RAK7285/RAK7285C LoRaWAN Configuration
This section explains how to configure the LoRa parameters of your WisGate gateway to connect it to different types of LoRaWAN® networks. Depending on your deployment scenario, the gateway can operate in one of the following modes:
Built-in Network Server
In this mode, the gateway functions as a LoRa Network Server (LNS), managing devices and processing packets locally. It also supports multi-gateway deployments by allowing extender gateways to join and be managed from the central gateway. This setup enables fully independent operation without external dependencies.
Packet Forwarder
The gateway forwards LoRa packets to an external network server, which handles all processing, device management, and application integration. This is ideal for integrating with public or private LoRaWAN infrastructures such as TTN or ChirpStack.
Basics Station
The gateway communicates with a remote LoRaWAN network server over a secure WebSocket (WSS) connection. This mode supports cloud-based deployments with enhanced security, certificate-based authentication, and dynamic server provisioning (via CUPS).
Built-In Network Server
This section explains how to configure your WisGate gateway to operate in Built-in Network Server (LNS) mode, enabling local LoRaWAN® packet processing and device management.
Set the Gateway Work Mode
Navigate to LoRa® > Configuration. For Work mode, select Built-in network server.
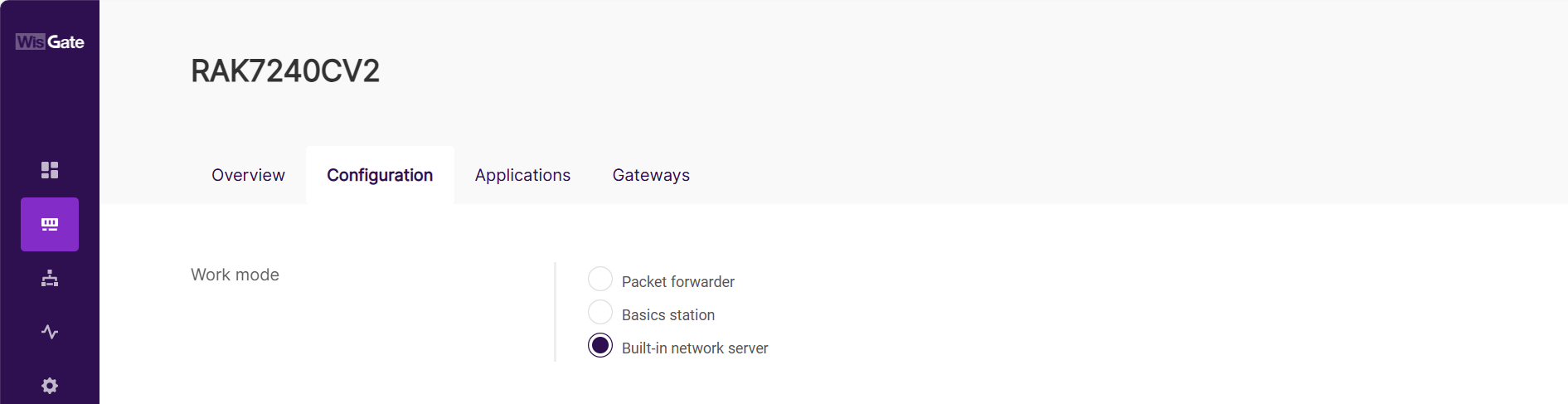 Figure 1: Set the gateway work mode
Figure 1: Set the gateway work modeSelect Your Region
Select your country and frequency band to ensure proper LoRa® operation.
