
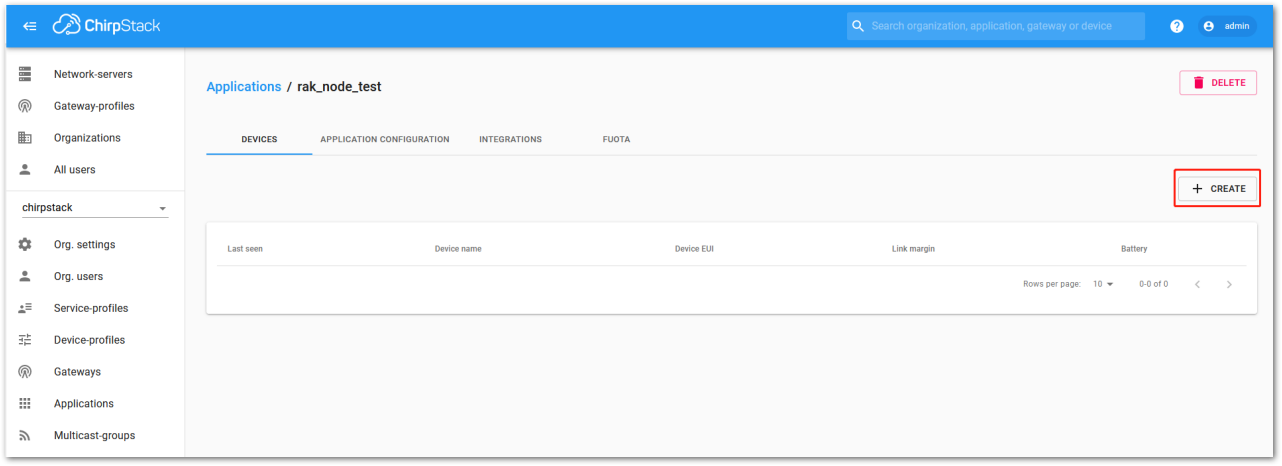 Figure 1: Add a new device
Figure 1: Add a new device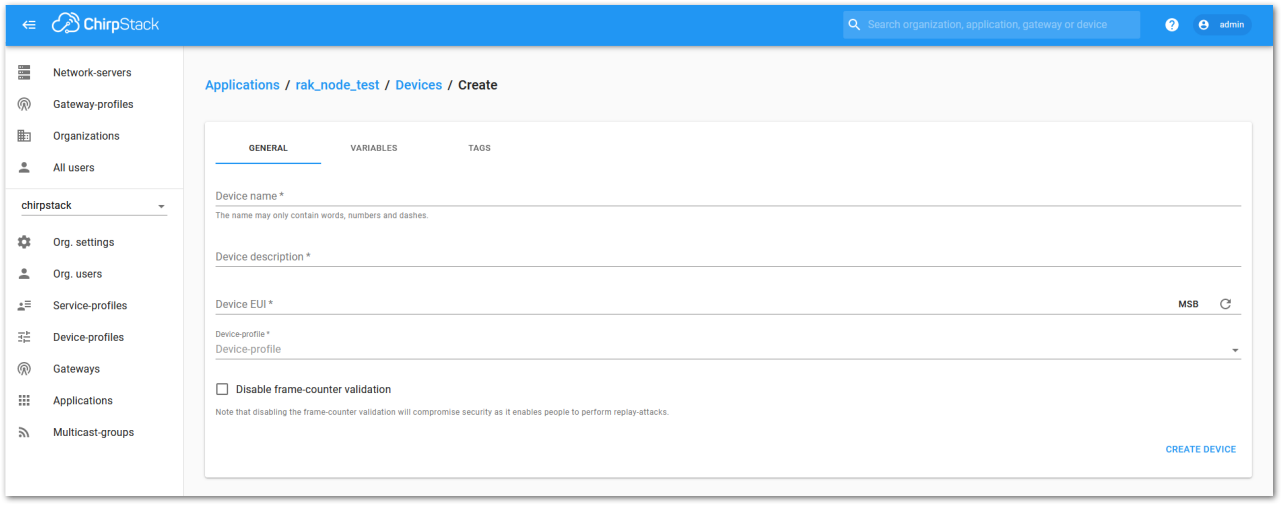 Figure 1: Chirpstack adding node into the RAK3172-SiP module
Figure 1: Chirpstack adding node into the RAK3172-SiP module- Once the node is created, fill in the necessary data. You can generate a Device EUI automatically by clicking the following icon, or you can write a correct Device EUI in the edit box.
Fill in the parameters requested:
- Device name and Device description: These are descriptive texts about your device.
- Device EUI: This interface allows you to generate a Device EUI automatically by clicking the generate icon. You can also add a specific Device EUI directly in the form.
- Device Profile:
- If you want to join in OTAA mode, select DeviceProfile_OTAA.
- If you want to join in ABP mode, select DeviceProfile_ABP.
Device profiles DeviceProfile_OTAA and DeviceProfile_ABP are only available if you are using the built-in Chirpstack LoRaWAN Server of RAK Gateways.
If you have your own Chirpstack installation, you can set up the device profile with LoRaWAN MAC version 1.0.4 and LoRaWAN Regional Parameters revision B to make it compatible with RAK3172-SiP.
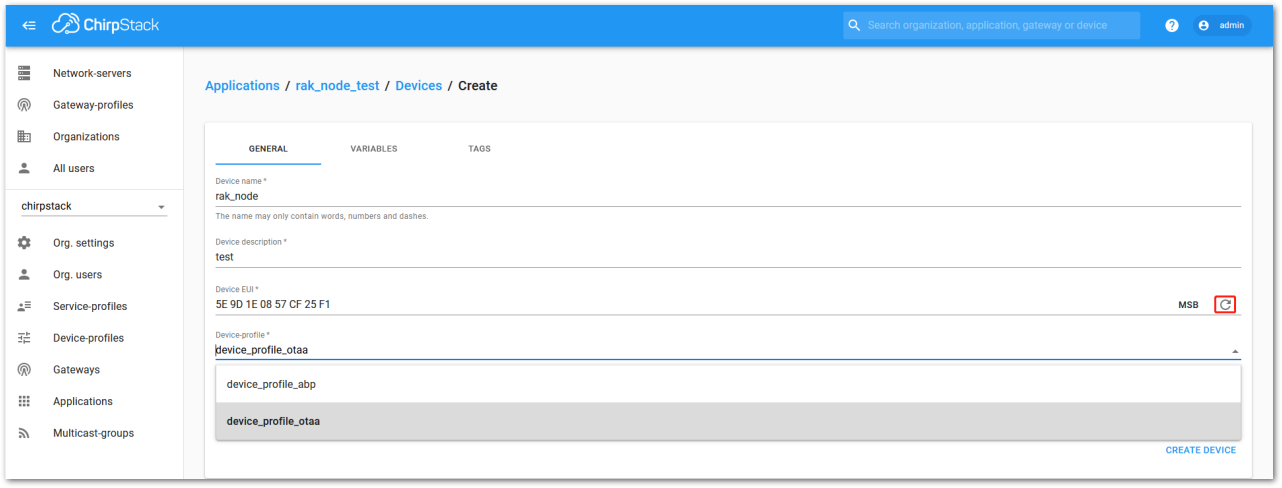 Figure 1: Generate a new device EUI
Figure 1: Generate a new device EUI Chirpstack OTAA Device Registration
- If you have selected DeviceProfile_OTAA, as shown in Figure 205, then after the device is created, an Application Key must be also created for this device.
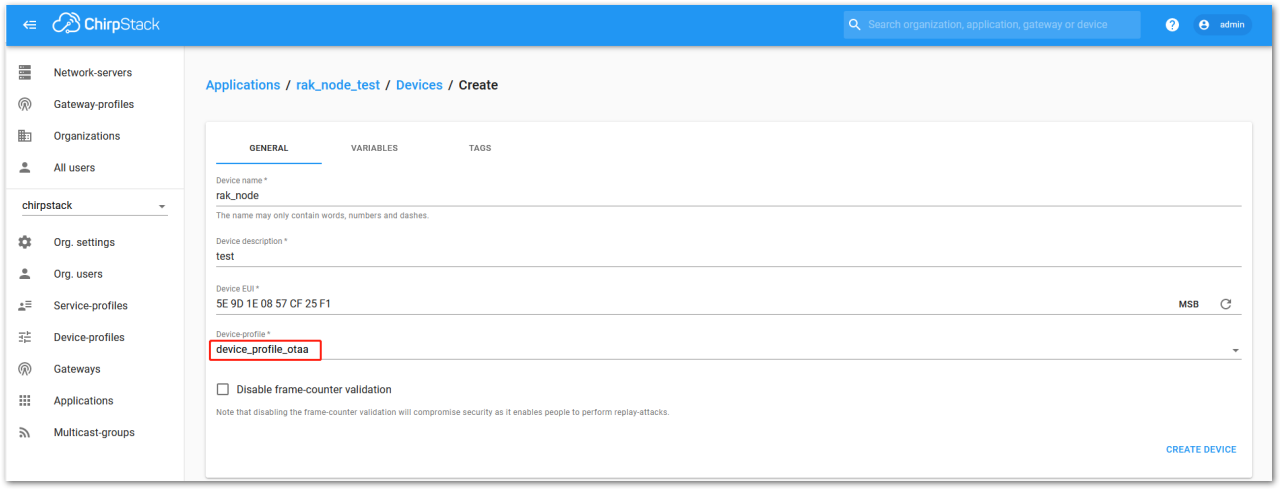 Figure 1: Chirpstack OTAA activation
Figure 1: Chirpstack OTAA activation- A previously created Application Key can be entered here, or a new one can be generated automatically by clicking the icon highlighted in red in Figure 206.
