WisGate OS Wi-Fi Modes Configuration
As mentioned in the Overview, the gateway can be configured to work in three modes:
-
Access point: You can connect to the gateway via the assigned IP.
-
Client: You can easily connect their gateway to a Wireless Network. AP won’t be available.
-
Access Point + Client: Both modes will be available.
Access Point
By default, the WisGate Edge Series work in Access Point (AP) mode.
In the ESSID field, the name of the AP is shown. The default name is RAKXXXX_YYYY, where XXXX is the model of the gateway (e.g. 7249), and YYYY are the last symbols of the MAC address of the gateway. The user can change that name to his desire.
To protect their AP, you can choose between three encryption types. In the drop-down menu in the Encryption field, you can choose any of the following options: WPA-PSK, WPA-PSK2, and WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK Mixed Mode.
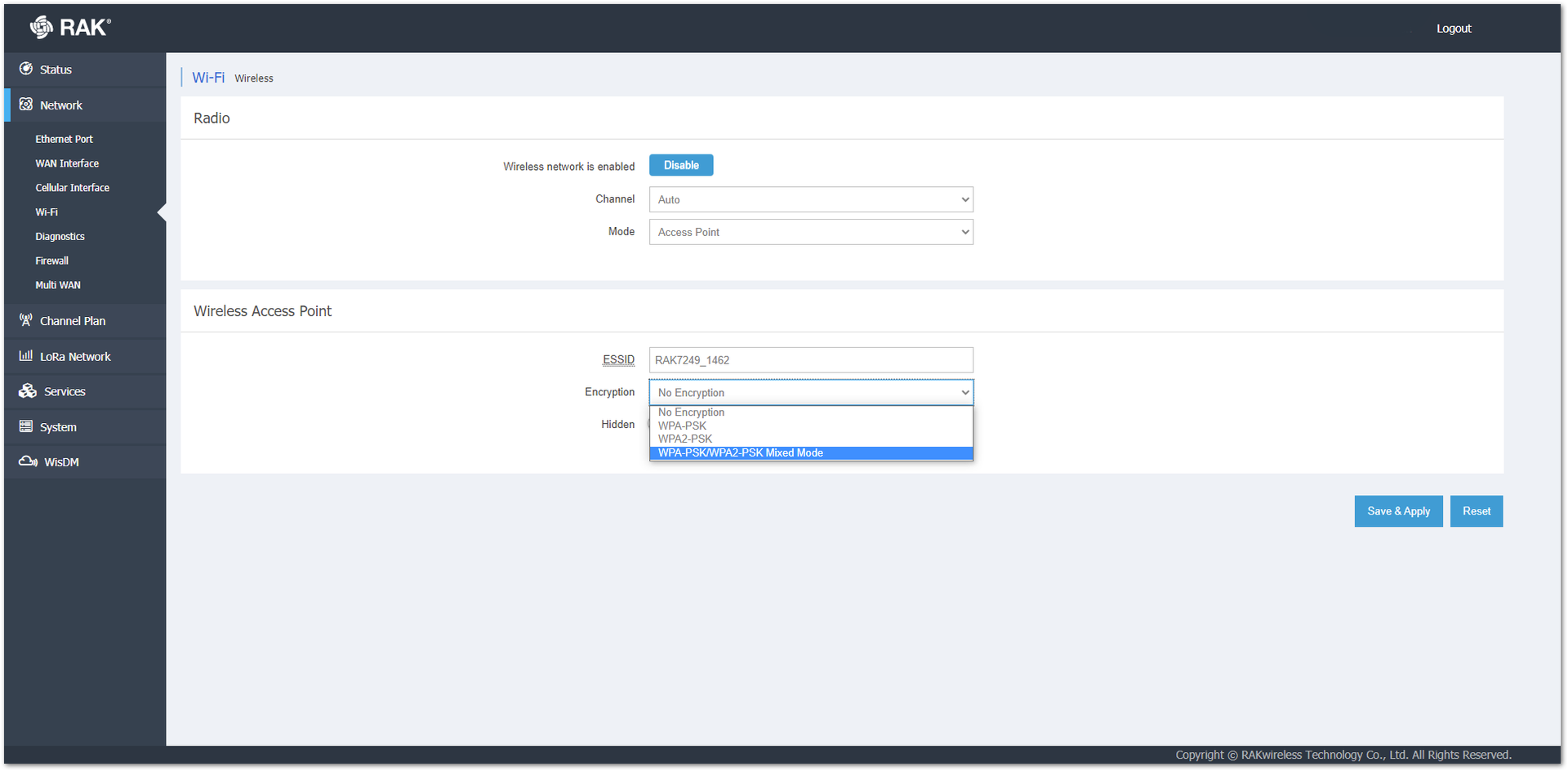 Figure 1: Access Point Encryption
Figure 1: Access Point EncryptionWPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK Mixed Mode is the recommended type of encryption.