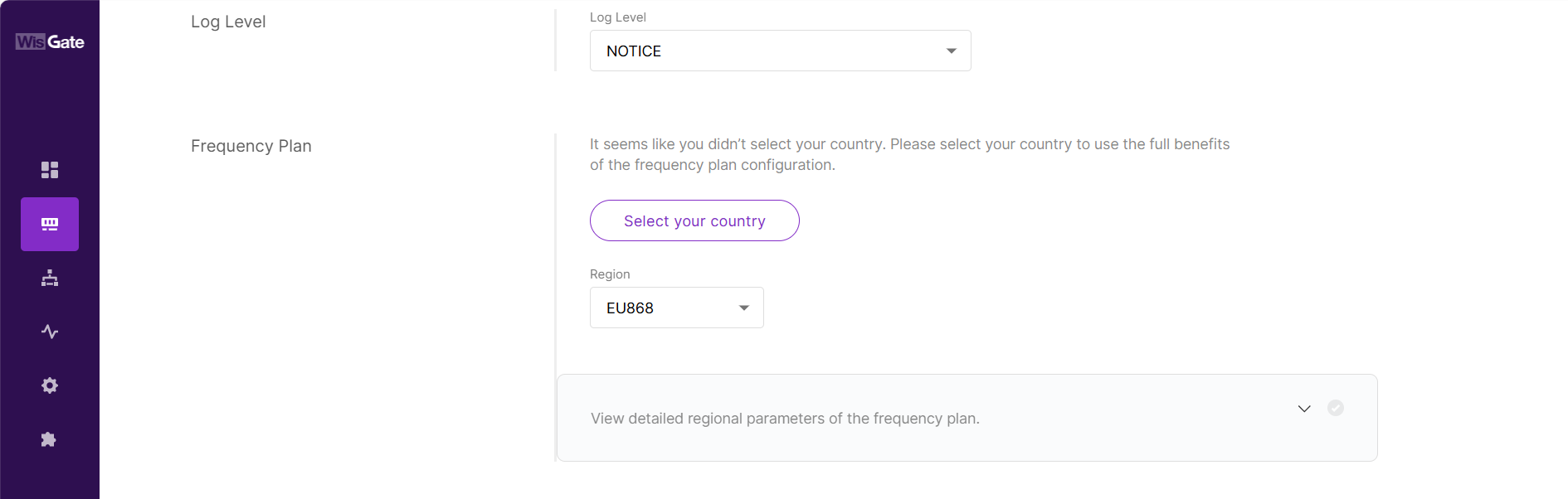 Figure 1: Configure frequency band
Figure 1: Configure frequency bandCreate an Application
Create an application to group LoRaWAN® devices logically for easier management and data routing.
For detailed instructions on how to create and manage applications, refer to the WisGateOS 2 User Manual > Create an Application .
Add End Devices
Add LoRaWAN® end devices to an application so they can join the network and begin transmitting data.
For detailed instructions on how to add and manage end devices, refer to the WisGateOS 2 User Manual > Add Devices.
Advanced Settings (Optional)
Once the basic configuration is complete, you can take advantage of additional features offered by the built-in network server to enhance device management, extend coverage, or integrate with external platforms.
The features described below are optional but useful for scaling and customizing your deployment.
Country Code Setting
Ensures the gateway follows regional frequency regulations. Selecting the correct country auto-sets transmit power and sub-bands.
Guide Link: How to Configure Country Code on RAK LoRaWAN Gateways for Rf Compliance
Packet Filter
Filters uplinks by applying whitelist rules, ensuring that only authorized devices are allowed while unknown devices are blocked to prevent network disruption.
Guide Link: Configure Packet Filter on RAK LoRa® Gateways
Gateway Backend
Enables communication between a central gateway and extender gateways using the MQTT protocol. Supports multi-gateway deployments.
Guide Link: How to Configure a RAK Multi-Gateway LoRaWAN® Network Using Gateway Backend (Built-in Network Server Mode)
AWS IoT Core Integration
Securely connects the gateway to AWS IoT Core using endpoint URL and certificates. Ideal for integrating with AWS cloud services.
Guide Link: How to Implement AWS Integration for WisGate Edge V2
Generic MQTT Integration
Forwards decoded uplinks to MQTT brokers, enabling integration with platforms like ThingsBoard.
Guide Link: Configure Generic MQTT Integration With Built-in Network Server
Auto Add Devices
Automatically adds end devices to the LNS when they send join requests, reducing manual setup.
Guide Link: How to Use Auto Add Device on RAK LoRaWAN® Gateways
Batch Add Devices
Allows bulk registration of end devices through CSV upload or auto-generation — ideal for large-scale deployments.
Guide Link: How to Batch Add Devices to a RAK LoRaWAN® Gateway
HTTP/HTTPS Integration
Forwards uplink data to HTTP(S) endpoints for integration with web services and IoT platforms.
Guide Link: HTTP/HTTPS Integration to Forward LoRaWAN® Data to the Cloud
Packet Forwarder
In this mode, the gateway forwards LoRaWAN® packets to an external network server. All packet processing, device management, and data routing are handled by the external server.
Supported Network Servers
Depending on the protocol type you choose, the gateway supports the following external network servers. Each listed server includes a link to the corresponding configuration guide.
Semtech UDP GWMP Protocol
-
The Things Network (TTN)
Configuration Guide: How to Connect RAK Gateways to TTN v3 via UDP
-
ChirpStack v3
Configuration Guide: How to Connect RAK Gateways to ChirpStack v3 via UDP
-
ChirpStack v4
-
Confiuration Guide: How to Connect RAK Gateways to ChirpStack v4 via UDP
-
Loriot
Configuration Guide: How to Connect RAK Gateways to LORIOT via UDP
LoRa® Gateway MQTT Bridge
-
MQTT for Built-in LNS
Used in multi-gateway deployments to connect extender gateways to the central gateway running Built-in Network Server via MQTT.