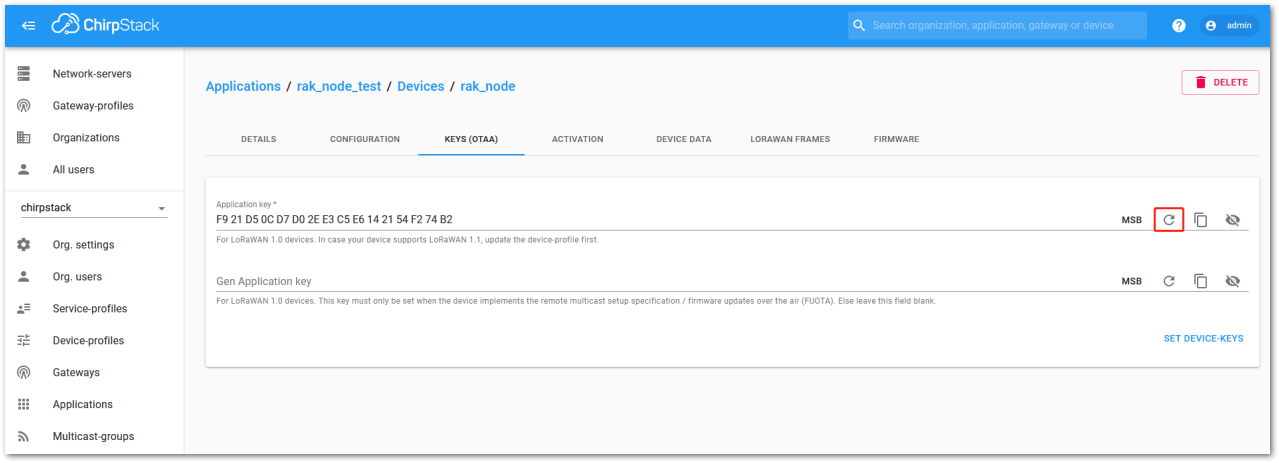 Figure 1: Chirpstack OTAA set application keys
Figure 1: Chirpstack OTAA set application keys- Once the Application Key is added to the form, the process can be finalized by clicking on the SET DEVICE-KEYS button.
- As shown in Figure 207, a new device should be listed in the DEVICES tab. The most important parameters, such as the Device EUI, are shown in the summary.
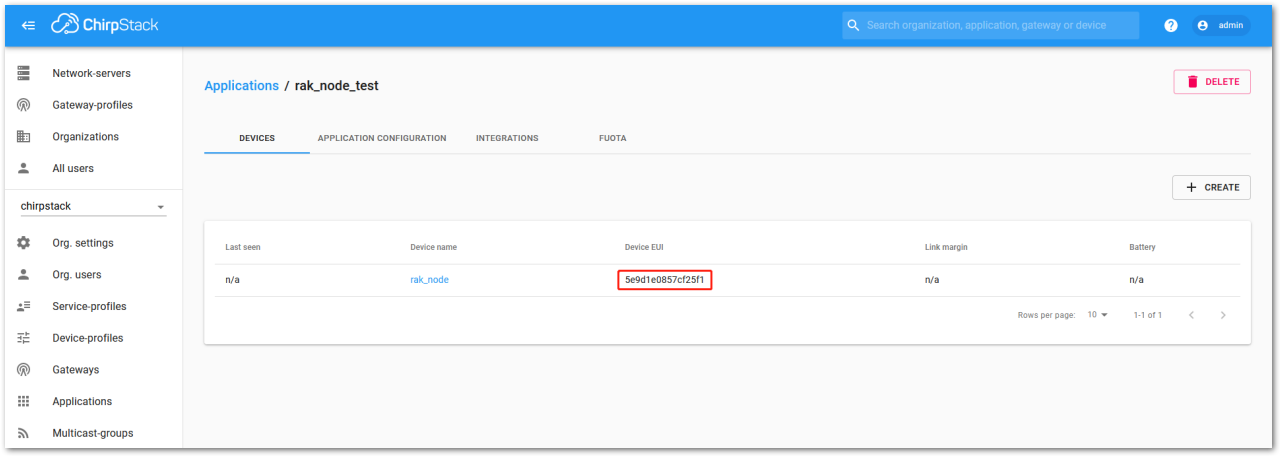 Figure 1: Chirpstack OTAA list of the device in the device tab
Figure 1: Chirpstack OTAA list of the device in the device tab- To end the process, it is a good practice to review that the Application Key is properly associated with this device. The Application Key can be verified in the KEYS (OTAA) tab, as shown in Figure 208.
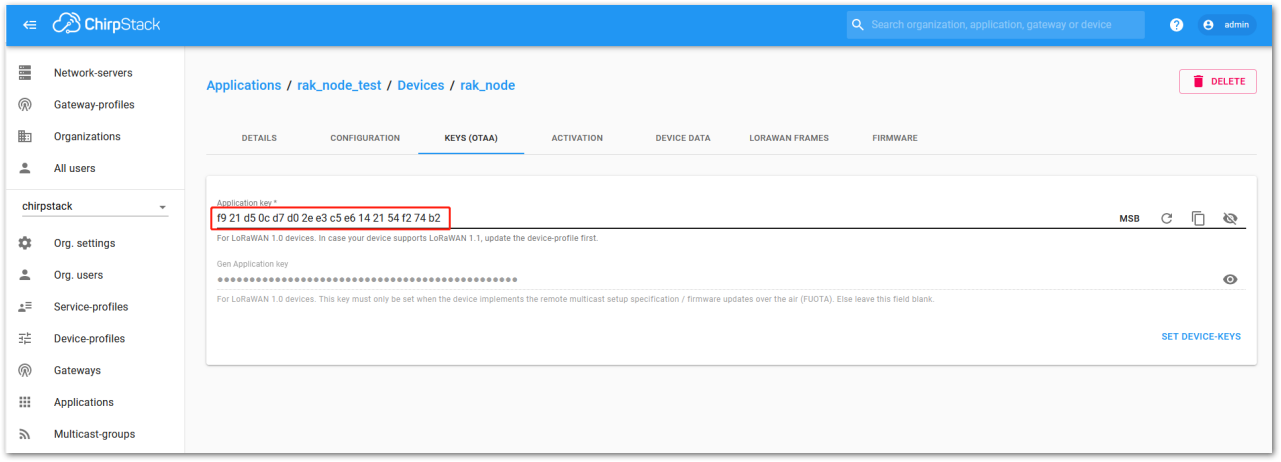 Figure 1: Application key associated with the new device
Figure 1: Application key associated with the new deviceStandard OTAA mode requires the Device EUI, Application Key, and Application EUI, but in ChirpStack’s implementation, only the Device EUI and the Application Key are mandatory. The Application EUI is not required and not recorded in the Application tab. Nevertheless, you can reuse the Device EUI as the Application EUI during the configuration on the side of the node.
OTAA Configuration for Chirpstack
The RAK3172-SiP supports a series of AT commands to configure its internal parameters and control the functionalities of the module.
- To set up the RAK3172-SiP to join the Chirpstack using OTAA, start by connecting the RAK3172-SiP to the Computer (see Figure 26) and open the RAK Serial Port Tool. Select the right COM port and set the baud rate to 115200.
It is recommended to start by testing the serial communication and verify that the current configuration is working by sending these two AT commands:
AT
ATE
ATE will echo the commands you input to the module, which is useful for tracking the commands and troubleshooting.
You will receive OK when you input the two commands. After setting ATE, see all the commands you input together with the replies. Try again AT and you should see it on the terminal followed by OK, as shown in Figure 209.
If haven't received an OK or any reply, you need to check if the wiring of your UART lines is correct and if the baud is correctly configured to 115200. Also, you can check if the device is powered correctly. If you are getting power from a USB port, ensure that you have a good USB cable.
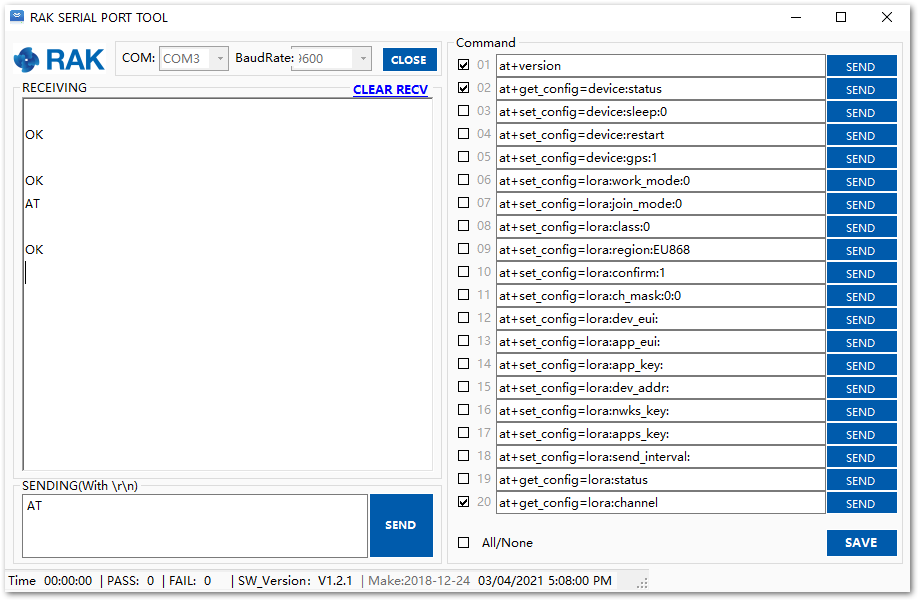 Figure 1: at+version command response
Figure 1: at+version command response- The next step is to configure the OTAA LoRaWAN parameters in RAK3172-SiP:
- LoRa work mode: LoRaWAN
- LoRaWAN join mode: OTAA
- LoRaWAN class: Class A
- LoRaWAN region: EU868
Set the work mode to LoRaWAN.
AT+NWM=1
Set the LoRaWAN activation to OTAA.
