RAK4631 WisBlock LoRaWAN Module Quick Start Guide
This guide introduces the RAK4631 WisBlock Core LoRaWAN Module and how to use it. RAK4631 consists of an nRF52840 MCU and an SX1262 LoRa chip making it ideal for various IoT projects.
Prerequisite
Before going through each and every step on using RAK4631 WisBlock Core, make sure to prepare the necessary items listed below:
Hardware
- RAK4631 WisBlock Core LoRaWAN Module
- Your choice of WisBlock Base
- Your choice of WisBlock Modules
- USB Cable
- Li-Ion/LiPo battery (optional)
- Solar charger (optional)
RAK4631 is also included in various WisBlock kits in the RAKwireless store:
- WisBlock Starter Kit - includes the RAK4631 with RAK5005-O WisBlock Base Board. This kit is ideal to get started immediately with WisBlock.
- WisBlock Kit - a Starter Kit with various WisBlock modules already included on the kit like sensors, IO, and other interfaces.
- WisBlock Connected Box - a WisBlock Kit but cheaper because some modules and peripherals are not included. Excluded parts are RAKBox-B5, RAK1921, RAKDAP1, electric screwdriver (manual is included), and battery holder.
- Helium Developer Kit - the WisBlock Kit for the Helium brand.
- Meshtatic Starter Kit - includes the RAK4631 with RAK19007 as its WisBlock Base Board.
Software
This software guide is only compatible with the RAK4631 Arduino BSP; it will not work with the RAK4631-R, but you can convert it to the RAK4631.
You can choose Arduino IDE or Platform IO in coding the RAK4631 WisBlock Core.
Programming RAK4631 via Arduino IDE:- Download and install the Arduino IDE.
If you are using Windows 10. Do NOT install the Arduino IDE from the Microsoft App Store. Instead, install the original Arduino IDE from the Arduino official website. The Arduino app from the Microsoft App Store has problems using third-party Board Support Packages.
- To add the WisBlock Core boards on your Arduino board, you need to install the RAKwireless Arduino BSP. You can follow this complete guide on adding the BSP in Arduino IDE. You can also have a look at the RAKwireless Arduino BSP GitHub repository.
In Arduino IDE, once you installed the BSP, some examples for RAK4631 will be automatically included on the list of examples when you select WisBlock Core RAK4631 Board in the Board Manager.
Programming RAK4631 via Platform IO:Updated and complete WisBlock examples can be found in the WisBlock Examples repository which contains source codes that you can copy-paste and upload.
Aside from that, each WisBlock Modules has its own quick start guide to help you in your WisBlock journey.
Product Configuration
Hardware Setup
RAK4631 to WisBlock Base
The RAK4631 will not work without a WisBlock Base board. The WisBlock Base provides a USB connection for programming the RAK4631. It also provides a power source and various interfaces to RAK4631 so that it can be connected to other WisBlock modules via different module slots.
RAKwireless offers many WisBlock Base Boards compatible with WisBlock Core. It is highly recommended for you to look on these WisBlock Base boards to see what matches your requirements in terms of available module slots, power supply options, and overall size.
To illustrate, RAK4631 can be connected to RAK5005-O WisBlock Base, as shown in Figure 1.
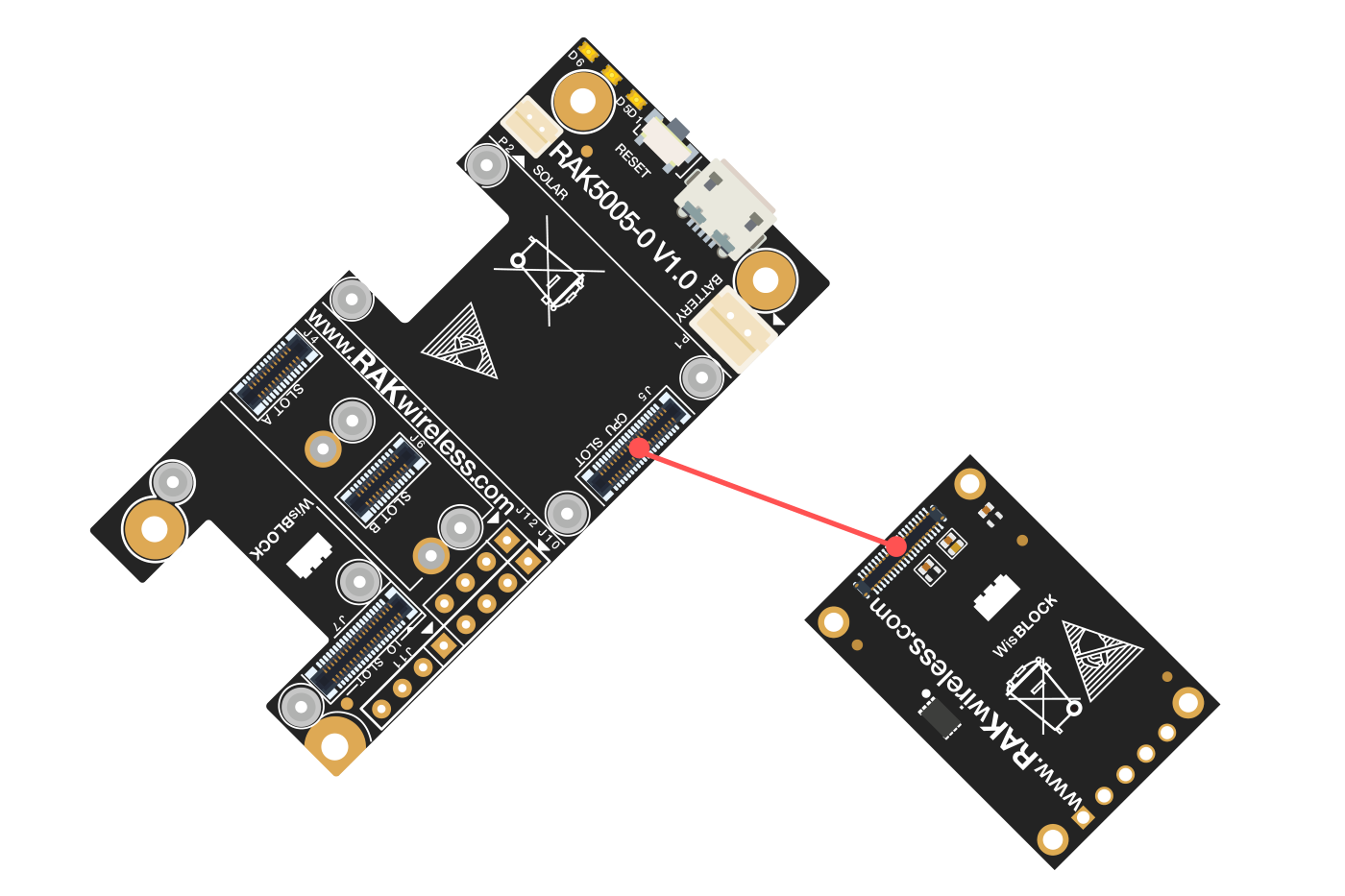 Figure 1: RAK4631 Connection to WisBlock Base RAK5005-O
Figure 1: RAK4631 Connection to WisBlock Base RAK5005-OThere are few pins that are exposed on RAK5005-O, and you can easily use them via header pins. The labels are at the back, as shown in Figure 2.
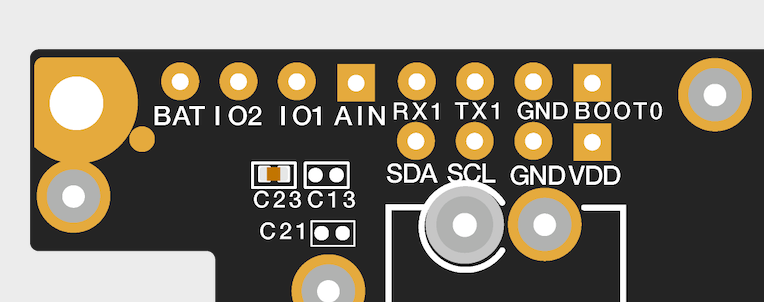 Figure 1: WisBlock Base exposed pins
Figure 1: WisBlock Base exposed pinsMore information can be found on the official documentation of the specific WisBlock Base you used in your project.
For RAK5005-O WisBlock Base with RAK4631 WisBlock Core, the accessible GPIO pins are defined as follows in the Arduino IDE and Platform IO:
WB_IO1for IO1 pinWB_IO2for IO2 pin (Also used to control the 3.3 V supply of some WisBlock Modules to achieve low-power IoT devices.)WB_A0for AIN
There are usable LEDs as well that can be controlled by the RAK4631 on the WisBlock Base board:
LED_GREENLED_BLUE
UART1 and I2C_1 are also exposed on the header of the WisBlock Base board.