Configuration Guide: How to Configure a RAK Multi-Gateway LoRaWAN® Network Using Gateway Backend (Built-in Network Server Mode) -
ChirpStack v2
ChirpStack v2 is a legacy version and no longer actively maintained. We recommend using the latest ChirpStack v4 for better performance, simplified deployment, and ongoing support.
-
ChirpStack v3
Configuration Guide:
-
ChirpStack v4
Configuration Guide: How to Connect RAK Gateways to ChirpStack v4 via MQTT
Advanced Settings (Optional)
In Packet Forwarder mode, RAK gateways offer additional features to improve flexibility and meet specific deployment requirements.
The features described below are optional but can be used to enhance compatibility, optimize network performance, or meet specific deployment requirements.
Country Code Setting
Ensures the gateway follows regional frequency regulations. Selecting the correct country auto-sets transmit power and sub-bands.
Guide Link: How to Configure Country Code on RAK LoRaWAN Gateways for Rf Compliance
Set Private Channel
Use this feature to define custom sub-bands or frequency channel sets that align with your external server’s configuration. This helps reduce interference and enables deployment in specialized scenarios.
Guide Link: How to Configure Private LoRaWAN® Channels on RAK Gateways
Auto Data Recovery
Enables temporary local buffering of uplinks during connection loss to external server. Once reconnected, the gateway can resend cached data to avoid loss.
Guide Link: How to Enable Auto Data Recovery for Packet Forwarder Mode
Secondary LNS Forwarding
Enables a RAK gateway in Packet Forwarder mode to forward uplink packets to two LoRaWAN® Network Servers simultaneously — one acting as the Primary LNS for device control, and the other as a Secondary LNS for uplink monitoring or redundancy.
Guide Link: Secondary LNS Forwarding: Forward Packets to a Secondary Network Server
Fake GPS
If your gateway lacks a built-in GPS module or has poor GPS signal reception, you can manually inject static GPS coordinates. This is useful for mapping and network diagnostics.
Guide Link: How to Set Up Fake GPS for Virtual Gateway Location
Fine Timestamp
Enables nanosecond-level timestamping of LoRa® packets for use in geolocation services such as TDOA. Requires hardware support.
Guide Link: How to Enable Fine Timestamp for Precise LoRaWAN® Geolocation on RAK Gateways
Packet Filter
Filters uplinks by applying whitelist rules, ensuring that only authorized devices are allowed while unknown devices are blocked to prevent network disruption.
Guide Link: Configure Packet Filter on RAK LoRa® Gateways
Auto Connect to The Things Network (EU1) Server
Automatically connects to The Things Network (EU1) when using Semtech UDP forwarding. Speeds up deployment for TTN users.
Guide Link: How to Auto-Connect RAK Gateway to TTN (EU1) in Packet Forwarder Mode
Basics Station
In Basics Station mode, the gateway supports connection to different types of servers. Based on your deployment platform, you can configure the gateway to connect using one of the following server types: LNS, CUPS, or CUPS-BOOT.
Supported Network Servers
The following server types are supported in Basics Station mode:
LNS Server
Direct WebSocket-based data forwarding.
-
AWS IoT Core
Configuration Guide: How to Connect RAK Gateways to AWS IoT Core Using Basics Station (LNS)
-
The Things Network (TTN)
Configuration Guide: How to Connect RAK Gateways to TTN v3 Using Basics™ Station (LNS)
-
ChirpStack v3
Configuration Guide: How to Connect RAK Gateways to ChirpStack v3 Using Basics™ Station (LNS)
-
ChirpStack v4
Configuration Guide: How to Connect RAK Gateways to ChirpStack v4 Using Basics™ Station (LNS)
CUPS Server
Enables remote gateway configuration and credential management.
-
AWS IoT Core
Configuration Guide: How to Connect RAK Gateways to AWS IoT Core Using Basics Station (CUPS)
-
The Things Network (TTN)
Configuration Guide: How to Connect RAK Gateways to TTN v3 Using Basics™ Station (CUPS)
-
Actility
Configuration Guide: How to Connect RAK Gateways to Actility ThingPark Using Basics™ Station (CUPS)
CUPS-BOOT Server
Used for initial provisioning before CUPS takes over. This option is generally not required during normal operation.
Advanced Settings (Optional)
In Basics Station mode, RAK gateways offer several optional features that enhance deployment flexibility.
The features described below are optional and can be enabled to improve network security, enhance compatibility, and provide greater flexibility for specific deployment needs.
16 Channel
Enables full 16-channel support for LoRaWAN® uplinks when using Basic Station mode. Useful for custom frequency plans and ensuring compatibility with network servers requiring extended channel configurations.
Guide Link: 16-Channel Support in Basics Station Mode
Packet Filter
Filters uplinks by applying whitelist rules, ensuring that only authorized devices are allowed while unknown devices are blocked to prevent network disruption.
Guide Link: Configure Packet Filter on RAK LoRa® Gateways