AT+NJM=1
Set the LoRaWAN class to Class A.
AT+CLASS=A
Set the frequency/region to EU868.
AT+BAND=4
- Depending on the regional band you selected, you might need to configure the sub-band of your RAK3172-SiP to match the gateway and LoRaWAN network server. This is especially important for Regional Bands like US915 and AU915.
- To configure the masking of channels for the sub-bands, you can use the
AT+MASKcommand that can be found on the AT Command Manual. - To illustrate, you can use sub-band 2 by sending the command
AT+MASK=0002.
List of band parameter options
| Code | Regional Band |
|---|---|
| 0 | EU433 (Not Supported) |
| 1 | CN470 (Not Supported) |
| 2 | RU864 |
| 3 | IN865 |
| 4 | EU868 |
| 5 | US915 |
| 6 | AU915 |
| 7 | KR920 |
| 8 | AS923 |
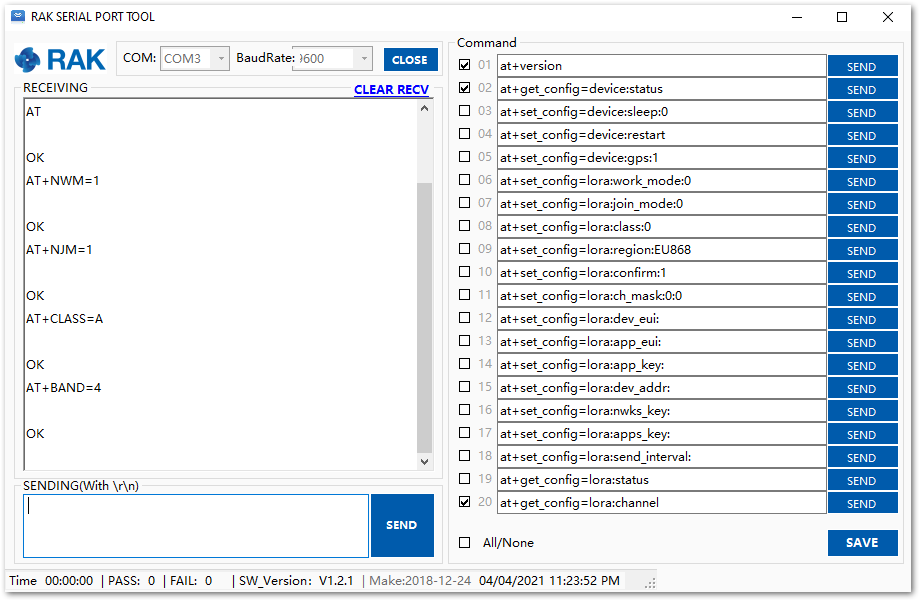 Figure 1: Configuring LoRa parameters
Figure 1: Configuring LoRa parameters- After the configuration of the LoRaWAN parameters, the next step is to set up the DevEUI and AppKey. You need the use the values from the Chirpstack device console.
The Application EUI parameter is not required in the ChirpStack platform; therefore, it is possible to use the same ID as the Device EUI.
- Device EUI: 5E9D1E0857CF25F1
- Application EUI: 5E9D1E0857CF25F1
- Application Key: F921D50CD7D02EE3C5E6142154F274B2
Set the Device EUI.
AT+DEVEUI=5E9D1E0857CF25F1
Set the Application EUI.
AT+APPEUI=5E9D1E0857CF25F1
Set the Application Key.
AT+APPKEY=F921D50CD7D02EE3C5E6142154F274B2
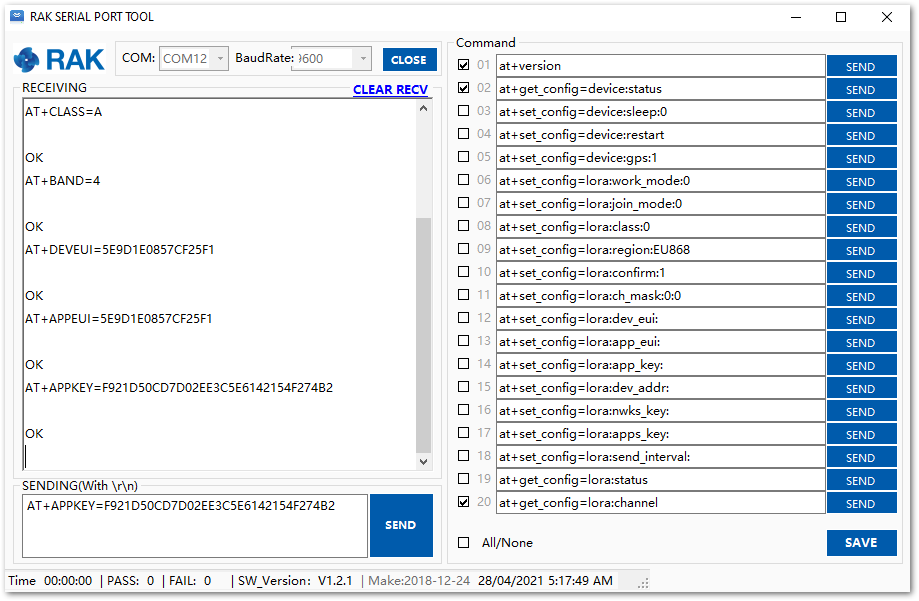 Figure 1: Configuring LoRa Parameters
Figure 1: Configuring LoRa Parameters- After EUI and key configuration, the device can now join the network and send some payload.
AT+JOIN=1:0:10:8
Join command format: AT+JOIN=w:x:y:z
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| w | Join command - 1: joining, 0: stop joining. |
| x | Auto-join config - 1: auto-join on power-up, 0: no auto-join |
| y | Reattempt interval in seconds (7-255) - 8 is the default. |
| z | Number of join attempts (0-255) - 0 is the default. |
After 5 or 6 seconds, if the request is successfully received by a LoRaWAN gateway, you should see the JOINED status reply.
If the OTAA device failed to join, you need to check if your device is within reach of a working LoRaWAN gateway that is configured to connect to Chirpstack. It is also important to check that all your OTAA parameters (DEVEUI and APPKEY) are correct, using the AT+DEVEUI=? and AT+APPKEY=? commands. Lastly, ensure that the antenna of your device is properly connected.
After checking all the things above, try to join again.
- With the end-device properly activated, try to send some payload after a successful join.
AT+SEND=2:12345678
Send command format: AT+SEND=<port>:<payload>
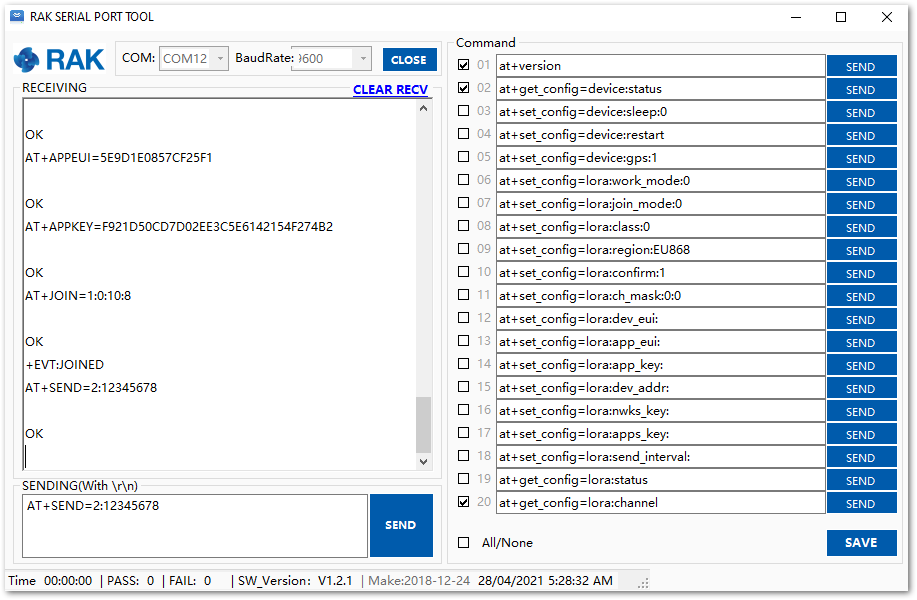 Figure 1: OTAA test sample data sent via RAK Serial Port Tool
Figure 1: OTAA test sample data sent via RAK Serial Port ToolOn the ChirpStack platform, you should see the join and uplink messages in the LORAWAN FRAMES tab, as shown in Figure 213. By convention, messages sent from nodes to gateways are considered as Uplinks while messages sent by gateways to nodes are considered as Downlinks.
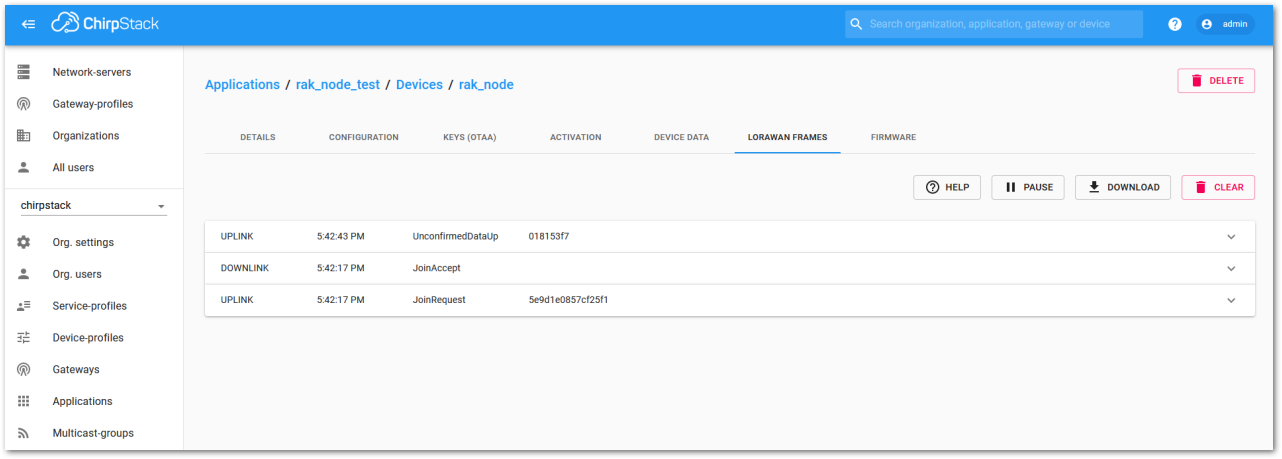 Figure 1: Chirpstack data received preview
Figure 1: Chirpstack data received previewChirpstack ABP Device Registration
- During the registration of a new device, if you select DeviceProfile_ABP, as shown in Figure 214, then the ChirpStack platform will assume that this device will join the LoRaWAN network using the ABP mode.