- RAK4631 has a native USB peripheral onboard (Serial), which is used for programming and Serial debugging and two usable hardware UART1 and UART2 (Serial 1 and Serial 2). UART1 is accessible to WisBlock Slot A, WisBlock IO slot, and the exposed header pins. UART2 is accessible only on the WisBlock IO slot.
- The I2C_1 header pins are as well shared to the WisBlock Base Slots A to D. The second I2C_2 is available only on the WisBlock IO slot.
RAK4631 to WisBlock Modules
RAK4631 WisBlock Core is designed to be interfaced with other WisBlock Modules like sensors, displays, and other interfaces. You need to connect these modules to the compatible slots on the WisBlock Base.
Each WisBlock Modules that will be used with RAK4631 WisBlock Core have a dedicated quick start guide you can follow on how to connect to the WisBlock Base.
Listed are the quick start guide of some WisBlock modules you can buy from our store:
The listed links are just examples. All WisBlock Modules have their own quick start guide that you can use as a reference to get started on specific modules.
Figure 3 shows an illustration on how you can combine various WisBlock Modules with the RAK4631 WisBlock Core via the WisBlock Base board.
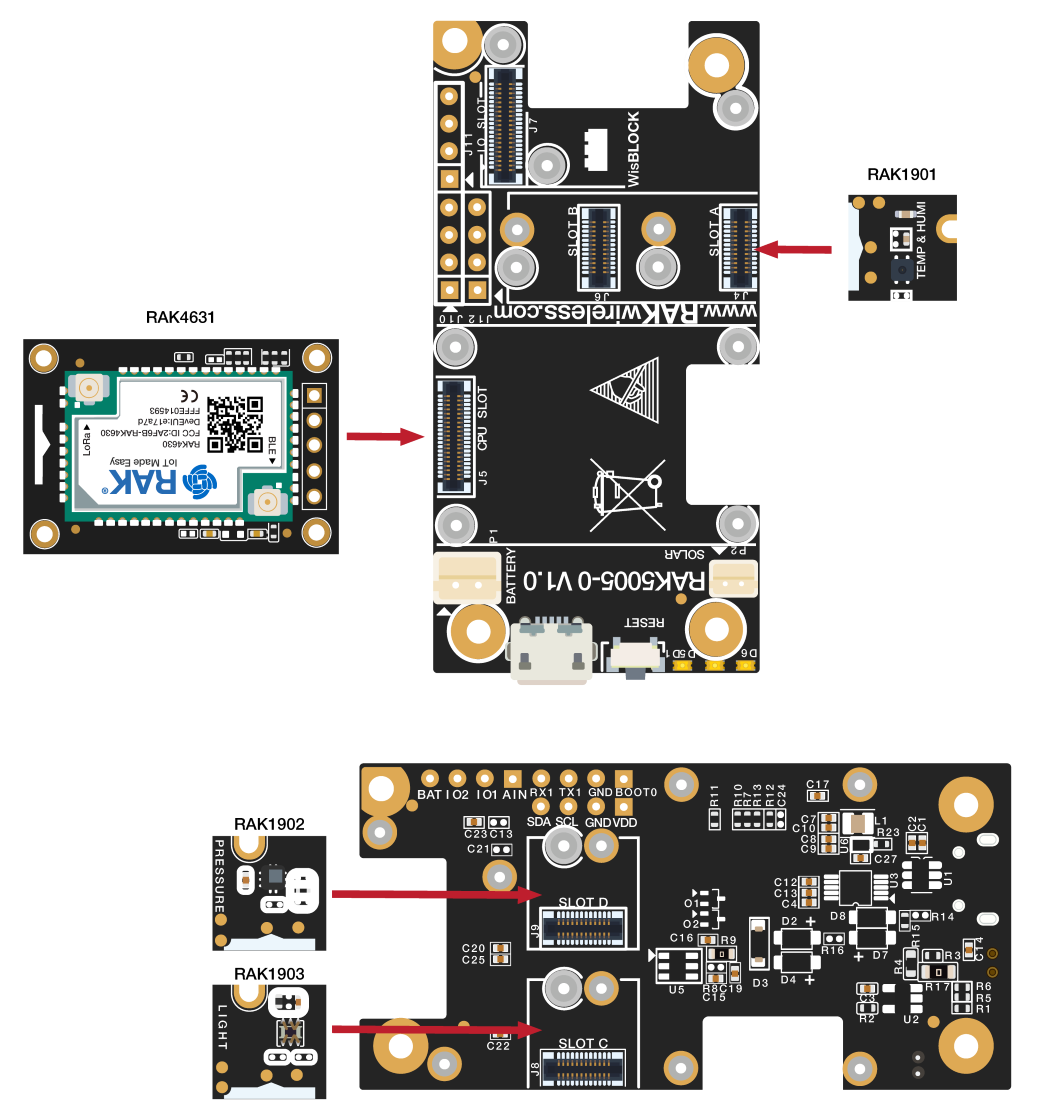 Figure 1: RAK4631 Connection to WisBlock Base and other WisBlock Modules
Figure 1: RAK4631 Connection to WisBlock Base and other WisBlock ModulesAssembling and Disassembling of WisBlock Modules
Assembling
Figure 4 shows how to mount the RAK4631 module on top of a WisBlock Base board (RAK5005-O). Follow carefully the procedure defined in WisBlock module assembly/disassembly instructions in order to secure the connection safely. Once attached, carefully fix the module with one or more pieces of M1.2 x 3 mm screws depending on the module.
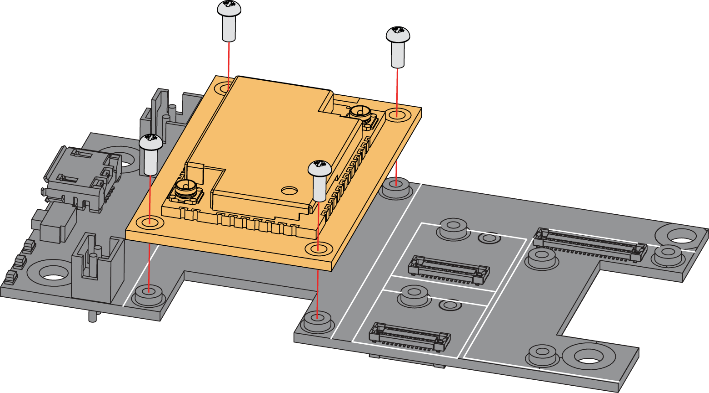 Figure 1: RAK4631 Mounting Sketch
Figure 1: RAK4631 Mounting SketchDisassembling
The procedure in disassembling any type of WisBlock modules is the same.
- First, remove the screws.
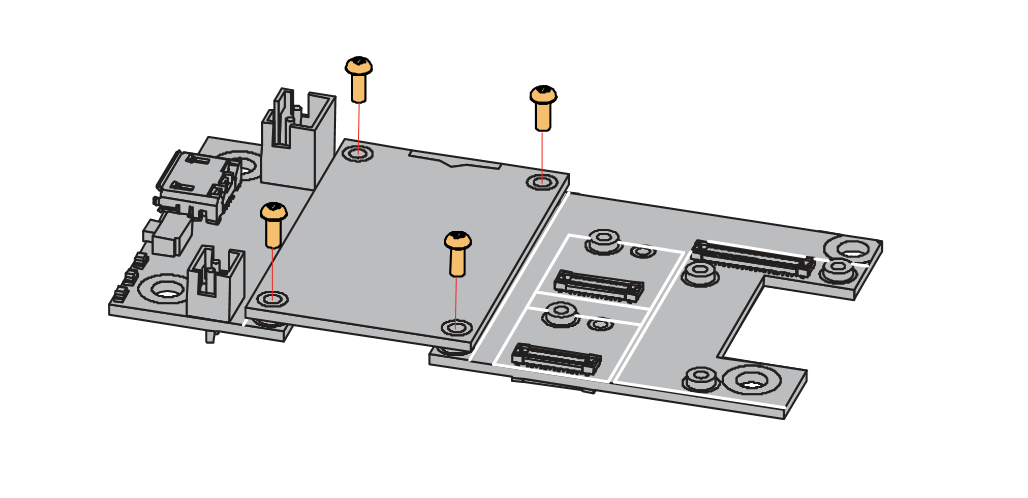 Figure 1: Removing screws from the WisBlock module
Figure 1: Removing screws from the WisBlock module- Once the screws are removed, check the silkscreen of the module to find the correct location where force can be applied.