When the desired protection is chosen, a Key field will pop up. In the Key field, enter a password to protect the AP. The green arrows  on the right will show/hide the password.
on the right will show/hide the password.
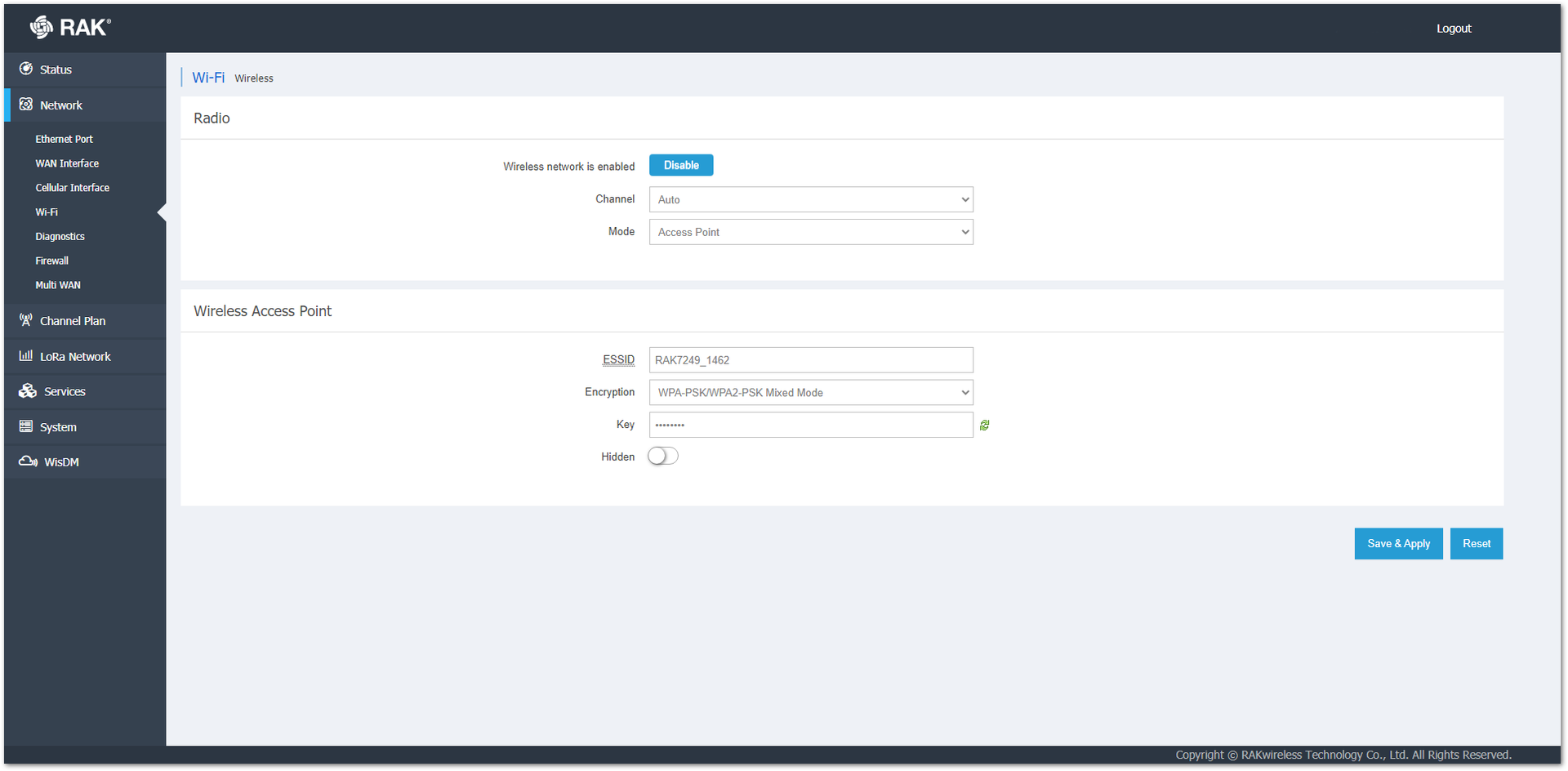 Figure 1: Access Point Password
Figure 1: Access Point PasswordOptionally, you can hide the AP by enabling the Hidden option. To connect to a hidden AP, you must manually type the ESSID, choose the correct encryption type, and type the password.