Check Disable counting frame verification. During the test, when the module is restarted, the frame counting number will also be restarted from zero. This would cause a synchronization problem with the ChirpStack server treating it as a replay attack. For testing purposes, it is safe to disable this feature, but remember to activate it in a production environment.
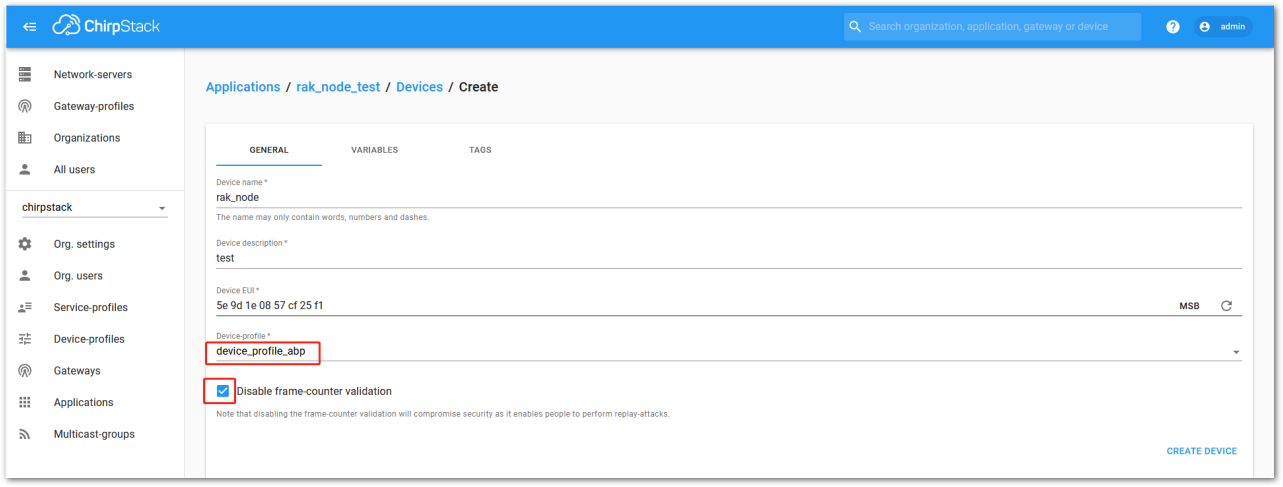 Figure 1: ChirpStack console, Configuring a device
Figure 1: ChirpStack console, Configuring a device- After selecting the ABP mode, the following parameters appear in the Activation tab. Then, you can see that there are some parameters for ABP in the ACTIVATION item:
- Device Address
- Network Session Key
- Application Session Key
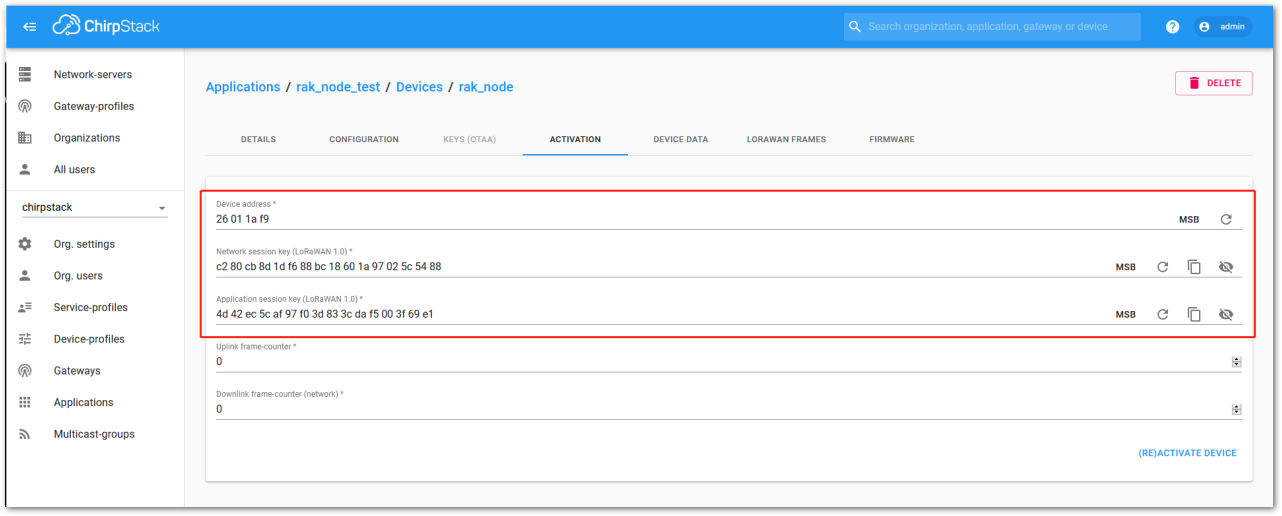 Figure 1: Chirpstack ABP activation parameters needed
Figure 1: Chirpstack ABP activation parameters needed- The parameters can be generated as random numbers by the platform or can be set with user values. Once these parameters are filled in properly, the process is completed by clicking on the ACTIVATE DEVICE button.
ABP Configuration for Chirpstack
- To set up the RAK3172-SiP to join the Chirpstack using ABP, start by connecting the RAK3172-SiP to the Computer (see Figure 26) and open the RAK Serial Port Tool. Select the right COM port and set the baud rate to 115200.
It is recommended to start by testing the serial communication and verify that the current configuration is working by sending these two AT commands:
AT
ATE
ATE will echo the commands you input to the module, which is useful for tracking the commands and troubleshooting.
You will receive OK when you input the two commands. After setting ATE, see all the commands you input together with the replies. Try again AT and you should see it on the terminal followed by OK, as shown in Figure 216.
If haven't received an OK or any reply, you need to check if the wiring of your UART lines is correct and if the baud is correctly configured to 115200. Also, you can check if the device is powered correctly. If you are getting power from a USB port, ensure that you have a good USB cable.
 Figure 1: at+version command response
Figure 1: at+version command response- The next step is to configure the ABP LoRaWAN parameters in RAK3172-SiP:
- LoRa work mode: LoRaWAN
- LoRaWAN join mode: ABP
- LoRaWAN class: Class A
- LoRaWAN region: EU868
Set the work mode to LoRaWAN. It can be set to P2P as well but by default, the device is in LoRaWAN mode.
AT+NWM=1
Set the LoRaWAN activation to ABP.
AT+NJM=0
Set the LoRaWAN class to Class A.
AT+CLASS=A
Set the frequency/region to EU868.
AT+BAND=4
- Depending on the regional band you selected, you might need to configure the sub-band of your RAK3172-SiP to match the gateway and LoRaWAN network server. This is especially important on Regional Bands like US915 and AU915.
- To configure the masking of channels for the sub-bands, you can use the
AT+MASK commandon the AT Commands Manual. - To illustrate, you can use sub-band 2 by sending the command
AT+MASK=0002.
List of band parameter options
| Code | Regional Band |
|---|---|
| 0 | EU433 (Not Supported) |
| 1 | CN470 (Not Supported) |
| 2 | RU864 |
| 3 | IN865 |
| 4 | EU868 |
| 5 | US915 |
| 6 | AU915 |
| 7 | KR920 |
| 8 | AS923 |
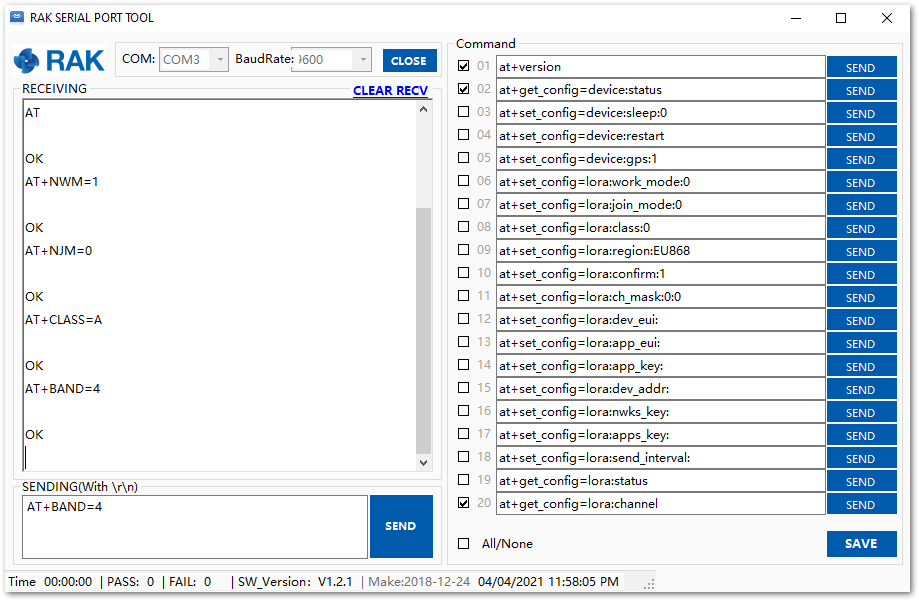 Figure 1: Configuring LoRa parameters
Figure 1: Configuring LoRa parameters- After the configuration of the LoRaWAN parameters, the next step is to set up the device address and session keys. You need the use the values from the TTN device console.