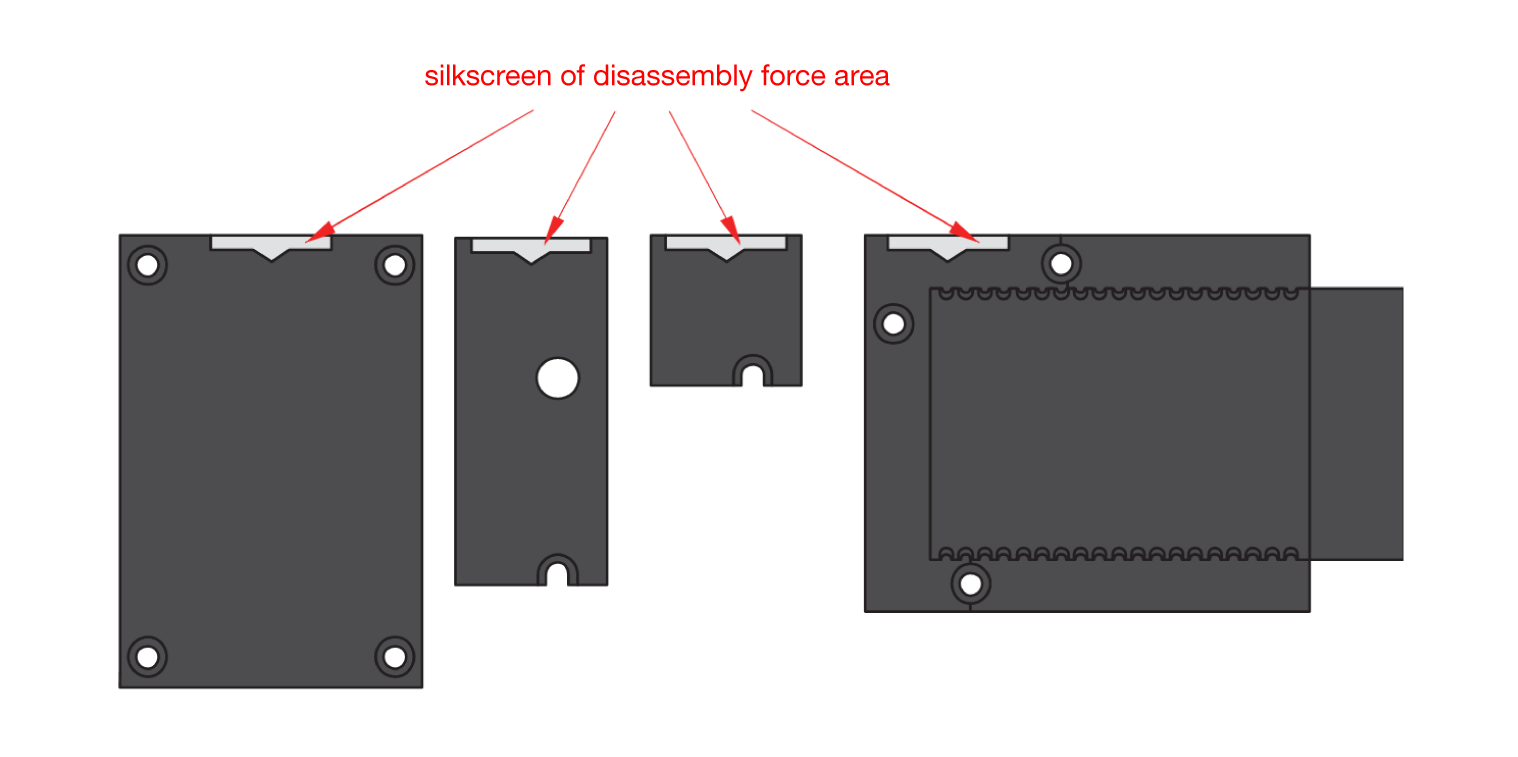 Figure 1: Detaching silkscreen on the WisBlock module
Figure 1: Detaching silkscreen on the WisBlock module- Apply force to the module at the position of the connector, as shown in Figure 7, to detach the module from the baseboard.
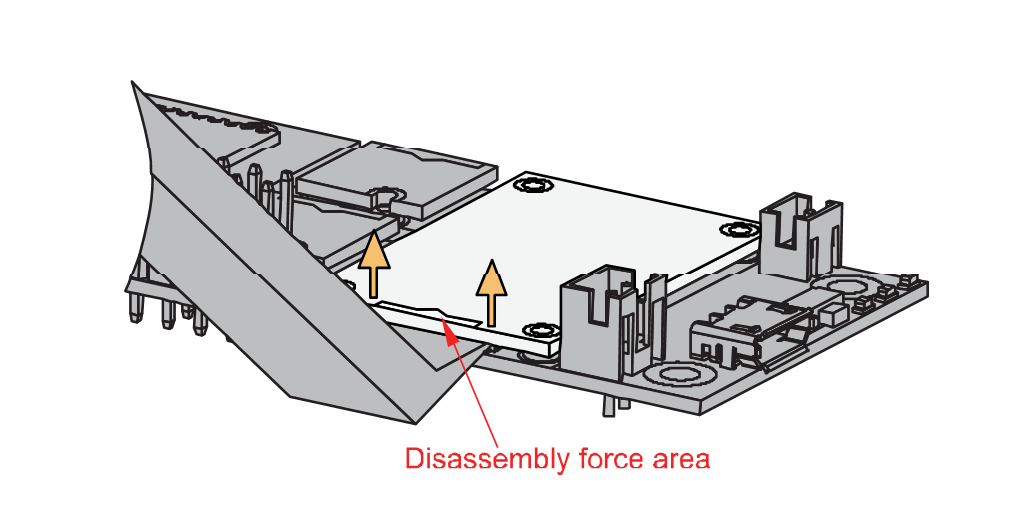 Figure 1: Applying even forces on the proper location of a WisBlock module
Figure 1: Applying even forces on the proper location of a WisBlock moduleLoRa and BLE Antenna
Another important part component of RAK4631 is the antennas.
 Figure 1: LoRa Antenna
Figure 1: LoRa Antenna Figure 1: BLE Antenna
Figure 1: BLE AntennaYou need to ensure that the antenna is properly connected to have a good LoRa signal. Do not power the module without an antenna connected to the IPEX connector to avoid damage to the RF section of the chip.
RAK4631 has a label on its sticker where to connect the antennas, as shown in Figure 10.
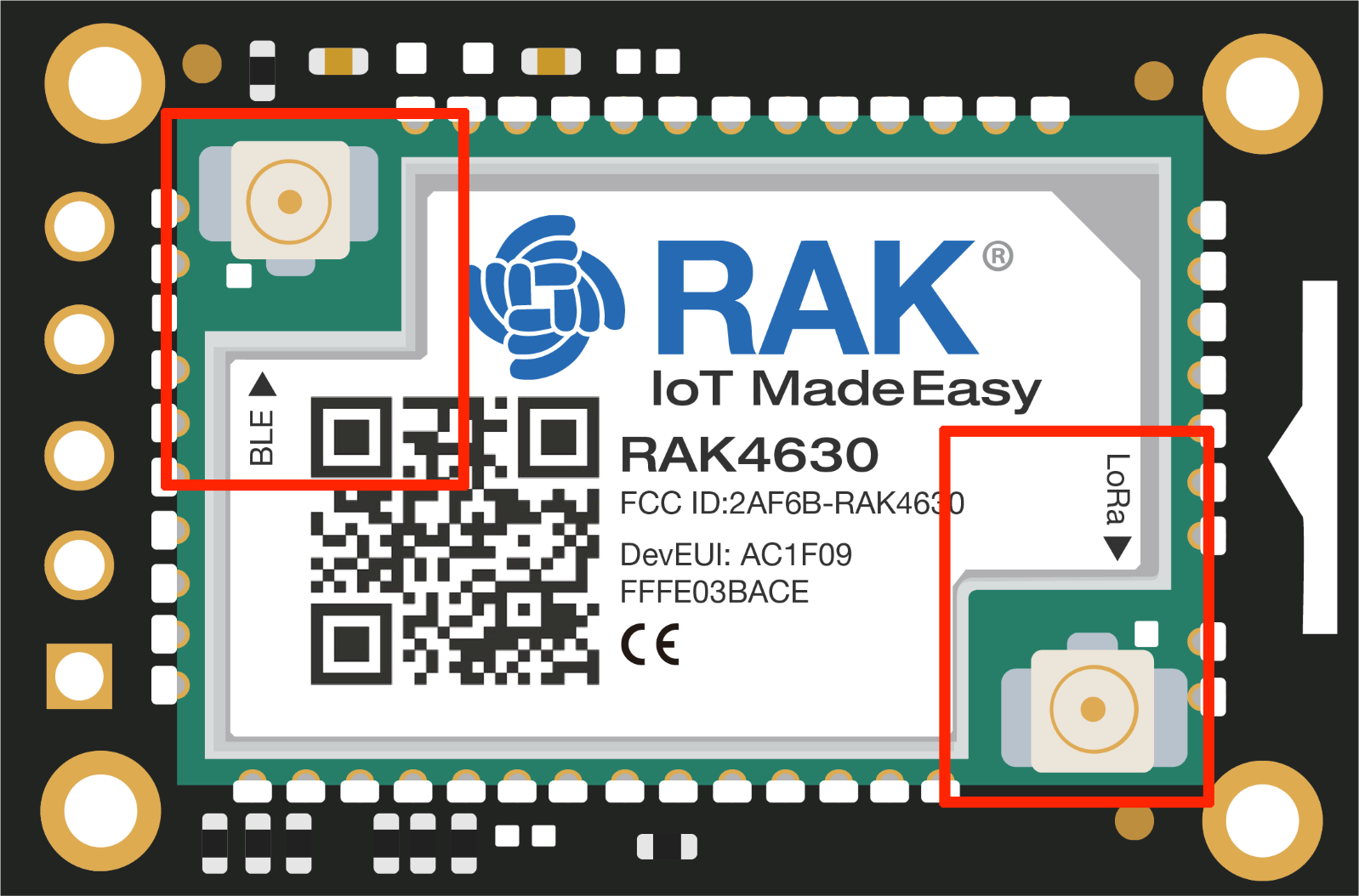 Figure 1: RAK4631 Antenna Label
Figure 1: RAK4631 Antenna LabelDetailed information about the RAK4631 BLE and LoRa antenna can be found on the antenna datasheet.