Client
In the ESSID field, you can type the name of their wireless network manually or click on the Scan button  and scan the available networks.
and scan the available networks.
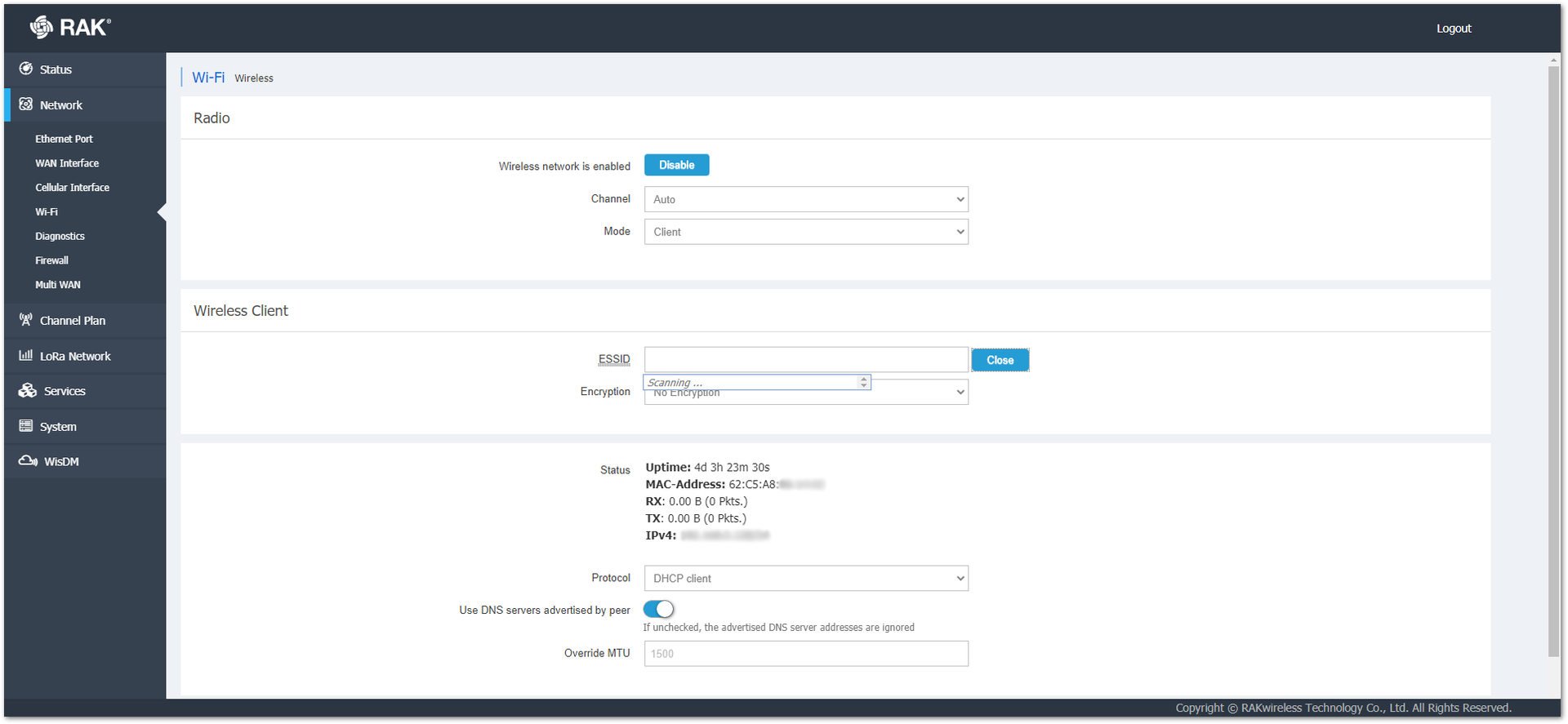 Figure 1: Client ESSID Scanning