- Device Address: 26011AF9
- Application Session Key: 4D42EC5CAF97F03D833CDAf5003F69E1
- Network Session Key: C280CB8D1DF688BC18601A97025C5488
Set the Device Address.
AT+DEVADDR=26011AF9
Set the Application Session Key.
AT+APPSKEY=4D42EC5CAF97F03D833CDAf5003F69E1
Set the Network Session Key.
AT+NWKSKEY=C280CB8D1DF688BC18601A97025C5488
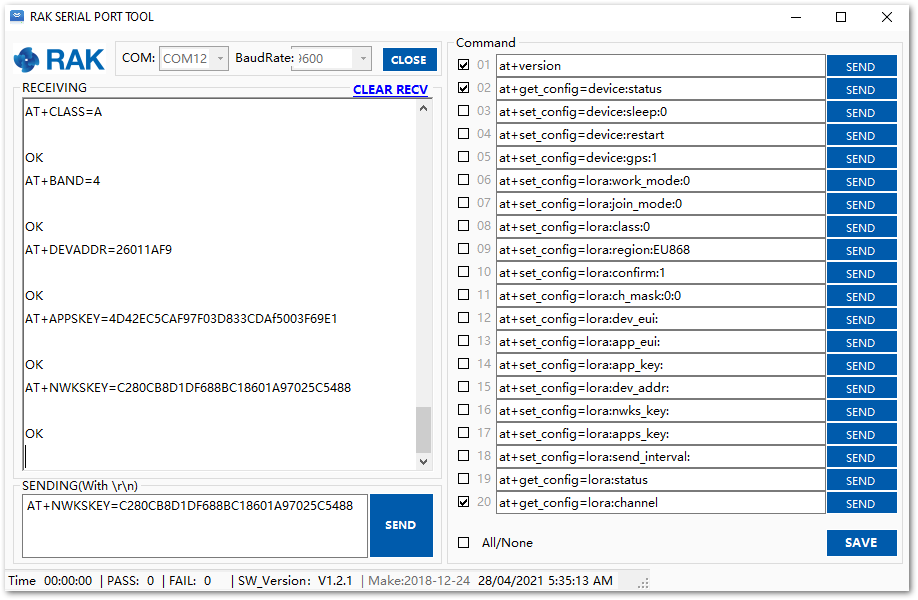 Figure 1: Configuring LoRa Parameters
Figure 1: Configuring LoRa ParametersAfter EUI and keys configuration, the device can now join the network and send some payload.
AT+JOIN=1:0:10:8
Join command format: AT+JOIN=w:x:y:z
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| w | Join command - 1: joining, 0: stop joining. |
| x | Auto-join config - 1: auto-join on power-up, 0: no auto-join |
| y | Reattempt interval in seconds (7-255) - 8 is the default. |
| z | Number of join attempts (0-255) - 0 is the default. |
-
After 5 or 6 seconds, if the request is successfully received by a LoRaWAN gateway, then you should see the JOINED status reply.
-
You can now try to send some payload after a successful join.
AT+SEND=2:12341234
Send command format: AT+SEND=<port>:<payload>
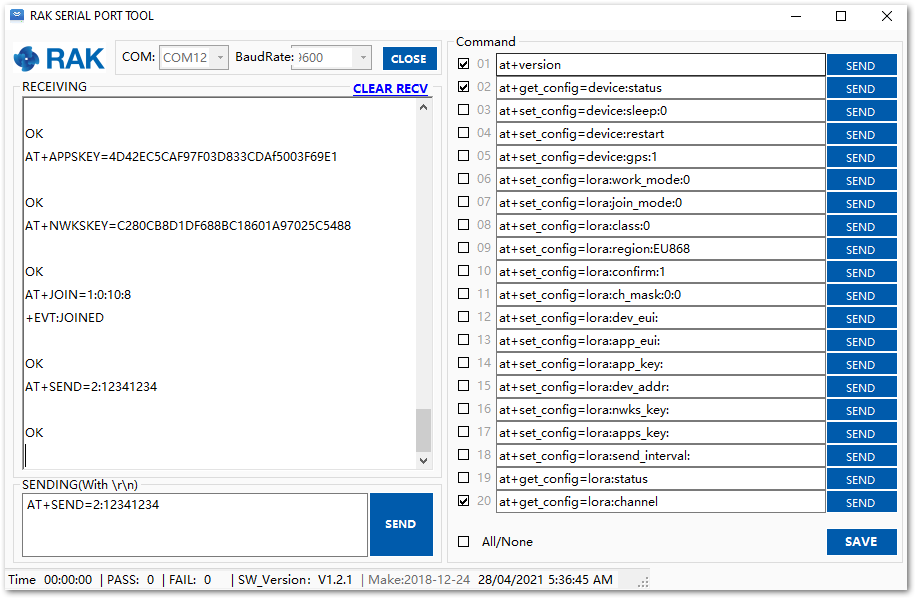 Figure 1: ABP test sample data sent via RAK Serial Port Tool
Figure 1: ABP test sample data sent via RAK Serial Port ToolLoRa P2P Mode
This section will show you how to set up and connect two RAK3172-SiP units to work in the LoRa P2P mode. The configuration of the RAK3172-SiP units is done by connecting the two modules to a general-purpose computer using a USB-UART converter. The setup of each RAK3172-SiP can be done separately, but testing the LoRa P2P mode will require having both units connected simultaneously. This could be done by having one computer with two USB ports or two computers with one USB port each.
It is recommended to start by testing the serial communication and verify the current configuration is working by sending these two AT commands:
AT
ATE
ATE will echo the commands you input to the module, which is useful for tracking the commands and troubleshooting.
You will receive OK when you input the two commands. After setting ATE, see all the commands you input together with the replies.
Try again AT and you should see it on the terminal followed by OK.
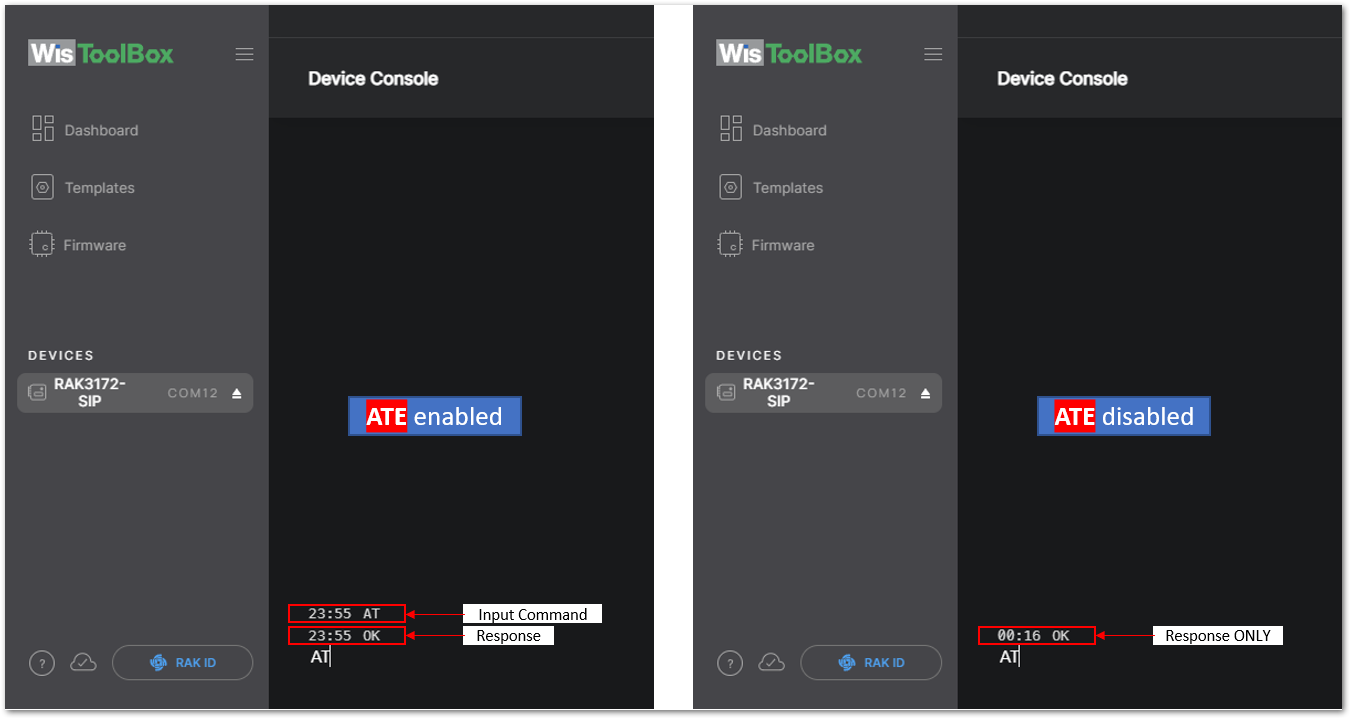 Figure 1: at+version command response
Figure 1: at+version command response- In setting up the RAK3172 to work in LoRa P2P mode, you need to change the LoRa network work mode command on both RAK3172 modules.
AT+NWM=0
AT+NWM parameter mode can be either 0=LoRa P2P or 1=LoRaWAN.