When using the LoRa or Bluetooth Low Energy transceivers, make sure that an antenna is always connected. Using these transceivers without an antenna can damage the system. Make sure to fix the module with the screws to ensure a proper function.
Battery and Solar Connection
RAK4631 can be powered via the USB cable or Li-Ion/LiPo battery via the dedicated connectors, as shown in Figure 11. The matching connector for the battery wires is an JST PHR-2 2 mm pitch female.
This illustration uses RAK5005-O as WisBlock Base. There are other WisBlock Base boards available and you need to check the datasheet of the specific WisBlock Base board for the right polarity and other parameters.
- Batteries can cause harm if not handled properly.
- Only 3.7-4.2 V Rechargeable LiPo batteries are supported. It is highly recommended not to use other types of batteries with the system unless you know what you are doing.
- If a non-rechargeable battery is used, it has to be unplugged first before connecting the USB cable to the USB port of the board to configure the device. Not doing so might damage the battery or cause a fire.
- Only 5 V solar panels are supported. Do not use 12 V solar panels. It will destroy the charging unit and eventually other electronic parts.
- Make sure the battery wires match the polarity on the WisBlock Base board. Not all batteries have the same wiring.
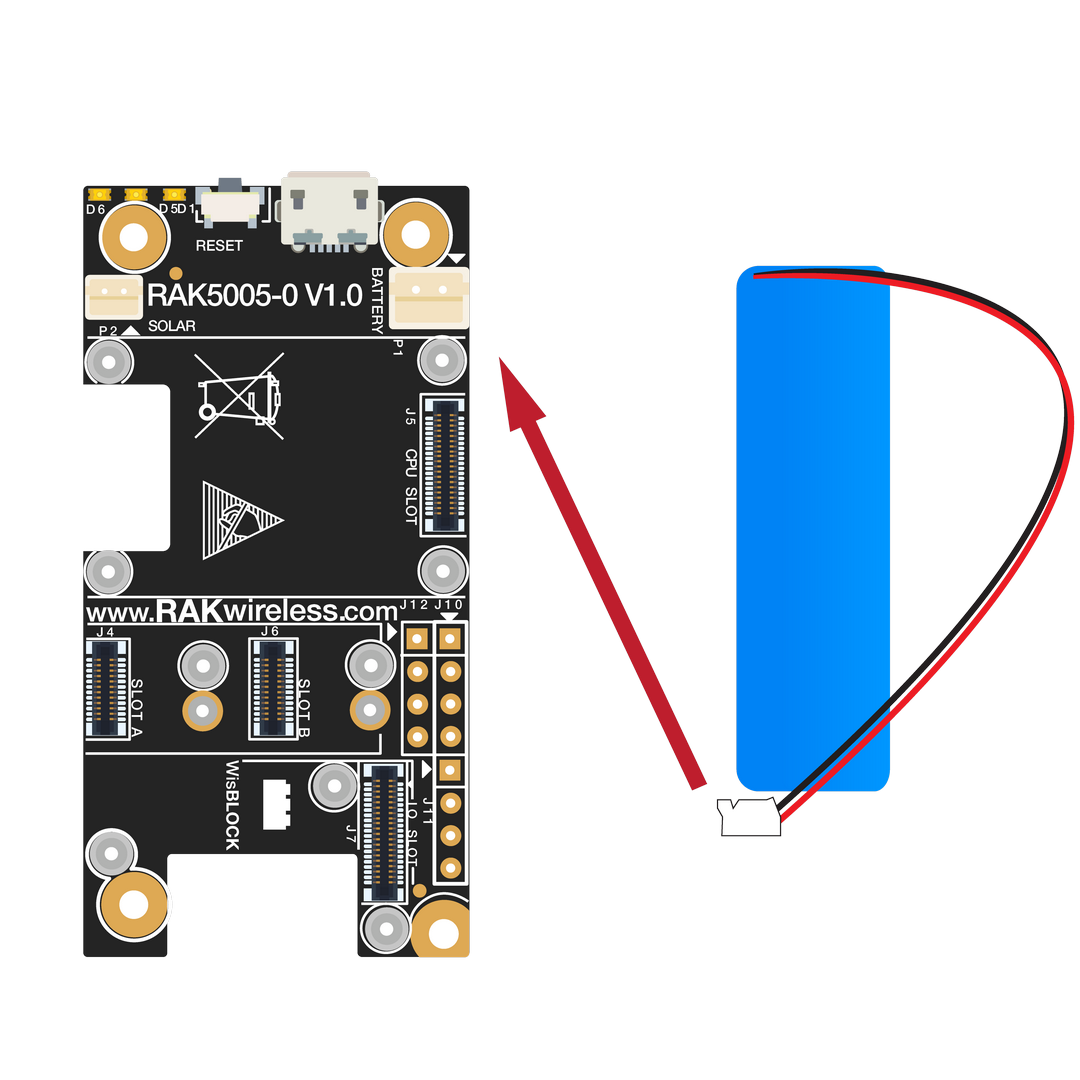 Figure 1: WisBlock Base Connection
Figure 1: WisBlock Base Connection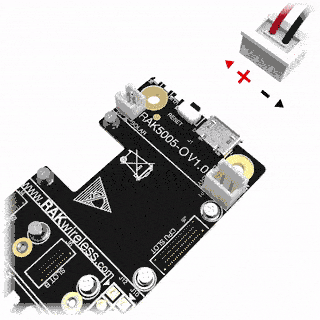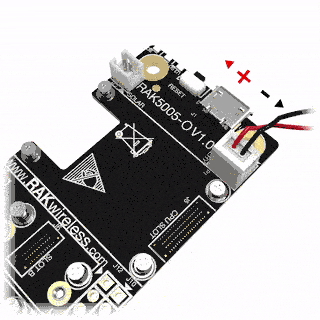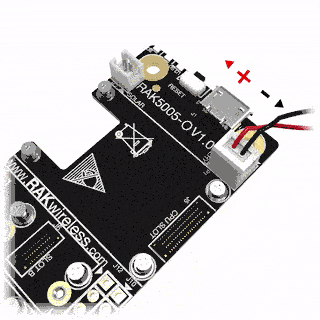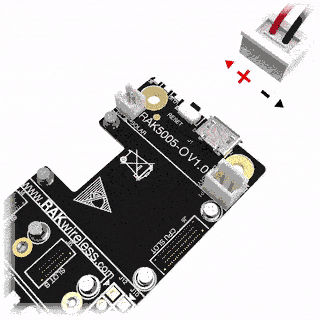 Figure 1: Battery Connection
Figure 1: Battery ConnectionThe battery can be recharged as well via small solar panel, as shown in Figure 13. The matching connector for the solar panel wires is an JST ZHR-2 1.5 mm pitch female.