Figure 1: Client ESSID Scanning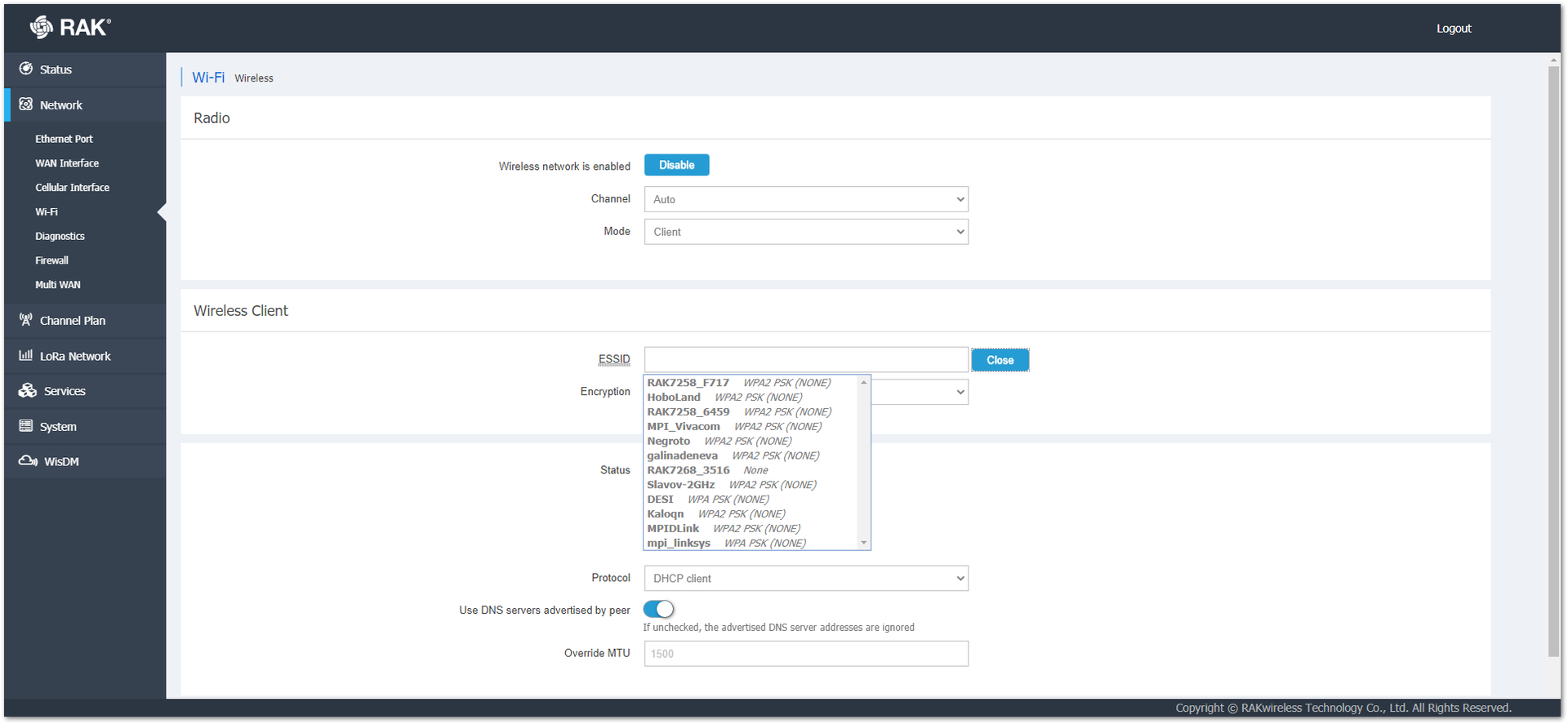 Figure 1: Client ESSID Available Networks
Figure 1: Client ESSID Available NetworksIn the Encryption field, you must choose what encryption is used by the network. After the correct one is selected, a Key field will pop up.