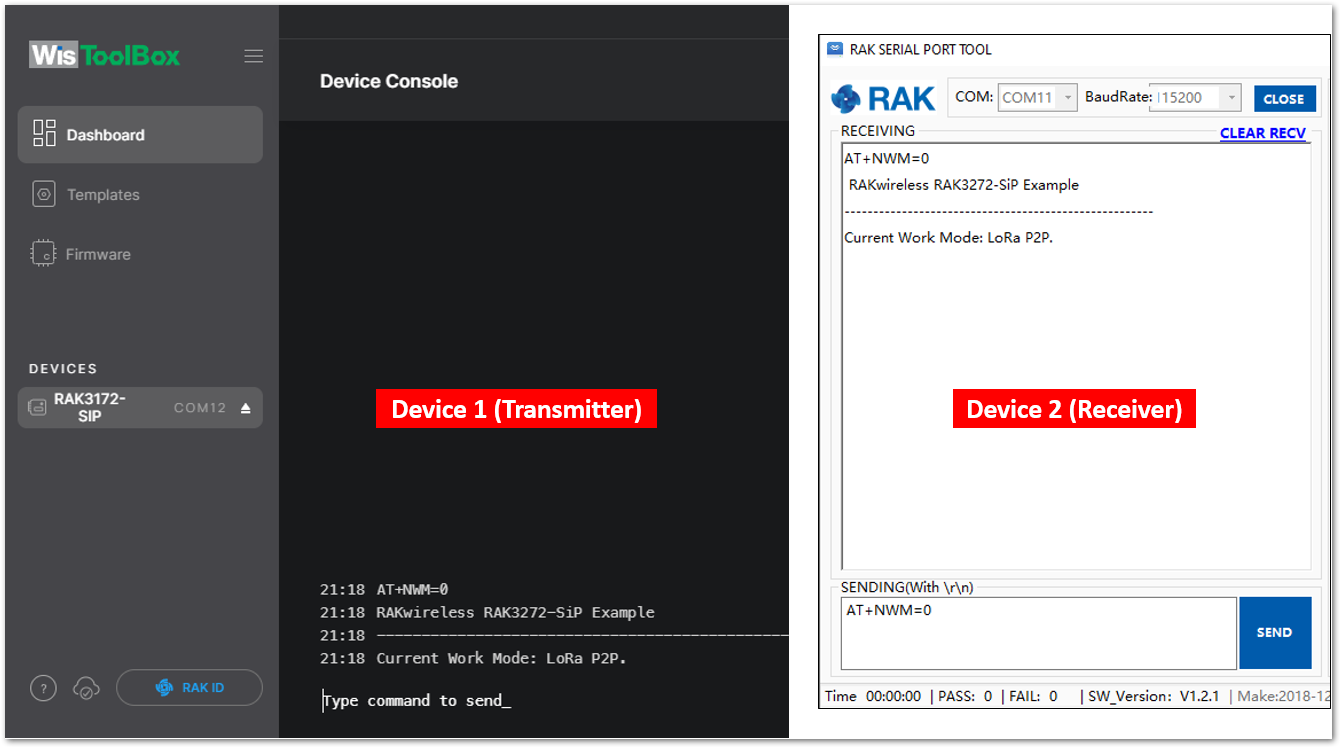 Figure 1: P2P Mode
Figure 1: P2P Mode- The device will start automatically if you change modes from LoRaWAN to LoRa P2P and vice-versa.
- You might need to input the
ATEcommand again to ensure that your succeeding commands on P2P mode echo on the terminal.
- You need to input the P2P setup on both RAK3172-SiP modules. The parameters should be exactly the same in the two modules.
AT+P2P=868000000:7:125:0:10:14
For this P2P setup, the LoRa parameters are the following:
- Link frequency: 868000000 Hz
- Spreading factor: 7
- Bandwidth: 125 kHz
- Coding Rate: 0 = 4/5
- Preamble Length: 10
- Power: 14 dBm
Refer to the P2P Mode section of the AT command documentation to learn more about the definition of the parameters used and the individual commands if you want specific parameters changed.
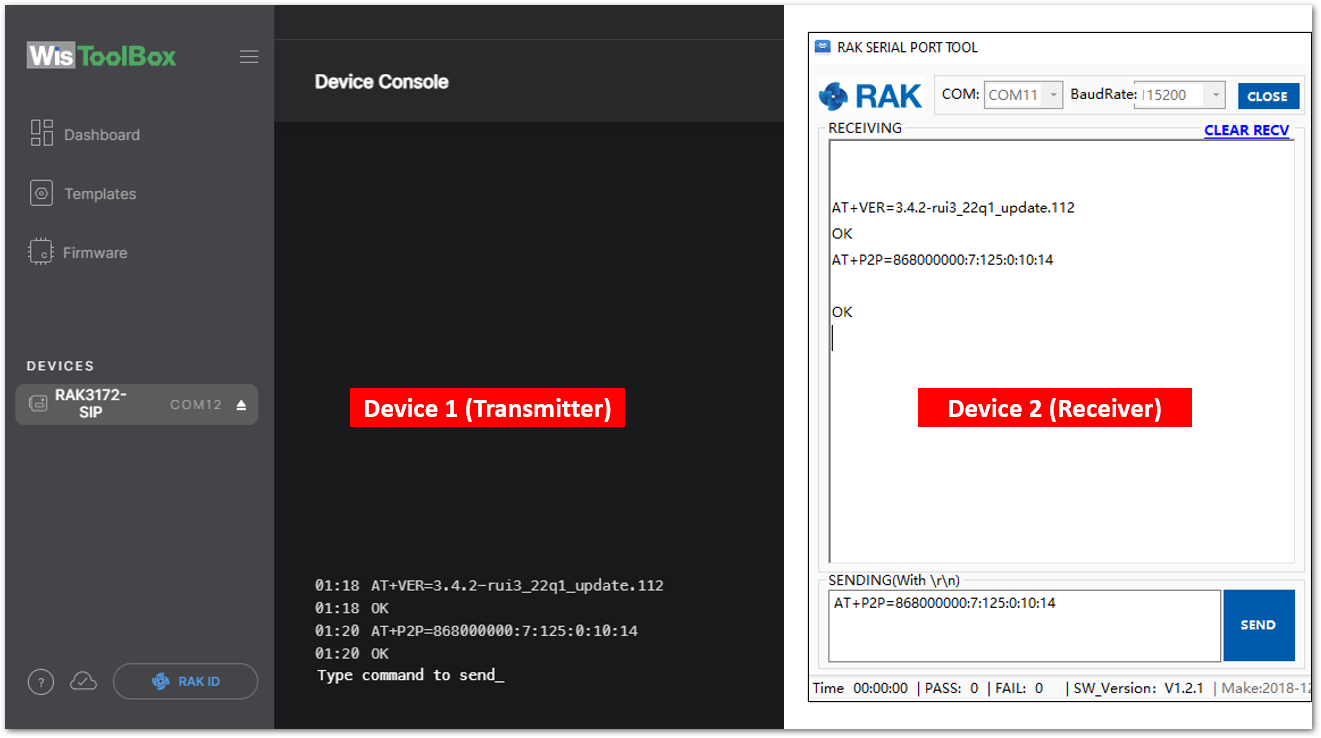 Figure 1: Configuring P2P in both RAK3172-SiP Module
Figure 1: Configuring P2P in both RAK3172-SiP Module- To set one module as the receiver (RX), you need to set the value of the P2P receive command.
LoRa P2P default setting is Transmitter (TX) mode. This consumes lower power compared to Receiver (RX) mode where the radio is always listening for LoRa packets.
a. P2P LoRa RX configurable duration value is from 1 to 65533 ms. In this example, the device will listen and wait for LoRa P2P Packets for 30000 ms or 30 seconds. It will automatically disable RX mode and switch to TX mode after the timeout. If the device did not receive any packets within the time period, then the callback after timeout is +EVT:RXP2P RECEIVE TIMEOUT.
AT+PRECV=30000
b. If the AT+PRECV value is set to 65535, the device will listen to P2P LoRa packets without a timeout, but it will stop listening once a P2P LoRa packet is received. After receiving the packets, it will disable RX mode and automatically switch to TX mode again.
AT+PRECV=65535
c. If the AT+PRECV value is set to 65534, the device will continuously listen to P2P LoRa packets without any timeout. It will continuously stay in RX mode until AT+PRECV is set to 0.
AT+PRECV=65534
d. If the AT+PRECV value is set to 0, the device will stop listening to P2P LoRa packets. It disables LoRa P2P RX mode and switches to TX mode.
AT+PRECV=0
- With one module configured as Transmitter (TX) and the other device will be the Receiver (RX), try to send or transmit P2P payload data.
AT+PSEND= <payload>
AT_PARAM_ERRORis returned when setting the wrong or malformed value.AT_BUSY_ERRORis returned if the device is still in RX mode and you try to send or reconfigure the RX period. If theAT+PRECVcommand is set to 65534, you need to execute firstAT+PRECV=0to be able to configure again the TX and RX state and avoidAT_BUSY_ERROR.<payload>: 2-500 digit length, must be an even number of digits and character 0-9, a-f, A-F only, representing 1~256 hexadecimal numbers. For example, if the payload is like0x03, 0xAA, 0x32, therefore the AT command should beAT+PSEND = 03AA32.