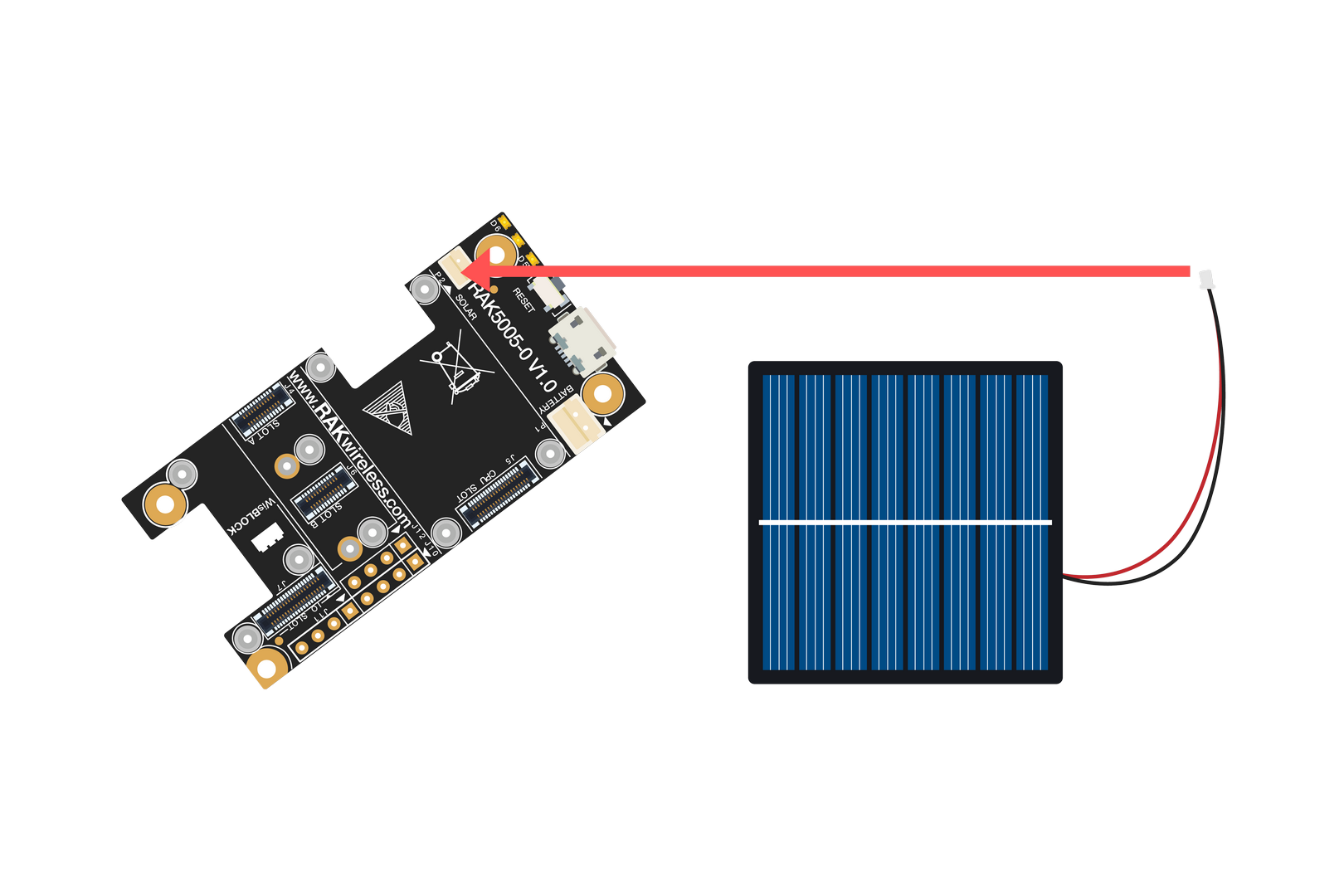 Figure 1: Solar Panel Connection
Figure 1: Solar Panel ConnectionSpecification of the battery and solar panel can be found on the datasheet of the WisBlock Base.
Software Setup
RAK4631 WisBlock Core is designed to be interfaced with other WisBlock Modules like sensors, displays, and other interfaces. To make useful devices, you need to upload a source code to the RAK4631. Before you continue, you should have either the Arduino BSP or Platform IO already setup.
RAK4631 Example Repository
To quickly build your IoT device with less friction, example codes for RAK4631 to be used on all WisBlock Modules are provided.
You can access the codes on the WisBlock Example code repository. The example codes compatible only with RAK4631 are in the folders RAK4631. The shared examples of the WisBlock Core are in the common folder.
To use these examples, you have two options: Arduino IDE or Platform IO.
RAK4631 on Arduino IDE
Some example codes of various WisBlock Modules like the RAK1901 and RAK1902 are available in the Arduino IDE once you install the BSP for the Arduino IDE, as shown in Figure 14. The updated and complete WisBlock examples are still in the WisBlock Examples.
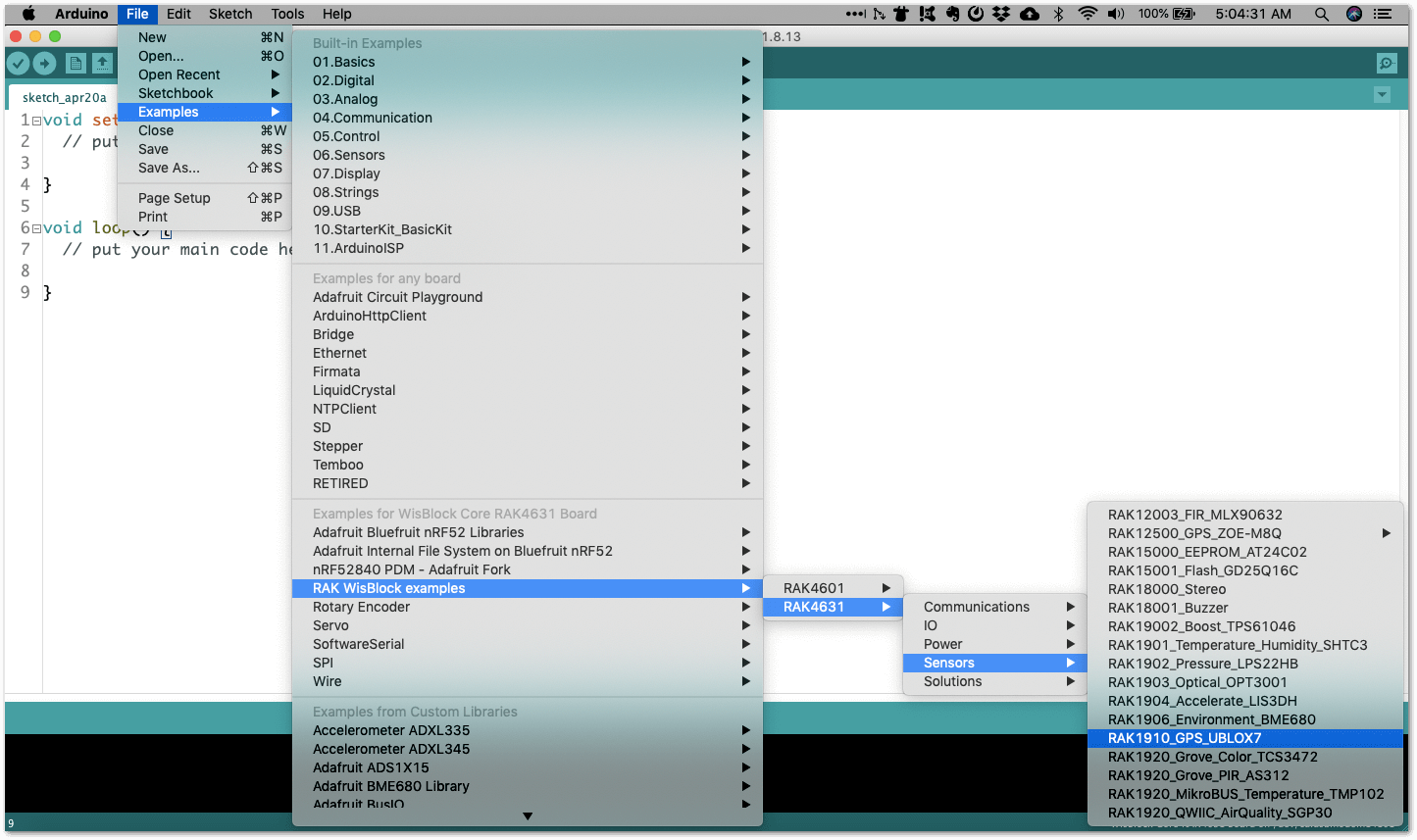 Figure 1: RAK4631 WisBlock Core Examples
Figure 1: RAK4631 WisBlock Core ExamplesIt is highly recommended to also check the dedicated quick start guide that you can follow on various WisBlock Modules. Each quick start guide of these modules contains the detailed steps on how to open the example codes and upload them to the RAK4631.
Listed are the examples where you can check the Software Setup on the quick start guide of the following WisBlock Modules:
The listed links are just examples. All WisBlock Modules have their own quick start guide that you can use as a reference to get started on specific modules.