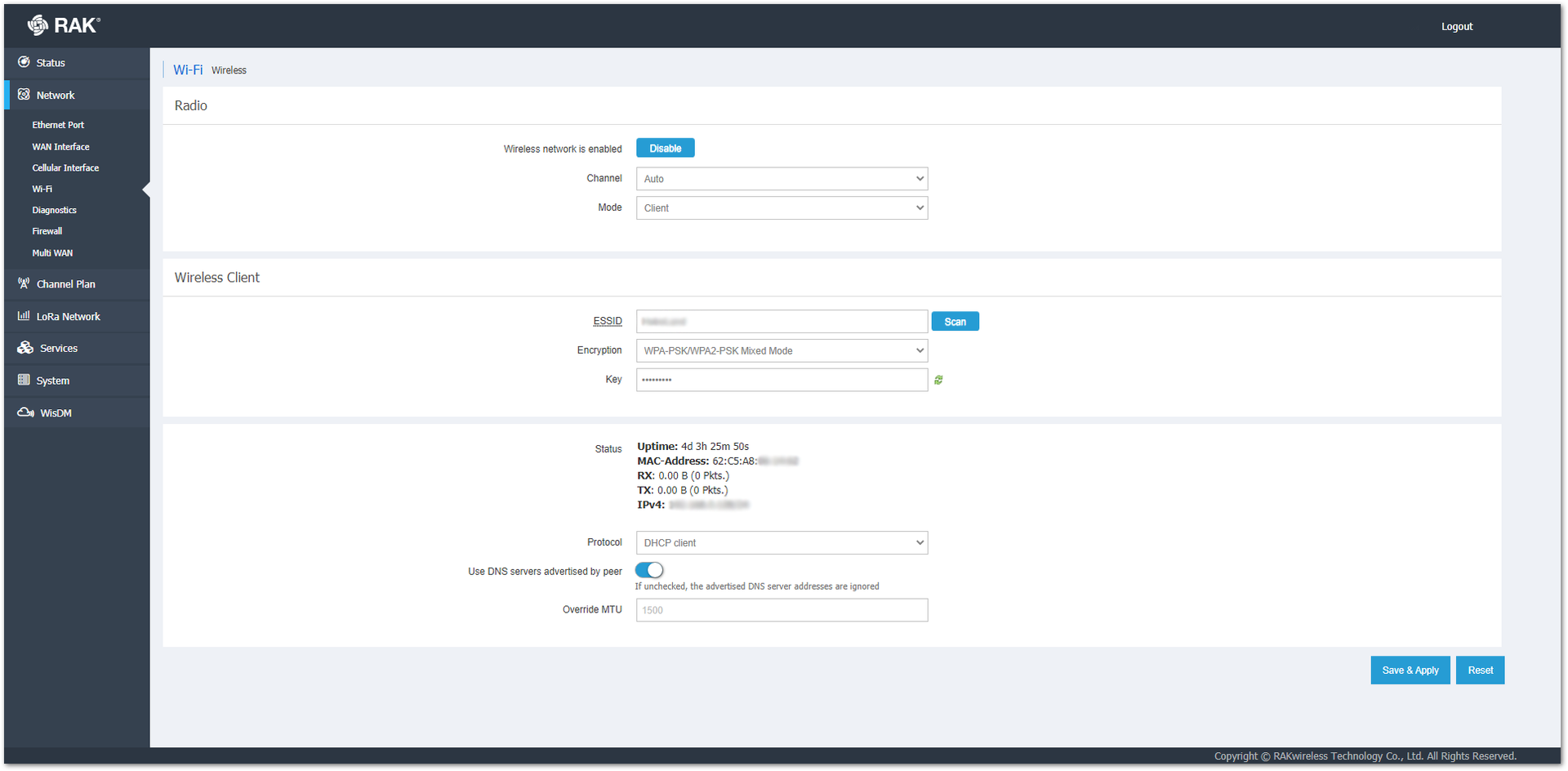 Figure 1: Client Encryption and Password
Figure 1: Client Encryption and PasswordIn the Key field, you must type the password that protects the wireless network. The green arrows  right to the field will show/hide the password.
right to the field will show/hide the password.
Below the Wireless Client menu, you can see the Status of the mode and select what protocol to use. You can choose between Static address or DHCP client.
In the DHCP mode, there is not much to configure. The DHCP server of the router will set an IP for the gateway. You can enable/disable the Use DNS servers advertised by peer button. If the button is unchecked, the advertised DNS server addresses are going to be ignored. Optionally, you can override the MTU.