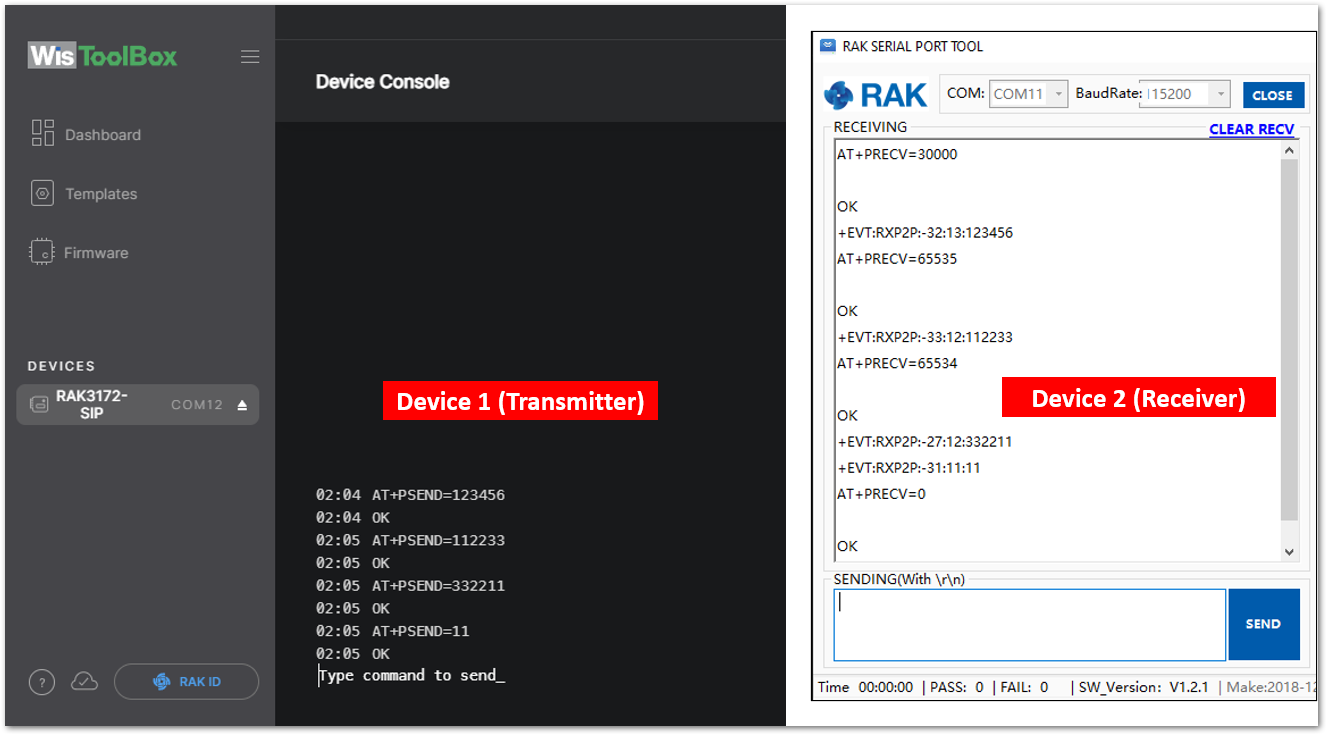 Figure 1: Configuring P2P in both RAK3172-SiP Module
Figure 1: Configuring P2P in both RAK3172-SiP ModuleMiscellaneous
Upgrading the Firmware
If you want to upgrade to the latest version of the firmware of the module, you can follow this section. The latest firmware can be found in the software section of RAK3172-SiP Datasheet.
What if the RAK3172-SiP stops responding to AT commands and firmware updates? You can recover your device by using the .hex file in the datasheet and uploading it using STM32CubeProgrammer. The guide on updating STM32 firmware using STM32CubeProgrammer can be found .here
Firmware Upgrade Through UART2
Minimum Hardware and Software Requirements
Refer to the table for the minimum hardware and software required to perform the firmware upgrade via UART2:
| Hardware/Software | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Computer | A Windows/Ubuntu/Mac computer |
| Firmware File | Bin firmware file downloaded from the website |
| Others | A USB to TTL module |
Firmware Upgrade Procedure
Execute the following procedure to upgrade the firmware in Device Firmware Upgrade (DFU) mode through the UART2 interface.
-
Download the latest application firmware of the RAK3172-SiP.
-
Download the RAK Device Firmware Upgrade (DFU) tool.
-
Connect the RAK3172-SiP with a computer through a USB to a Serial converter. Refer to Figure 26.
-
Open the Device Firmware Upgrade tool. Select the serial port and baud rate (115200) of the module and click the Select Port button.
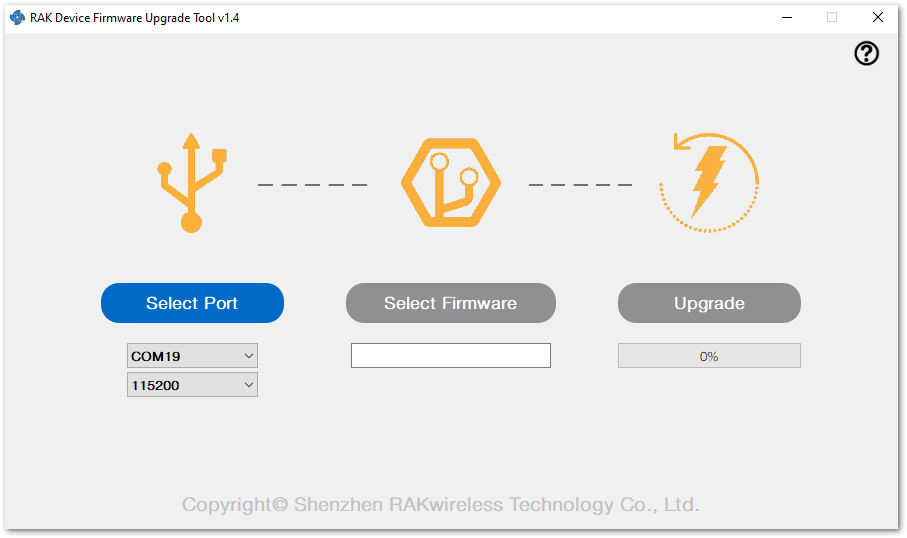 Figure 1: Device Firmware Upgrade Tool
Figure 1: Device Firmware Upgrade Tool- Select the application firmware file of the module with the suffix .bin.
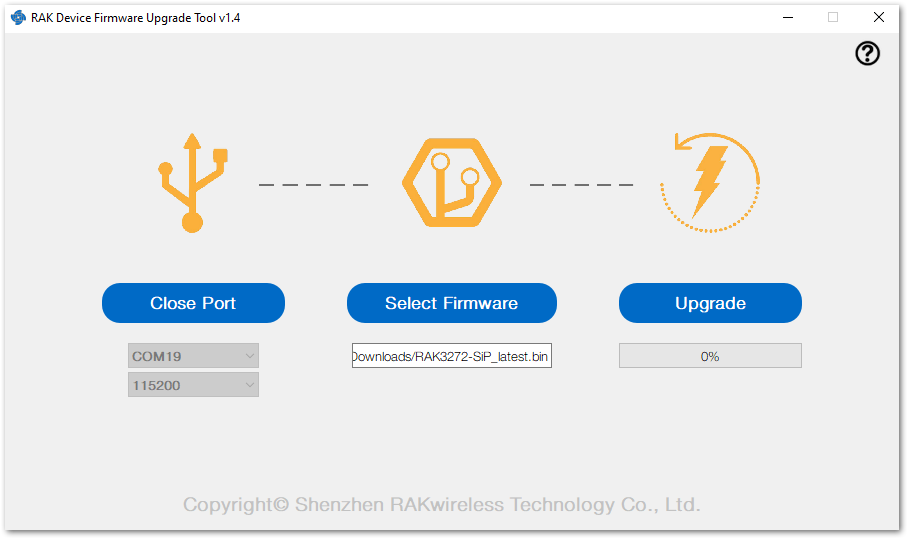 Figure 1: Select firmware
Figure 1: Select firmware- Click the Upgrade button to upgrade the device. After the upgrade is complete, the RAK3172-SiP will be ready to work with the new firmware.
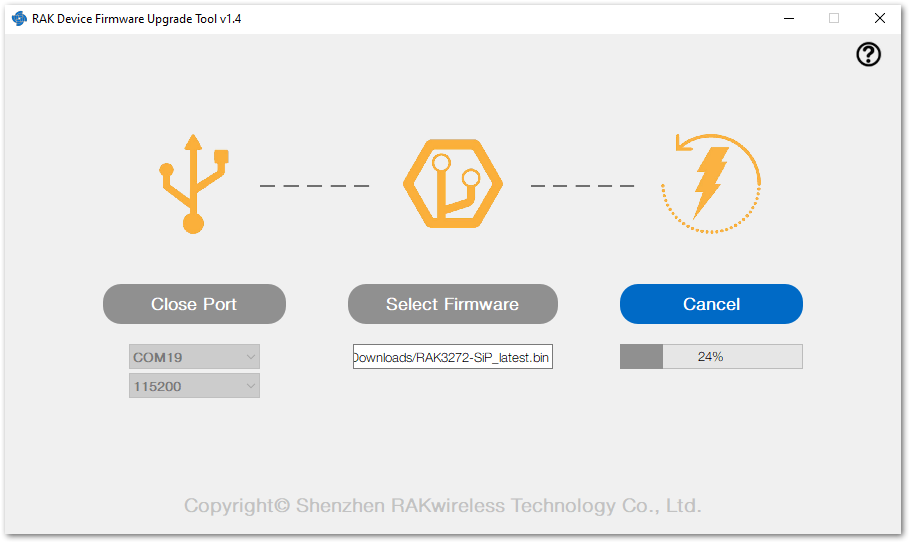 Figure 1: Firmware upgrading
Figure 1: Firmware upgrading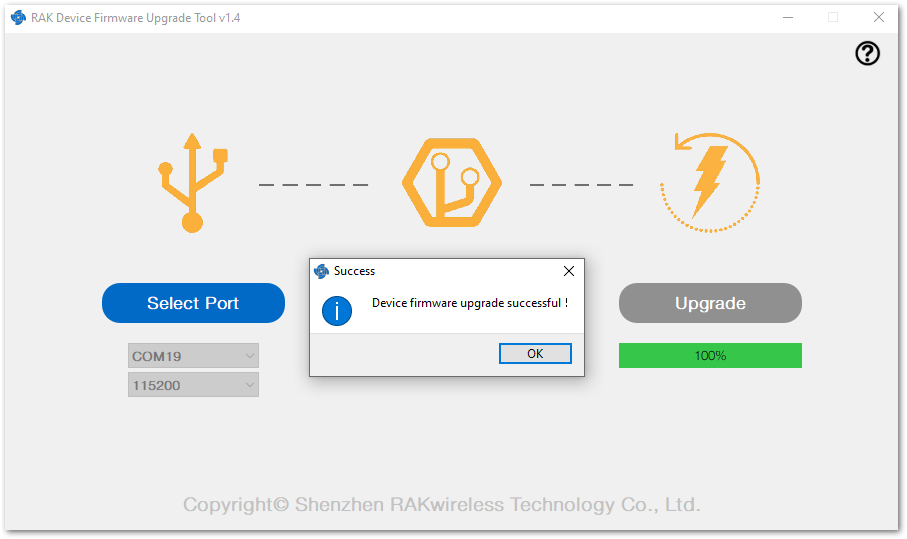 Figure 1: Upgrade successful
Figure 1: Upgrade successfulArduino Installation
Go to the Arduino official website and download the Arduino IDE. You can see the multiple versions available for Windows, Linux, and Mac OS X. Choose the correct version of Arduino IDE and download it.