RAK4631 on Platform IO
For the Platform IO, get the example codes on the WisBlock Example code repository and add the necessary libraries individually. Then you can compile the example code.
Connecting RAK4631 to LoRaWAN
RAK4631 is the WisBlock Core capable of LoRaWAN connectivity.
There is an example on how to start with LoRaWAN in the RAK WisBlock examples in Arduino IDE named LoRaWAN_OTAA_ABP. This is also available in the WisBlock Repository.
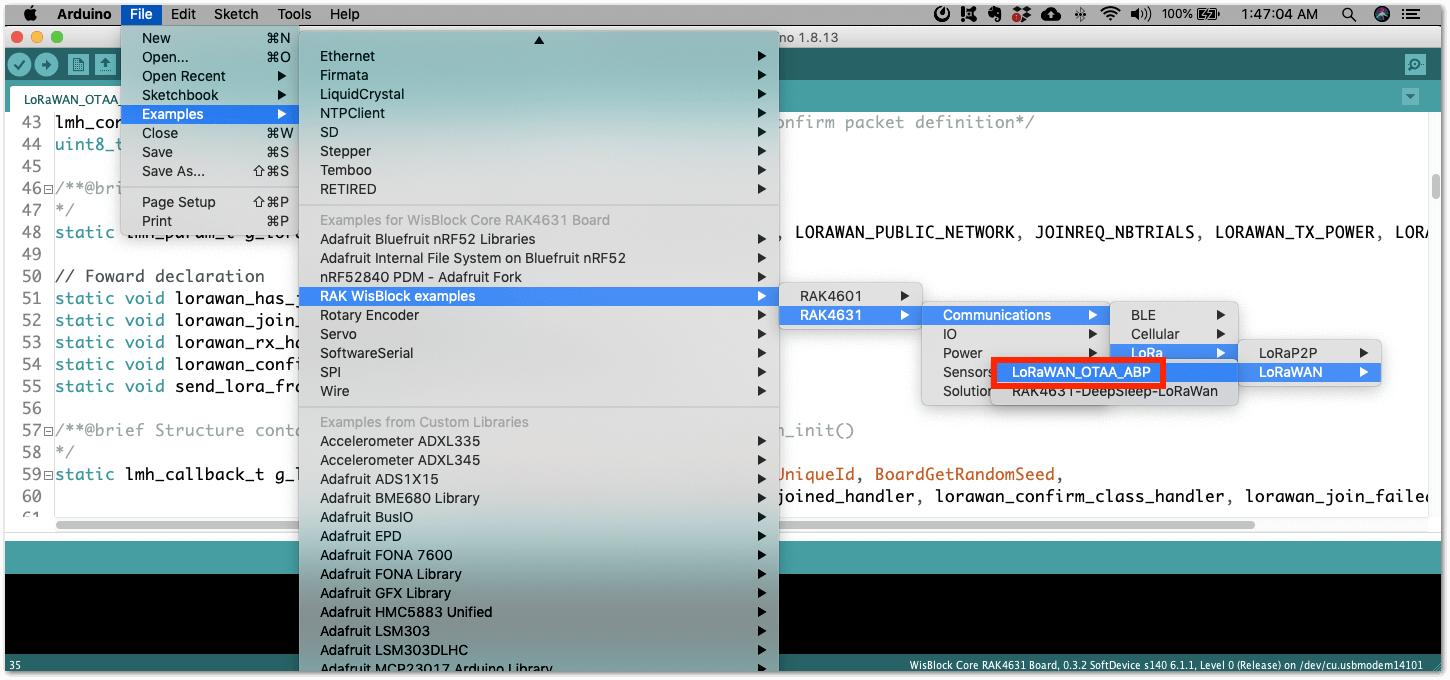 Figure 1: RAK4631 LoRaWAN Example
Figure 1: RAK4631 LoRaWAN ExampleConfiguration of LoRaWAN Example Code
There are configurations that you need to set up to ensure that the device can join a LoRaWAN Network server.
The guide below will explain the default settings and how to configure them.
- Setup the region.
Default is EU868.
LoRaMacRegion_t g_CurrentRegion = LORAMAC_REGION_EU868;
You can change this to a region that is applicable to you like LORAMAC_REGION_US915, LORAMAC_REGION_AU915, etc.
- Setup the activation method.
Default is OTAA.
bool doOTAA = true;
To configure the device to ABP, you need to make this boolean variable false.
- Setup the message type if confirmed or not.
Default is confirmed message.
lmh_confirm g_CurrentConfirm = LMH_CONFIRMED_MSG;
You can change to unconfirmed message by changing the value to LMH_UNCONFIRMED_MSG.
- Setup device class.
Default is Class A.
DeviceClass_t g_CurrentClass = CLASS_A;
You can change this to CLASS_B (still under development) or CLASS_C.
- Setup the keys.
If configured for OTAA Activation,
uint8_t nodeDeviceEUI[8] = {0x88, 0x88, 0x88, 0x88, 0x88, 0x88, 0x33, 0x33};
uint8_t nodeAppEUI[8] = {0xB8, 0x27, 0xEB, 0xFF, 0xFE, 0x39, 0x00, 0x00};
uint8_t nodeAppKey[16] = {0x88, 0x88, 0x88, 0x88, 0x88, 0x88, 0x88, 0x88, 0x88, 0x88, 0x88, 0x88, 0x88, 0x88, 0x88, 0x88};
If configured for ABP Activation,
uint32_t nodeDevAddr = 0x260116F8;
uint8_t nodeNwsKey[16] = {0x7E, 0xAC, 0xE2, 0x55, 0xB8, 0xA5, 0xE2, 0x69, 0x91, 0x51, 0x96, 0x06, 0x47, 0x56, 0x9D, 0x23};
uint8_t nodeAppsKey[16] = {0xFB, 0xAC, 0xB6, 0x47, 0xF3, 0x58, 0x45, 0xC7, 0x50, 0x7D, 0xBF, 0x16, 0x8B, 0xA8, 0xC1, 0x7C};
- Setup uplink period.
The default is 20000 mS.
#define LORAWAN_APP_INTERVAL 20000
You can make the transmission interval faster or slower by changing this value.
LoRaWAN Payload
This default example will send a string Hello! to the LoRaWAN server. This is a setup on the void send_lora_frame(void) function.
memset(m_lora_app_data.buffer, 0, LORAWAN_APP_DATA_BUFF_SIZE);
m_lora_app_data.port = gAppPort;
m_lora_app_data.buffer[i++] = 'H';
m_lora_app_data.buffer[i++] = 'e';
m_lora_app_data.buffer[i++] = 'l';
m_lora_app_data.buffer[i++] = 'l';
m_lora_app_data.buffer[i++] = 'o';
m_lora_app_data.buffer[i++] = '!';
m_lora_app_data.buffsize = i;
The LoRaWAN payload is packaged in this function.
You can change this section to format your payload.
Formatting the Payload
For illustration, you can check how the 32-bit ilat variable is formatted to a 4-byte size array.
This is the exact code snippet in formatting the Latitude data of the GPS Tracker example.
gps.f_get_position(&flat, &flon, &age);
flat == TinyGPS::GPS_INVALID_F_ANGLE ? 0.0 : flat;
ilat = flat * 100000;
// longitude section...
m_lora_app_data.port = gAppPort;
m_lora_app_data.buffer[0] = 0x09;
//lat data
m_lora_app_data.buffer[1] = (ilat & 0xFF000000) >> 24;
m_lora_app_data.buffer[2] = (ilat & 0x00FF0000) >> 16;
m_lora_app_data.buffer[3] = (ilat & 0x0000FF00) >> 8;
m_lora_app_data.buffer[4] = ilat & 0x000000FF;
Another important part of the code is configuring the size of the payload.
This is done on the m_lora_app_data.buffsize variable. For illustration above with only ilat as the value to send, you need to set the buffer size to 5 because the array starts from 0 up to 4.
m_lora_app_data.buffsize = 5;
Decoding the Payload on the LoRaWAN Network Server
On the LoRaWAN network server side like TTN, Chirpstack, Helium, etc., the value transmitted can be retrieved via decoding the payload.
latitude_int = (bytes[1] << 24) | (bytes[2] << 16) | (bytes[3] << 8) | (bytes[4]);
decoded.latitude = latitude_int / 100000;
Important Function in the LoRaWAN Example.
LoRa periodic transmission function should be very short and all reading and processing of the data must be in the main loop.
void tx_lora_periodic_handler(void)
The same with the transmission function, the receiving event handler should be short as well. All processing of the received data should be in the main loop.
void lorawan_rx_handler(lmh_app_data_t *app_data)
Uploading the LoRaWAN Code
After all the configuration is done and the payload is already formatted properly, you can now compile and upload the code.