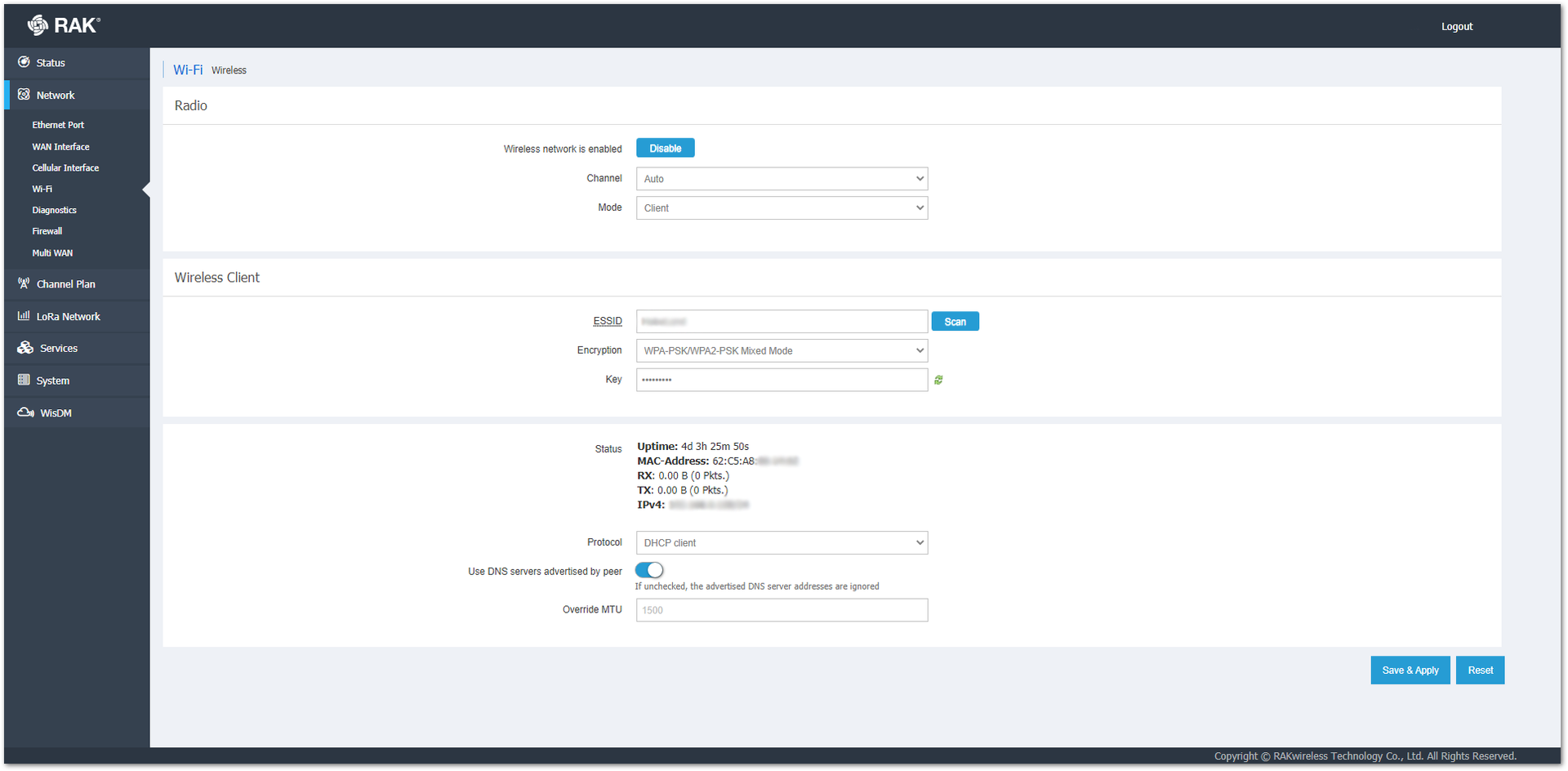 Figure 1: DHCP Client Protocol
Figure 1: DHCP Client ProtocolIf you chooses the Static address protocol, it can set a static IP address for the gateway. This way, after a reboot or restart of the router, the gateway will keep the assigned IP address.
To do so, you must type the IP of the network in the IPv4 address field (or the IPv6 address one if that version is used). In the IPv4 netmask field (or in IPv6 routed prefix), you must type the subnet mask (prefix for IPv6) of the IP address. For example the netmask for 192.168.0.128 is 255.255.255.0.
In the IPv4 gateway (or IPv6 gateway) field, you must type the IP that will be assigned to the gateway.
Additionally, you can use custom DNS servers via the Use custom DNS servers field. You can add more than one server with the list button  .
.