 Figure 1: Arduino IDE latest version
Figure 1: Arduino IDE latest versionFor Windows
For Windows 10 users: Do NOT install the Arduino IDE from the Microsoft App store. Install the original Arduino IDE from the Arduino official website instead, since the Arduino app from the Microsoft App Store has problems using third-party Board Support Packages.
- Install the Arduino IDE, which you just downloaded, on your Windows PC.
- Click I Agree then Next to proceed.
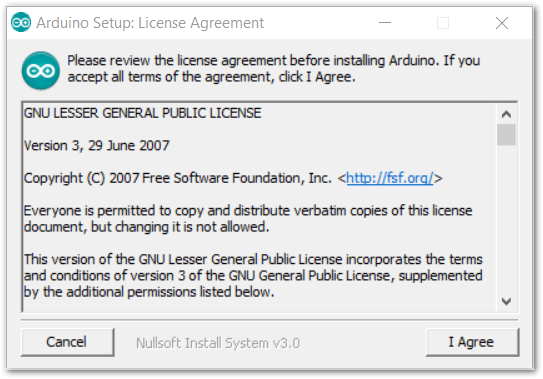 Figure 1: Arduino setup license agreement
Figure 1: Arduino setup license agreement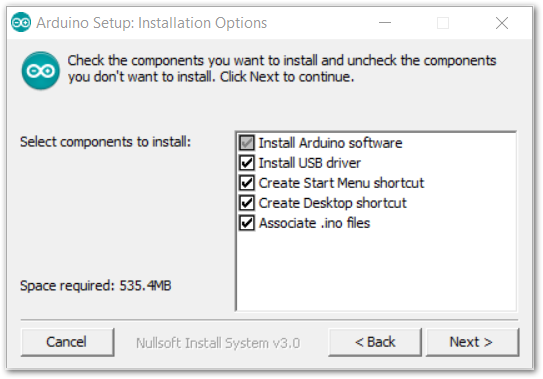 Figure 1: Arduino setup installation options
Figure 1: Arduino setup installation options- Click Install.
 Figure 1: Installing Arduino IDE
Figure 1: Installing Arduino IDE Figure 1: Ongoing installation
Figure 1: Ongoing installationAfter 100% progress, the Arduino IDE has been installed successfully.
 Figure 1: Successful installation
Figure 1: Successful installationFor Linux
First, you need the check the compatibility with your system and choose between the 32-bit, 64-bit, and ARM versions of the Arduino IDE for Linux.
Installing via a Tarball
After downloading the correct Arduino version, open a terminal, then run ls to check the installation file on the download folder.
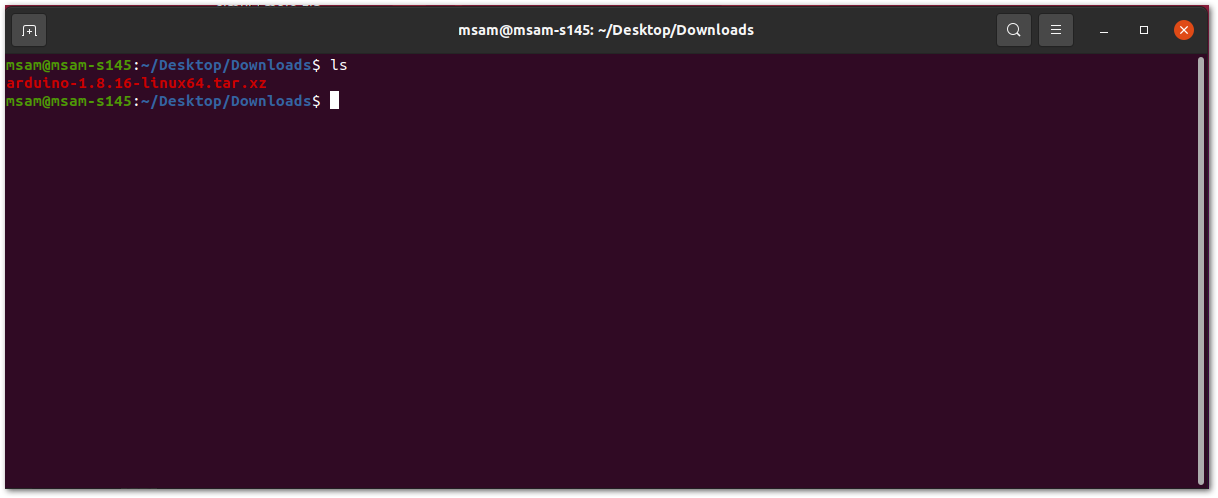 Figure 1: Check the download folder
Figure 1: Check the download folderA tarball is a type of compressed folder, like a .zip file, commonly used to distribute software in Linux. To extract the files from the tarball, change the directory to where the downloaded tarball is, then run:
tar xvf arduino-version.xz
 Figure 1: Tarball extract command
Figure 1: Tarball extract commandWhen the tar command finishes, run ls again. A folder named arduino-version will be created.
 Figure 1: Arduino install folder created
Figure 1: Arduino install folder createdChange the current directory and go to the newly created folder directory. There will be a file named install.sh in the folder. Execute sudo ./install.sh to install the Arduino IDE.
 Figure 1: Arduino install script running
Figure 1: Arduino install script runningThe sudo command temporarily elevates privileges allowing the installer to complete sensitive tasks without logging in as the root user.
For Mac OS X
In Mac OS X, the same as Linux, there is no installation process. It is just a process of decompression, then you can open Arduino IDE successfully.
Arduino IDE Parts Guide
Figure 238 shows the five (5) parts of Arduino IDE.
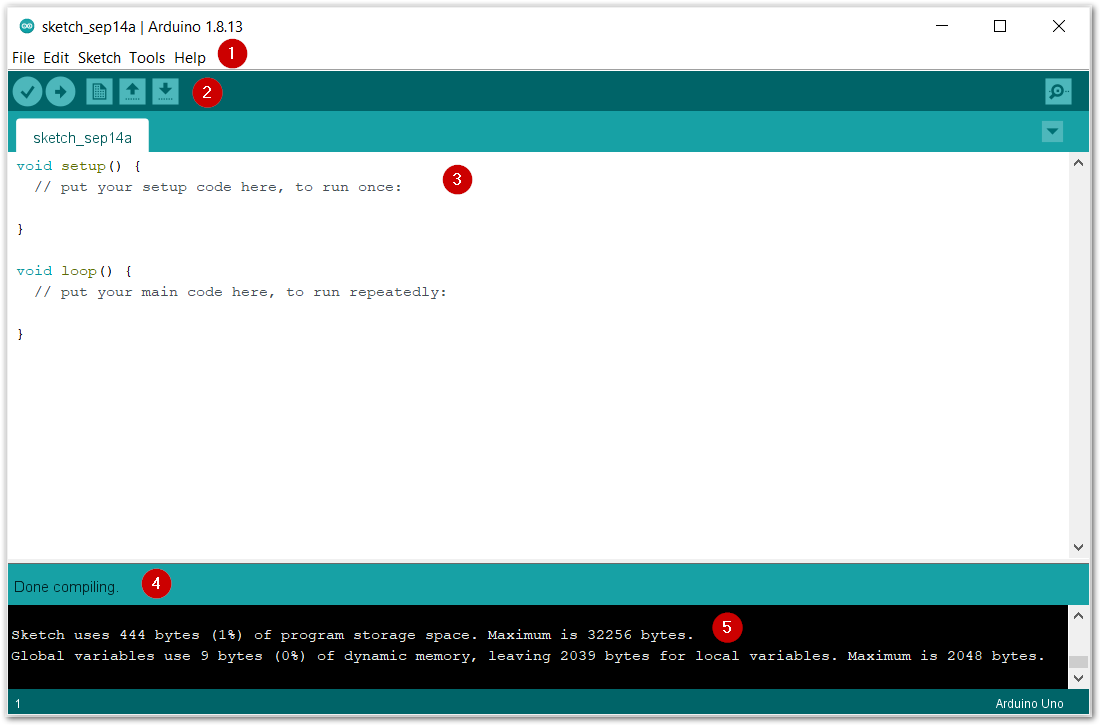 Figure 1: Arduino IDE
Figure 1: Arduino IDE- IDE Option Menu
You can configure some general parameters such as the serial port, the board information, the libraries, the edit parameters, and so on.
- Operating Buttons
The operating buttons have five operations:
- Verify/Compile the source code;
- Upload the compiled code into WisBlock;
- Open a New Arduino IDE window or existing application;
- Save the current application.
 Figure 1: Operating buttons
Figure 1: Operating buttons- Code Area
You can edit the source code, which will be compiled and uploaded into WisBlock later in this area.
-
State Area
-
Output Message Area You can see the output message in this area, whether it's a failure or success information.