If you get errors compiling the LoRaWAN example, ensure that you have an updated BSP by checking it in the board manager.
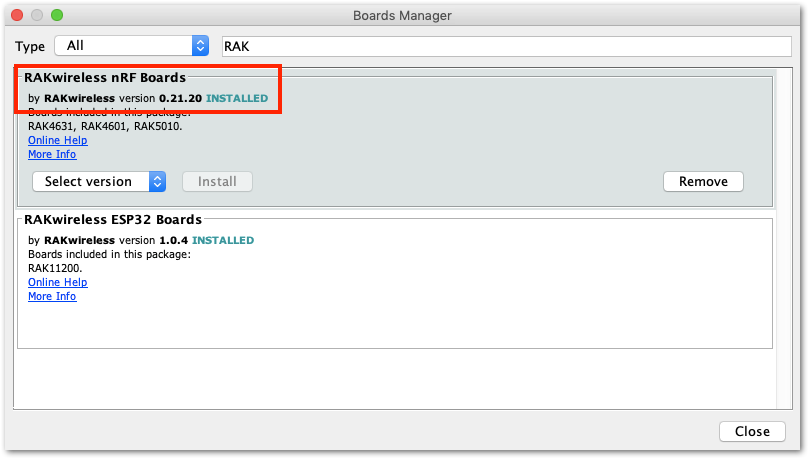 Figure 1: RAK4631 BSP(Board Support Package) in Arduino IDE Board Manager
Figure 1: RAK4631 BSP(Board Support Package) in Arduino IDE Board ManagerYou also need to ensure that you have the updated SX126x.
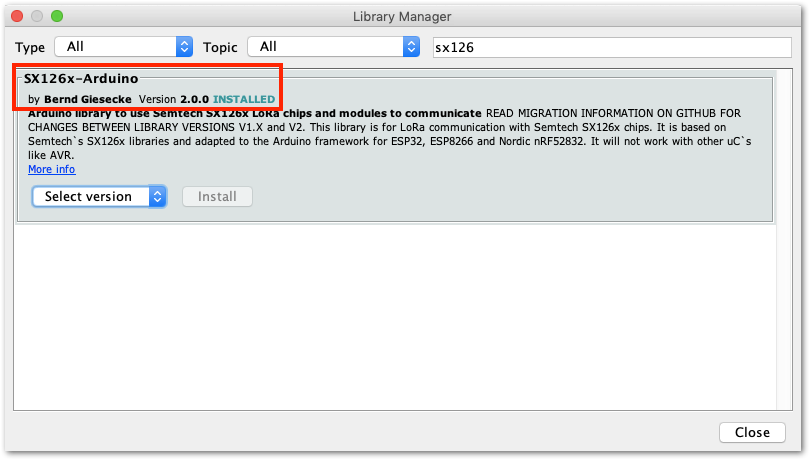 Figure 1: SX126x-Arduino Library
Figure 1: SX126x-Arduino LibraryOn the other hand, if the error is related to the difficulty of uploading the FW, try to double click the reset button on the WisBlock Base board and reupload it again.
RAK4631 LoRa Mesh via Meshtastic
Meshtastic is an open-source community project that uses LoRa technology to make a long-range mesh communicator. You need to download the latest Meshtastic firmware and upload it to your RAK4631 to make it compatible with the Meshtastic network.
For firmware version 1.2 (which is EOL by now but is still useful for the ATAK forwarder plugin), you need to use the right firmware of Meshtastic for your RAK4631, depending on the WisBlock Base board you use.
- RAK5005-O -
firmware-rak4631_5005-1.2.yy.zzzzzzz.uf2 - RAK19003 -
firmware-rak4631_19003-1.2.yy.zzzzzzz.uf2
For Firmware 1.3 and 2.0 (from Nov 1st, 2022), the WisBlock Base board is autodetected. There's a special firmware if you have the RAK14000 WisBlock E-Ink Display connected. All other use cases are covered in the stock firmware.
- All the base boards with RAK4631 -
firmware-rak4631-w.x.yy.zzzzzzz.uf2 - RAK4631 with RAK14000 -
firmware-rak4631_eink-w.x.yy.zzzzzzz.uf2
To upload the Meshtastic firmware to the RAK4631 board, connect the RAK4631 to the PC via USB. Then double click the reset button on the WisBlock Base board to see the RAK4631 drive in your computer.
You then need to drag the Meshtastic .uf2 firmware file to the RAK4631 drive.
Once you successfully dragged the Meshtastic FW file, restart the device. After reset, if the Meshtastic firmware was successfully uploaded, you will see the Meshtastic messages on the OLED display and the serial output.
You can also get an android device and download Meshtastic App then connect to RAK4631 via Bluetooth.
Meshtastic is constantly changing and it is advisable to check the Meshtastic device repository every time you will use RAK4631 as a Meshtastic node.
The bootloader of RAK4631 is not overwritten by the Meshtastic FW. You also override the Meshtastic FW by uploading another Arduino or Platform IO code.
Miscellaneous
How to Check If You Have the Updated RAK4631 Bootloader
You need to connect the RAK4631 to the PC via USB cable and double click the reset button on the WisBlock Base.
There will be a new drive named RAK4631 that will be shown on your folder explorer. Inside this drive, there will be a text file named INFO_UF2.TXT, as shown in Figure 18.
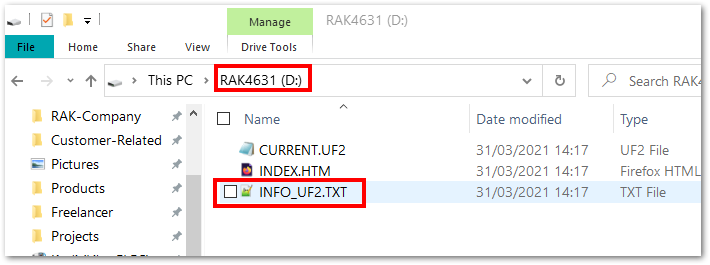 Figure 1: RAK4631 drive content
Figure 1: RAK4631 drive contentIf you open INFO_UF2.TXT, you'll see Date: Dec 1 2021, as shown in Figure 19.
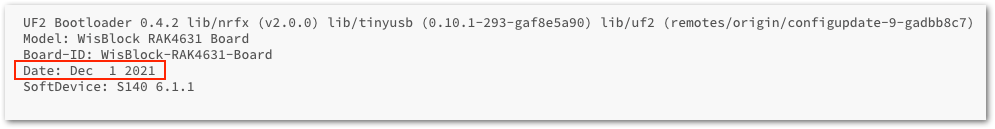 Figure 1: INFO_UF2.TXT content
Figure 1: INFO_UF2.TXT contentIf you have a different drive name or folder date, it means you do not have the updated RAK4631 Bootloader and you need to update it.
Updating the Bootloader
RAK4631 WisBlock Core is programmed with a USB bootloader so that you can upload application firmware to it without using any external tools like Jlink and other programmers/debuggers. However, there are situations that you need to update the bootloader when there is an updated version that supports new features, improvements, and bug fixes.
There are various ways to update the bootloader like via USB, Bluetooth, and Jlink. The procedure for these methods is explained in this guide.
Bootloader Update via USB
In this method, you need two things that must be in the same directory:
- Adafruit-nrfutil utility program
- RAK4631 Bootloader FW
For Windows
Download the adafruit-nrfutil.exe (you need to unzip the downloaded file) and the latest RAK4631 bootloader firmware.
Detailed information about the RAK4631 Bootloader can be found on the bootloader repository.
Once you downloaded these files, you need to put them in the same directory/folder on your computer.
For simplicity, this guide will assume the files are in C: drive.