In the Override MTU field, you can set a size for the largest packet or frame that can be sent over the network. The MTU of an Ethernet connection is 1500 bytes.
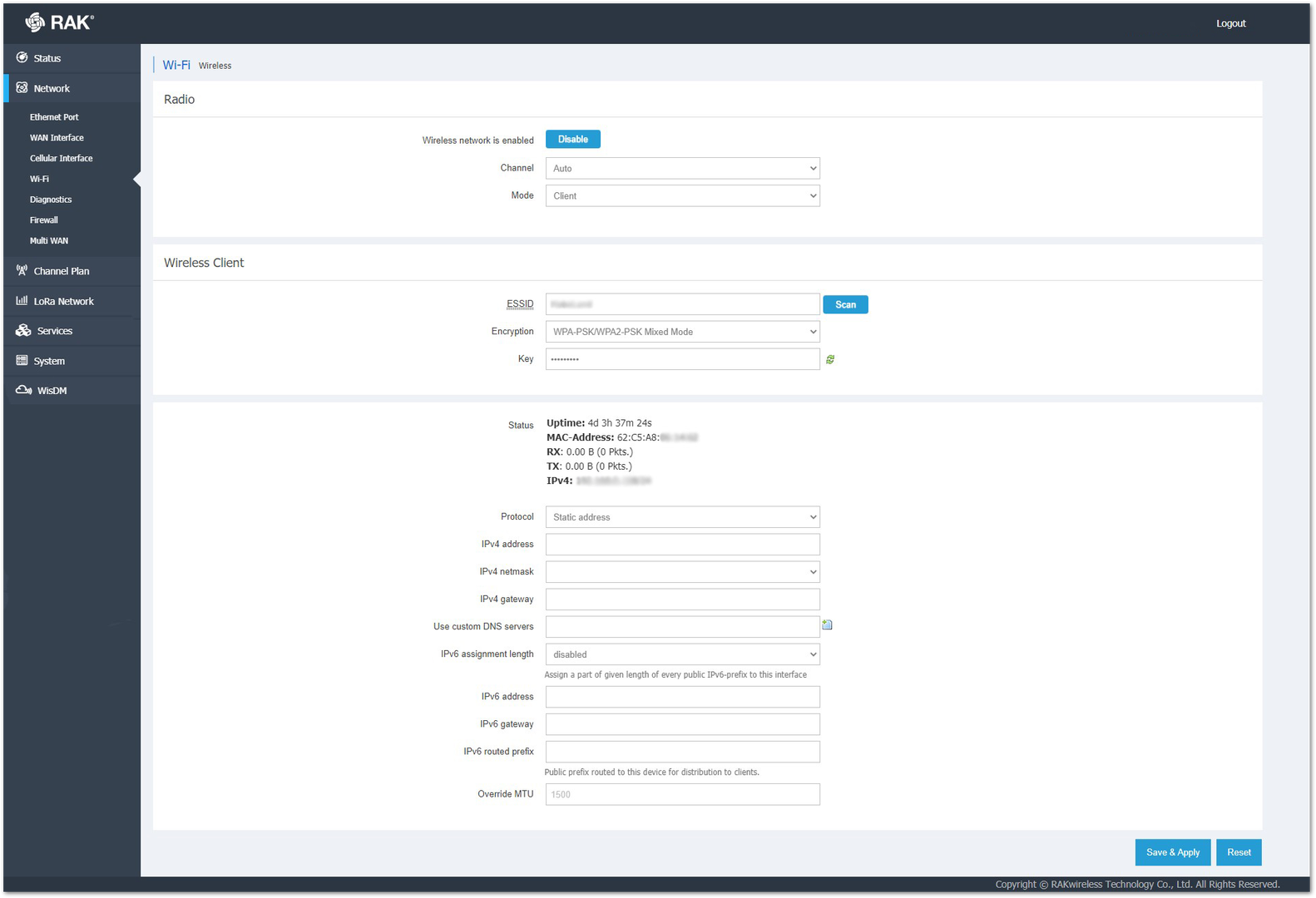 Figure 1: Static Address Protocol
Figure 1: Static Address ProtocolAccess Point + Client
If this mode is selected, both the Access Point and Client mode will be available. You can connect the gateway to a wireless network and access it via the assigned IP.
The steps to configure the mode are the same as the explained above for the Access Point (for configuring AP) and Client (for configuring Client mode).