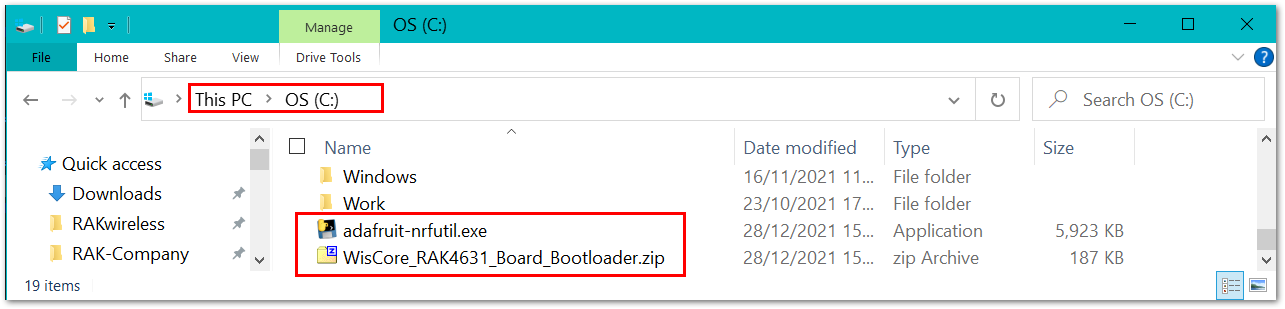 Figure 1: Adafruit-nrfutil and RAK4631 Bootloader file in C: drive
Figure 1: Adafruit-nrfutil and RAK4631 Bootloader file in C: driveWhen the files are ready, you need to open the Windows Command Prompt application. Then you need to change the location to C:.
cd C:\
After that, you can now execute the update using this command:
adafruit-nrfutil.exe --verbose dfu serial --package WisCore_RAK4631_Board_Bootloader.zip --port COM19 -b 115200 --singlebank --touch 1200
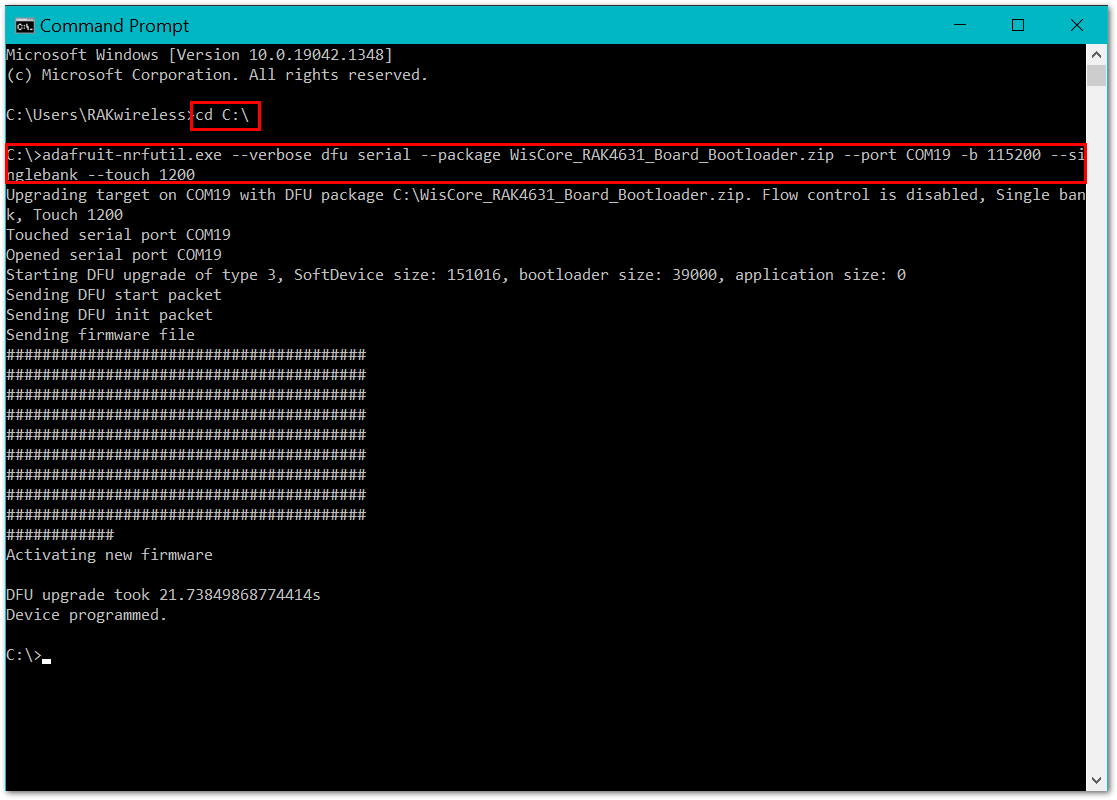 Figure 1: RAK4631 Bootloader Updated Successfully
Figure 1: RAK4631 Bootloader Updated SuccessfullyYou need to determine the right COM port number of your device. COM19 on the command above is only for illustration. You will get an error if you are not connected to the right COM port number.
For Linux
You can get and install adafruit-nrfutil via pip3.
sudo pip3 install adafruit-nrfutil
or
pip3 install --user adafruit-nrfutil
Then download the latest RAK4631 bootloader firmware.
Open a new terminal window and connect the RAK4631 to the PC via USB. Now use the dmesg command to display system information and check if the USB device has been recognized by Linux.
If the RAK4631 USB device is recognized, a listing for the device similar to the one below will be displayed.
usb 1-1: New USB device found, idVendor=239a, idProduct=0029, bcdDevice= 1.00
usb 1-1: New USB device strings: Mfr=1, Product=2, SerialNumber=3
usb 1-1: Product: WisBlock RAK4631
usb 1-1: Manufacturer: RAKWireless
usb 1-1: SerialNumber: XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
usb-storage 1-1:1.2: USB Mass Storage device detected
scsi host1: usb-storage 1-1:1.2
usbcore: registered new interface driver usb-storage
cdc_acm 1-1:1.0: ttyACM0: USB ACM device
usbcore: registered new interface driver cdc_acm
The line cdc_acm 1-1:1.0: ttyACM0: USB ACM device indicates that the port /dev/ttyACM0 has been allocated for RAK4631.
After determining the port name, go to the directory where the bootloader FW file WisCore_RAK4631_Board_Bootloader.zip is located.
Then execute the following command:
adafruit-nrfutil --verbose dfu serial --package WisCore_RAK4631_Board_Bootloader.zip -p /dev/ttyACM0 -b 115200 --singlebank --touch 1200
For macOS
The same with Windows and Linux procedures, download the latest RAK4631 bootloader firmware.
There are two ways to update the RAK4631 bootloader in macOS:
-
If you have Python installed, you can follow the same steps for Linux.
-
Another way is by creating a macOS executable. To do this method, download adafruit-nrfutil-macos and make it executable.
Usually, the adafruit-nrfutil-macos file will go to the downloads folder.
The next step after downloading the file is to open the terminal and go to the downloads directory or the location where you put the downloaded file. It will be the change directory command where the username will depend on your macbook cd /Users/username/Downloads or you can directly try cd Downloads.
And then execute this command:
chmod +x adafruit-nrfutil-macos
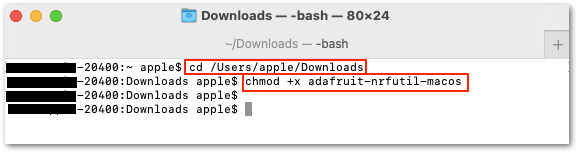 Figure 1: Executable adafruit-nrfutil-macos
Figure 1: Executable adafruit-nrfutil-macosYou also need to determine the port name of the RAK4631 using the command:
ls /dev/cu.*.
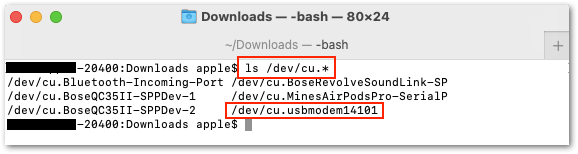 Figure 1: Checking the RAK4631 USB port connection
Figure 1: Checking the RAK4631 USB port connectionAfter all these steps, you can now upload the latest RAK4631 Bootloader Firmware by executing this command:
./adafruit-nrfutil-macos --verbose dfu serial --package WisCore_RAK4631_Board_Bootloader.zip -p /dev/cu.usbmodem411 -b 115200 --singlebank --touch 1200
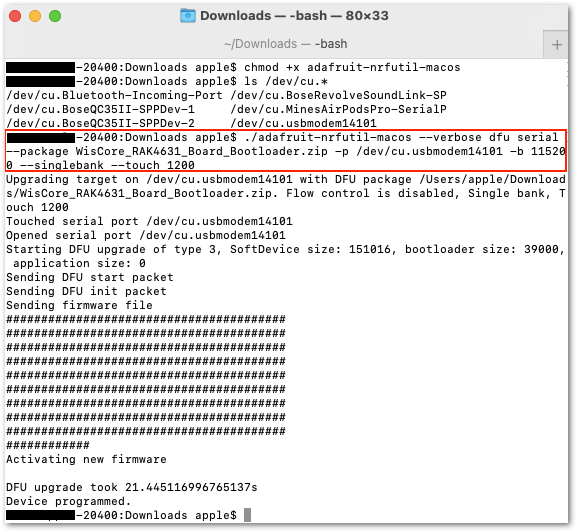 Figure 1: Updated RAK4631 Bootloader
Figure 1: Updated RAK4631 BootloaderYour RAK4631 will now have the updated Bootloader Firmware.
Bootloader Update via Bluetooth
Updating the firmware via BLE is also possible.
The complete guide is on the RAK4631 Bootloader repository using BLE.
Bootloader Update via Jlink
Updating the firmware via Jlink is possible as well.
The complete guide is on the RAK4631 Bootloader repository using Jlink.
